随机链表的复制-leetcode
题目描述
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
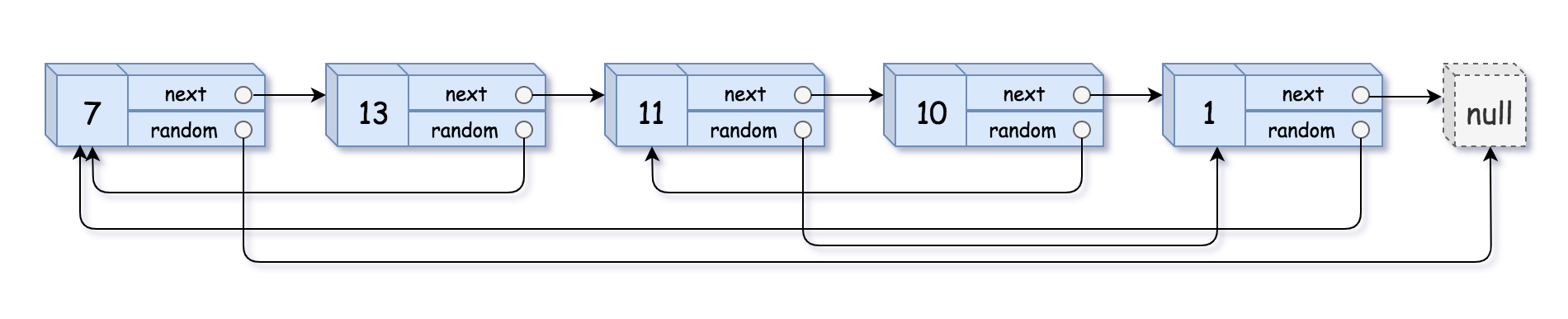
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
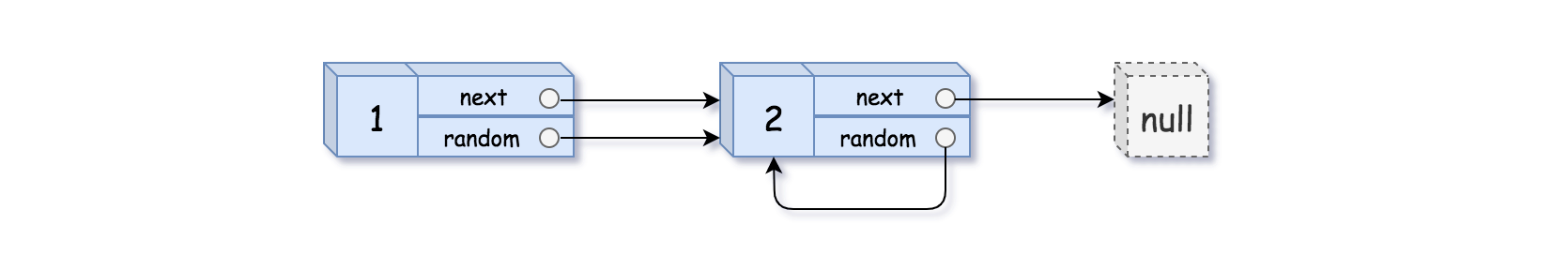
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
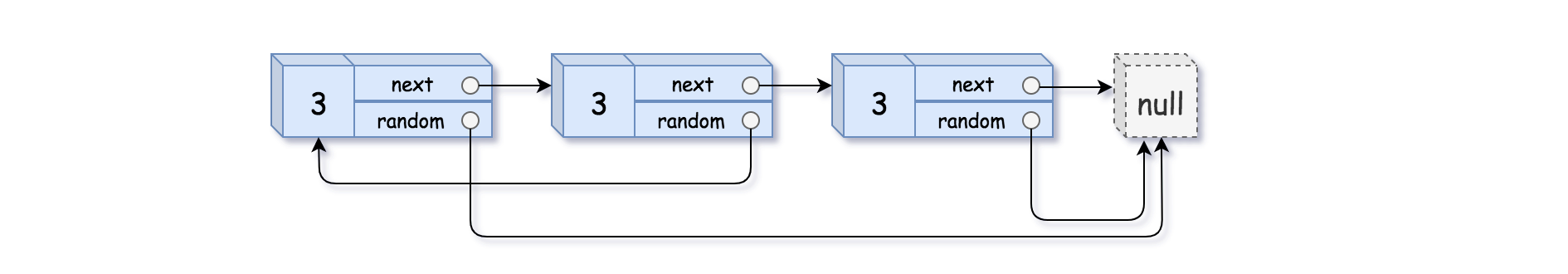
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
提示:
0 <= n <= 1000-104 <= Node.val <= 104Node.random为null或指向链表中的节点。
解法一
思路:
首先不管随机节点,进行一轮普通的拷贝,同时采用哈希表记录原始节点与索引,再记录索引与新节点的关系。再次遍历,查看随机节点,找到原始节点的随机节点的索引,根据该索引去寻找新的节点,进行连接。
