密码学部分笔记:古典密码
该部分为本科期间密码学课程复习笔记的备份。
Introduction
-
All classical encryption algorithms:symmetric-key(对称密码)
-
two basic principles:substitution(替换) and transposition (置换)
-
four types of classical ciphers:
Ⅰ.Monoalphabetic cipher(单表密码)
Ⅱ.Polyalphabetic cipher(多表密码)
Ⅲ.Polygraphics cipher(多图密码)
Ⅳ.Transposition cipher(置换密码)
Monoalphabetic cipher
definition
a cipher which each plaintext character is replaced by exactly one ciphertext character
Introduction
- substitution cipher(替换密码)
- three concerned ciphers:
Caesar cipher、Keyword cipher、Affine ciopher。
Caesar cipher
Principle
Monoalphabetic Substitution
Encryption
Replaces each plaintext character by the character k positions to the right
in the alphabet , k is the key.
Decryption
Replaces each ciphertext character by the character k positions to the left
in the alphabet.
Example:
key=5
| plaintext | v | e | n | i | v | i | d | i | v | i | c | i |
| ciphertext | a | j | s | n | a | n | i | n | a | n | h | n |
ciphertext="ajsnaninanhn"
Specialty(特性)
Simple,Frangibility(简单,脆弱)
Brute-force attack
- Always possible to simply try every key
- Although seems not to be clever, but brute-force attack is useful in many cases
Keyword cipher
principle
Monoalphabetic Substitution
Encryption
- Select a keyword - if any letters are repeated drop the second and all other occurrences from the keyword. eg:
success⤇suce - Write the keyword below the alphabet, fill in the rest of the space with the remaining letters in the alphabet in their standard order
Example
Keyword is "count"
| plaintext | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M |
| ciphertext | C | O | U | N | T | A | B | D | E | F | G | H | I |
| plaintext | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
| ciphertext | J | K | L | M | P | Q | R | S | V | W | X | Y | Z |
Frequency analysis
- The most basic observation of cryptanalysis is that every letter of a language has a personality(个性) of its own
if every plaintext
tis changed to a ciphertextm, then in the
ciphertext,massumes the personality oftto the trained observer, the personality of a letter gives away its identity
-
Some of these personality characteristics are
(1). frequency of occurrence (发生的频率)
(2). contact with other letters (与其他字母的联系)
(3). position within words (单词位置)
digrams(连字)
digrams:the set of preferred associations a useful personality characteristic.
method:
look at the frequency of digrams
Another is to try to identify possible words in the ciphertext
Affine Cipher
principle
Monoalphabetic Substitution
Encryption
- Each letter of the alphabet is assigned(指派) a number,A = 0, B = 1, . . ., Z
= 25 - Two numbers are selected (
a,b) between 0 and 25 such that thegcd(a,26)= 1.For example,a=5 will work, buta=2 will not work - Let
pandcrepresent letters (p,care numbers between 0 and 25)
wherepis a plaintext letter andcis a ciphertext letter then:
Decryption
如果为放射密码方程组,利用中国剩余定理求解。
求逆元
- 求解逆元的一次同余式:\[a^{-1}*x≡1\mod{26} \]
- 转化公式为等价的二元一次不定方程。\[a^{-1}*m+{26}*n=1 \]
- 最后,用欧几里得逆过程求解,得到
x=m。
Polyalphabetic Cipher
definition
a substitution cipher in which each plaintext character is represented by more than one ciphertext character and each ciphertext character represents more than one plaintext character
feature(特点)
- difficult to break codes using frequency analysis.
- goal:spread the personality characteristics of each plaintext letter over several ciphertext letters.
- Typical eg:Vigenere Cipher
Vigenere cipher
Principle
Polyalphabetic substitution
Encryption
- A keyword is selected and it is repeatedly written above the plaintext until the length of plaintext, so each plaintext character is associated with one keyword character.
- The substitution between plaintext letter and keyword letter is by means of the Vigenere table
example
key="HOLD"
| keyword | H | O | L | D | H | O | L | D | H | O | L | D | H | O | L | D | H | O |
| Plaintext | T | H | I | S | I | S | T | H | E | L | P | I | A | T | N | X | E | T |
Table

