nginx的核心数据结构
typedef struct ngx_module_s ngx_module_t;
typedef struct ngx_conf_s ngx_conf_t;
typedef struct ngx_cycle_s ngx_cycle_t;
typedef struct ngx_pool_s ngx_pool_t;
typedef struct ngx_chain_s ngx_chain_t;
typedef struct ngx_log_s ngx_log_t;
typedef struct ngx_open_file_s ngx_open_file_t;
typedef struct ngx_command_s ngx_command_t;
typedef struct ngx_file_s ngx_file_t;
typedef struct ngx_event_s ngx_event_t;
typedef struct ngx_event_aio_s ngx_event_aio_t;
typedef struct ngx_connection_s ngx_connection_t;
typedef struct ngx_thread_task_s ngx_thread_task_t;
typedef struct ngx_ssl_s ngx_ssl_t;
typedef struct ngx_ssl_connection_s ngx_ssl_connection_t;
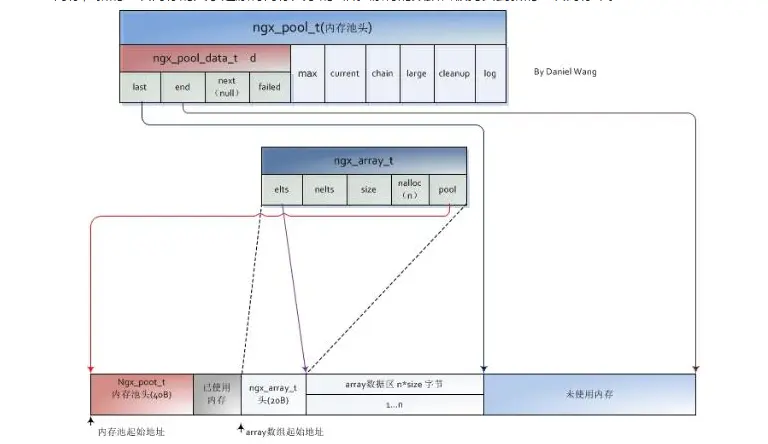
数组
ngx_array_t结构
typedef struct {
void *elts; '实际的数据存储区起始地址'
ngx_uint_t nelts; '数组实际元素个数'
size_t size; '数组单个元素的大小,单位是字节'
ngx_uint_t nalloc; '数组的容量:表示该数组在不引发扩容的前提下,可以最多存储的元素的个数'
ngx_pool_t *pool; '该数组结构,分配的的内存在内存池中的位置'
} ngx_array_t;
-
特点:
- 当nelts增长到达nalloc 时,如果再往此数组中存储元素,则会引发数组的扩容。数组的容量将会扩展到原有容量的2倍大小。实际上是分配新的一块内存,新的一块内存的大小是原有内存大小的2倍。原有的数据会被拷贝到新的一块内存中。
![]()
- 当nelts增长到达nalloc 时,如果再往此数组中存储元素,则会引发数组的扩容。数组的容量将会扩展到原有容量的2倍大小。实际上是分配新的一块内存,新的一块内存的大小是原有内存大小的2倍。原有的数据会被拷贝到新的一块内存中。
函数
ngx_array_init:数组初始化
/**
*/
static ngx_inline ngx_int_t
ngx_array_init(ngx_array_t *array, ngx_pool_t *pool, ngx_uint_t n, size_t size)
{
/*
* set "array->nelts" before "array->elts", otherwise MSVC thinks
* that "array->nelts" may be used without having been initialized
*/
array->nelts = 0;
array->size = size;
array->nalloc = n;
array->pool = pool;
array->elts = ngx_palloc(pool, n * size); 'n个数组数据地址,在内存池中的位置'
if (array->elts NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
return NGX_OK;
}
- 特点:初始化n*size大小的内存池,并连接到 *array上,
初始化:ngx_array_create:创建
/**
先在内存池中分配一个数组头,然后在分配 n*size 大小的内存
ngx_pool_t:内存池
ngx_uint_t:数组大小
*/
ngx_array_t *
ngx_array_create(ngx_pool_t *p, ngx_uint_t n, size_t size)
{
ngx_array_t *a;
a = ngx_palloc(p, sizeof(ngx_array_t)); '初始化一个数组大小的内存池,作为数组的引用'
if (a NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (ngx_array_init(a, p, n, size) != NGX_OK) { '初始化n个数组内存空间,存储数组'
return NULL;
}
return a;
}
销毁一个数组空间:ngx_array_destroy
void
ngx_array_destroy(ngx_array_t *a)
{
ngx_pool_t *p;
p = a->pool;
if ((u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nalloc p->d.last) { '如果数组满'
p->d.last -= a->size * a->nalloc; '清理所有数组'
}
if ((u_char *) a + sizeof(ngx_array_t) p->d.last) {
p->d.last = (u_char *) a;
}
}
获取下一个成员的其实地址:ngx_array_push
-
特点:
- 如果数组满:
- nalloc=1且这个内存池中没有人使用,直接分配一个
- 扩容成2倍大小
- 直接获取下一个数的起始地址。
- 如果数组满:
void *
ngx_array_push(ngx_array_t *a)
{
void *elt, *new;
size_t size;
ngx_pool_t *p;
if (a->nelts a->nalloc) {
/* the array is full */
size = a->size * a->nalloc;
p = a->pool;
// 数组才个数=1
// 未分配空间>已使用空间+size
