JAVASE进阶day06(ArrayList集合 & 常用api&时间工具类)
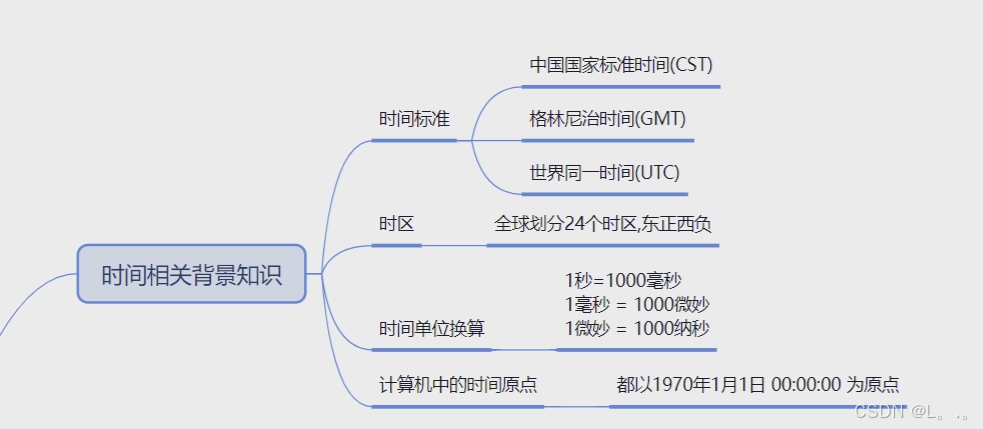
时间相关背景知识
 时间相关类
时间相关类

1.1.0 java.util下相关类
Date(年月日时分秒)
package com.lu.day06.date01;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateDome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//date对象就代表当前时间
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
//date.compareTo()比较时间
//获取当前时间戳
long time = date.getTime();
System.out.println(time);
//获取当前时间戳
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(l);
}
}
SimpleDateFormat格式化时间类
package com.lu.day06.date01;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 时间格式化
*/
public class SimpleDateFormatDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();
//时间对象格式化成时间字符串
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
System.out.println(simpleDateFormat.format(date));
//时间字符串转换成时间对象
String s = "2024/07/07 10:21:59.937";
try {
//声明了一个编译时异常->捕获此编译异常->catch抛出一个运行时异常
Date parse = simpleDateFormat.parse(s);
System.out.println(parse);
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
TimeZone时区类
package com.lu.day06.date01;
import java.util.TimeZone;
/**
* 时区类
*/
public class TimeZoneDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取当前系统时区Asia/Shanghai上海时间就是北京时间
TimeZone aDefault = TimeZone.getDefault();
System.out.println(aDefault.getDisplayName());
System.out.println(aDefault.getID());
}
}
练习
package com.lu.day06.date01;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 秒杀活动 : 小汉堡秒杀活动 ,
* 活动起始时间为2022/09/16 10:00:00 至 2022/09/16 10:10:10
* 老八在 2022/9/16 10:09:00 下单 用代码实现老八是否抢到了小汉堡
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
Date parse = simpleDateFormat.parse("2022/09/16 10:00:00");
Date parse1 = simpleDateFormat.parse("2022/09/16 10:10:10");
Date parse2 = simpleDateFormat.parse("2022/09/16 10:09:00");
if (parse2.compareTo(parse) >=0 && parse2.compareTo(parse1) <= 0){
System.out.println("抢到了");
}else {
System.out.println("没抢到");
}
}
}
2.1.8 java.time下相关类
package com.lu.day06.date08;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
/**
* 三个时间日期类具体可以获取当前时间(now),解析格式化时间(format),
* 转时间戳(toInstant),以及一些时间判断(is开头),还有时间加减操作(minus,plus开头)
*/
public class LocalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//now 获取当前时间
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
LocalDate now1 = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println(now1);
LocalTime now2 = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println(now2);
//时间格式化成字符串->各自对象的成员format方法
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter1 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日");
String format = now.format(dateTimeFormatter);
System.out.println(format);
System.out.println(now1.format(dateTimeFormatter1));
String fmt1 = now.format(dateTimeFormatter);
System.out.println(fmt1);
System.out.println(now1.format(dateTimeFormatter1));
String s = "2024年07月07日 11:56:33";
//字符串转换成时间对象->各自类中的静态方法parse
LocalDateTime parse = LocalDateTime.parse(s, dateTimeFormatter);
System.out.println(parse);
}
}
Instant
package com.lu.day06.date08;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
/**
* 时刻类
* 专门用来获取时间戳
*/
public class InstantDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//时刻时一个与时区无关的概念
Instant now = Instant.now();
//获取秒时间戳
long epochSecond = now.getEpochSecond();
//获取毫秒时间戳
long l = now.toEpochMilli();
System.out.println(epochSecond);
System.out.println(l);
//如何定义时间
LocalDateTime now1 = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime of = LocalDateTime.of(2025, 8, 8, 15, 34, 20);
//转换时间戳
Instant instant = of.toInstant(ZoneOffset.UTC);
System.out.println(instant.toEpochMilli());
}
}
Duration
package com.lu.day06.date08;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 时间日期区间类
* 专门计算两个时间区间的差值(一系列的to,例如toDays,toHours...)
