软件工程笔记:设计与实现
该部分为本科期间软件工程课程笔记备份。
Software design and implementation is the stage in the software engineering process at which an executable software system is developed. 软件设计和实现是软件工程过程中开发可执行软件系统的阶段。
Software design and implementation activities are invariably inter-leaved(相互交错). 软件设计和实现活动总是相互交错的。
- Software design is a creative activity in which you identify software components and their relationships, based on a customer’s requirements. 软件设计是一种创造性的活动,在这种活动中,您可以根据客户的需求识别软件组件及其关系。
- Implementation is the process of realizing the design as a program. 实现是将设计作为一个程序实现的过程。
Build or buy: 开发与购买
- In a wide range of domains, it is now possible to buy off-the-shelf systems (COTS,现成的系统) that can be adapted and tailored to the users’ requirements. 在广泛的领域中,现在可以购买现成的系统(COTS),这些系统可以根据用户的需求进行调整和定制
For example, if you want to implement a medical records system, you can buy a package that is already used in hospitals. It can be cheaper and faster to use this approach rather than developing a system in a conventional programming language .例如,如果您想要实现一个病历系统,您可以购买一个已经在医院使用的包。使用这种方法比用传统编程语言开发系统更便宜、更快。
- When you develop an application in this way, the design process becomes concerned with how to use the configuration features(配置特性) of that system to deliver the system requirements 以这种方式开发应用程序时,设计过程将关注如何使用该系统的配置特性来交付系统需求。
An object-oriented design process 一个面向对象设计过程
Structured object-oriented design processes involve(涉及到) developing a number of different system models. 结构化面向对象设计过程涉及到开发许多不同的系统模型。
They require a lot of effort for development and maintenance of these models and, for small systems, this may not be cost-effective(成本效益). 它们需要大量的工作来开发和维护这些模型,对于小型系统,这可能不具有成本效益。
However, for large systems developed by different groups design models are an important communication mechanism(通信机制). 然而,对于由不同群体开发的大型系统来说,设计模型是一种重要的通信机制。
Process stages 过程阶段
There are a variety of different object-oriented design processes that depend on the organization using the process. 有许多不同的面向对象的设计过程依赖于使用该过程的组织。
Common activities in these processes include:这些过程中的常见活动包括:
- Define the context and modes of use of the system; 定义系统的上下文和使用模式;
- Design the system architecture; 设计系统架构;
- Identify the principal system objects;识别主要系统对象;
- Develop design models;开发设计模型;
- Specify object interfaces. 指定对象接口
Process illustrated here using a design for a wilderness weather station. 使用野外气象站的设计说明了这一过程。
System context and interactions 系统上下文和交互
- Understanding the relationships between the software that is being designed and its external environment is essential for deciding how to provide the required system functionality and how to structure the system to communicate with its environment.
- 了解正在设计的软件与其外部环境之间的关系对于决定如何提供所需的系统功能以及如何构造系统以与其环境通信至关重要。
- Understanding of the context also lets you establish the boundaries of the system. Setting the system boundaries helps you decide what features are implemented in the system being designed and what features are in other associated systems.
- 了解上下文还可以建立系统的边界。设置系统边界有助于确定在正在设计的系统中实现了哪些功能,以及在其他关联系统中实现了哪些功能。
Context and interaction models 上下文和交互式模型
A system context model is a structural model that demonstrates the other systems in the environment of the system being developed.系统上下文模型是一种结构模型,演示正在开发的系统环境中的其他系统。
An interaction model is a dynamic model that shows how the system interacts with its environment as it is used.交互模型是一个动态模型,显示系统在使用时如何与环境交互。
eg.