if ((u_char *) a->elts + size p->d.last
&& p->d.last + a->size <= p->d.end)
{
/*
* the array allocation is the last in the pool
* and there is space for new allocation
*/
//容量+1
p->d.last += a->size;
a->nalloc++;
} else {
/* allocate a new array */
// 容量*2
new = ngx_palloc(p, 2 * size);
if (new NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ngx_memcpy(new, a->elts, size);
a->elts = new;
a->nalloc *= 2;
}
}
//数字其实地址+个数*size
elt = (u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nelts; //下一个数的起始地址
a->nelts++; //个数+1
return elt;
}
-
特点:
- (u_char *) a->elts + size p->d.last
&& p->d.last + a->size <= p->d.end- 未分配空间>一个数组值的大小:
- 数组值起始位置+一个数组值的大小=未分配空间起始地址:
- (u_char *) a->elts + size p->d.last
压入(存入)个数:ngx_array_push_n
void *
ngx_array_push_n(ngx_array_t *a, ngx_uint_t n)
{
void *elt, *new;
size_t size;
ngx_uint_t nalloc;
ngx_pool_t *p;
size = n * a->size;
if (a->nelts + n > a->nalloc) {
/* the array is full */
p = a->pool;
if ((u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nalloc p->d.last
&& p->d.last + size <= p->d.end)
{
/*
* the array allocation is the last in the pool
* and there is space for new allocation
*/
p->d.last += size;
a->nalloc += n;
} else {
/* allocate a new array */
nalloc = 2 * ((n >= a->nalloc) ? n : a->nalloc);
new = ngx_palloc(p, nalloc * a->size);
if (new NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ngx_memcpy(new, a->elts, a->nelts * a->size);
a->elts = new;
a->nalloc = nalloc;
}
}
elt = (u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nelts;
a->nelts += n;
return elt;
}
ngx_list_t:列表
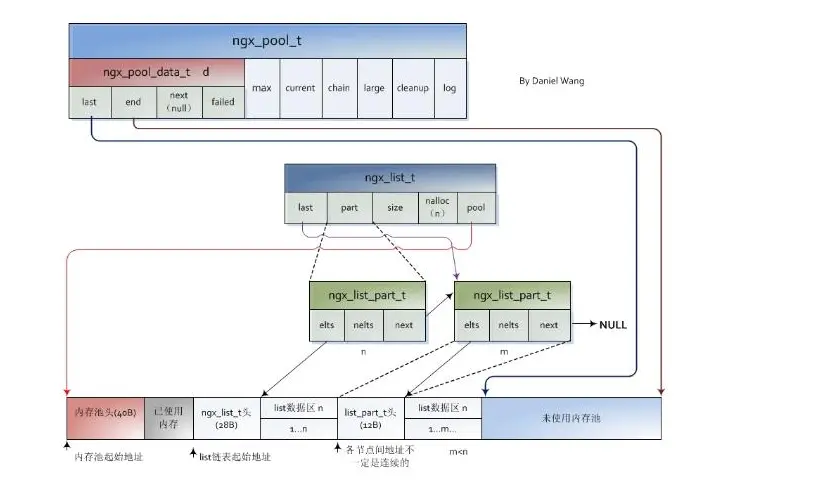
//连接头
typedef struct {
ngx_list_part_t *last; '指向链表中最后一个ngx_list_part_t,用于管理整个链表,含义很明确'
ngx_list_part_t part; '链表第一个节点,表示一块连续的内存空间。'
size_t size; '链表中每个节点中存放元素大小'
ngx_uint_t nalloc; '链表中每个节点可以存放的元素个数。'
ngx_pool_t *pool; '链表使用的内存池。'
} ngx_list_t;
//连接表
struct ngx_list_part_s {
void *elts; '链表节点使用的内存块地址'
ngx_uint_t nelts; '当前链表节点已经存放的元素个数'
ngx_list_part_t *next; '指向链表的下一个节点'
};
创建和初始化:ngx_list_create、ngx_list_init
//创建链表引用
ngx_list_t *
ngx_list_create(ngx_pool_t *pool, ngx_uint_t n, size_t size)
{
ngx_list_t *list;
list = ngx_palloc(pool, sizeof(ngx_list_t));
if (list NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (ngx_list_init(list, pool, n, size) != NGX_OK) {
return NULL;
}
return list;
}
//初始化
static ngx_inline ngx_int_t
ngx_list_init(ngx_list_t *list, ngx_pool_t *pool, ngx_uint_t n, size_t size)
{
list->part.elts = ngx_palloc(pool, n * size);
if (list->part.elts NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
list->part.nelts = 0;
list->part.next = NULL;
list->last = &list->part;
list->size = size;
list->nalloc = n;
list->pool = pool;
return NGX_OK;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号