C++中有析构函数,用于销毁对象时释放内存,而Java中因为有gc(垃圾回收机制)所以就没有析构函数,但是java有finalize() 方法,两者的用途相近。
具体请参考链接:http://blog.csdn.net/jemasw/article/details/8470480
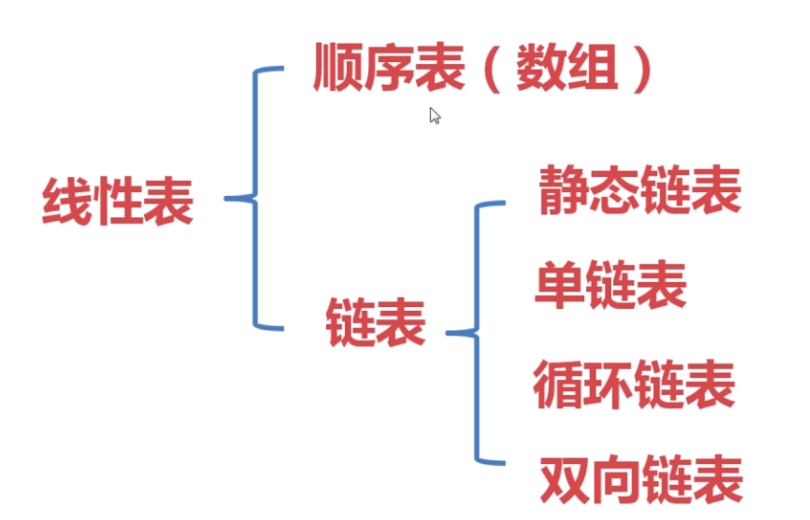
什么是线性表?
官方定义:线性表是n个数据元素的有限序列
顺序表和链表互为补充;
定义解读:n个(个数),元素(可以是复杂元素对象,也可以是单个数据),有限(有限的),序列(是一个序列集合)
线性表分为两大类:数组和链表
顺序表
前驱:指定元素前一个元素
后继:指定元素的后一个元素
优点:可以通过下标遍历寻址,所以遍历和寻址极为快速。
缺点:插入和删除元素,因为要移动后面的所有元素,所以较为缓慢。
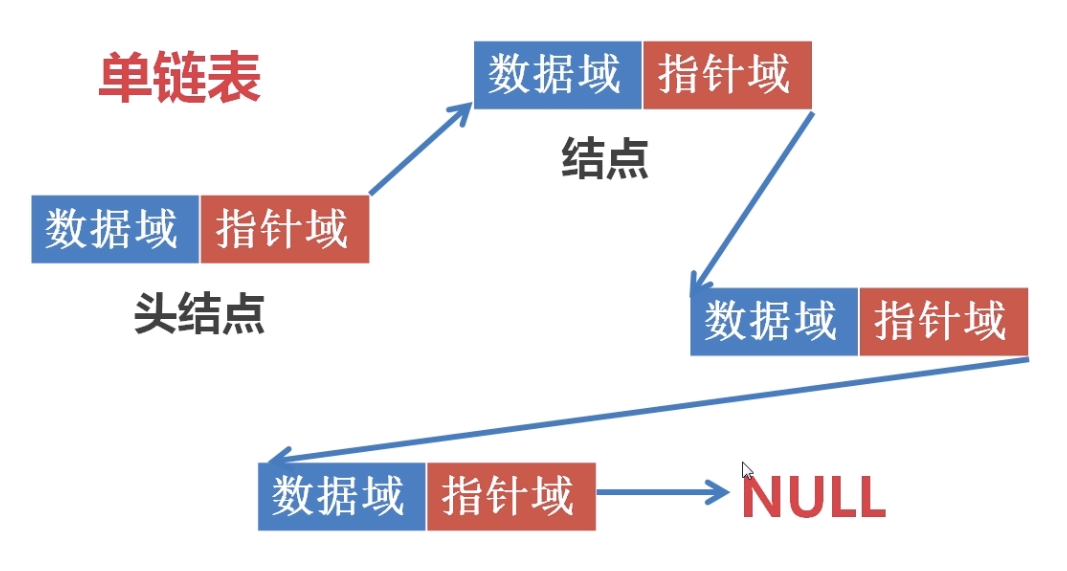
链表
单链表:
单链表,每个节点分为两部分,分别为 数据域 和 指针域
initChainList(); 初始化链表
void destroyList(); 销毁链表,废弃
boolean isListEmpty(); 判断链表是否为空
int listLength(); 获取链表的长度
void clearList(); 清空链表的所有元素
Node listInsertHead(Node node); 插入头节点
Node listInsertTail(Node node); 插入尾节点
Node insertElement(int i, Node node); 指定位置插入节点
Node deleteElement(int i); 删除指定节点
Node getElement(int i); 获取指定位置节点
int elementLocate(Node node); 获取指定节点所在的位置
Node priorElement(Node node); 找到指定节点的前驱
Node nextElement(Node node); 找到指定节点的后继
void listTraverse(); 遍历链表
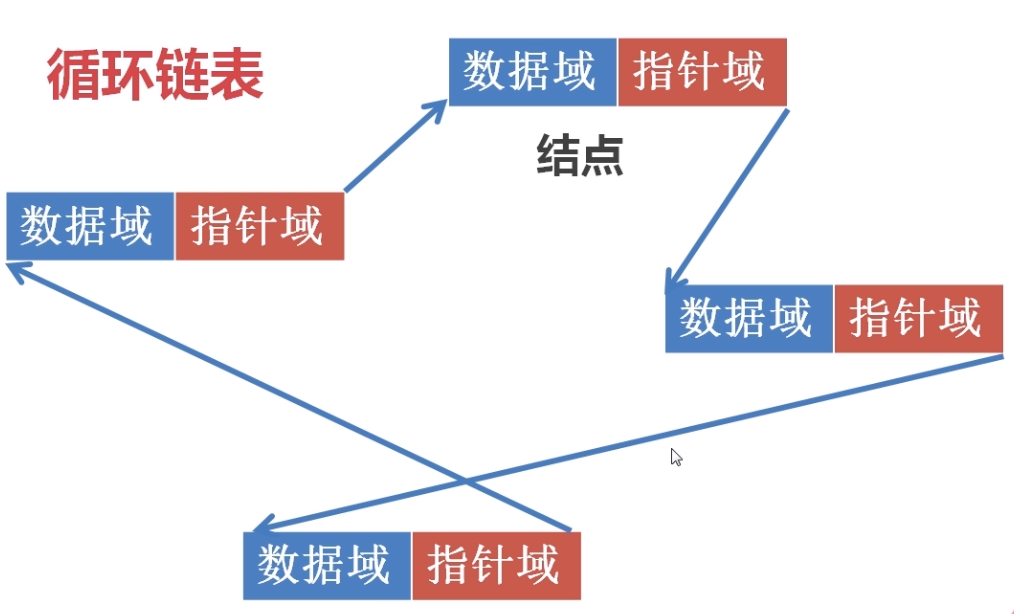
循环链表
简单的说,就是首尾相连的单链表即尾节点的指针域指向首节点的位置
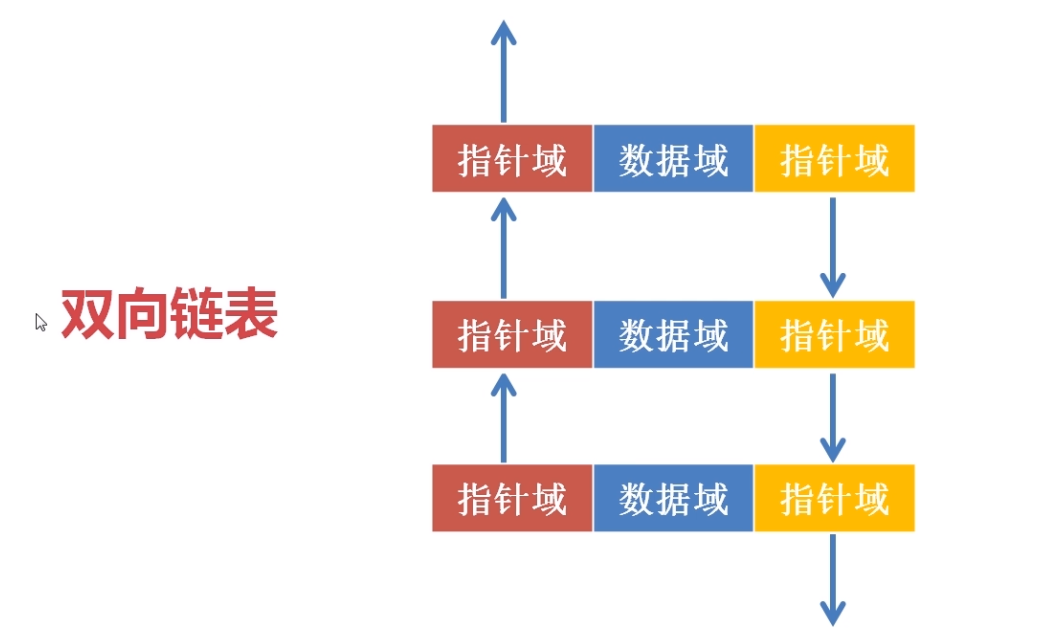
双向链表
双向链表,每个节点分为三部分,分别为:
前指针域:顺向指向下一个节点的位置
数据域:数据节点
后指针域:逆向指向下一个节点的位置
静态链表

此处附上顺序表的创建代码:
package util;
public class MyList {
//线性表本身
private Object myList[];
//线性表的大小,即最大容量
private int listSize;
//线性表的长度,即线性表中的元素个数
private int myLength;
public MyList() {
super();
}
/**
* 初始化线性表 - 顺序表
* @param size
*/
public MyList(int size) {
listSize = size;
//申请线性表内存
myList = new Object[listSize];
myLength = 0;
}
/**
* 销毁线性表
*/
public void DestroyList(){
myList = null;
}
/**
* 清空线性表元素
*/
public void clearList(){
myLength = 0;
}
/**
* 判断线性表是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isListEmpty(){
return myLength == 0 ? true : false;
}
/**
* 获取线性表的元素个数
* @return
*/
public int listLength(){
return myLength;
}
/**
* 获取下标位置的元素
*/
public Object getElement(int i)
{
//需要将i入参进行一定的限制,因为元素存在的位置坐标仅限于0到线性表的个数减一(即0~myLength-1),所以如果i小于0或者i大于等于线性表的长度都判定为获取失败返回null
if(i < 0 || i >= myLength){
return null;
}
return myList[i];
}
/**
* 获取线性表中元素所在的位置(只获取第一个遇到的位置)
