1,c++的编程模板
1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 6 { 7 cout << "1,hello world" << endl; 8 cout << "2,hello,world" << '\n'; 9 10 return 0; 11 }
2,c++输出标志-->cout
1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 6 { 7 cout << "hello" << ' ' << "world" << endl; 8 9 return 0; 10 }
3,c++输入标志-->cin
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 6 { 7 int a = 0; 8 char b = '\0'; 9 float c = 0; 10 char buf[128] = {'\0'}; 11 12 //数据给的先后:a -> b -> c -> buf 13 cin >> a >> b >> c >> buf; 14 cout << a << ' ' << b << ' ' << c << ' ' << buf << endl; 15 16 return 0; 17 }
4,c++布尔型-->bool
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> //string 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 7 { 8 bool sign = true; //数值上->1 9 bool flag = false; //数值上->0 10 cout << sizeof(bool) << ' ' << sign << ' ' << flag << endl; //1 1 0 11 12 sign = 18; 13 flag = -90; 14 cout << sign << ' ' << flag << ' ' << endl; //1 1 15 16 char c = 18; 17 cout << "c的数值:" << (int)c << endl; //18 18 cout << "c对应的ASC码:" << c << endl; 19 memcpy(&sign, &c, 1); 20 cout << "sign = " << sign << endl; //sign = 18 21 22 //布尔型是非负数,数据存储是以补码的形式保存 23 char c2 = -90; 24 // cout << "c2对应的ASC码:" << c2 << endl; //负数没有ASC码 25 cout << "c2的值:" << (int)c2 << endl; 26 memcpy(&flag, &c2, 1); 27 cout << "flag = " << flag << endl; //166 -90的补码 28 29 return 0; 30 }

5,c++字符串的拷贝、拼接
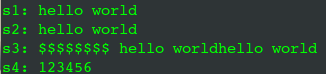
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 7 { 8 string s1 = "hello world"; 9 cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl; 10 11 string s2; 12 s2 = s1; //拷贝 13 cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl; 14 15 string s3 = "$$$$$$$$"; 16 s3 = s3 + ' ' + s2 + s1; //拼接 17 cout << "s3: " << s3 << endl; 18 19 //字符串拼接前两个必须有string对象 20 string s4 = ""; 21 /*错误示例 22 s4 = "123" + "456"; 23 cout << "s4: " << s4 << endl; 24 */ 25 s4 = s4 + "123" + "456"; 26 cout << "s4: " << s4 << endl; 27 28 return 0; 29 }
6,c++冒泡排序法实现字符串比较
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 7 { 8 string s1 = "hello world"; 9 string s2 = "1234"; 10 // if(s1 > s2) 11 // if(s1 >= s2) 12 // if(s1 < s2) 13 // if(s1 <= s2) 14 // if(s1 == s2) 15 // {} 16 17 string str[5] = {"apple","orange","banama","baa","cola"}; 18 //冒泡排序 19 int i = 0,j = 0; 20 string tmp; 21 for(;i<5-1;i++) 22 { 23 for(j=0; j<5-i-1; j++) 24 { 25 if(str[j] > str[j+1]) 26 { 27 tmp = str[j]; 28 str[j] = str[j+1]; 29 str[j+1] = tmp; 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 for(i=0; i<5; i++) 34 { 35 cout << str[i] << endl; 36 } 37 38 return 0; 39 }

7,c++字节数sizeof
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 /* 6 typedef struct Test 7 { 8 char *data; 9 }Test; 10 */ 11 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 12 { 13 //1 14 string str[5] = {"apple","orange","banama","baa","cola"}; 15 cout << sizeof(string) << ' ' << sizeof(str) << endl; //4 20 16 17 //2 18 string s = "12345678asdfghjk"; 19 cout << sizeof(s) << endl; //4 20 cout << s.length() << endl; //获得有效数据的大小 16 21 s.clear(); //清除数据,但是保留数据存储空间 22 cout << s.length() << endl; //0 23 /* 24 //3 25 Test t; //sizeof(t) 26 t->data = (char*)malloc(1024); //sizeof(t) 27 char *p = NULL; //sizeof(p) 28 char *p = (char *)malloc(1024); //sizeof(p) 29 sizeof(*p) = sizeof(char) -->1 30 */ 31 return 0; 32 }

8,c++初始化与赋值
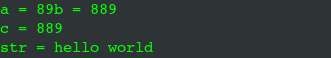
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 7 { 8 int a(90); //c++初始化 9 int b = 90; //c初始化 10 11 // a(998); //错误,二次初始化 12 a = 89; //c++赋值 13 b = 889; 14 cout << "a = " << a << "b = " << b << endl; 15 16 int c(b); //初始化 17 cout << "c = " << c << endl; 18 19 string str("hello world"); //c++初始化 20 cout << "str = " << str << endl; 21 22 return 0; 23 }
9,c++之for循环
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 7 { 8 int a[6] = {1,2,3,4,5,6}; 9 int i = 0; 10 for(int i=0; i<6; i++) 11 { 12 cout << a[i] << ' '; 13 } 14 cout << endl; 15 16 for(int i=0; i<6; i++) 17 { 18 a[i] += 10; 19 cout << a[i] << ' '; 20 } 21 cout << endl; //换行 22 23 return 0; 24 }

