In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation
DZY loves Fibonacci numbers very much. Today DZY gives you an array consisting of n integers: a1, a2, ..., an. Moreover, there are mqueries, each query has one of the two types:
- Format of the query "1 l r". In reply to the query, you need to add Fi - l + 1 to each element ai, where l ≤ i ≤ r.
-
Format of the query "2 l r". In reply to the query you should output the value of
![]() modulo 1000000009 (109 + 9).
modulo 1000000009 (109 + 9).
Help DZY reply to all the queries.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 300000). The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — initial array a.
Then, m lines follow. A single line describes a single query in the format given in the statement. It is guaranteed that for each query inequality 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n holds.
For each query of the second type, print the value of the sum on a single line.
4 4 1 2 3 4 1 1 4 2 1 4 1 2 4 2 1 3
17 12
After the first query, a = [2, 3, 5, 7].
For the second query, sum = 2 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 17.
After the third query, a = [2, 4, 6, 9].
For the fourth query, sum = 2 + 4 + 6 = 12.
大意:用fib去加到每个节点,求区域的和
代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAXNODE = 2097152; // == (1 << 21) - 1 depth:21
const int MAXS = 300003;
struct SOILD{
int left,right; // 数组模拟满二叉树, 区间 [left,right]
long value;
}Soldier[MAXNODE];
long fib[300005];
int father[MAXS]; // 存每一个士兵的父结点
void BuildTree(int i,int left,int right,int devalue){ // 初始值为0
Soldier[i].left = left;
Soldier[i].right = right;
Soldier[i].value = devalue;
if (left == right){
father[left] = i; // 可以瞬间知道第i个士兵的父节点是哪个
return;
}
BuildTree(i*2, left, (int)floor((right+left)/2.0), 0);
BuildTree(i*2+1, (int)floor((right+left)/2.0)+1, right, 0);
}
void UpdataTree(int ri,int iKilln){ // 单点更新: 点p[i,i] 更新为iKilln (初始为0)
if (ri == 1){
Soldier[ri].value += iKilln;
return;
}
Soldier[ri].value += iKilln; // iKilln 设为全局变量应该快一点
UpdataTree(ri/2,iKilln);
}
long res;
void Query(int i,int a,int b){ // [a,b]区间的和
if (a == Soldier[i].left && b == Soldier[i].right){
res += Soldier[i].value;
return ;
}
if (a <= Soldier[i*2].right){ // 左端点小于右端点(几何含义:区间横跨过中点) 则区间需要分割
if (b <= Soldier[i*2].right){
Query(i*2, a, b); // 左边全包含
}else{
Query(i*2, a, Soldier[i*2].right); // 横跨取左
}
}
if (b >= Soldier[i*2+1].left){
if (a >= Soldier[i*2+1].left){
Query(i*2+1, a, b); // 右边全包含
}else{
Query(i*2+1, Soldier[i*2+1].left, b); // 横跨取右
}
}
}
int main(){
int n_s,n_q;
long iKilln,a,b;
cin >> n_s >> n_q;
BuildTree(1,1,n_s,0);
fib[1]=1;fib[2]=1;
for(int k2=3;k2<300005;k2++)
{
fib[k2]=fib[k2-1]+fib[k2-2];
}
for (int ii = 1 ;ii <= n_s; ii++){ // 建树
scanf("%d",&iKilln); // iKilln 为第 i 个增加的杀敌数
UpdataTree(father[ii],iKilln); // 瞬间找到士兵的结点序号
}
int order;
for (int i = 1; i <= n_q; i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&order,&a,&b); // [a,b] ; a + kill b
if (order==2){
res = 0;
Query(1,a,b);
printf("%d\n", res);
}else
{
for(int kk=a;kk<=b;kk++)
UpdataTree(father[kk],fib[kk-a+1]);
}
//for(int ttt=1;ttt<=n_s;ttt++)
// printf("%d;;",Soldier[father[ttt]].value);
// printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。



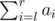 modulo
modulo 
 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号