* @param element
* @return
*/
public int elementLocate(Object element){
for (int i = 0; i <= myLength; i++){
if (element.equals(myList[i]))
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 获取指定元素前驱
* @param element
* @return
*/
public Object priorElement(Object element){
int i = elementLocate(element);
if(i == -1){
//如果i==-1那么则表示当前线性表中没有找到元素,所以直接判定失败,返回null
return null;
}else if(i == 0){
//如果i==0则该元素本身就是第一个元素,前面不可能再有前驱,所以返回null
return null;
}else{
return myList[i - 1];
}
}
/**
* 获取指定元素后缀
* @param element
* @return
*/
public Object nextElement(Object element){
int i = elementLocate(element);
if(i == -1){
return null;
}else if(i == myLength-1){
return null;
}else{
return myList[i + 1];
}
}
/**
* 在指定位置插入元素
* @param i
* @param element
* @return
*/
public Object insertElement(int i, Object element)
{
if(i < 0 || i > myLength)
{
return null;
}
//此处注意要从后向前依次将i后面的元素向后移位
for (int j = myLength-1; j >= i; j--){
//依次把前面的元素向后移位
myList[j + 1] = myList[j];
}
myList[i] = element;
myLength++;
return element;
}
/**
* 删除指定位置元素
* @param i
* @return
*/
public Object deleteElement(int i){
if (i < 0 || i >= myLength){
return null;
}
Object element = myList[i];
//此处注意要从前向后依次将i后面的元素向后移位,不用单独执行删除操作,因为在移位的过程中已经把i坐标的元素给覆盖了
for (int j = i + 1; j < myLength; j++){
//依次把后面的元素向前移位
myList[j - 1] = myList[j];
}
myLength--;
return element;
}
/**
* 遍历线性表中的元素
*/
public void listTraverse(){
for (int i = 0; i <= myLength-1; i++){
System.out.println(myList[i].toString());
}
}
}
此处附上链表的结构代码:
package util;
import test.entity.Node;
public class MyChainList {
private Node myChainList;
private int listLength;
/**
* 初始化链表
*/
public MyChainList() {
//申请节点内存
myChainList = new Node();
myChainList.data = null;
myChainList.next = null;
listLength = 0;
}
/**
* 销毁链表,废弃
*/
public void destroyList(){
clearList();
myChainList = null;
}
/**
* 判断链表是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isListEmpty(){
return 0 == listLength ? true :false;
}
/**
* 获取链表的长度
* @return
*/
public int listLength(){
return listLength;
}
/**
* 清空链表的所有元素