10,c++之结构体
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct STU 7 { 8 int iId; 9 string strName; 10 float fScore; 11 12 void info() //c++区别于c,c++可在结构体中定义函数 13 { 14 cout << iId << ' ' << strName << ' ' << fScore << endl; 15 } 16 }; 17 18 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 19 { 20 // struct STU s = {1001,"aaa",89}; //c语言用法 21 STU s = {1001,"aaa",99}; //c++用法 22 cout << s.iId << ' ' << s.strName << ' ' << s.fScore << endl; 23 24 STU s2 = {1002,"rose",100}; 25 // info(); //错误用法 26 s2.info(); 27 28 cout << sizeof(STU) << ' ' << sizeof(s2) << endl; //32位机 29 30 return 0; 31 }

11,c++之构造函数
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct STU 7 { 8 int iId; 9 string strName; 10 float fScore; 11 12 //构造函数:在对象产生的时候自动调用 13 STU(int id,string name,float score) //函数名和结构体名一致 14 { 15 iId = id; 16 strName = name; 17 fScore = score; 18 cout << "STU be called" << endl; 19 } 20 21 void info() //c++区别于c,c++可在结构体中定义函数 22 { 23 cout << iId << ' ' << strName << ' ' << fScore << endl; 24 } 25 }; 26 27 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 28 { 29 //自动调用构造函数对成员赋值 30 STU s(1001,"jack",89); 31 s.info(); 32 33 return 0; 34 }

12,c++之动态申请空间
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 7 { 8 // int *p = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)); //c语言申请动态空间 free(p); 9 // int *p = new int; //c++动态申请空间 delete p; 10 11 int *p = new int(1998); // --> delete p; 12 cout << *p << endl; //1998 13 delete p; 14 cout << *p << endl; 15 16 // int *p2 = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*10); //c语言用法 free(p2); 17 int *p2 = new int[10]; //c++用法(存放10个整数的空间) delete []p2; 18 int *p3 = new int[1]; // --> delete []p3; 19 20 return 0; 21 }

13,c++之结构体指针
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct STU 7 { 8 int iId; 9 string strName; 10 float fScore; 11 12 //构造函数:在对象产生的时候自动调用 13 STU(int id,string name,float score) //函数名和结构体名一致 14 { 15 iId = id; 16 strName = name; 17 fScore = score; 18 cout << "STU be called" << endl; 19 } 20 21 void info() //c++区别于c,c++可在结构体中定义函数 22 { 23 cout << iId <<' ' << strName << ' ' << fScore << endl; 24 } 25 }; 26 27 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 28 { 29 // STU *s = (STU *)malloc(sizeof(STU)); 30 //产生对象的同时,调用构造函数对对象赋值 31 STU *s = new STU(1001,"jack",100); 32 s->info(); 33 34 return 0; 35 }

14,c++之npc
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct NPC 7 { 8 string strName; 9 int iBlood; 10 int iAttack; 11 string strSkill; 12 13 //构造函数:在对象产生的时候自动调用 14 NPC(string name,int blood,string skill,int attack) //函数名和结构体名一致 15 { 16 strName = name; 17 iBlood = blood; 18 iAttack = attack; 19 strSkill = skill; 20 } 21 22 void info() //c++区别于c,c++可在结构体中定义函数 23 { 24 cout << "人物:" << strName << " 血量:" << iBlood << " 技能:" << strSkill << " 攻击力:" << iAttack << endl; 25 } 26 }; 27 28 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 29 { 30 NPC *npc[3] = {NULL}; //产生指针数组 31 string strName=""; 32 int iBlood = 0; 33 string strSkill = ""; 34 int iAttack = 0; 35 36 for(int i=0;i<3;i++) 37 { 38 cout << "请输入游戏任务的名字,血量值,技能,攻击值\n"; 39 cin >> strName >> iBlood >> strSkill >> iAttack; 40 npc[i] = new NPC(strName,iBlood,strSkill,iAttack); 41 } 42 for(int i=0;i<3;i++) 43 { 44 npc[i]->info(); 45 } 46 47 return 0; 48 }
15,c++之数组指针重命名
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 //数组指针重命名 8 typedef int(*PP)[5]; 9 10 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 11 { 12 //int a[4][5]; --> (int[5]) a[4] //a+1 --> 5*sizeof(int) 13 void *p = malloc(sizeof(int)*4*5); 14 int (*p2)[5] = (PP)p; 15 16 int data=0; 17 for(int i=0; i<4; i++) 18 { 19 for(int j=0; j<5; j++) 20 { 21 p2[i][j] = data; 22 data++; 23 } 24 } 25 26 for(int i=0; i<4; i++) 27 { 28 for(int j=0; j<5; j++) 29 { 30 cout << p2[i][j] << ' '; 31 } 32 cout << endl; 33 } 34 35 return 0; 36 }

16,c++之数组动态申请空间
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 8 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 9 { 10 //int a[4][5]; //a+1 --> 5*sizeof(int) 11 //int(*p)[5] --> a 12 13 //int b[2][3][4]; 14 //int (*p)[3][4] --> b 15 16 int (*p)[5] = new int[4][5]; 17 18 int data=0; 19 for(int i=0; i<4; i++) 20 { 21 for(int j=0; j<5; j++) 22 { 23 p[i][j] = data; 24 data++; 25 } 26 } 27 for(int i=0; i<4; i++) 28 { 29 for(int j=0; j<5; j++) 30 { 31 cout << p[i][j] << ' '; 32 } 33 cout << endl; 34 } 35 36 return 0; 37 }

17,c++之多维数组动态申请空间
1 #include <iostream> //输入输出流 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 8 { 9 //int a[2][3][4][5]; // a+1 --> sizeof(int)*3*4*5; 10 //int[3][4][5] a[2]; 11 //a --> int (*p)[3][4][5] 12 int (*p)[3][4][5] = new int[2][3][4][5]; 13 14 return 0; 15 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号