题解:P3756 [CQOI2017] 老C的方块
我们发现,所谓 ” 讨厌的图形 “ 也就是在关键边两侧各有两个方格,因而我们可以将与关键边相邻的方格染成黑色,将不相邻的染成白色,则一个不合法的图形就是 \(白\to黑\to黑\to白\)。但这个东西是双向的,因而可以加一个颜色的维度,将两列关键边所夹的部分交替染成不同的颜色,如下图:
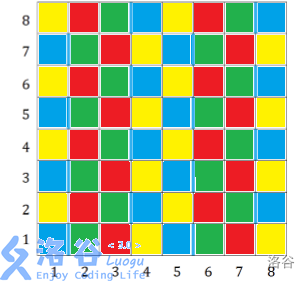
(可以令蓝为黑-黑,黄为白-黑,绿为黑-白,红为白-白)
于是一个不合法的图形变成了 \(s\to白-黑\to黑-黑\to黑-白\to白-白\to t\),网络流建边跑最小割即可,其中 \(w(s,白-黑)=w(白-黑)\),\(w(白-白,t)=w(白-白)\),\(w(黑-黑,黑-白)=\min\{w(黑-黑),w(黑-白)\}\)。
可以将每个点的坐标映射到一个唯一的整数上(比如 \(x\) 列 \(y\) 行可以是 \(x+cy\)),并将这个整数用 map 映射到点的编号上做。注意看一下 \(r\) 和 \(c\) 有没有读反。
参考资料:P3756题解
Code:
//wo ai ii tm ts
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#define rep(i,l,r) for(int i=(l);i<=(r);i++)
#define per(i,l,r) for(int i=(l);i>=(r);i--)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=1e5+10,inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
int ic,ir,in;
typedef long long ll;
struct NetWork{
struct edge{
int to,cf,nxt;
}ae[maxn<<5];
int head[maxn],curh[maxn],dep[maxn],s,t,tot,ecnt;
queue<int> q;
NetWork(){
ecnt=s=1,t=2,tot=2;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
}
inline void addedge(int fr,int to,int w){
ae[++ecnt]={to,w,head[fr]};
head[fr]=ecnt;
ae[++ecnt]={fr,0,head[to]};
head[to]=ecnt;
}
inline bool bfs(){
rep(v1,1,tot)dep[v1]=inf;
dep[s]=0;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int cur=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int v1=head[cur];~v1;v1=ae[v1].nxt)if(ae[v1].cf){
int v=ae[v1].to;
if(dep[v]==inf){
dep[v]=dep[cur]+1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return dep[t]<inf;
}
inline int dinic(int cur,int flow){
if(cur==t||!flow)return flow;
int res=0;
for(int &v1=curh[cur];~v1;v1=ae[v1].nxt){
int v=ae[v1].to;
if(!ae[v1].cf||dep[v]!=dep[cur]+1)continue;
int k=dinic(v,min(flow-res,ae[v1].cf));
ae[v1].cf-=k;
ae[v1^1].cf+=k;
res+=k;
if(res==flow)break;
}
return res;
}
inline int cal(){
int res=0;
while(bfs()){
rep(v1,1,tot)curh[v1]=head[v1];
res+=dinic(s,inf);
}
return res;
}
}tt;
map<ll,int> mp;
inline ll point(int x,int y){
return ll(x)*ic+y;
}
int ax[maxn],ay[maxn],aw[maxn],typ[maxn],dx[10]={0,0,-1,0,1},dy[10]={0,1,0,-1,0};
int main(){
cin>>ic>>ir>>in;
rep(v1,1,in){
scanf("%d %d %d",ay+v1,ax+v1,aw+v1);
typ[v1]=(ay[v1]%4<=1?0:2)+((ax[v1]^ay[v1])&1);
mp[point(ax[v1],ay[v1])]=++tt.tot;
if(typ[v1]==1)tt.addedge(tt.s,tt.tot,aw[v1]);
if(typ[v1]==2)tt.addedge(tt.tot,tt.t,aw[v1]);
}
rep(v1,1,in){
int x=ax[v1],y=ay[v1];
rep(v2,1,4){
int nx=x+dx[v2],ny=y+dy[v2];
if(nx<1||ny<1||nx>ir||ny>ic||!mp.count(point(nx,ny)))continue;
int t=mp[point(nx,ny)];
if(!typ[v1]){
if(typ[t-2]==1)tt.addedge(t,v1+2,inf);
else tt.addedge(v1+2,t,min(aw[v1],aw[t-2]));
}
else if(typ[v1]==3&&typ[t-2]==2)tt.addedge(v1+2,t,inf);
}
}
cout<<tt.cal()<<endl;
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号