最上行字母为
Keyword字母,最左列字母为plaintext字母
result
| keyword | H | O | L | D | H | O | L | D | H | O | L | D | H | O | L | D | H | O |
| Plaintext | T | H | I | S | I | S | T | H | E | L | P | I | A | T | N | X | E | T |
| Ciphertext | A | V | T | V | H | K | E | G | Q | H | E | B | Q | D | W | D | L | E |
Decryption
To decipher a vigenere cipher, the lookup(查找的) process is reversed(翻转) using the same vigenere table.
Cryptanalysis of Vigenere Cipher
Kasiski’s breakthrough
The conjuction(连接) of a repeated portion(部分) of the key with a repetition in the plaintext produces a repetition in the ciphertext.
Kasiski’s conclusion
- Find repetitions in the ciphertext
- Count the number of characters between the repetitions
- Find the factors of the numbers discovered in step2
- The most common factor is likely to be the keyword length
After kwon keyword length
- Get the all enciphered by the same letter and get
ndifferent monoalphabetic ciphers - breaking n different monoalphabetic ciphers
- Since monoalphabetic ciphers can be easily solved
providing the ciphertext is large enough to produce a reasonable statistical sample, the Vigenere cipher is also easy to solve
Autokey cipher
Principle
Polyalphabetic substitution
Encryption
- Select a keyword
- Use the keyword to encipher the first segment of the plaintext
- Use the ciphertext (or the plaintext segment which was just enciphered) as the key for the next segment
Weakness
An error anywhere in the encryption or decryption propagates(传播) throughout the remaining text
Good idea
use the plaintext as the key
Rotor cipher
Principle
Polyalphabetic substitution
Encryption
A rotor is a disk with electrical contacts, one for each letter of the alphabet around the side
The internal path of the wires defines a monoalphabetic substitution
each rotor is wired internally to represent a possible substitution pattern of 26 letters,the number of possible rotor is:
\(\ 26!=403,291,461,126,605,635,584,000,000\)
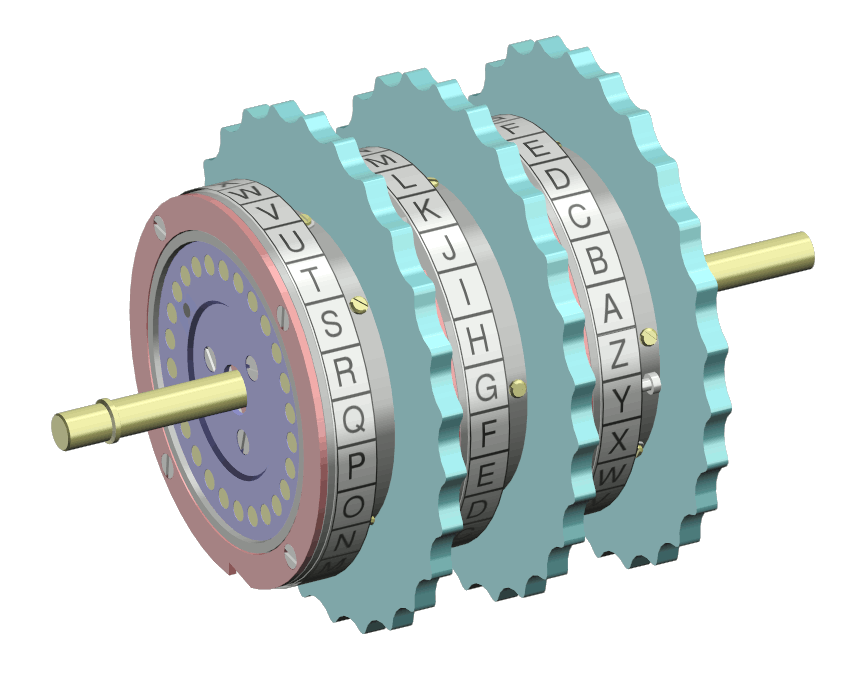

process
Several rotors are connected and rotated at different rates
eg

Enigma
Principle
Polyalphabetic substitution
Encryption
- use several variations on the basic Enigma structure, but fundamentally consisted three rotors, a reflector(反射器) and a plugboard(插接板)
- The reflector was used to create a longer path by using each rotor twice
- The plugboard was a fixed substitution which usually involved only a few characters

