软件工程笔记:软件测试
该部分为本科期间软件工程课程笔记备份。
Program testing
Testing is intended to show that a program does what it is intended to do and to discover program defects before it is put into use. 测试的目的在于确认程序做了它该做的事情以及在投入使用前发现问题
When you test software, you execute a program using artificial data. 测试软件的时候使用人造数据执行程序
You check the results of the test run for errors, anomalies or information about the program’s non-functional attributes.您可以检查测试运行的结果,以查找错误、异常或有关程序非功能属性的信息。
Can reveal the presence of errors NOT their absence.可以揭示错误的存在,而不是错误的缺失。
Testing is part of a more general verification and validation process, which also includes static validation techniques.测试是更一般的验证和验证过程的一部分,其中还包括静态验证技术。
Program testing goals(two goals)
- To demonstrate to the developer and the customer that the software meets its requirements. 向开发人员和客户演示软件满足其需求。
- For custom software, this means that there should be at least one test for every requirement in the requirements document. For generic software products, it means that there should be tests for all of the system features, plus combinations of these features, that will be incorporated in the product release. 对于自定义软件,这意味着对于需求文档中的每个需求,至少应该有一个测试。对于通用软件产品,这意味着应该对所有的系统特性以及这些特性的组合进行测试,这些特性将包含在产品发行版中
- To discover situations in which the behavior of the software is incorrect, undesirable or does not conform to its specification. 发现软件行为不正确、不受欢迎或不符合其规范的情况。
- Defect testing is concerned with rooting out undesirable system behavior such as system crashes, unwanted interactions with other systems, incorrect computations and data corruption.缺陷测试关注于根除不需要的系统行为,例如系统崩溃、与其他系统不需要的交互、不正确的计算和数据损坏。
Validation and defect testing
- The first goal leads to validation testing 第一个目标是验证测试
- You expect the system to perform correctly using a given set of test cases that reflect the system’s expected use. 您期望系统使用一组反映系统预期用途的给定测试用例正确地执行。
- The second goal leads to defect testing 第二个目标导致缺陷测试
- The test cases are designed to expose defects. The test cases in defect testing can be deliberately obscure and need not reflect how the system is normally used. 测试用例的目的是暴露缺陷。缺陷测试中的测试用例可以故意模糊,并且不需要反映系统是如何正常使用的。
Testing process goals
- Validation testing 验证测试
- To demonstrate to the developer and the system customer that the software meets its requirements 向开发人员和系统客户演示软件满足其需求
- A successful test shows that the system operates as intended.一次成功的测试表明,系统运行正常。
- Defect testing 缺陷测试
- To discover faults or defects in the software where its behaviour is incorrect or not in conformance with its specification 发现软件中行为不正确或不符合规范的错误或缺陷
- A successful test is a test that makes the system perform incorrectly and so exposes a defect in the system.成功的测试是使系统执行不正确,从而暴露系统缺陷的测试。
An input-output model of program testing:

Inputs in the set Ie;Outputs in the set Oe
Verification vs validation
Validation:确认
- "Are we building the right product ?”我们正在开发正确的产品吗
- The software should do what the user really requires.软件应该做用户真正需要做的事情
Verification: 验证
- "Are we building the product right ?”我们生产的产品对吗
- The software should conform to its specification.软件应符合其规范
V & V confidence
Aim of V & V is to establish confidence that the system is ‘fit for purpose’.V & V的目的是建立信心,使人们相信该体系“适合目标”。
Depends on system’s purpose, user expectations and marketing environment取决于系统的目的、用户期望和营销环境
- Software purpose 软件目的
- The level of confidence depends on** how critical** the software is to an organisation.信心的程度取决于软件对组织的重要性
- User expectations 用户期望
- Users may have low expectations of certain kinds of software.用户可能对某些软件的期望值很低。
- Marketing environment 市场环境
- Getting a product to market early may be more important than finding defects in the program. If a software product is very cheap, users may be willing to tolerate a lower level of reliability.尽早将产品推向市场可能比在程序中发现缺陷更重要。如果软件产品非常便宜,用户可能愿意忍受较低的可靠性
Inspections and testing 检查和测试
Software inspections Concerned with analysis of the static system representation to discover problems (static verification) 与分析静态系统表示以发现问题有关的软件检查(静态验证)
May be supplement by tool-based document and code analysis.
