密码学笔记:块密码
该部分为本科期间密码学课程复习笔记的备份。
Introduction
Block Ciphers are a natural generalization(一般化) of the classical substitution-transposition ciphers.
Block
- divides the plaintext into m blocks of fixed size, and perform the same process on each block to produce m blocks of ciphertext
- The block size can be any number of bits, but is usually large
- All the bits in the cipher block should depend on all the bits in the plaintext block
Process
- First define a block of computer bits which represent several characters
- Then Encrypt the complete block at one time
Feistel Structure
In 1973, Feistel suggest a form of product cipher.
product cipher( substitution- permutation (SP) cipher )
- The overall process involves several stages of a substitution followed by a transposition
- The master key is subdivided into a set of subkeys – one for each stage
- At each stage the data block is divided into a left and a right segment, the segments are swapped, and one segment is mixed with subkey for that stage.

数学表述
令F为轮函数,并令\(K_0,K_1,...,K_n\)分别为轮0,1,...,n的子密钥。将明文拆分成两个等长的块\((L_0,R_0)\)。
加密过程
对每轮\(i=0,1,...,n\),计算:
则密文为:\((R_{n+1},L_{n+1})\)。
解密过程
对于\((R_{n+1},L_{n+1})\),通过计算\(i=n,n-1...,0\) :
则明文为\((L_0,R_0)\)。
DES
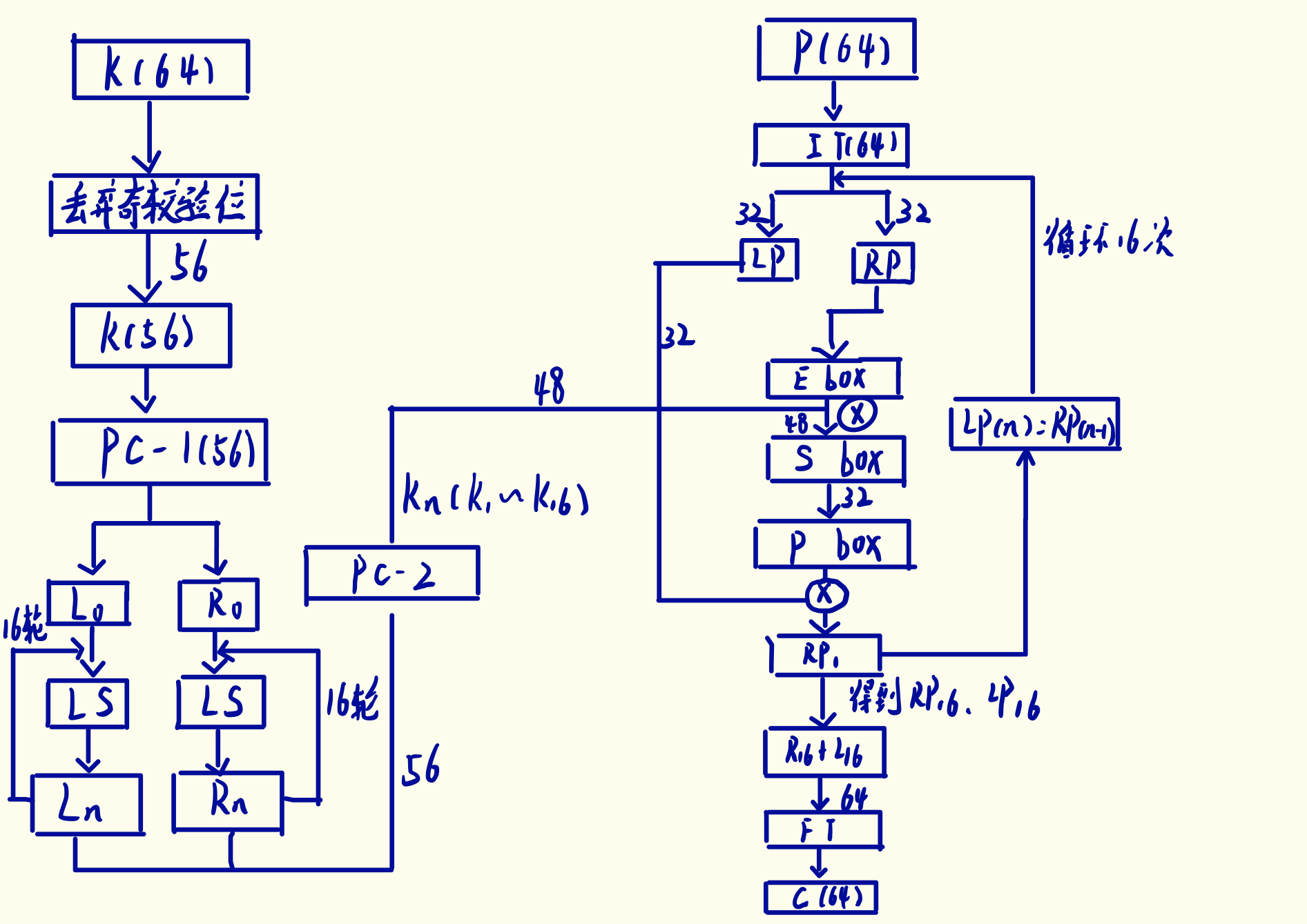
Principle
- substitution-permutation cipher
- 16 SP stages
- DES works on 64 bit blocks
- 56 bit key
Key
The key for DES is an arbitrary 56 bit string of 0 and 1
Often it is given as a 7 letter word
DES expands this key to 64 bits by adding 8 additional 0 and 1
- Bits 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, and 64 are added so that each 8 bit block has odd parity (odd number of ‘0’)(即8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56,64位为奇偶校验位)
- The key is divided, shifted, and shuffled 16 times to form 16 different (but related) subkeys each of which is 48 bits long