Polygraphic Cipher
Note Monoalphabetic Cipher and Polyalphabetic Cipher are monographic
ciphers.
Introduction
A polygraphic cipher works on more than one plaintext character at a time. Groups of plaintext characters are replaced by assigned groups of ciphertext characters
example: digraphic cipher
looks at pairs of characters in the plaintext
feature
- stronger than monographic cipher
- makes simple frequency analysis useless
Playfair cipher
Principle
Polygraphic substitution
Encryption
- Playfair is designed to invalidate(使无效) single frequency analysis
- The key is a
5 x 5matrix of letters arranged by a keyword, dropping any repeated letters and the letterj, the remaining slots(插槽) in the square are filled with the unused letters of the alphabet in their nature order - The square is used to transform plaintext letter pairs \((m_1, m_2)\) into ciphertext letter pairs by looking up the plaintext in the square and selecting ciphertext pairs based on three rules
If \(m_1\) and \(m_2\) are in the same row in the key matrix, then they are replaced by the characters to their right
If \(m_1\) and \(m_2\) are in the same column then they are replaced by the letters below them
If \(m_1\) and \(m_2\) are in different rows and columns then they are replaced by the letters found on the other two corners of a rectangle formed by \(m_1\) and \(m_2\)
至于横向替换还是纵向替换要事先约好,或自行尝试
Note:
- same row rule
- before the rules will work, the plaintext has to be processed:
jare replaced withia null(等于零的) letter such as
qis placed between any identical(相同的) pairs of letters. eg:tt→tqtif the plaintext has an odd number of letters, the null letter is added on to the end.
example
keyword:
harpsichord
matrix key
| H | A | R | P | S |
| I | C | O | D | B |
| E | F | G | K | L |
| M | N | Q | T | U |
| V | W | X | Y | Z |
Cryptanalysis of playfair Cipher
verify whether a cipher is a playfair cipher.
examining the features of playfair ciphertext. look for several characteristics:
- There must be even(偶数) number of characters in the ciphertext
- No double letters(双字母) can appear in a ciphertext pair
- No single letter in the plaintext can ever be represented by itself
- Two reversed digraphs(翻转的连字) in the plaintext such as ER and RE will always be enciphered by two reversed digraphs in the ciphertext
- Each single letter in the plaintext can be enciphered by one of only 5 other letters
Probable Word attack
based on known-plaintext attack
Given the Playfair ciphertext,assume that it is known that the plaintext phase is in the ciphertext.
process

- During the first step, if the pairs produced by the current lineup(一组阵容) of the known plaintext with the ciphertext violate any of these conditions(指前面的检测方法条件),then the known plaintext is shifted over one character and check again
- When looking at possible structure, we may need to guess that the keyword.
Double Playfair
The cipher is formed from the plaintext using rules similar to those for the single Playfair
Principle
Polygraphic substitution
Encryption
- uses two Playfair squares formed from two keywords
- Select two keywords,and form the two Playfair squares.
note:简单来说就是两表两次表中字母变换
Example
- We begin by choosing a period(周期), then breaking the message into groups of period, with the second below the first, the fourth below the third, and so on.If the last group is incomplete, break it into equal pieces.eg: If it has an odd number of letters, add a 'x' to fill it out.
- Given the Double Playfair on the prior slide encipher the phrase.
- First select a cipher period
- Encipher the top/bottom letter pairs in two steps
- Find the top letter in the first Playfair square and the bottom letter in the second Playfair square
- If they form a rectangle(矩形) then take the other two corner letters (same row rule)
- If they are in the same row then take the letter to the right of each one in the other square
- Use the letters discovered above in the same way to determine the actual substitution
- Note:except the first letter is found in the second square and the second letter is found in first square
differences with Playfair
- Reversed plaintext digraphs need not correspond to reversed ciphertext digraphs, For example, ‘SR’ and ‘RS’
- Double letters can be encrypted without inserting a null, For example, ‘OO’
- Double letters can appear in ciphertext, For example, ‘LW’
Note:
- 在Double Playfair cipher中,存在两种位置关系:同行不同列、不同行不同列。
- 当同行不同列时,遵循同表同行循环向右寻找的规则,但要将第一个表进行加密后得到的字母结果,与第一个表加密后得到的字母结果交换位置,再次用同样方法重复两表加密才能得到最终的密文对。
eg
key:software、computer
| S | O | F | T | W | C | O | M | P | U | |
| A | R | E | B | C | T | E | R | A | B | |
| D | G | H | I | K | D | F | G | H | I | |
| L | N | M | P | Q | K | L | N | Q | S | |
| U | X | V | Y | Z | V | W | X | Y | Z |
plaintext:thisisadifficultbutn
group:each group length is 10
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t | h | i | s | i | s | a | d | i | f |
| f | i | c | u | l | t | b | u | t | n |
Transposition Cipher
all the pieces are present but are merely disarranged
two types of transpositions
- Monographic methods
- deal with individual letters
- Polygraphic methods
- deal with units greater than single letters (words,phases, etc)
involve a geometric(几何学的) figure
- The letters are inscribed(内接) in the figure is some agreed upon direction
- The letters are then transcribed(转录) or rewritten according to another direction to form the ciphertext
specific key controls
- The geometric figure and its dimension(规模)
- The variation in the direction of inscription and transcription
Skytable
Principle
Transposition
Encryption
- It consists of a staff of wood around which a strip of papyrus(草纸) or parchment(羊皮纸) is wrapped
- The secret message is written on the parchment down the length of the staff
- When the parchment is unwrapped it appears to contain a series of disconnected letters

