ConcurrentHashMap (jdk1.8)源码学习
一.介绍
1.ConcurrentHashMap
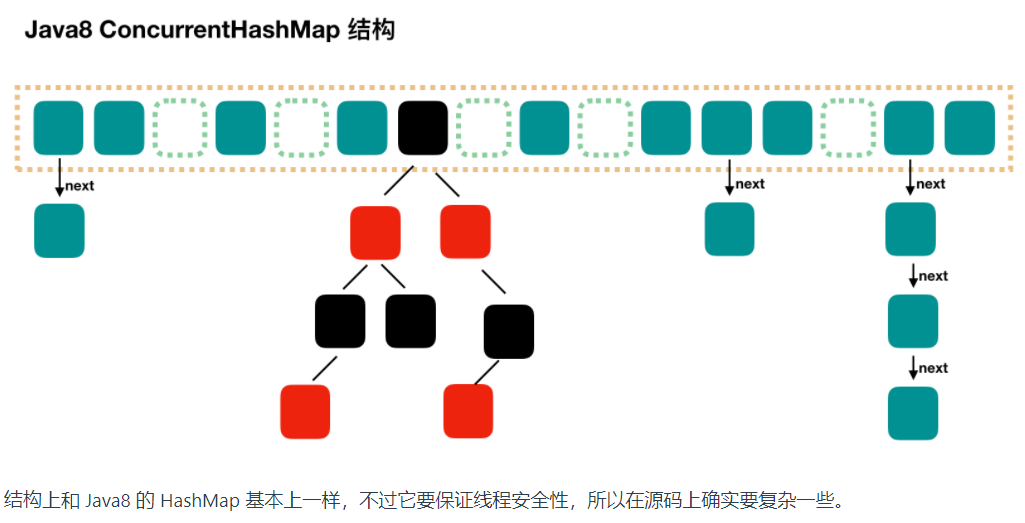
2.jdk1.7和jdk1.8区别
- 底层数据结构
- 1.7: segment + hashentry
- 1.8: 数组 + 链表 + 红黑树
- 线程安全
- 1.7: 分段锁机制实现
- 1.8:Synchronized + CAS
- 锁的粒度
- Segment加锁
- node加锁
二、源码部分
1.属性
AbstractMap是 Map 接口的的实现类之一,也是 HashMap, TreeMap, ConcurrentHashMap 等类的父类。
ConcurrentMap它是一个接口,是一个能够支持并发访问的java.util.map集合
Serializable:一个对象序列化的接口,一个类只有实现了Serializable接口,它的对象才能被序列化
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements ConcurrentMap<K,V>, Serializable {
//定义序列化ID
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7249069246763182397L;
// 表的最大容量
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认表的大小
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
// 最大数组大小
static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
// 默认并发数
private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
// 负载因子
private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 转化为红黑树的阈值
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// 由红黑树转化为链表的阈值
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// 转化为红黑树的表的最小容量
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
// 每次进行转移的最小值
private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;
// 生成sizeCtl所使用的bit位数
private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;
// 进行扩容所允许的最大线程数
private static final int MAX_RESIZERS = (1 << (32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS)) - 1;
// 记录sizeCtl中的大小所需要进行的偏移位数
private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS;
/* ---------------- Fields -------------- */
/**
* The array of bins. Lazily initialized upon first insertion.
* 容器数组。在第一次插入时惰性初始化
* Size is always a power of two. Accessed directly by iterators.
* 大小总是2的幂。由迭代器直接访问
*/
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
/**
* The next table to use; non-null only while resizing.
* 要使用的下一table;仅在调整大小时为非空
*/
private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
/**
* Base counter value, used mainly when there is no contention,
* but also as a fallback during table initialization
* races. Updated via CAS.
* 主要在没有竞争时使用,但也可以作为表初始化争用期间的回退。
* 基本计数
*/
private transient volatile long baseCount;
/**
* 多个线程的共享变量,表初始化和调整大小控制
* -1代表正在初始化
* -N代表有N-1个线程正在进行扩容操作
* 0代表hash表还没有被初始化
* 正数表示扩容阈值
*/
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
/**
* The next table index (plus one) to split while resizing.
* 在调整大小时要分割的下一个表索引
*/
private transient volatile int transferIndex;
/**
* Spinlock (locked via CAS) used when resizing and/or creating CounterCells.