Example
K(64bit) = 133457799BBCDFF1
K(64bit) = 00010011 00110100 01010111 01111001 10011011 10111100 11011111 11110001 (加注的bits为奇偶校验位,若前7bits为奇数个1,则校验位为0;如果为偶数个1,则校验位为1)
using 56bit key=0001001 0011010 0101011 0111100 1001101 1011110 1101111 1111000
note:我们提供的一般为64位 key,但实际DES用到的却只有56bits,通过缩小变换表变为56位。
Subkey Generation Process

-
PC-1 置换(64bits变56bits):Discarding: 8、16、24、32、40、48、56、64 bit
PC-1(缩小变换表)57 49 41 33 25 17 9 1 58 50 42 34 26 18 10 2 59 51 43 35 27 19 11 3 60 52 44 36 63 55 47 39 31 23 15 7 62 54 46 38 30 22 14 6 61 53 45 37 29 21 13 5 28 20 12 4 (从左向右按行进行数) -
LSC: one bit in 1、2、9、16 stage, tow bits in other stages(即在第1、2、9、16轮子密钥生成时密钥循环左移1位;在其他轮循环左移2位)
-
PC-2 (Compressing,压缩变换)
14 17 11 24 1 5 3 28 15 6 21 10 23 19 12 4 26 8 16 7 27 20 13 2 41 52 31 37 47 55 30 40 51 45 33 48 44 49 39 56 34 53 46 42 50 36 29 32
code
def getSubKeys(key):
res=[]
key_56=[key[PC_1[i]-1] for i in range(56)]#PC-1变换
shift_list=[1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1]#移位数表
for i in range(16):#进行16轮子密钥获取
key_l=shift(key_56[:28],shift_list[i])
key_r=shift(key_56[28:],shift_list[i])
key_56=key_l+key_r#分别移位后交换Key_L、Key_R
key_48=[key_56[PC_2[i]-1] for i in range(48)]#压缩变换
res.append(key_48)
return res#返回subkey
Encryption
-
Initial Transposition(初始置换)
通过初始置换表进行64bits明文的初始置换
58 50 42 34 26 18 10 2 60 52 44 36 28 20 12 4 62 54 46 38 30 22 14 6 64 56 48 40 32 24 16 8 57 49 41 33 25 17 9 1 59 51 43 35 27 19 11 3 61 53 45 37 29 21 13 5 63 55 47 39 31 23 15 7 -
Each stage of DES includes some processes, which are defined in three “boxes” called the expansion box (Ebox), the substitution box (Sbox), and the permutation box (Pbox),then XOR

-
E-Box

EBox-Table
|||||||||||||
|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|
|32|1|2|3|4|5|4|5|6|7|8|9|
|8|9|10|11|12|13|12|13|14|15|16|17|