Permutation cipher
Note:与Double Permutation cipher加密方法有很多操作上的不同!而且两者是同一层次的,而非包含关系。
Principle
Transposition
Encryption
- Break the plaintext up into groups of a fixed size(d为length)
- Define a permutation of the integers 1 to d called f(f为分组顺序)
- Within each block, permute the letters according to f
- The key is (d, f)
Example
d=5 , f=\((3,4,1,5,2)\)
plaintext:gettheball
| type | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plaintext | g | e | t | t | h | e | b | a | l | l | |
| ciphertext | t | h | g | e | t | a | l | e | b | l |
Column permutation cipher
Principle
Transposition
Encryption
- Write the plaintext into a matrix by rows, then generate the ciphertext by selecting the columns in a given order
- The key is the given order
Example
key:\((4,2,1,3)\)
plaintext:encryptionalgorithms
5*4 matrix:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| E | N | C | R |
| Y | P | T | I |
| O | N | A | L |
| G | O | R | I |
| T | H | M | S |
根据key的order将对应数字的列全部内容按列写行的形式,构成5*4的密文matrix
| R | I | L | I |
| S | N | P | N |
| O | H | E | Y |
| O | G | T | C |
| T | A | R | M |
或者写成字符串:
RILISNPNOHEYOGTCTARM
Key
- The key for a column transposition is the number of columns and the order in which they are selected
- Both can be specified by a keyword
- the length of the keyword is the number of columns
- the order of the letters in the keyword determines the order in which the columns are selected
Cryptanalysis of Column permutation cipher
- Find possible rectangle sizes
- determining the number of columns
- completely filled transposition: the number of characters is the product of the number of rows and the number of columns
- factor the number of characters to determine possible row and column sizes
- determining the number of columns
- Select the correct rectangle
- rely on a general characterristics of English to detect the most likely arrangement of the ciphertext
- count the vowels(元音字母) in each row of each possible rectangle
- The one with the best match to 40% is the best choice for the actual rectangle
- \(difference=sum_{vowels}-length_{column}*0.4\)
- rely on a general characterristics of English to detect the most likely arrangement of the ciphertext
- Find the column order
- Advantage:taken of all the characteristics of the plaintext language
- certain letters usually of medium or low frequency which combine with other letters to form diagrams of high frequency
- eg1:
Hcombines withTto formTH(highest frequency) - eg2:
Hcombines withCto formCH - eg3:
Vmbines withEto form `VE(medium frequency in military text)
- eg1:
- usually in every language at least one letter which can be followed by only certain other letters forming an obligatory(必须的) sequence or invariable digraph(不变的连字)
- pilot letters(先导字母)
- Letters such as these with limited affinity are called pilot letters
- Breaking a column permutation cipher is a process of anagramming by selecting a pilot letter and trying to form digrams with the other letters in its row
Double-Transposition cipher
用transposition cipher加密2次
Principle
Transposition
Encryption
- The plaintext is enciphered using a column permutation cipher
- The resulting ciphertext is enciphered using column permutation cipher again
- The keyword may be the same for both transpositions or not
- The result is a thorough mixing of the positions of the plaintext
Example
\(plaintext\):Theresultisathoroughmixingofthepositionsoftheplaintext
\(key_1\):what,即:\(key_1=(4,2,1,3)\)
\(key_2\):next,即:\(key_2=(2,1,4,3)\)
\(ciphertext\):irfehvhtthiianfnygfamhcpotnishctesmeegitieeelrtcywepuerrcpoi


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号