| System | Weather station |
|---|---|
| Use case | Report weather |
| Actors | Weather information system, Weather station |
| Description | The weather station sends a summary of the weather data that has been collected from the instruments in the collection period to the weather information system. The data sent are the maximum, minimum, and average ground and air temperatures; the maximum, minimum, and average air pressures; the maximum, minimum, and average wind speeds; the total rainfall; and the wind direction as sampled at five-minute intervals. |
| Stimulus | The weather information system establishes a satellite communication link with the weather station and requests transmission of the data. |
| Response | The summarized data is sent to the weather information system. |
| Comments | Weather stations are usually asked to report once per hour but this frequency may differ from one station to another and may be modified in the future. |
Architectural design 体系结构设计
Once interactions between the system and its environment have been understood, you use this information for designing the system architecture.一旦理解了系统及其环境之间的交互,就可以使用这些信息来设计系统架构。
You identify the major components that make up the system and their interactions, and then may organize the components using an architectural pattern such as a layered or client-server model.您识别组成系统及其交互的主要组件,然后可以使用体系结构模式(如分层或客户机-服务器模型)组织组件。
The weather station is composed of independent subsystems that communicate by broadcasting messages on a common infrastructure.气象站由独立的子系统组成,这些子系统通过在公共基础设施上广播信息进行通信。
High-level architecture of the weather station 气象站的高级体系结构:

Architecture of data collection system 数据采集系统架构:

Object class identification 对象类的识别
Identifying object classes is often a difficult part of object oriented design.识别对象类通常是面向对象设计中的一个困难部分。
There is no 'magic formula' for object identification. It relies on the skill, experience and domain knowledge of system designers.对象标识没有“魔力公式”。它依赖于系统设计者的技能、经验和领域知识。
Object identification is an iterative process. You are unlikely to get it right first time.对象识别是一个迭代过程。你不可能第一次就把它弄好。
Approaches to identification 识别方法
- Use a grammatical approach based on a natural language description of the system (used in Hood OOD method).
- 使用基于系统自然语言描述的语法方法(用于Hood-OODood方法)。
- Base the identification on tangible things in the application domain.
- 基于应用程序域中的有形事物进行标识。
- Use a behavioural approach and identify objects based on what participates in what behaviour.
- 使用行为方法,根据参与什么行为来识别对象。
- Use a scenario-based analysis. The objects, attributes and methods in each scenario are identified.
- 使用基于场景的分析。识别每个场景中的对象、属性和方法。
Weather station description 气象站说明
A weather station is a package of software controlled instruments which collects data, performs some data processing and transmits this data for further processing. The instruments include air and ground thermometers, an anemometer, a wind vane, a barometer and a rain gauge. Data is collected periodically.气象站是由软件控制的仪器组成的一个软件包,它收集数据,进行一些数据处理,并将这些数据传输给进一步的处理。这些仪器包括空气和地面温度计、风速计、风向标、气压计和雨量计。定期收集数据。
When a command is issued to transmit the weather data, the weather station processes and summarises the collected data. The summarised data is transmitted to the mapping computer when a request is received.当发出传送天气数据的命令时,气象站处理并汇总收集的数据。当收到请求时,汇总的数据被传输到映射计算机。
Weather station object classes 气象站的对象类
Object class identification in the weather station system may be based on the tangible hardware and data in the system:气象站系统中的对象类标识可以基于系统中的有形硬件和数据:
- Ground thermometer, Anemometer, Barometer 地面温度计、风速计、气压计
- Application domain objects that are ‘hardware’ objects related to the instruments in the system. 应用程序域对象是与系统中的仪器相关的“硬件”对象。
- Weather station 气象站
- The basic interface of the weather station to its environment. It therefore reflects the interactions identified in the use-case model. 气象站与环境的基本接口。因此,它反映了用例模型中确定的交互。
- Weather data 气象资料
- Encapsulates the summarized data from the instruments.封装来自仪器的汇总数据。

Design models设计模型
-
Design models show the objects and object classes and relationships between these entities.设计模型显示对象和对象类以及这些实体之间的关系。
-
Static models describe the static structure of the system in terms of object classes and relationships.静态模型根据对象类和关系描述系统的静态结构。
-
Dynamic models describe the dynamic interactions between objects.动态模型描述了对象之间的动态交互。
Examples of design models 设计模型的例子
-
Subsystem models that show logical groupings of objects into coherent subsystems.显示对象逻辑分组为连贯子系统的子系统模型。
-
Sequence models that show the sequence of object interactions.显示对象交互顺序的时序模型。
-
State machine models that show how individual objects change their state in response to events.状态机模型,显示单个对象如何响应事件更改其状态。
-
Other models include use-case models, aggregation models, generalization models, etc.其他模型包括用例模型、聚合模型、泛化模型等。
Subsystem models 子系统模型
Shows how the design is organised into logically related groups of objects.显示如何将设计组织成逻辑相关的对象组。
In the UML, these are shown using packages - an encapsulation construct. This is a logical model. The actual organisation of objects in the system may be different.在UML中,这些都是使用包(封装结构)来显示的。这是一个逻辑模型。系统中对象的实际组织可能不同。