可以通过基于工具的文档和代码分析进行补充。
Software testing Concerned with exercising and observing product behaviour (dynamic verification)与实践和观察产品行为有关的软件测试(动态验证)
The system is executed with test data and its operational behaviour is observed.系统使用测试数据执行,并观察其运行行为。
Inspections and testing

Software inspections 软件检查
These involve people examining the source representation with the aim of discovering anomalies and defects.这涉及到人们检查源表示的目的是发现异常和缺陷。
Inspections not require execution of a system so may be used before implementation.检查不需要执行系统,因此可以在实现之前使用。
They may be applied to any representation of the system (requirements, design, configuration data, test data, etc.).检查不需要执行系统,因此可以在实现之前使用。
They have been shown to be an effective technique for discovering program errors.它们已被证明是发现程序错误的有效技术。
Advantages of inspections 检查的优点
- During testing, errors can mask (hide) other errors. Because inspection is a static process, you don’t have to be concerned with interactions between errors.在测试期间,错误可以掩盖(隐藏)其他错误。因为检查是一个静态的过程,所以您不必关心错误之间的交互。
- Incomplete versions of a system can be inspected without additional costs. If a program is incomplete, then you need to develop specialized test harnesses to test the parts that are available. 不完整的系统版本可以在不增加成本的情况下进行检查。如果程序不完整,那么您需要开发专门的测试工具来测试可用的部件。
- As well as searching for program defects, an inspection can also consider broader quality attributes of a program, such as compliance with standards, portability and maintainability. 除了搜索程序缺陷之外,检查还可以考虑程序的更广泛的质量属性,比如是否符合标准、可移植性和可维护性。
Inspections and testing 检查和测试
Inspections and testing are complementary and not opposing verification techniques.检查和测试是相辅相成的,而不是相反的核查技术。
Both should be used during the V & V process.两者都应该在V & V过程中使用
Inspections can check conformance with a specification but not conformance with the customer’s real requirements.检验可以检查是否符合规格,但不能检查是否符合客户的实际要求。
Inspections** cannot check non-functional characteristics** such as performance, usability, etc.检查不能检查诸如性能、可用性等非功能特性。
A model of the software testing process:

Stages of testing
Development testing, where the system is tested during development to discover bugs and defects. 开发测试,系统在开发过程中测试来发现bug和缺陷
Release testing, where a separate testing team test a complete version of the system before it is released to users. 发布测试,在发布给用户之前,一个单独的测试团队来测试完整的系统
User testing, where users or potential users of a system test the system in their own environment.用户测试,即系统的用户或潜在用户在自己的环境中测试系统
Development testing
Development testing includes all testing activities that are carried out by the team developing the system. 开发测试包括由开发系统的团队执行的所有测试活动
- Unit testing, where individual program units or object classes are tested. Unit testing should focus on testing the functionality of objects or methods.单元测试,即对单个程序单元或对象类进行测试。单元测试应该集中于测试对象或方法的功能。
- Component testing, where several individual units are integrated to create composite components. Component testing should focus on testing component interfaces.组件测试,其中几个单独的单元被集成来创建复合组件。组件测试应该关注组件接口的测试。
- System testing, where some or all of the components in a system are integrated and the system is tested as a whole. System testing should focus on testing component interactions.系统测试,将系统中的部分或全部组件集成在一起,并将系统作为一个整体进行测试。系统测试应该集中于测试组件的交互。
Unit testing