* 自旋锁(通过CAS锁定)用于调整大小和/或创建CounterCells。
*/
private transient volatile int cellsBusy;
/**
* Table of counter cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.
* 计数器单元格表。当非空时,size是2的幂
*/
private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
2.构造函数
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16).
* 使用默认初始表大小(16)创建一个新的空映射。
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size
* accommodating the specified number of elements without the need
* to dynamically resize.
* 该构造函数用于创建一个带有指定初始容量、默认加载因子 (0.75) 和 concurrencyLevel (16) 的新的空映射。
* @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal
* sizing to accommodate this many elements.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
//初始容量<0抛出异常
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
//因为loadfactor默认为0.75,所以容量!=元素个数
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
Java/**
* Creates a new map with the same mappings as the given map.
* 使用与给定映射相同的映射创建一个新映射。
* @param m the map
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.sizeCtl = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
putAll(m);
}
//该构造函数用于创建一个带有指定初始容量、加载因子和默认 concurrencyLevel (1) 的新的空映射。
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);
}
//该构造函数用于创建一个带有指定初始容量、加载因子和并发级别的新的空映射。
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
//合法性检查
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
3.内部类
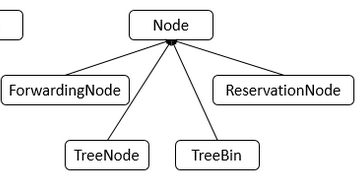
Node
链表中的元素为 Node 对象。他是链表上的一个节点,内部存储了 key、value 值
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V val;
volatile Node<K,V> next;
//val和next都会在扩容时发生变化,所以加上volatile来保持可见性和禁止重排序
Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
Object k, v, u; Map.Entry<?,?> e;
return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&
(k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null &&
(v = e.getValue()) != null &&
(k == key || k.equals(key)) &&
(v == (u = val) || v.equals(u)));
}
/**
* Virtualized support for map.get(); overridden in subclasses.
* 虚拟化支持map.get();在子类覆盖。
*/
Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
Node<K,V> e = this;
if (k != null) {
do {
K ek;
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
return null;
}
}
ForwardingNode
当进行扩容时,要把链表迁移到新的哈希表,在做这个操作时,会在把数组中的头节点替换为 ForwardingNode 对象。
ForwardingNode 中不保存 key 和 value,只保存了扩容后哈希表(nextTable)的引用。此时查找相应 node 时,需要去 nextTable 中查找。
/**
* A node inserted at head of bins during transfer operations.
* 在传输操作期间,在容器头部插入的一个节点。
*/
static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
final Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
//哈希值默认为-1
super(MOVED, null, null, null);
this.nextTable = tab;
}
TreeBin
当链表转为红黑树后,数组中保存的引用为 TreeBin,TreeBin 内部不保存 key/value,他保存了 TreeNode 的 list 以及红黑树 root。
TreeNode
红黑树的节点
4.put过程
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent put和putIfAbsent的实现*/
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
//如果key或value为空,抛出异常
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
//用来计算当前链表上的元素个数
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
//如果table为空,则初始化table
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
//否则,找到对应的下标,如果为空则通过CAS操作添加结点
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
////若为-1,说明当前数组正在进行扩容,则需要当前线程帮忙迁移数据
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
//如果没在扩容中,且发生哈希冲突
V oldVal = null;
/**
* 当一个线程进入 synchronizer 代码块后,
* 线程获取到锁,会清空本地内存,
* 然后从主内存中拷贝共享变量的最新值到本地内存作为副本,执行代码,
* 又将修改后的副本值刷新到主内存中,最后线程释放锁。
*/
synchronized (f) {
//检查最新的头节点是否还是f
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
//如果hash值大于等于0,说明是正常的链表结构
if (fh >= 0) {
//从头结点开始遍历,每次binCount++
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
//如果找到了相同的key,则用新的value替换原来的
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
//否则,则在链表的最后面插入新的结点
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
//如果该位置为树结点
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
//如果结点数超过了8,则树化链表
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
//count++
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
5.initTable()
/**
* Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl.