*/
public void clearList(){
Node currentNode = myChainList;
//初始节点的下一个节点,为第一个节点,找到第一个节点判断是否为空
while(null != currentNode.next){
Node temp = currentNode.next;
//将当前节点删除
currentNode = null;
//查找下一个节点
currentNode = temp;
}
currentNode.data = null;
currentNode.next = null;
listLength = 0;
}
/**
* 插入头节点
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Node listInsertHead(Node node){
//将第一个元素指向的下一个节点,存放备用
Node temp = myChainList.next;
//从堆内存中申请空间,将数据放入内存
Node newNode = new Node();
if(null == newNode){
return null;
}
newNode.data = node.data;
//让新的节点指向,第一个节点原指向的节点
newNode.next = temp;
//将node节点放入第一个节点的后面
myChainList.next = newNode;
listLength ++;
return newNode;
}
/**
* 插入尾节点
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Node listInsertTail(Node node){
Node currentNode = myChainList;
//重第一个节点开始循环查找下一个节点,知道找到尾节点
while(null != currentNode.next)
{
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
//从堆内存中申请空间,将数据放入内存
Node newNode = new Node();
if(null == newNode){
return null;
}
newNode.data = node.data;
newNode.next = null;
//将新节点插入尾节点的后面
currentNode.next = newNode;
listLength ++;
return newNode;
}
/**
* 指定位置插入节点
* @param i
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Node insertElement(int i, Node node){
//判断i是否合法
if (i < 0 || i > listLength){
return null;
}
//遍历节点找到 i 位置的上一个节点
Node currentNode = myChainList;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++){
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
Node newNode = new Node();
if (null == newNode){
return null;
}
newNode.data = node.data;
//将原位于i位置的节点放入新节点的后面
newNode.next = currentNode.next;
//将新节点,放入i上一个节点的后面
currentNode.next = newNode;
listLength ++;
return newNode;
}
/**
* 删除指定节点
* @param i
* @return
*/
public Node deleteElement(int i){
if (i < 0 || i >= listLength){
return null;
}
//找到第i个节点,和i的上一个节点
Node currentNode = myChainList;
Node currentNodeBefore = null;
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++){
currentNodeBefore = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