Sequence models 时序模型
Sequence models show the sequence of object interactions that take place 时序模型显示发生的对象交互的时序
- Objects are arranged horizontally across the top;对象在顶部水平排列;
- Time is represented vertically so models are read top to bottom;时间是垂直表示的,所以模型是自上而下读取的;
- Interactions are represented by labelled arrows, Different styles of arrow represent different types of interaction;交互用带标签的箭头表示,不同类型的箭头表示不同类型的交互;
- A thin rectangle in an object lifeline represents the time when the object is the controlling object in the system.对象生命线中的细矩形表示对象是系统中控制对象的时间。
Sequence diagram describing data collection 描述数据收集的时序


State diagrams 状态图
State diagrams are used to show how objects respond to different service requests and the state transitions triggered by these requests. 状态图用于显示对象如何响应不同的服务请求以及这些请求触发的状态转换。
State diagrams are useful high-level models of a system or an object’s run-time behavior. 状态图是系统或对象运行时行为的有用高级模型。
You don’t usually need a state diagram for all of the objects in the system. Many of the objects in a system are relatively simple and a state model adds unnecessary detail to the design. 您通常不需要系统中所有对象的状态图。系统中的许多对象相对简单,状态模型为设计添加了不必要的细节。
Weather station state diagram气象站状态图:

Interface specification 接口规范
Object interfaces have to be specified so that the objects and other components can be designed in parallel. 必须指定对象接口,以便对象和其他组件可以并行设计。
Designers should avoid designing the interface representation but should hide this in the object itself.设计人员应避免设计接口表示,但应将其隐藏在对象本身中。
Objects may have several interfaces which are viewpoints on the methods provided.对象可以有多个接口,这些接口是所提供方法的视角。
The UML uses class diagrams for interface specification but Java may also be used. UML使用类图来进行接口规范,但是Java也可以使用。
Weather station interfaces 气象站接口:


Design patterns 设计模式
A design pattern is a way of reusing abstract knowledge about a problem and its solution. 设计模式是一种复用有关问题及其解决方案的抽象知识的方法。
A pattern is a description of the problem and the essence of its solution. 模式是对问题及其解决方法的本质的描述。
It should be sufficiently abstract to be reused in different settings.它应该足够抽象,可以在不同的设置中复用。
Pattern descriptions usually make use of object-oriented characteristics such as inheritance and polymorphism.模式描述通常利用面向对象的特性,如继承和多态性。
Pattern elements 模式元素
- Name 名字
- A meaningful pattern identifier.有意义的模式标识符。
- Problem description. 问题描述。
- Solution description.解决方案描述。
- Not a concrete design but a template for a design solution that can be instantiated in different ways.不是一个具体的设计,而是一个可以用不同方式实例化的设计解决方案的模板。
- Consequences 后果
- The results and trade-offs of applying the pattern. 应用模式的结果和权衡。
The Observer pattern 观察者模式
Gang of Four(GoF): Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson,John Vlissides
- Name 名字
- Observer.观察者。
- Description 描述
- Separates the display of object state from the object itself. 将对象状态的显示与对象本身分离。
- Problem description问题描述
- Used when multiple displays of state are needed.当需要多个状态显示时使用。
- Solution description 解决方案描述
- See slide with UML description.请参阅带UML描述的幻灯片。
- Consequences后果
-
Optimizations to enhance display performance are impractical. 为了提高显示性能而进行的优化是不切实际的。
-
More details
Pattern name Observer Description Separates the display of the state of an object from the object itself and allows alternative displays to be provided. When the object state changes, all displays are automatically notified and updated to reflect the change. Problem description In many situations, you have to provide multiple displays of state information, such as a graphical display and a tabular display. Not all of these may be known when the information is specified. All alternative presentations should support interaction and, when the state is changed, all displays must be updated. This pattern may be used in all situations where more than one display format for state information is required and where it is not necessary for the object that maintains the state information to know about the specific display formats used. Solution description This involves two abstract objects, Subject and Observer, and two concrete(具体的) objects, ConcreteSubject and ConcreteObject, which inherit the attributes of the related abstract objects. The abstract objects include general operations that are applicable in all situations. The state to be displayed is maintained in ConcreteSubject, which inherits operations from Subject allowing it to add and remove Observers (each observer corresponds to a display) and to issue a notification when the state has changed. The ConcreteObserver maintains a copy of the state of ConcreteSubject and implements the Update() interface of Observer that allows these copies to be kept in step. The ConcreteObserver automatically displays the state and reflects changes whenever the state is updated. Consequences The subject only knows the abstract Observer and does not know details of the concrete class. Therefore there is minimal coupling between these objects. Because of this lack of knowledge, optimizations that enhance display performance are impractical. Changes to the subject may cause a set of linked updates to observers to be generated, some of which may not be necessary.