Unit testing is the process of testing individual components in isolation.单元测试是孤立地测试单个组件的过程。
It is a defect testing process.这是一个缺陷测试过程。
Units may be:
- Individual functions or methods within an object 对象中的单个函数或方法
- Object classes with several attributes and methods 具有多个属性和方法的对象类
- Composite components with defined interfaces used to access their functionality. 具有用于访问其功能的定义接口的复合组件。
Object class testing
Complete test coverage of a class involves包含类的完整测试覆盖
- Testing all operations associated with an object 测试与对象关联的所有操作
- Setting and interrogating all object attributes 设置和询问所有对象属性
- Exercising the object in all possible states.在所有可能的状态下行使该对象。
Inheritance makes it more difficult to design object class tests as the information to be tested is** not localized.继承使得设计对象类测试更加困难,因为要测试的信息没有本地化**。
The weather station object interface:

eg. Weather station testing
Need to define test cases for reportWeather, calibrate, test, startup and shutdown.需要为reportWeather、校准、测试、启动和关闭定义测试用例。
Using a state model, identify sequences of state transitions to be tested and the event sequences to cause these transitions 使用状态模型,识别要测试的状态转换时序和导致这些转换的事件时序
Examples of state sequences:
- Shutdown -> Running-> Shutdown 关机->运行->关机
- Configuring-> Running-> Testing -> Transmitting -> Running 配置->运行->测试->传输->运行
- Running-> Collecting-> Running-> Summarizing -> Transmitting -> Running 运行->采集->运行->汇总->传输->运行
These state sequences should be tested in the weather station. 这些状态时序应该在气象站进行测试。
Automated testing 自动化测试
Whenever possible, unit testing should be automated so that tests are run and checked without manual intervention.只要有可能,单元测试就应该自动化,这样测试就可以在没有人工干预的情况下运行和检查。
In automated unit testing, you make use of a test automation framework (such as JUnit) to write and run your program tests. 在自动化单元测试中,您使用测试自动化框架(如JUnit)来编写和运行程序测试。
Unit testing frameworks provide generic test classes that you extend to create specific test cases. They can then run all of the tests that you have implemented and report, often through some GUI, on the success or failure of the tests. 单元测试框架提供了通用的测试类,您可以扩展这些类来创建特定的测试用例。然后,它们可以运行您已经实现的所有测试,并经常通过一些GUI报告测试的成功或失败。
Automated test components 自动化测试组成
A setup part, where you initialize the system with the test case, namely the inputs and expected outputs.一个设置部分,在这里您用测试用例初始化系统,即输入和预期输出。
A call part, where you call the object or method to be tested.调用部分,在其中调用要测试的对象或方法。
An assertion part, where you compare the result of the call with the expected result. If the assertion evaluates to true, the test has been successful; if false, then it has failed.断言部分,在该部分中,您将调用的结果与预期的结果进行比较。如果断言的计算结果为true,则测试已经成功;如果是假的,那么它就失败了。
Choosing unit test cases 选择单元测试用例
The test cases should show that, when used as expected, the component that you are testing does what it is supposed to do.测试用例应该显示,当按照预期使用时,您测试的组件执行了它应该执行的任务。
If there are defects in the component, these should be revealed by test cases. 如果组件中存在缺陷,则应该通过测试用例来揭示这些缺陷。
This leads to 2 types of unit test case:
- The first of these should reflect normal operation of a program and should show that the component works as expected. 第一个应该反映程序的正常操作,并且应该显示组件按预期工作。
- The other kind of test case should be based on testing experience of where common problems arise. It should use abnormal inputs to check that these are properly processed and do not crash the component. 另一种测试用例应该基于出现常见问题的测试经验。它应该使用异常输入来检查这些输入是否被正确处理,并且不会使组件崩溃。