代码:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Map<Node,Integer> mapOld = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer,Node> mapNew = new HashMap<>();
Node cur = head;
Node pre=null;
Node newHead =new Node(0);
pre = newHead;
//创建完成所有的节点
int item=0;
while (cur != null) {
Node newNode = new Node(cur.val);
mapOld.put(cur,item);
mapNew.put(item,newNode);
cur = cur.next;
pre.next = newNode;
pre = newNode;
item++;
}
Node curOld = head;
Node curNew = newHead.next;
while (curOld != null) {
if(curOld.random != null) {
int i=mapOld.get(curOld.random);
Node tmp=mapNew.get(i);
curNew.random = tmp;
}else{
curNew.random = null;
}
curOld=curOld.next;
curNew=curNew.next;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}
解法二
思路:
来自官方的解答。一个可行方案是,我们利用回溯的方式,让每个节点的拷贝操作相互独立。对于当前节点,我们首先要进行拷贝,然后我们进行「当前节点的后继节点」和「当前节点的随机指针指向的节点」拷贝,拷贝完成后将创建的新节点的指针返回,即可完成当前节点的两指针的赋值。
具体地,我们用哈希表记录每一个节点对应新节点的创建情况。遍历该链表的过程中,我们检查「当前节点的后继节点」和「当前节点的随机指针指向的节点」的创建情况。如果这两个节点中的任何一个节点的新节点没有被创建,我们都立刻递归地进行创建。当我们拷贝完成,回溯到当前层时,我们即可完成当前节点的指针赋值。注意一个节点可能被多个其他节点指向,因此我们可能递归地多次尝试拷贝某个节点,为了防止重复拷贝,我们需要首先检查当前节点是否被拷贝过,如果已经拷贝过,我们可以直接从哈希表中取出拷贝后的节点的指针并返回即可。
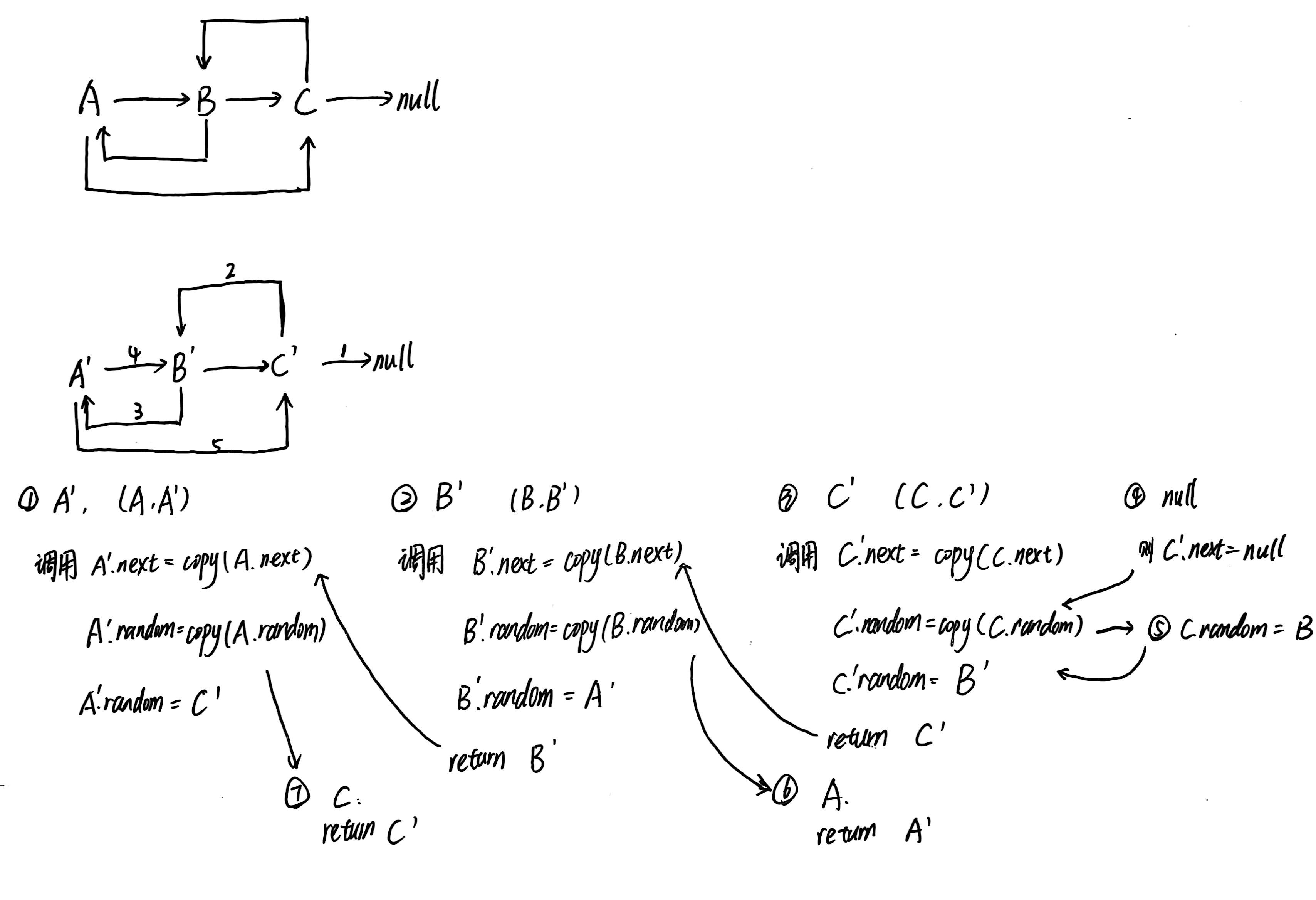
代码:
class Solution {
Map<Node, Node> cachedNode = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
if (!cachedNode.containsKey(head)) {