|16|17|18|19|20|21|20|21|22|23|24|25|
|24|25|26|27|28|29|28|29|30|31|32|1| -
S-Box

S1:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 14 4 13 1 2 15 11 8 3 10 6 12 5 9 0 7 1 0 15 7 4 14 2 13 1 10 6 12 11 9 5 3 8 2 4 1 14 8 13 6 2 11 15 12 9 7 3 10 5 0 3 15 12 8 2 4 9 1 7 5 11 3 14 10 0 6 13 S2:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 15 1 8 14 6 11 3 4 9 7 2 13 12 0 5 10 1 3 13 4 7 15 2 8 14 12 0 1 10 6 9 11 5 2 0 14 7 11 10 4 13 1 5 8 12 6 9 3 2 15 3 13 8 10 1 3 15 4 2 11 6 7 12 0 5 14 9 S3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 10 0 9 14 6 3 15 5 1 13 12 7 11 4 2 8 1 13 7 0 9 3 4 6 10 2 8 5 14 12 11 15 1 2 13 6 4 9 8 15 3 0 11 1 2 12 5 10 14 7 3 1 10 13 0 6 9 8 7 4 15 14 3 11 5 2 12 S4:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 7 13 14 3 0 6 9 10 1 2 8 5 11 12 4 15 1 13 8 11 5 6 15 0 3 4 7 2 12 1 10 14 9 2 10 6 9 0 12 11 7 13 15 1 3 14 5 2 8 4 3 3 15 0 6 10 1 13 8 9 4 5 11 12 7 2 14 S5:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 2 12 4 1 7 10 11 6 8 5 3 15 13 0 14 9 1 14 11 2 12 4 7 13 1 5 0 15 10 3 9 8 6 2 4 2 1 11 10 13 7 8 15 9 12 5 6 3 0 14 3 11 8 12 7 1 14 2 13 6 15 0 9 10 4 5 3 S6:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 12 1 10 15 9 2 6 8 0 13 3 4 14 7 5 11 1 10 15 4 2 7 12 9 5 6 1 13 14 0 11 3 8 2 9 14 15 5 2 8 12 3 7 0 4 10 1 13 11 6 3 4 3 2 12 9 5 15 10 11 14 1 7 6 0 8 13 S7:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 4 11 2 14 15 0 8 13 3 12 9 7 5 10 6 1 1 13 0 11 7 4 9 1 10 14 3 5 12 2 15 8 6 2 1 4 11 13 12 3 7 14 10 15 6 8 0 5 9 2 3 6 11 13 8 1 4 10 7 9 5 0 15 14 2 3 12 S8:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 13 2 8 4 6 15 11 1 10 9 3 14 5 0 12 7 1 1 15 13 8 10 3 7 4 12 5 6 11 0 14 9 2 2 7 11 4 1 9 12 14 2 0 6 10 13 15 3 5 8 3 2 1 14 7 4 10 8 13 15 12 9 0 3 5 6 11 note:将6bits分组的第一个bit位与第6个bit位拼在一起,其值为行位置;第2、3、4、5bit位拼在一起,其为作列位置。