//将i位置后面的节点,放在i前面节点的后面
currentNodeBefore.next = currentNode.next;
Node temp = currentNode;
currentNode = null;
listLength --;
return temp;
}
/**
* 获取指定位置节点
* @param i
* @return
*/
public Node getElement(int i){
//过滤i的合理范围
if (i < 0 || i >= listLength){
return null;
}
// 找到第i个节点
Node currentNode = myChainList;
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++){
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return currentNode;
}
/**
* 获取指定节点所在的位置
* @param node
* @return
*/
public int elementLocate(Node node){
//循环查找所有节点
Node currentNode = myChainList;
int count = 0;
while(null != currentNode.next){
currentNode = currentNode.next;
//找到链表中第一个与指定节点匹配的节点
if (currentNode.data.equals(node.data)){
//返回当前循环的次数
return count;
}
//每执行一次表示当前位置没有匹配的节点,注意不能放在if前面
count++;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 找到指定节点的前驱
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Node priorElement(Node node){
//找到 指定节点 和 指定节点的 上一个节点
Node currentNode = myChainList;
Node currentNodeBefore = null;
while(null != currentNode.next){
currentNodeBefore = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
//匹配到了第一个与指定节点相同的节点
if (node.data.equals(currentNode.data)){
//如果找到的对象是线性表中的第一个元素,那么他就没有前驱,返回null
if (currentNodeBefore.equals(myChainList)){
return null;
}
return currentNodeBefore;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 找到指定节点的后继
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Node nextElement(Node node){
//遍历线性表,找到指定节点
Node currentNode = myChainList;
while(null != currentNode.next){
currentNode = currentNode.next;
//如果找到了元素
if (currentNode.data.equals(node.data)){
//判断该元素是否为线性表中的最后一个元素,最后一个元素没有后缀,直接返回null
if (currentNode.next == null){
return null;
}
return currentNode.next;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 遍历链表
*/
public void listTraverse(){
//遍历链表中的所有元素,依次打印出他们的 数据域
Node currentNode = myChainList;
while(null != currentNode.next){
currentNode = currentNode.next;
currentNode.printNode();
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号