*/
public class DurationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime start = LocalDateTime.of(2003, 8, 8, 8, 8, 20);
LocalDateTime of = LocalDateTime.of(2003, 7, 7, 7, 7, 20);
Duration between = Duration.between(start, of);
System.out.println(between.toDays());
System.out.println(between.toHours());
/*
day06最重要(1.0和1.8不一样全要记住)
1.如何获取当前时间?
1.0:new Date()
1.8:静态方法now();
2.如何获得时间戳?
1.0:System类,getTime()方法;
1.8:toInstant()
3.如何进行时间日期转换?
format parse
1.0 new SDT(模式)
1.8 DTF.of(模式)
*/
}
}
3.实体类日期时间格式转换收集
@Test
public void testSelectNewsAll(){
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
ArrayList<News> news = mapper.selectAllNews();
List<News> collect = news.stream().map(t -> {
t.setTitle(t.getTitle());
t.setAuthor(t.getAuthor());
t.setContent(t.getContent());
t.setPubTime(t.getPubTime());
String format = t.getPubTime().format(dateTimeFormatter);
t.setSPubTime(format);
return t;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
log.info("全部信息{}",collect);
}
集合
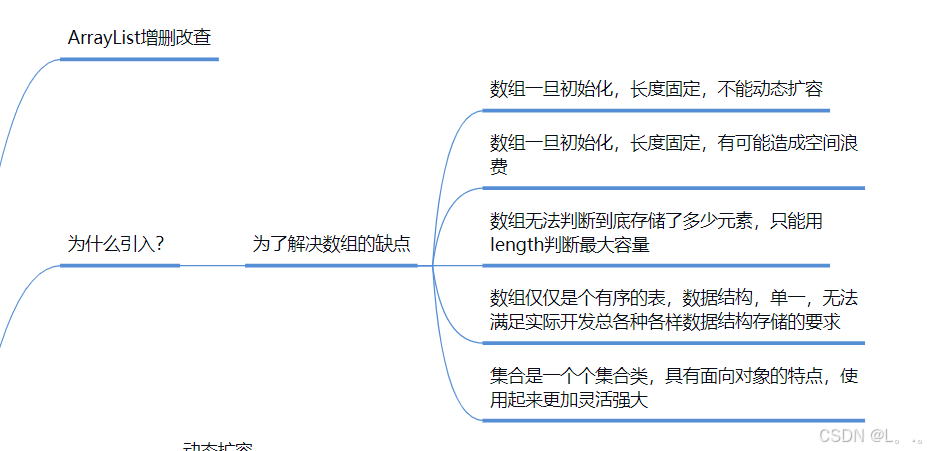
1.为什么要用
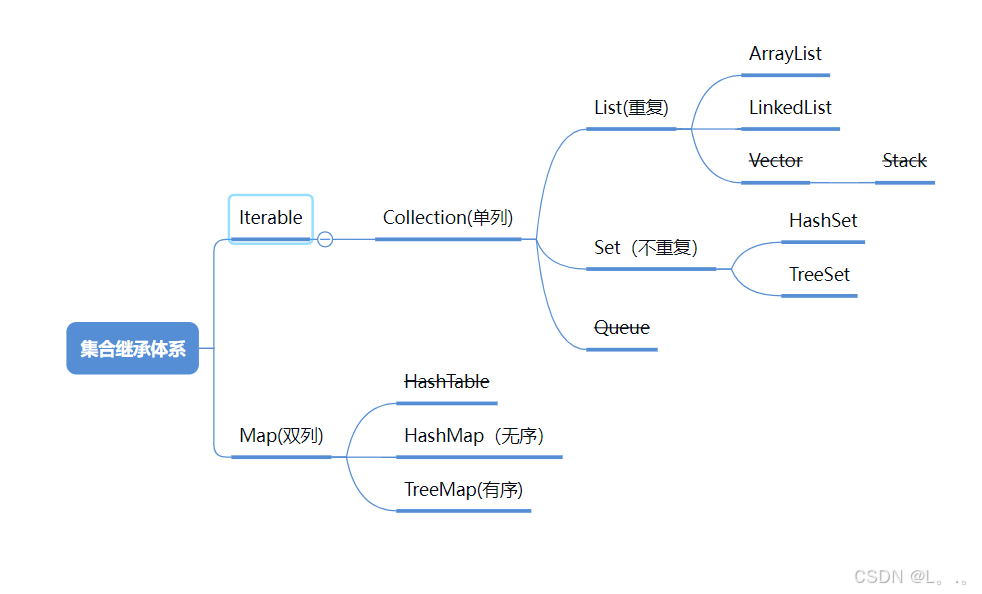
2.集合特征体系
3.特点
动态扩容,不能存储基本类型,存储数据结构多种多样
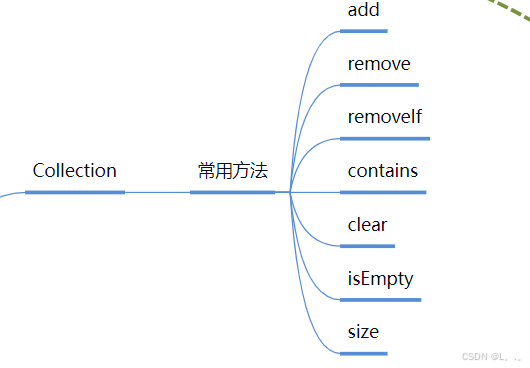
4.Collection(所有单列集合的父类)
package com.lu.day06.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("小明");
list.add("催命");
list.add("王彪");
list.add("小虎");
list.add("马蚤");
list.remove("小虎");
//删除(所有的单列集合都能用)
//list.removeIf(t->t>=4);
//System.out.println(list);
//只有单列集合可以使用
//list.sort((o1,o2)->o1-o2);
//System.out.println(list);
//定义在单例集合的父接口Iterable中
//Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
//while (iterator.hasNext()){
//String next = iterator.next();
//if (next.equals("小虎")){
//iterator.remove();
//}
//}
System.out.println(list);
}
}
5.Iterator迭代器
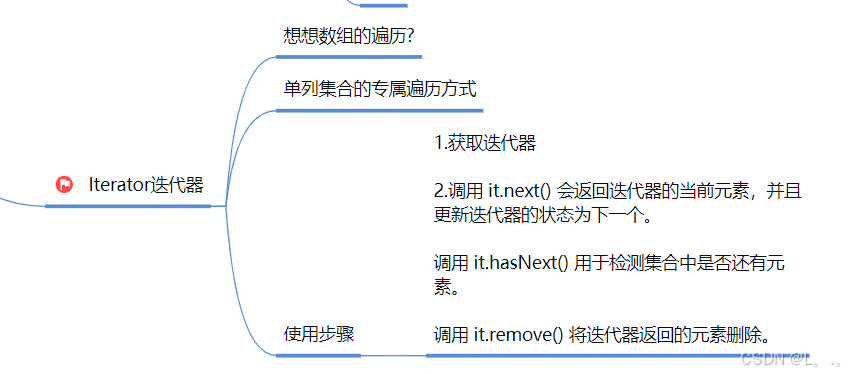
6.增强for

package com.lu.day06.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class EnhanceFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("小明");
list.add("催命");
list.add("王彪");
list.add("小虎");
list.add("马蚤");
for (String s : list) {//底层用的是迭代器//缺点只能遍历不能操作元素(无大碍)
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
7.forEach集合遍历
package com.lu.day06.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 定义在单例集合父类Iterable接口中
* 函数式的集合遍历方式->函数式接口->lambda表达式
* foreach就是一个函数式方法->1.8->参数必然式函数式接口
*/
public class ForeachDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.forEach(t-> System.out.println(t));
}
}
8.三种迭代方式使用场景
操作索引普通for,遍历过程中删除iterator,仅仅遍历增强for
List
1.特点
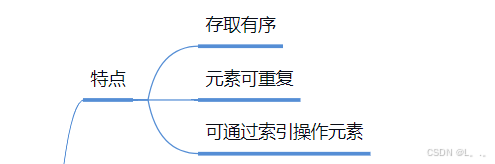
2.特有方法
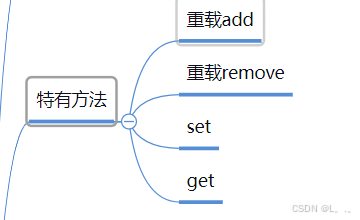
3.ArrayList数据结构
数据结构
1.why
java集合的底层实现中,往往都采用了一种甚至几种数据结构结合运用来实现,从而保证在某些方面更高效,例如ArrayList采用数组
2.概念
数据结构是计算机存储、组织数据的方式。是指相互之间存在一种或多种特定关系的数据元素的集合。通常情况下,精心选择的数据结构可以带来更高的运行或者存储效率。
3.几种常见的数据结构(背会)



LinkedList

面试题
1.说一下java集合继承结构
Java 集合类主要包括 Collection 和 Map 两个接口,它们的继承结构如下:
Collection接口:List接口:有序、可重复的集合。ArrayList:基于动态数组实现,随机访问效率高。LinkedList:基于双向链表实现,插入和删除效率高。Vector:与ArrayList类似,但线程安全。- ArrayList和
LinkedList的区别
Set接口:无序、不可重复的集合。HashSet:基于哈希表实现,不保证元素的顺序。LinkedHashSet:基于哈希表和链表实现,保证元素的插入顺序。TreeSet:基于红黑树实现,保证元素的自然顺序。