-
Multiple displays using the Observer pattern 使用观察者模式 的多个显示器:
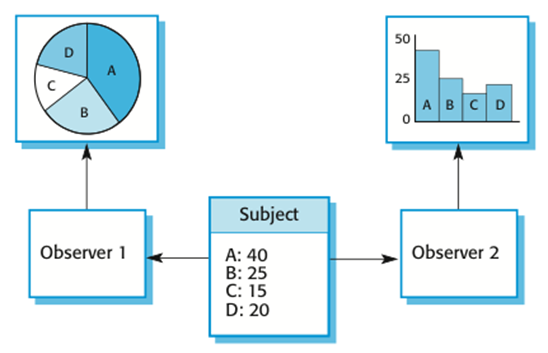
A UML model of the Observer pattern 观察者模式的UML模型:

Implementation problems 实现问题
Focus here is not on programming, although this is obviously important, but on other implementation issues that are often not covered in programming texts:这里的重点不是编程,尽管这显然很重要,而是编程文本中经常没有涉及的其他实现问题:
- Reuse. Most modern software is constructed by reusing existing components or systems. When you are developing software, you should make as much use as possible of existing code. 复用。大多数现代软件都是通过重用现有的组件或系统来构建的。在开发软件时,应该尽可能多地使用现有代码。
- Configuration management. During the development process, you have to keep track of the many different versions of each software component in a configuration management system.配置管理。在开发过程中,您必须跟踪配置管理系统中每个软件组件的许多不同版本。
- Host-target development. Production software does not usually execute on the same computer as the software development environment. Rather, you develop it on one computer (the host system) and execute it on a separate computer (the target system).主机目标开发。生产软件通常不与软件开发环境在同一台计算机上执行。相反,您在一台计算机(主机系统)上开发它,并在另一台计算机(目标系统)上执行它。
Reuse 复用
From the 1960s to the 1990s, most new software was developed from scratch, by writing all code in a high-level programming language. 从20世纪60年代到90年代,大多数新软件都是通过用高级编程语言编写所有代码而从头开始开发的
- The only significant reuse or software was the reuse of functions and objects in programming language libraries. 唯一重要的重用或软件是在编程语言库中重用函数和对象。
Costs and schedule pressure mean that this approach became increasingly unviable, especially for commercial and Internet-based systems. 。成本和进度压力意味着这种方法变得越来越不可行,特别是对于商业和基于互联网的系统。
An approach to development based around the reuse of existing software emerged and is now generally used for business and scientific software.一种基于现有软件重用的开发方法出现了,现在普遍用于商业和科学软件。
Reuse levels 复用水平
- The abstraction level 抽象层次
- At this level, you don’t reuse software directly but use knowledge of successful abstractions in the design of your software.在这个层次上,您不直接重用软件,而是在软件设计中使用成功抽象的知识。
- The object level 对象级别
- At this level, you directly reuse objects from a library rather than writing the code yourself.在这个级别上,您直接重用库中的对象,而不是自己编写代码。
- The component level 组件级别
- Components are collections of objects and object classes that you reuse in application systems.组件是在应用程序系统中重用的对象和对象类的集合。
- The system level 系统级别
- At this level, you reuse entire application systems.在这个级别上,您可以重用整个应用程序系统。
Reuse costs 复用成本
-
The costs of the time spent in looking for software to reuse and assessing whether or not it meets your needs.在寻找可重用的软件和评估它是否满足您的需求上花费的时间成本
-
Where applicable, the costs of buying the reusable software. For large off-the-shelf systems, these costs can be very high.在适用的情况下,购买可重用软件的成本。对于大型现成系统,这些成本可能非常高。
-
The costs of adapting and configuring the reusable software components or systems to reflect the requirements of the system that you are developing.调整和配置可重用软件组件或系统以反映您正在开发的系统的需求的成本。
-
The costs of integrating reusable software elements with each other (if you are using software from different sources) and with the new code that you have developed. 。将可重用软件元素相互集成(如果您使用的是来自不同来源的软件)以及与您开发的新代码集成的成本。
Configuration management配置管理
Configuration management is the name given to the general process of managing a changing software system. 配置管理是指管理变更软件系统的一般过程。
The aim of configuration management is to support the system integration process so that all developers can access the project code and documents in a controlled way, find out what changes have been made, and compile and link components to create a system.配置管理的目的是支持系统集成过程,以便所有开发人员都能以受控的方式访问项目代码和文档,了解所做的更改,并编译和链接组件以创建系统。
Configuration management activities 配置管理活动
-
Version management, where support is provided to keep track of the different versions of software components. Version management systems include facilities to coordinate development by several programmers.版本管理,提供支持以跟踪软件组件的不同版本。版本管理系统包括由几个程序员协调开发的工具。