* 使用sizeectl中记录的大小初始化表
*/
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
//循环判断表是否为空,直到初始化成功为止
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
//如果一个线程发现sizeCtl<0,意味着另外的线程执行CAS操作成功,当前线程只需要让出cpu时间片
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin 失去了初始化竞争;只是自旋
//否则,CAS操作将SIZECTL为改为-1,表示初始化状态,成功返回true
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//新建个默认大小的数组
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
//负载因子0.75 * 当前容量n
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
//扩容阈值
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
//返回表
return tab;
}
6.addCount()方法
put 方法元素插入成功之后,则会调用此方法,传入参数为 addCount(1L, binCount)
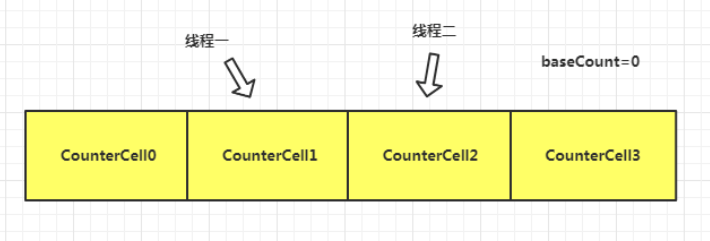
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
//当counterCells,即线程分配到的格子不为空
//basecount为size
//所以 || 后的代表原子操作,就是在counterCells为空的时候,直接CAS给size+1
//成功返回true,失败返回false,则失败的话,进入if方法体
//总结就是,多线程时要利用counterCells格子中的value+1,进行size+1
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
//线程竞争标识,先标记为true
boolean uncontended = true;
//若数组为空
//ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() 方法会给当前线程生成一个随机数
//若数组不为空,且线程所在格子不为空,则尝试 CAS 修改此格子对应的 value 值加1。
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
//让当前线程一定把 1 加成功
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
//<=1则不需要检查扩容
if (check <= 1)
return;
////计算总共的元素个数
s = sumCount();
}
// 这里用于检查是否需要扩容
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
//检查当前集合元素个数 s 是否达到扩容阈值 sizeCtl ,扩容时 sizeCtl 为负数,依旧成立,
//同时还得满足数组非空且数组长度不能大于允许的数组最大长度这两个条件才能继续
//这个 while 循环除了判断是否达到阈值从而进行扩容操作之外
// 还有就是当一条线程完成自己的迁移任务后,如果集合还在扩容,则会继续循环,继续加入扩容大军,申请后面的迁移任务
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
//扩容时的校验标识
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
// sc < 0 说明集合正在扩容当中
if (sc < 0) {
//判断扩容是否结束或者并发扩容线程数是否已达最大值,如果是的话直接结束while循环
//sc的高16位是数据校验标识,低16位代表当前有几个线程正在帮助扩容
//判断校验标识是否相等,扩容是否完成或者不需要线程帮忙都会结束循环
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
//需要线程帮忙的话, transfer,nt = nextTable
//然后CAS将线程数+1
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
//如果集合还未处于扩容状态中,则进入扩容方法,首先初始化 nextTab 数组,也就是新数组
//(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2 为首个扩容线程所设置的特定值
// 后面扩容时会根据线程是否为这个值来确定是否为最后一个线程
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
8.transfer()方法
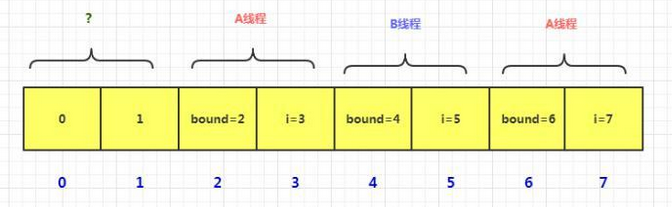
。。。
三.总结
sizeCtl:
-
新建而为初始化的时候:
sizeCtl 用于记录初始容量大小,仅用于记录集合在实际创建时应该使用的大小的作用
-
初始化过程中:
值为- 1,表示集合正在初始化中,其他线程发现该值为-1时会让出cpu资源
-
初始化完成后:
sizeCtl 用于记录当前集合的负载容量值,也就是触发集合扩容的极限值
-
正在扩容时:
sizeCtl 用于记录当前扩容的并发线程数情况,此时 sizeCtl 的值为:((rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2) + (正在扩容的线程数) ,并且该状态下 sizeCtl < 0 。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号