Bloom filter简介
An empty Bloom filter is a bit array of m bits, all set to 0. There must also be k different hash functions defined, each of which maps or hashes some set element to one of the m array positions, generating a uniform random distribution. Typically, k is a small constant which depends on the desired false error rate ε, while m is proportional to k and the number of elements to be added.
To add an element, feed it to each of the k hash functions to get k array positions. Set the bits at all these positions to 1.
To query for an element (test whether it is in the set), feed it to each of the k hash functions to get k array positions. If any of the bits at these positions is 0, the element is definitely not in the set; if it were, then all the bits would have been set to 1 when it was inserted. If all are 1, then either the element is in the set, or the bits have by chance been set to 1 during the insertion of other elements, resulting in a false positive. In a simple Bloom filter, there is no way to distinguish between the two cases, but more advanced techniques can address this problem.
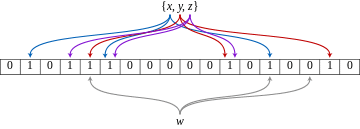
An example of a Bloom filter, representing the set {x, y, z} . The colored arrows show the positions in the bit array that each set element is mapped to. The element w is not in the set {x, y, z} , because it hashes to one bit-array position containing 0. For this figure, m = 18 and k = 3.
A Bloom filter is a space-efficient probabilistic data structure, conceived by Burton Howard Bloom in 1970, that is used to test whether an element is a member of a set. False positive matches are possible, but false negatives are not - in other words, a query returns either "possibly in set" or "definitely not in set". Elements can be added to the set, but not removed (though this can be addressed with the counting Bloom filter variant); the more items added, the larger the probability of false positives.
六级/考研单词: bloom, filter, array, random, desire, query, insert, arrow, data, conceive




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号