-
P-Box
16 7 20 21 29 12 28 17 1 15 23 26 5 18 31 10 2 8 24 14 32 27 3 9 19 13 30 6 22 11 4 25 -
XOR

- Final Transposition
40 8 48 16 56 24 64 32 39 7 47 15 55 23 63 31 38 6 46 14 54 22 62 30 37 5 45 13 53 21 61 29 36 4 44 12 52 20 60 28 35 3 43 11 51 19 59 27 34 2 42 10 50 18 58 26 33 1 41 9 49 17 57 25
Code
def encrypt(plaintext,key):
subkeys=getSubKeys(key)#获取子密钥
text=inputIT(plaintext)#进行初始置换
for i in range(16):
text_l=text[:32]
text_r=text[32:]
r_extend=extendPlain(text_r)#E-Box变换
xor1=xor(r_extend,subkeys[i])#与子密钥进行XOR
res_sBox=SBoxPermutation(xor1)#S-Box变换
res_pBox=PBoxPermutation(res_sBox)#进行P-Box置换
res=xor(text_l,res_pBox)#进行PL与进过处理后的PR进行最终XOR
text=text_r+res#进行换位
text=text[32:]+text[:32]
text=inputFT(text)
return text
SDES
Encryption
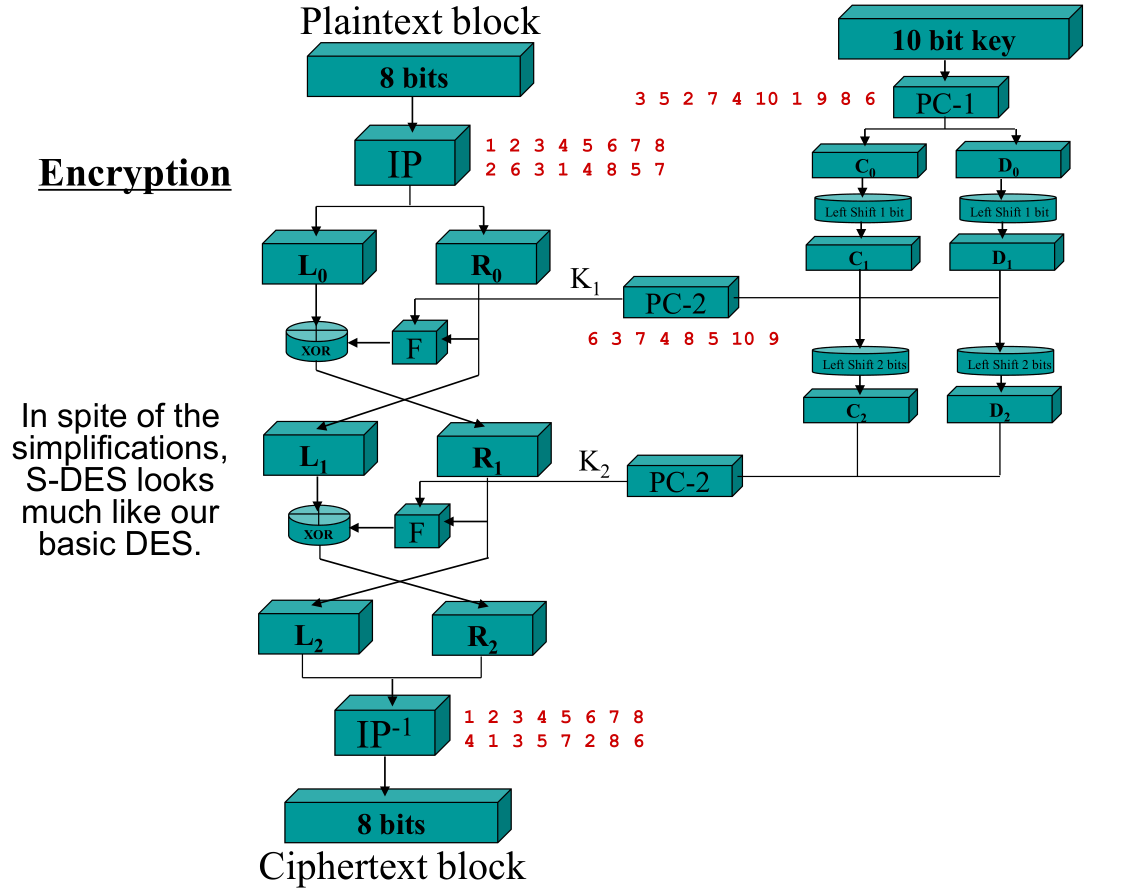
It operates on 8-bit data blocks (in other words, single characters)
using a 10-bit key (only \(2^{10}\) = 1024 possibilities) and two stages
The function F on the prior slide contains an EBox, PBox and 2
SBoxes (much like DES)
- EBox: 4 1 2 3 2 3 4 1
- PBox: 2 4 3 1
- two S-Boxes:
-
The input is a 4 bit value
-
The first and last bits define the row
-
The middle bits define the column
-
The output is a 2 bit value
\(S_0\):
0 1 2 3 0 1 0 2 3 1 3 1 0 2 2 2 0 3 1 3 1 3 2 0 \(S_1\):
0 1 2 3 0 0 3 1 2 1 3 2 0 1 2 1 0 3 2 3 2 1 3 0
-
Decryption
将key转换成subkey之后,subkey进行逆序翻转过来,再经过相同的DES 加密过程
Code
def decrypt(cipher,key):
subkeys=getSubKeys(key)[::-1]
text=inputIT(cipher)
for i in range(16):
text_l=text[:32]
text_r=text[32:]
r_extend=extendPlain(text_r)
xor1=xor(r_extend,subkeys[i])
res_sBox=SBoxPermutation(xor1)
res_pBox=PBoxPermutation(res_sBox)
res=xor(text_l,res_pBox)
text=text_r+res
text=text[32:]+text[:32]
text=inputFT(text)
return text
DES FAQ
Why DES has 16 stages?