Testing strategies测试策略
Partition testing, where you identify groups of inputs that have common characteristics and should be processed in the same way. 分区测试,在该测试中,您可以识别具有共同特征的输入组,并且应该以相同的方式处理这些输入。
You should choose tests from within each of these groups.您应该从每个组中选择测试。
Guideline-based testing, where you use testing guidelines to choose test cases. 基于指南的测试,其中使用测试指南选择测试用例。
These guidelines reflect previous experience of the kinds of errors that programmers often make when developing components.这些指导原则反映了程序员在开发组件时经常犯的错误的经验。
Partition testing
Input data and output results often fall into different classes with common characteristics.输入数据和输出结果通常属于具有共同特征的不同类。
Each of these classes is an equivalence partition or domain where the program behaves in an equivalent way for each class member.这些类中的每一个都是一个等价分区或域,其中程序对每个类成员的行为都是等价的。
Test cases should be chosen from each partition.应该从每个分区中选择测试用例。
Equivalence partitioning 等价划分

- A program being tested should process all of the members of an input equivalence partitions in the same way. 正在测试的程序应该以相同的方式处理输入等价分区的所有成员。
- Output equivalence partitions are partitions within which all of the outputs have something in common.输出等价分区是所有输出都有一些共同点的分区
- Sometimes there is a 1:1 mapping between input and output equivalence partitions. However, this is not always the case; 有时候,输入和输出等价分区之间存在1:1的映射。然而,情况并非总是如此;
- you may need to define a separate input equivalence partition, where the only common characteristic of the inputs is that they generate outputs within the same output partition.您可能需要定义一个单独的输入等价分区,其中输入的唯一共同特征是它们在相同的输出分区中生成输出。
For example, a program specification states that the program accepts 4 to 8 inputs which are five-digit integers greater than 10000. We use this information to identify the input partitions and possible test input values).例如,程序规范声明程序接受4到8个输入,这些输入是大于10000的5位整数。我们使用这些信息来标识输入分区和可能的测试输入值)。
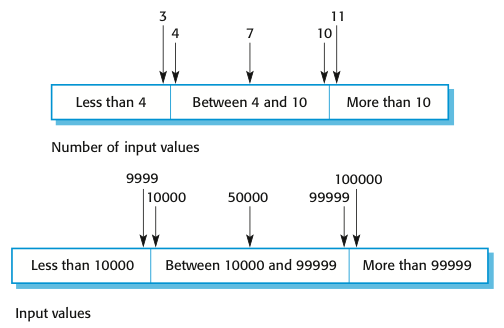
- Once you have identified a set of partitions, you choose test cases from each of these partitions. A good rule of thumb for test case selection is to choose test cases on the boundaries of the partitions, plus cases close to the midpoint of the partition.一旦您确定了一组分区,您就可以从这些分区中选择测试用例。对于测试用例的选择,一个好的经验法则是选择分区边界上的测试用例,加上靠近分区中点的用例。
- Boundary values are often atypical so are sometimes overlooked by developers. Program failures often occur when processing these atypical values.边界值通常是非典型的,因此有时会被开发人员忽略。当处理这些非典型值时,程序常常发生故障
Testing guidelines (sequences)
Test software with sequences which have only a single value.用只有一个值的时序测试软件
Use sequences of different sizes in different tests.在不同的测试中使用不同大小的时序
Derive tests so that the first, middle and last elements of the sequence are accessed.派生测试,以便访问时序的第一个、中间和最后一个元素。
Test with sequences of zero length.用长度为零的时序进行测试。
General testing guidelines
Choose inputs that force the system to generate all error messages 选择强制系统生成所有错误消息的输入
Design inputs that cause input buffers to overflow 设计导致输入缓冲区溢出的输入
Repeat the same input or series of inputs numerous times 多次重复相同的输入或一系列输入
Force invalid outputs to be generated 强制生成无效输出
Force computation results to be too large or too small.
