java基础:I/O流
一.概述
1.1 简介
系统(这里可以理解为CPU)和不同的设备设备交换数据都是通过物理上的I/O总线。在java中交换数据一般分为2步,第一步联通设备(File和Url),确认可以使;第二版就是通过I/O流交互数据。这样记忆,第一步就是修路,第二版就是拉货。 路通了,才能让车一次次拉货。
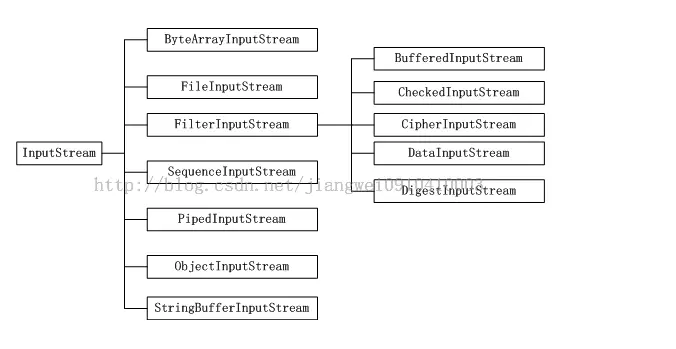
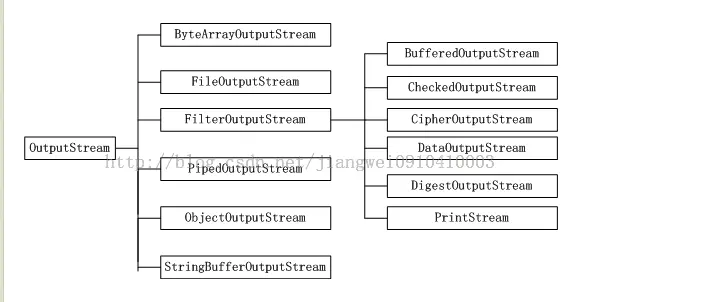
1.2 I/O流图
- a) 字节流:
![]()
![]()
- b) 字符流:
![]()
![]()
- c) 总结
- 1. 字节流操作对象:byteArray,file,piped,object,string(现在建议在字符流方式操作)
- 2.字符流操作对象:charArray,file,string
- 3.字节流-》字符流类:inputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter
- 4.处理类:BufferedInputStream,DataInputStream,BufferedReader。如果说input、read是最小单位处理,则处理类就是对其增强,加快处理的方式。
- 5.在使用完后一定要把 input/output、reader/writer都关闭
二.实例
2.1 字节流的
/**
* byteArray:读取字节流
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void getByteArrayInputStream() throws IOException {
String io = "d:\\project\\test\\1231.txt";
byte b[] = io.getBytes();
InputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(b);
int readbyte;
while ((readbyte = is.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(readbyte);
}
Reader r=new InputStreamReader(is);
}
/**
* 文件io 文件流修改的读取使用了 native方法
*
* @throws IOException
*/
public void getFileInputStream() throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\project\\test\\1231.txt");
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
int readbyte;
while ((readbyte = is.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(readbyte);
}
}
/**
* stringinputStream 过期
*
* @throws IOException
*/
public void getStringInputStream() throws IOException {
String io = "d:\\project\\test\\1231.txt";
InputStream is = new StringBufferInputStream(io);
int readbyte;
while ((readbyte = is.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(readbyte);
}
}
2.2 字符流
/**
* reader : file、string、charArray都会将数据转化为byte
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void StringReader() throws IOException {
String io = "d:\\project\\test\\1231.txt";
Reader r = new StringReader(io);
int temp;
while ((temp = r.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(temp);
}
}
@Test
public void BufferReader() throws IOException {
String io = "d:\\project\\test\\1231.txt";
BufferedReader r = new BufferedReader(new StringReader(io));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = r.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(temp);
}
}
3.3 压缩
@Test
public void zipTest() throws IOException {
/**
* @see 将D:\project\test下的3个文件,压缩到 my.zip中
*/
File directory = new File("d:\\project\\test");
String zipFileName = "my.zip";// 压缩文件的名字
ZipOutputStream os = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("d:\\project", zipFileName)));
InputStream is = null;
for (File fs : directory.listFiles()) {
is = new FileInputStream(fs);
int fileByte;
os.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(fs.getName()));// 创建一个压缩文件中的文件
while ((fileByte = is.read()) != -1) {
os.write(fileByte);
}
}
os.close();
is.close();
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号