Node headNew = new Node(head.val);
cachedNode.put(head, headNew);
headNew.next = copyRandomList(head.next);
headNew.random = copyRandomList(head.random);
}
return cachedNode.get(head);
}
}
解法三
思路:
我们首先将该链表中每一个节点拆分为两个相连的节点,例如对于链表 A→B→C,我们可以将其拆分为 A→A′→B→B′→C→C′。对于任意一个原节点 S,其拷贝节点 S′ 即为其后继节点。
这样,我们可以直接找到每一个拷贝节点 S′ 的随机指针应当指向的节点,即为其原节点 S 的随机指针指向的节点 T 的后继节点 T′。需要注意原节点的随机指针可能为空,我们需要特别判断这种情况。
当我们完成了拷贝节点的随机指针的赋值,我们只需要将这个链表按照原节点与拷贝节点的种类进行拆分即可,只需要遍历一次。同样需要注意最后一个拷贝节点的后继节点为空,我们需要特别判断这种情况。
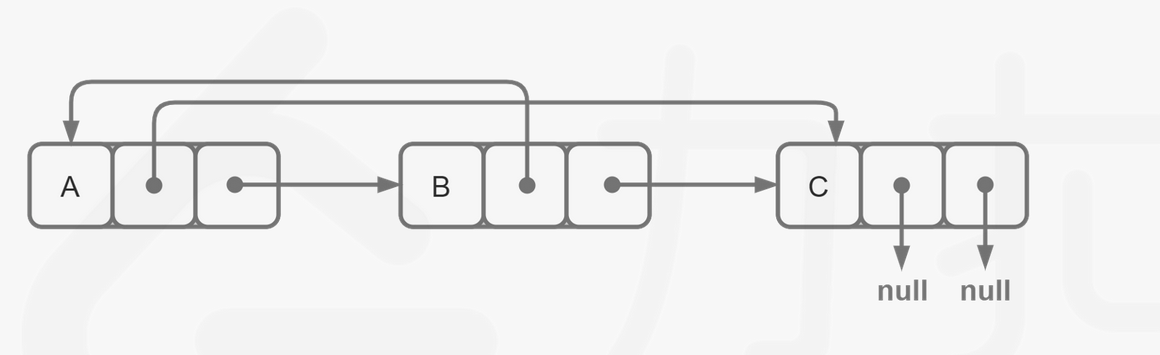
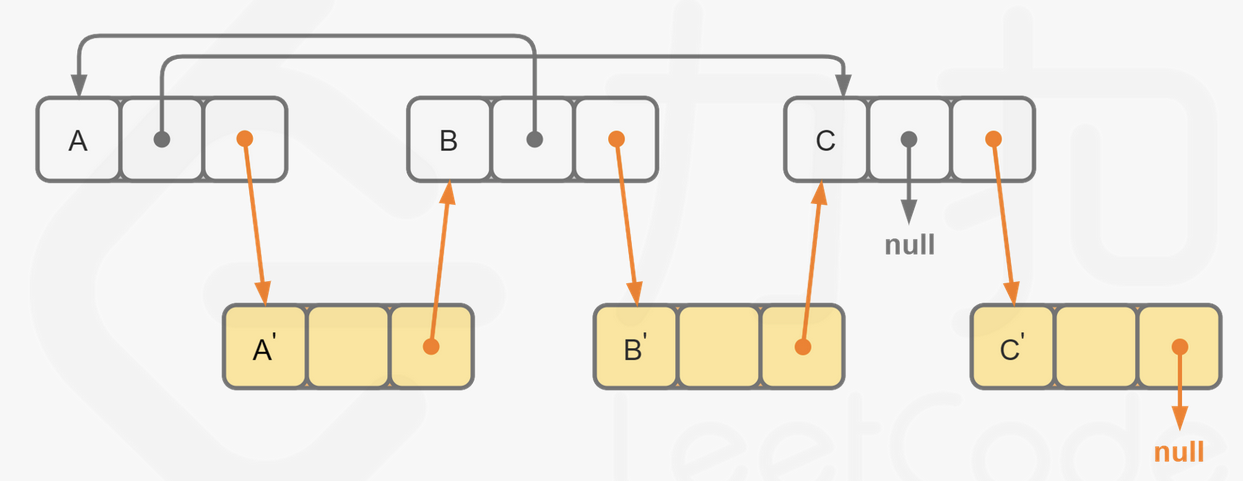
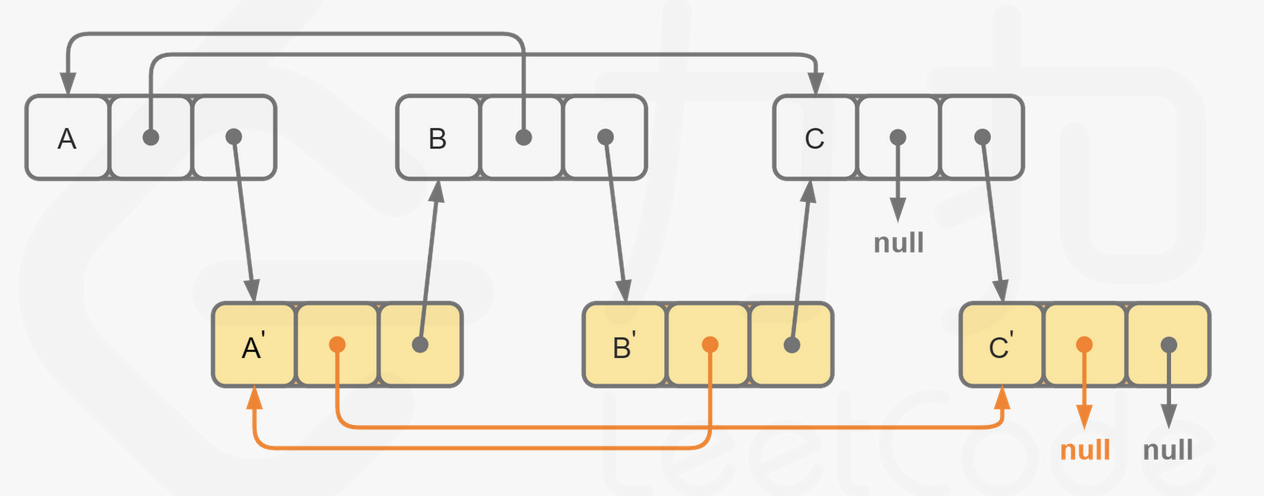
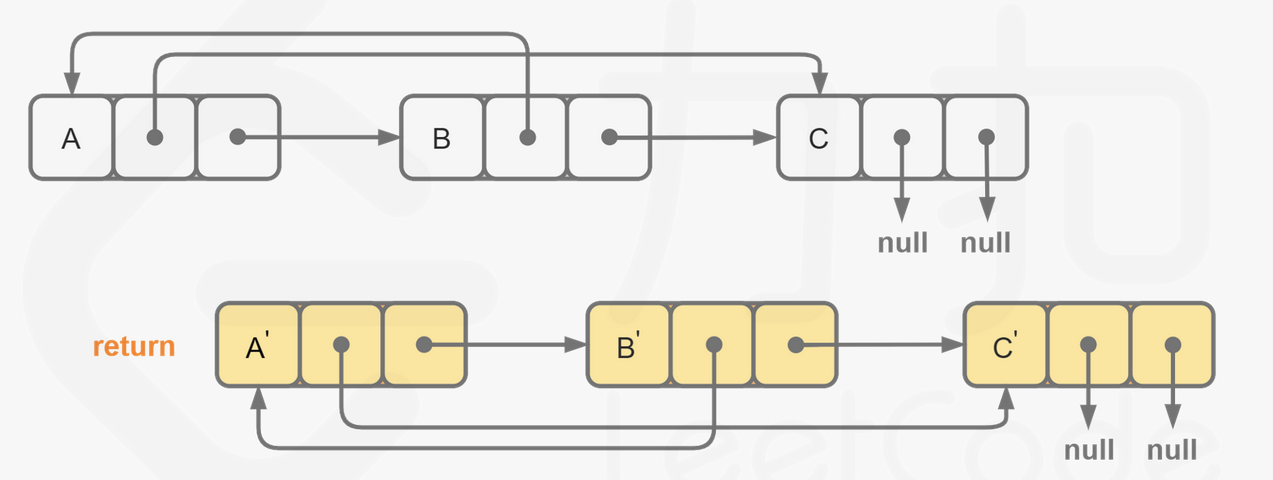
代码:
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next.next) {
Node nodeNew = new Node(node.val);
nodeNew.next = node.next;
node.next = nodeNew;
}
for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next.next) {
Node nodeNew = node.next;
nodeNew.random = (node.random != null) ? node.random.next : null;
}
Node headNew = head.next;
for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next) {
Node nodeNew = node.next;
node.next = node.next.next;
nodeNew.next = (nodeNew.next != null) ? nodeNew.next.next : null;
}
return headNew;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号