力的计算结果不宜过大或过小。
Component testing
Software components are often composite components that are made up of several interacting objects. 软件组件通常是由几个交互对象组成的组合组件
- For example, in the weather station system, the reconfiguration component includes objects that deal with each aspect of the reconfiguration. 例如,在气象站系统中,重新配置组件包括处理重新配置各个方面的对象。
You access the functionality of these objects through the defined component interface. 您可以通过定义的组件接口访问这些对象的功能。
Testing composite components should therefore focus on showing that the component interface behaves according to its specification. 因此,测试复合组件应该集中于显示组件接口的行为是否符合其规范。
- You can assume that unit tests on the individual objects within the component have been completed. 您可以假设已经完成了对组件中各个对象的单元测试。
**Component Interface **testing

Component A, B, and C have been integrated to create a larger component or subsystem.组件A、B和C已经集成,以创建更大的组件或子系统。
Interface errors in the composite component may not be detectable by testing the individual objects because these errors result from interactions between the objects in the component.复合组件中的接口错误可能无法通过测试单个对象检测到,因为这些错误是由组件中的对象之间的交互造成的。
Interface testing 接口测试
Objectives are to detect faults due to interface errors or invalid assumptions about interfaces.目标是检测由于接口错误或有关接口的无效假设而引起的故障。
- Interface types 接口类型
- Parameter interfaces. Data passed from one method or procedure to another.参数界面。从一个方法或过程传递到另一个方法或过程的数据。
- Shared memory interfaces. Block of memory is shared between procedures or functions.共享内存接。内存块在过程或函数之间共享。
- Procedural interfaces. Sub-system encapsulates a set of procedures to be called by other sub-systems.程序接口。子系统封装了一组由其他子系统调用的过程。
- Message passing interfaces. Sub-systems request services from other sub-systems消息传递接口。子系统从其他子系统请求服务
Interface errors 接口错误
Interface misuse 接口误用
- A calling component calls another component and makes an error in its use of its interface e.g. parameters in the wrong order.调用组件调用另一个组件,并在使用接口时出错,例如参数顺序错误。
Interface misunderstanding 界面误解
- A calling component embeds assumptions about the behaviour of the called component which are incorrect.调用组件嵌入关于被调用组件行为的不正确假设。
Timing errors 时间错误
- The called and the calling component operate at different speeds and out-of-date information is accessed.被调用组件和调用组件以不同的速度运行,并且访问过期的信息
Interface testing guidelines 界面测试指南
Design tests so that parameters to a called procedure are at the extreme ends of their ranges.设计测试,使被调用过程的参数处于其范围的极端末端。
Always test pointer parameters with null pointers.始终使用空指针测试指针参数。
Design tests which cause the component to fail.设计导致组件失败的测试。
Use stress testing in message passing systems.在消息传递系统中使用压力测试。
In shared memory systems, vary the order in which components are activated.在共享内存系统中,改变激活组件的顺序。
System testing 系统测试
System testing during development involves integrating components to create a version of the system and then testing the integrated system.开发期间的系统测试包括集成组件以创建系统的版本,然后测试集成的系统。
The focus in system testing is testing the interactions between components. 开发期间的系统测试包括集成组件以创建系统的版本,然后测试集成的系统。
System testing checks that components are compatible, interact correctly and transfer the right data at the right time across their interfaces. 系统测试检查组件是否兼容,是否正确交互,以及是否在正确的时间跨接口传输正确的数据。
System testing tests the emergent behavior of a system. 系统测试测试系统的紧急行为。
System and component testing 系统和组件测试
During system testing, reusable components that have been separately developed and off-the-shelf systems may be integrated with newly developed components. The complete system is then tested.在系统测试期间,可以将单独开发的可复用组件和现成的系统集成到新开发的组件中。然后对整个系统进行测试。
Components developed by different team members or sub-teams may be integrated at this stage. System testing is a collective rather than an individual process. 由不同团队成员或子团队开发的组件可以在此阶段集成。系统测试是一个集体的过程,而不是一个单独的过程。