16 stages is a threshold limit value (TLV)
Does DES key has some weakness?
Yes.
- The simplest attack to DES is brute-force attack which will test all the feasible keys (\(2^{56}\)).
- With the development of computer and network, the time reduced greatly.
- Some analysis algorithms such as differential
- cryptanalysis and linear cryptanalysis were also suggested to reduce the work
- Key Weakness
- One of the early discoveries was that DES had some weak keys:
-
keys that generate the same subkey for each round
-
four such DES keys:
0101 0101 0101 0101FEFE FEFE FEFE FEFE1F1F 1F1F 0E0E 0E0EE0E0 E0E0 F1F1 F1F1
-
- There are also 12 semi-weak DES keys
- Semi-weak keys generate only two subkeys which alternate rounds
- One of the early discoveries was that DES had some weak keys:
Double DES
Encryption
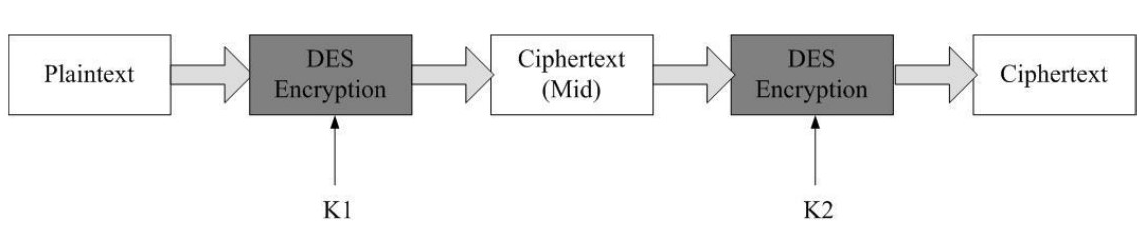
Decryption
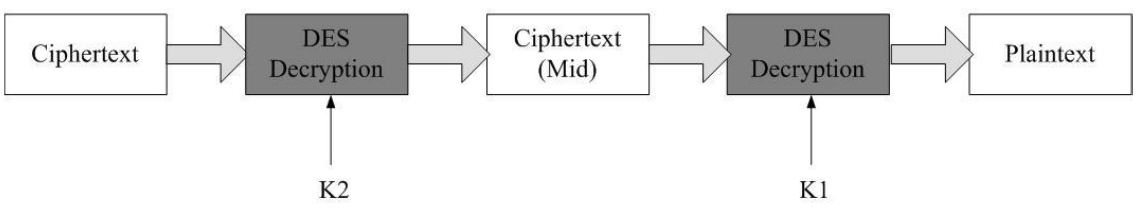
Meet-in-the-middle Attack
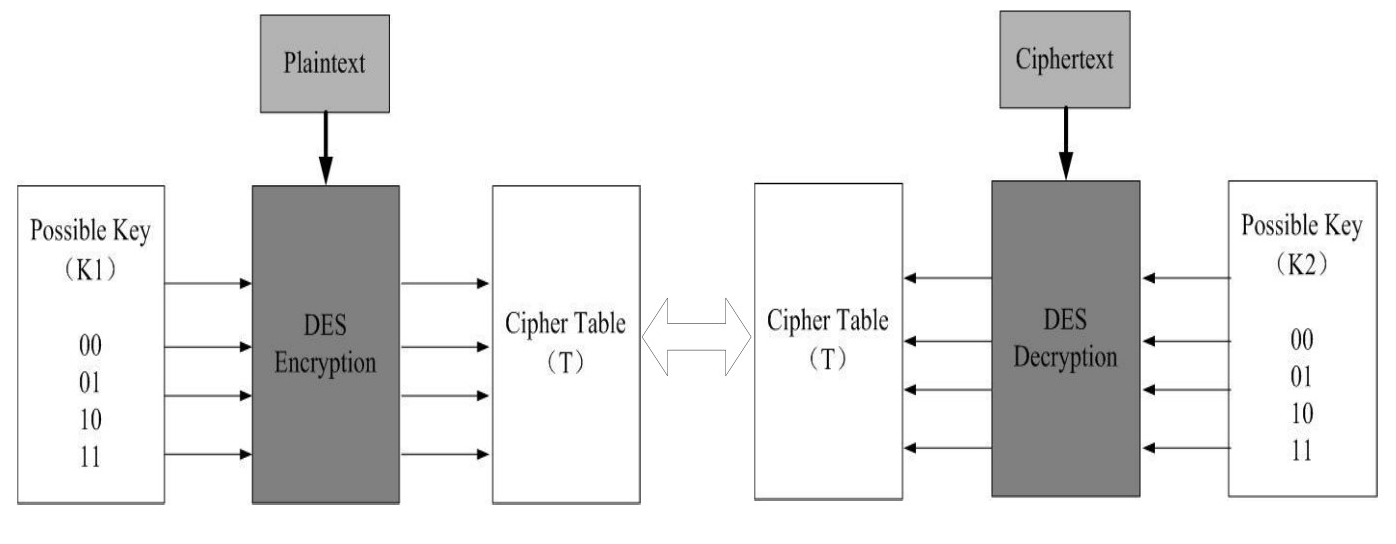
Triple DES
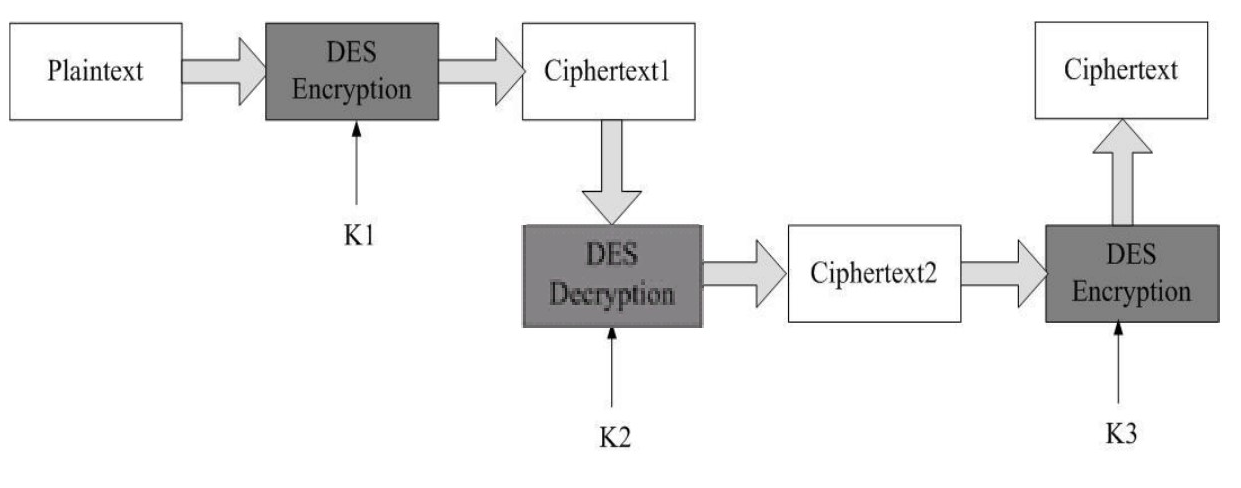
3DES with 3 keys (EDE-3)
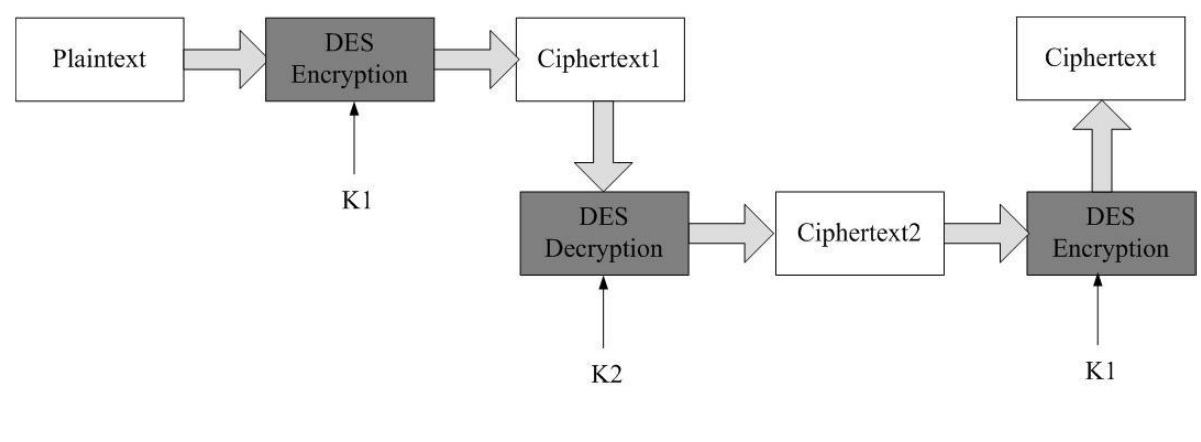
3DES with 2 keys (EDE-2)
AES
Rijndael
- One of the fastest and strongest algorithms.