-
System integration, where support is provided to help developers define what versions of components are used to create each version of a system. This description is then used to build a system automatically by compiling and linking the required components.系统集成,提供支持以帮助开发人员定义用于创建系统每个版本的组件的版本。然后,通过编译和链接所需的组件,使用此描述自动构建系统。
-
Problem tracking, where support is provided to allow users to report bugs and other problems, and to allow all developers to see who is working on these problems and when they are fixed.问题跟踪,提供支持,允许用户报告错误和其他问题,并允许所有开发人员查看谁在处理这些问题以及何时修复问题。
Host-target development主机目标开发
Most software is developed on one computer (the host), but runs on a separate machine (the target).大多数软件是在一台计算机(主机)上开发的,但运行在一台单独的计算机(目标计算机)上。
More generally, we can talk about a development platform and an execution platform.更一般地说,我们可以讨论开发平台和执行平台。
- A platform is more than just hardware.平台不仅仅是硬件。
- It includes the installed operating system plus other supporting software such as a database management system or, for development platforms, an interactive development environment.它包括已安装的操作系统以及其他支持软件,例如数据库管理系统,或者对于开发平台,包括交互式开发环境。
Development platform usually has different installed software than execution platform; these platforms may have different architectures. 开发平台通常具有不同于执行平台的安装软件;这些平台可能具有不同的体系结构。
Development platform tools 开发平台工具
An integrated compiler and syntax-directed editing system that allows you to create, edit and compile code.一个集成的编译器和面向语法的编辑系统,允许您创建、编辑和编译代码。
A language debugging system.语言调试系统。
Graphical editing tools, such as tools to edit UML models.图形编辑工具,例如用于编辑UML模型的工具。
Testing tools, such as Junit(Massol, 2003) that can automatically run a set of tests on a new version of a program.测试工具,例如JUnit(Massol,2003),它可以在程序的新版本上自动运行一组测试。
Project support tools that help you organize the code for different development projects.帮助您为不同的开发项目组织代码的项目支持工具。
Integrated development environments (IDEs) 集成开发环境
Software development tools are often grouped to create an integrated development environment (IDE).软件开发工具通常被分组以创建集成开发环境(IDE)。
An IDE is a set of software tools that supports different aspects of software development, within some common framework and user interface. IDE是一组软件工具,在一些公共框架和用户界面中支持软件开发的不同方面。
IDEs are created to support development in a specific programming language such as Java. The language IDE may be developed specially, or may be an instantiation of a general-purpose IDE, with specific language-support tools. IDE是为了支持特定编程语言(如Java)的开发而创建的。语言IDE可以是专门开发的,也可以是具有特定语言支持工具的通用IDE的实例。
Component/system deployment factors 组件/系统部署因素
If a component is designed for a specific hardware architecture, or relies on some other software system, it must obviously be deployed on a platform that provides the required hardware and software support.如果一个组件是为特定的硬件体系结构设计的,或者依赖于其他软件系统,那么它显然必须部署在提供所需硬件和软件支持的平台上。
High availability systems may require components to be deployed on more than one platform. This means that, in the event of platform failure, an alternative implementation of the component is available.高可用性系统可能需要在多个平台上部署组件。这意味着,在平台失败的情况下,组件的另一个实现是可用的。
If there is a high level of communications traffic between components, it usually makes sense to deploy them on the same platform or on platforms that are physically close to one other. This reduces the delay between the time a message is sent by one component and received by another.如果组件之间存在高级别的通信流量,则通常有必要将它们部署在同一平台或物理上彼此接近的平台上。这减少了一个组件发送消息和另一个组件接收消息之间的延迟。
Open source development开源开发
Open source development is an approach to software development in which the source code of a software system is published and volunteers are invited to participate in the development process.开源开发是软件开发的一种方法,其中发布软件系统的源代码,并邀请志愿者参与开发过程。