In some companies, system testing may involve a separate testing team with no involvement from designers and programmers. 在一些公司中,系统测试可能涉及到一个独立的测试团队,没有来自设计人员和程序员的参与。
Use-case testing 用例测试
The use-cases developed to identify system interactions can be used as a basis for system testing.开发用于识别系统交互的用例可以用作系统测试的基础。
Each use case usually involves several system components so testing the use case forces these interactions to occur.每个用例通常包含几个系统组件,因此测试用例会强制这些交互发生。
The sequence diagrams associated with the use case documents the components and interactions that are being tested.与用例相关联的时序图记录了正在测试的组件和交互。
Collect weather data sequence chart:
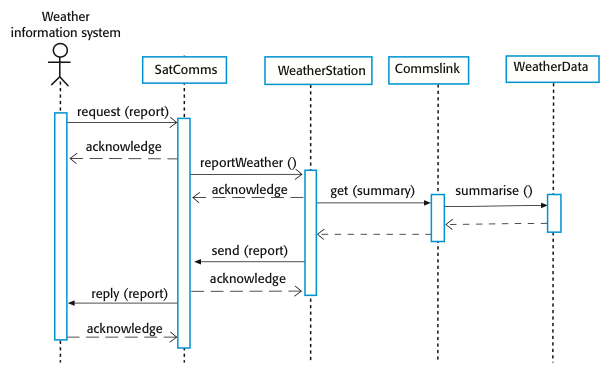
Testing policies 测试政策
Exhaustive system testing is impossible so testing policies which define the required system test coverage may be developed. 彻底的系统测试是不可能的,因此可以开发定义所需的系统测试覆盖率的测试策略。
Examples of testing policies:
- All system functions that are accessed through menus should be tested.应该测试通过菜单访问的所有系统功能。
- Combinations of functions (e.g. text formatting) that are accessed through the same menu must be tested.必须测试通过相同菜单访问的函数组合(例如文本格式)
- Where user input is provided, all functions must be tested with both correct and incorrect input.在提供用户输入的地方,必须用正确和错误的输入测试所有函数。
Test-driven development
Test-driven development (TDD) is an approach to program development in which you inter-leave testing and code development.测试驱动开发(Test-driven development, TDD)是一种程序开发方法,您可以在其中交叉进行测试和代码开发。
Tests are written before code and ‘passing’ the tests is the critical driver of development. 测试是在编写代码之前编写的,“通过”测试是开发的关键驱动力。
You develop code incrementally, along with a test for that increment. You don’t move on to the next increment until the code that you have developed passes its test. 您以增量的方式开发代码,并对该增量进行测试。在开发的代码通过测试之前,不会继续下一个增量。
TDD was introduced as part of agile methods such as Extreme Programming. However, it can also be used in plan-driven development processes. TDD是作为敏捷方法(如极限编程)的一部分引入的。但是,它也可以用于计划驱动的开发过程。
Test-driven development:
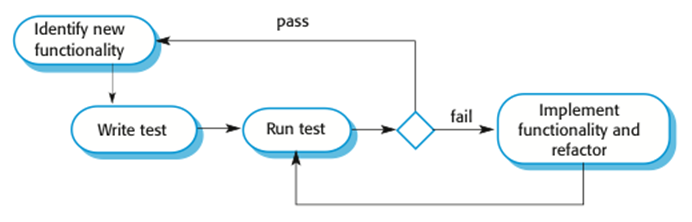
TDD process activities
Start by identifying the increment of functionality that is required. This should normally be small and implementable in a few lines of code.首先确定所需的功能增量。这通常应该很小,并且可以在几行代码中实现。
Write a test for this functionality and implement this as an automated test. 为该功能编写一个测试,并将其实现为自动化测试。
Run the test, along with all other tests that have been implemented. Initially, you have not implemented the functionality so the new test will fail. 运行测试,以及已经实现的所有其他测试。最初,您没有实现该功能,因此新测试将失败。
Implement the functionality and re-run the test. 实现功能并重新运行测试。
Once all tests run successfully, you move on to implementing the next chunk of functionality.一旦所有测试都成功运行,您将继续实现下一个功能块。
Benefits of test-driven development 测试驱动开发的好处
- Code coverage
- Every code segment that you write has at least one associated test so all code written has at least one test.您编写的每个代码段都至少有一个相关的测试,因此所有编写的代码都至少有一个测试。
- Regression testing 回归测试
- A regression test suite is developed incrementally as a program is developed. :随着程序的开发,逐步开发回归测试套件。
- Simplified debugging 简化调试
- When a test fails, it should be obvious where the problem lies. The newly written code needs to be checked and modified. 当测试失败时,问题所在应该很明显。需要检查和修改新编写的代码。
- System documentation 系统文献
- The tests themselves are a form of documentation that describe what the code should be doing. 测试本身是描述代码应该做什么的文档形式。
Regression testing 回复测试
Regression testing is testing the system to check that changes have not ‘broken’ previously working code.回归测试是测试系统,以检查更改是否“破坏”了以前工作的代码。
In a manual testing process, regression testing is expensive but, with automated testing, it is simple and straightforward. All tests are rerun every time a change is made to the program.在手工测试过程中,回归测试是昂贵的,但是使用自动化测试,它是简单和直接的。每次对程序进行更改时,都会重新运行所有测试。
Tests must run ‘successfully’ before the change is committed.