Map接口:存储键值对的数据结构。HashMap:基于哈希表实现,不保证键值对的顺序。LinkedHashMap:基于哈希表和链表实现,保证键值对的插入顺序。TreeMap:基于红黑树实现,保证键值对按照键的自然顺序排序。Hashtable:与HashMap类似,但线程安全。
2.说一下List中常用的类及其特点
在 Java 中,List 是一个接口,它继承自 Collection 接口,表示一个有序的集合。常用的实现类有以下几种:
-
ArrayList
- 特点:底层数据结构是数组,支持随机访问。它的增删操作相对较慢(特别是在中间插入或删除),因为需要移动数组中的元素。
- 线程安全:不是线程安全的。
- 适用场景:适合频繁读取数据的场景。
-
LinkedList
- 特点:底层数据结构是双向链表,插入和删除操作速度较快(在任意位置),但随机访问较慢,因为需要遍历链表。
- 线程安全:不是线程安全的。
- 适用场景:适合频繁插入、删除操作的场景。
3.说一下如何使用LinkedList模拟栈和队列
LinkedList 是 Java 中一个非常灵活的类,它不仅可以用来实现链表,还可以用来模拟栈(Stack)和队列(Queue)。这是因为 LinkedList 提供了许多方便的方法来操作它的头部和尾部元素。
使用 LinkedList 模拟栈
栈(Stack)是一种后进先出(LIFO, Last In First Out)的数据结构。在 LinkedList 中,可以使用以下方法来实现栈的功能:
push(E e): 将元素推入栈顶。pop(): 移除并返回栈顶的元素。peek(): 返回栈顶的元素但不移除它。
使用 LinkedList 模拟队列
队列(Queue)是一种先进先出(FIFO, First In First Out)的数据结构。在 LinkedList 中,可以使用以下方法来实现队列的功能:
offer(E e): 将元素插入队列尾部。poll(): 移除并返回队列头部的元素。peek(): 返回队列头部的元素但不移除它。
4.说一下常见的数据结构
常见的数据结构有,栈(特点先进后出),队列(先进先出),数组(它可以存储固定类型的元素序列。),链表(它由节点组成,每个节点包含数据和指向下一个节点的引用。)
5.说一下数组和集合的区别
在 Java 中,集合和数组有以下一些区别:
- 长度可变与否
-
数组:创建后长度固定,不能动态地增加或减少元素数量。
-
集合:大部分集合类(如
ArrayList、HashSet等)可以在运行时动态地添加、删除元素,长度是可变的。
2.存储元素类型
-
数组:在创建时就确定了存储元素的类型,并且只能存储同一种数据类型的元素。
-
集合:许多集合类(如
ArrayList)可以存储不同类型的对象,因为它们实际上存储的是对象的引用。不过如果使用泛型集合(如ArrayList<String>),也可以指定存储的元素类型。
3.元素存储方式
-
数组:元素在内存中是连续存储的。
-
集合:不同的集合类有不同的内部存储结构,如
HashSet基于哈希表存储,LinkedList基于双向链表存储等。
4.方法和功能
-
集合类提供了丰富的方法用于对元素进行添加、删除、查找、遍历等操作,并且不同的集合类针对不同的场景进行了优化和功能扩展。
-
数组虽然也有一些基本的操作方法,但功能相对简单。
5.数据结构
-
数组是一种基本的数据结构。
-
集合类基于不同的数据结构实现,以满足不同的需求,例如列表、集合、映射、栈、队列等。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号