Its roots are in the Free Software Foundation (www.fsf.org), which advocates that source code should not be proprietary but rather should always be available for users to examine and modify as they wish.它的根源是自由软件基金会(www. fsf.org),它主张源代码不应该是专有的,而是应该总是可以供用户根据自己的意愿进行检查和修改。
Open source software extended this idea by using the Internet to recruit a much larger population of volunteer developers. Many of them are also users of the code.开源软件通过使用互联网来招募更多的志愿者开发人员来扩展这一想法。他们中的许多人也是代码的用户。
Open source systems 开源系统
The best-known open source product is, of course, the Linux operating system which is widely used as a server system and, increasingly, as a desktop environment.当然,最著名的开源产品是Linux操作系统,它被广泛用作服务器系统,并且越来越多地被用作桌面环境。
Other important open source products are Java, the Apache web server and the mySQL database management system.其他重要的开源产品有Java、Apache Web服务器和MySQL数据库管理系统。
Open source issues 开源问题
Should the product that is being developed make use of open source components? 正在开发的产品是否应该使用开源组件?
Should an open source approach be used for the software’s development?软件开发是否应该使用开源方法?
Open source business 开源商业
More and more product companies are using an open source approach to development.越来越多的产品公司使用开源的开发方法。
Their business model is not reliant on selling a software product but on selling support for that product. 他们的商业模式并不依赖于销售软件产品,而是销售对该产品的支持。
They believe that involving the open source community will allow software to be developed more cheaply, more quickly and will create a community of users for the software.他们认为,加入开源社区将使软件开发更便宜、更快,并将为软件创建一个用户社区。
Open source licensing 开源许可
A fundamental principle of open-source development is that source code should be freely available, this does not mean that anyone can do as they wish with that code.开源开发的一个基本原则是源代码应该是免费可用的,这并不意味着任何人都可以使用该代码来做他们希望做的事情。
- Legally, the developer of the code (either a company or an individual) still owns the code. They can place restrictions on how it is used by including legally binding conditions in an open source software license.在法律上,代码的开发人员(公司或个人)仍然拥有代码。他们可以通过在开源软件许可证中包含具有法律约束力的条件来限制如何使用它。
- Some open source developers believe that if an open source component is used to develop a new system, then that system should also be open source. 。一些开源开发人员认为,如果一个开源组件被用来开发一个新的系统,那么这个系统也应该是开源的。
- Others are willing to allow their code to be used without this restriction. The developed systems may be proprietary and sold as closed source systems.其他人愿意允许他们的代码在没有这种限制的情况下使用。开发的系统可能是专有的,并作为封闭源代码系统出售。
License models 许可证模型
- The GNU General Public License (GPL). This is a so-called ‘reciprocal’ license that means that if you use open source software that is licensed under the GPL license, then you must make that software open source. GNU通用公共许可证(GPL)。这是一个所谓的“互惠”许可证,这意味着如果您使用的开放源码软件是根据GPL许可证授权的,那么您必须使该软件开放源码。
- The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) is a variant of the GPL license where you can write components that link to open source code without having to publish the source of these components. GNU较小的通用公共许可证(LGPL)是GPL许可证的一个变体,您可以在其中编写链接到开放源代码的组件,而无需发布这些组件的源代码。
- The Berkley Standard Distribution (BSD) License. This is a non-reciprocal license, which means you are not obliged to re-publish any changes or modifications made to open source code. You can include the code in proprietary systems that are sold. Berkley Standard Distribution(BSD)许可证。这是一个非互惠许可证,这意味着您没有义务重新发布对开源代码所做的任何更改或修改。您可以将代码包含在销售的专有系统中。
License management 许可证管理
- Establish a system for maintaining information about open-source components that are downloaded and used.建立一个系统来维护有关下载和使用的开源组件的信息。
- Be aware of the different types of licenses and understand how a component is licensed before it is used.了解不同类型的许可证,并了解组件在使用前是如何获得许可的。
- Be aware of evolution pathways for components.注意组件的进化路径。
- Educate people about open source.教育人们开放源码。
- Have auditing systems in place.建立审计制度。
- Participate in the open source community.参与开源社区。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号