在提交更改之前,测试必须“成功”运行。
Release testing 发布测试
Release testing is the process of testing a particular release of a system that is intended for use outside of the development team. 发布测试是测试一个特定的系统发布版本的过程,这个系统发布版本是为开发团队之外的人使用的。
The primary goal of the release testing process is to convince the supplier of the system that it is good enough for use.发布测试过程的主要目标是使系统的供应商相信它足够好可以使用。
- Release testing, therefore, has to show that the system delivers its specified functionality, performance and dependability, and that it does not fail during normal use. 因此,发布测试必须表明系统交付了指定的功能、性能和可靠性,并且在正常使用期间不会失败。
Release testing is usually a black-box testing process where tests are only derived from the system specification. 发布测试通常是一个黑盒测试过程,其中的测试仅派生自系统规范。
Release testing and system testing
Release testing is a form of system testing.发布测试是系统测试的一种形式。
Important differences:
- A separate team that has not been involved in the system development, should be responsible for release testing.没有参与系统开发的独立团队应该负责发布测试。
- System testing by the development team should focus on discovering bugs in the system (defect testing). The objective of release testing is to check that the system meets its requirements and is good enough for external use (validation testing).
开发团队的系统测试应该集中于发现系统中的bug(缺陷测试)。发布测试的目的是检查系统是否满足它的需求,并且足够好地用于外部使用(验证测试)。
Requirements based testing 基于需求的测试
Requirements-based testing involves examining each requirement and developing a test or tests for it.基于需求的测试包括检查每个需求并为其开发一个或多个测试。
MHC-PMS requirements:
- If a patient is known to be allergic to any particular medication, then prescription of that medication shall result in a warning message being issued to the system user.如果已知患者对任何特定药物过敏,则该药物的处方应向系统用户发出警告信息。
- If a prescriber chooses to ignore an allergy warning, they shall provide a reason why this has been ignored.如果处方者选择忽视过敏警告,他们应该提供一个被忽视的原因。
Requirements tests
- Set up a patient record with no known allergies. Prescribe medication for allergies that are known to exist. Check that a warning message is not issued by the system.建立一个没有已知过敏史的病人记录。为已知存在的过敏开药方。检查系统是否发出警告消息。
- Set up a patient record with a known allergy. Prescribe the medication to that the patient is allergic to, and check that the warning is issued by the system.建立一个已知过敏的病人记录。开对患者过敏的药物,并检查系统是否发出警告。
- Set up a patient record in which allergies to two or more drugs are recorded. Prescribe both of these drugs separately and check that the correct warning for each drug is issued.建立对两种或两种以上药物过敏的患者记录。分别开这两种药,并检查每种药的警告是否正确。
- Prescribe two drugs that the patient is allergic to. Check that two warnings are correctly issued.开两种病人过敏的药。检查两个警告是否正确发出。
- Prescribe a drug that issues a warning and overrule that warning. Check that the system requires the user to provide information explaining why the warning was overruled. 开一种会发出警告的药物,并推翻这种警告。检查系统是否要求用户提供解释警告为何被否决的信息。
Features tested by scenario 通过场景测试的特性
Authentication by logging on to the system.登录到系统进行身份验证。
Downloading and uploading of specified patient records to a laptop.下载和上传指定的病人记录到笔记本电脑。
Home visit scheduling.家访调度。
