java基础10网络编程
1.基本概念
网络通信:
1.定位主机 IP和端口号
2.进行通信 协议
OSI七层模型
TCP/IP四层
主要在 TCP和UDP
1.1 IP地址
IP地址:唯一标识一台网路上的计算机
127.0.0.1 本机localhost
-
IP v4地址:4字节
-
IP v6地址:16字节128位
常用类 InetAddress
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| public static InetAddress getLocalHost() | 获得存有本机IP的InetAddress对象 |
| public static InetAddress getByName(String host) | 获得存有其他电脑IP地址的InetAddress对象 |
| public String getHostName() | 从InetAddress对象中获得主机名 |
| public String getHostAddress() | 从InetAddress对象中获得IP地址 |
1.2 端口
端口表示进程
0-65535 端口不能冲突
-
公共端口:0-1023
HTTP:80
HTTPS:443
FTP:21
Telent:23
-
程序端口:1024-49151
Tomcat:8080
MySQL:3306
Oracle:1521
-
动态 私有 49152-65535
1.3 协议
TCP/IP协议
-
TCP:稳定连接
三次握手四次挥手:A--->B B--->A A--->B
A--->B B--->A B--->A A--->B
C/S
-
UDP:无连接不稳定
2.Socket
两个进程间可以通过一个双向的网络通信连接实现数据交换,这种通信链路的端点被称为“套接字”(Socket = IP + port)
Socket通常用来实现Client-Server连接
Java.net包中定义的两个类Socket和ServerSocket,分别用来实现双向链接的client和server端。
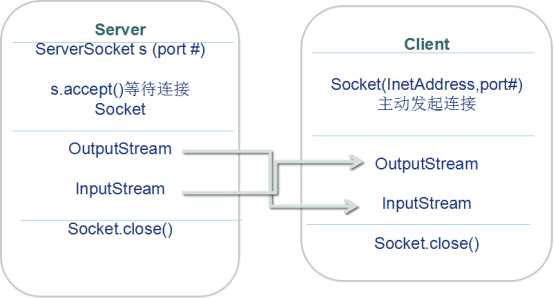
2.1 TCP
//服务器端
public void server(){
ServerSocket ss = null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream boas = null;
try {
//服务端套接字
ss = new ServerSocket(9999);
//接收来自客户端的套接字
socket = ss.accept();
//获取输入流
is = socket.getInputStream();
//接收信息
boas = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[5];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
boas.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(boas.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//关闭资源
try {
boas.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//客户端
public void client() {
InetAddress inet = null;
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
//获取地址
inet = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
//创建套接字
socket = new Socket(inet, 8888);
//获取输出流
os = socket.getOutputStream();
//输出
os.write("客户端666".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//关闭流
if (os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//关闭套接字
if (socket != null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.2 UDP
public void sender() throws IOException {
//目标地址
InetAddress inet = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
//建立套接字
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();
//发送数据
byte[] data = "哈哈哈哈".getBytes();
//数据包
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data,0,data.length,inet,9999);
socket.send(packet);
//关闭
socket.close();
}
public void receiver() throws IOException {
//建立套接字
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(9999);
//缓冲
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
//数据包
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer,0,buffer.length);
//接收在包里
socket.receive(packet);
System.out.println(new String(packet.getData(),0,packet.getLength()));
socket.close();
}
3.URL
统一资源定位符. 指向万维网上的“资源”
URL url = new URL(path);
| 常用方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| url.getAuthority() | 授权内容 |
| url.getProtocol() | 协议 |
| url.getPort() | 端口 |
| url.getFile() | 文件 |
| url.getContent() | 资源 |
| url.getHost() | 主机 |
| url.getPath() | 文件路径 |
| url.getQuery() | 查询名 |
| url.getRef() | |
| url.getUserInfo() |
//调用接口(服务)
URL url = new
//抓取一些数据
//读到 一些数据 --->输入流
URLConnection connection = url.openConnection();
connection.connect();
//数据目前都在inputStream里面
InputStream inputStream = connection.getInputStream();
connection.disconnect();



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号