- Variable block length: 128, 192, 256 bits
- Variable key length: 128, 192, 256 bits
- Variable number of rounds (iterations): 10, 12, 14
- Number of rounds depend on key/block length
- The number of rounds \(N=max(N_k , N_b ) +6\),where \(N_b\) is the block length and \(N_k\) is the key length, every 32bits is a unit
Rijndael structure
Rather than using just a substitution and a permutation at each stage like
DES, Rijndael consists of multiple cycles of Substitution, Shifting, Column
mixing and a KeyAdd operation
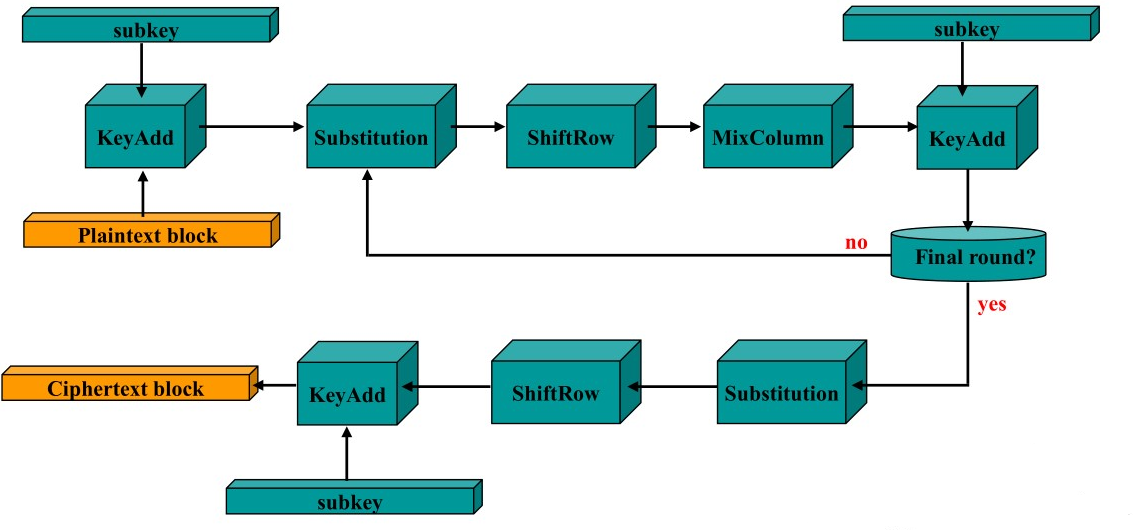
Note: 其中判断为从第一轮之后的新一轮开始就判断,因此开头生成一个subkey,循环流程N-2轮,生成N-2个subkey,最后一轮判断并进入最终一轮,生成一个subkey。
Encryption
- Key Schedule
- The key is grouped into a column array and then expanded by adding 40 new columns
- If the first four columns (given by the key) are C(0), C(1), C(2) and C(3), then the new columns are generated in a recursive(递归) manner
- If i is not a multiple of 4 then column i is determined by: C(i) = C(i-4) XOR C(i-1)
- If i is a multiple of 4 then column i is determined by:C(i) = C(i-4) XOR T(C(i-1))
Where T(C(i-1)) is a transformation of C(i-1) implemented as:
- Cyclically shift (UP) the elements of C(i-1) by one byte
- Use each of these 4 bytes as input into the S-box to create four new bytes e,f,g,h
- Calculate a round constant r(i) = 2 (i-4)/4
- Create the transformed column as: (e XOR r(i), f, g, h)
The round key for the jth round consists of the columns C(4j), C(4j+1), C(4j+2), C(4j+3)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号