Encryption and decryption of patient records on a mobile device. 在移动设备上对患者记录进行加密和解密。
Record retrieval and modification.记录检索和修改。
Links with the drugs database that maintains side-effect information.与维护副作用信息的药物数据库的链接
The system for call prompting.呼叫提示系统。
Performance testing 性能测试\
Part of release testing may involve testing the emergent properties of a system, such as performance and reliability.发布测试的一部分可能包括测试系统的紧急特性,例如性能和可靠性。
Tests should reflect the profile of use of the system.测试应该反映系统的使用情况。
Performance tests usually involve planning a series of tests where the load is steadily increased until the system performance becomes unacceptable.性能测试通常包括计划一系列的测试,其中负载会稳步增加,直到系统性能变得不可接受为止。
Stress testing is a form of performance testing where the system is deliberately overloaded to test its failure behavior.压力测试是一种性能测试形式,其中系统被故意重载以测试其故障行为。
User testing 用户测试
User or customer testing is a stage in the testing process in which users or customers provide input and advice on system testing. 用户或客户测试是测试过程中的一个阶段,在这个阶段中,用户或客户提供关于系统测试的输入和建议。
User testing is essential, even when comprehensive system and release testing have been carried out. 即使进行了全面的系统和发布测试,用户测试也是必不可少的。
- The reason for this is that influences from the user’s working environment have a major effect on the reliability, performance, usability and robustness of a system. These cannot be replicated in a testing environment.其原因是用户工作环境的影响对系统的可靠性、性能、可用性和健壮性有重要影响。这些不能在测试环境中复制。
Types of user testing
- Alpha testing
- Users of the software work with the development team to test the software at the developer’s site.软件的用户与开发团队一起在开发人员的站点上测试软件。
- Beta testing
- A release of the software is made available to users to allow them to experiment and to raise problems that they discover with the system developers.用户可以使用该软件的一个版本进行试验,并向系统开发人员提出他们发现的问题。
- Acceptance testing
- Customers test a system to decide whether or not it is ready to be accepted from the system developers and deployed in the customer environment. Primarily for custom systems.客户测试系统,以确定系统开发人员是否已经准备好接受系统并将其部署到客户环境中。主要用于定制系统。
The acceptance testing process
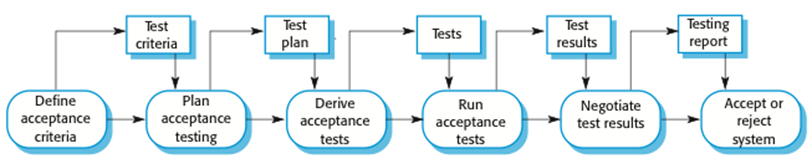
Stages in the acceptance testing process验收测试过程中的各个阶段
- Define acceptance criteria定义验收标准
- Plan acceptance testing计划验收测试
- Derive acceptance tests得到验收测试
- Run acceptance tests运行验收测试
- Negotiate test results协商测试结果
- Reject/accept system拒绝/接受系统
Agile methods and acceptance testing敏捷方法和验收测试
In agile methods, the user/customer is part of the development team and is responsible for making decisions on the acceptability of the system.在敏捷方法中,用户/客户是开发团队的一部分,负责决定系统的可接受性。
Tests are defined by the user/customer and are integrated with other tests in that they are run automatically when changes are made.测试由用户/客户定义,并与其他测试集成在一起,在进行更改时自动运行这些测试
There is no separate acceptance testing process.没有单独的验收测试过程。
Main problem here is whether or not the embedded user is ‘typical’ and can represent the interests of all system stakeholders.这里的主要问题是嵌入式用户是否“典型”,是否能代表所有系统涉众的利益。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号