NIO网络编程原理与实战
一.NIO网络编程模型
1.NIO简介
Non-blocking I/O或New I/O,JDK1.4版本开始有,高并发网络服务器支持。
2.编程模型
模型:对事物共性的抽象
编程模型:对编程共性的抽象
3.BIO网络模型
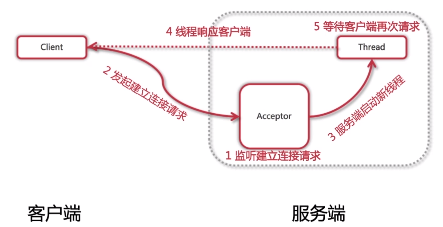
BIO模型的缺点:在大量并发的情况下,接入客户端过多,出现问题。
4.BIO网络模型缺点
阻塞式I/O模型、弹性伸缩能力差、多线程耗资源。
5.NIO网络模型猜想
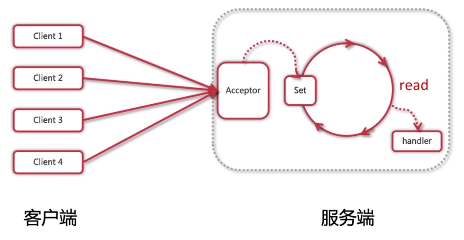
6.NIO网络模型
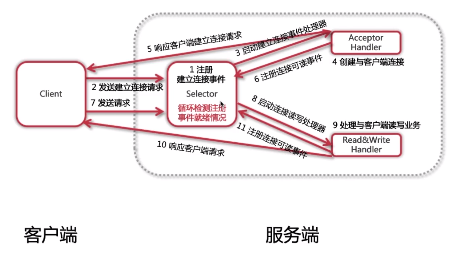
7.NIO网络模型改进
非阻塞式I/O模型、弹性伸缩能力强、单线程节省资源(因为服务端只有一个线程,线程的频繁创建与销毁、线程上下文之间的切换这两个问题都解决了)。
二.NIO网络编程详解
Channel:通道;Buffer:缓冲区;Selector:选择器或多路复用器
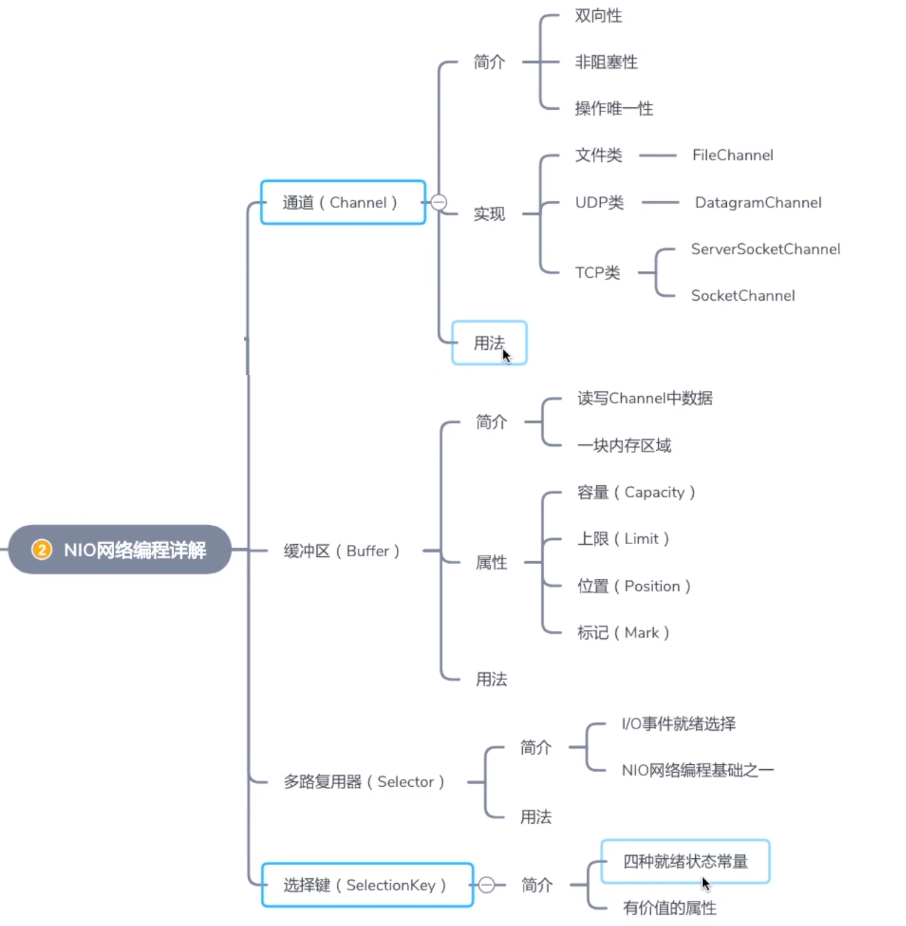
1.NIO核心类之Channel
1).Channel简介
a.双向性
对信息传输的通道,JDK NIO中对输入、输出方式的另一种抽象,可以类比BIO中的流的概念,但与流不同的是,流是单向传输,有InputStream、OutStream之分,而通道支持双向传输,一个Channel既可读又可写。
b.非阻塞性
Channel可以工作在非阻塞模式下,也正是这个特点,构成了NIO网络编程的基础。
c.操作唯一性
NIO中操作Channel的唯一方式是使用Buffer,通过Buffer操作Channel实现数据块的读写。
2).Channel实现
文件类:FileChannel,对文件处理读写的
UDP类:DatagramChannel,UDP的数据读写
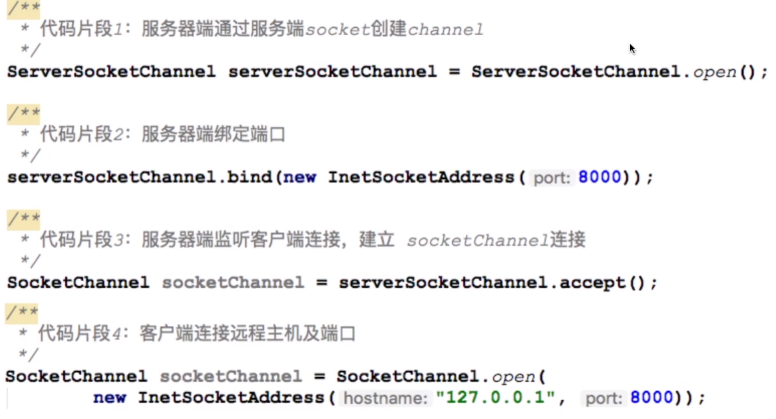
TCP类:ServerSocketChannel/SocketChannel,基于TCP类的数据的读写
3).Socket回顾
服务端:

客户端:
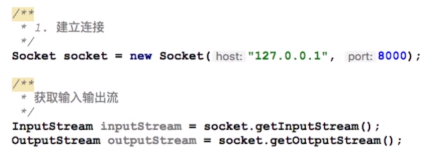
4).Channel使用
2.NIO核心类之Buffer
1).Buffer简介
Buffer是NIO API中新加入的类,提示唯一与Channel进行交互的方式,通过Buffer可以从Buffer中读取数据或者将数据写入到Buffer中。
作用:读写Channel中数据
本质:一块内存区域,是一块可以写入数据,也可以从中读取数据的内存,这块内存被NIO包装也了NIOBuffer对象,并提供了一组方法,用于方便操作这块内存。
2).Buffer属性
四个核心属性。
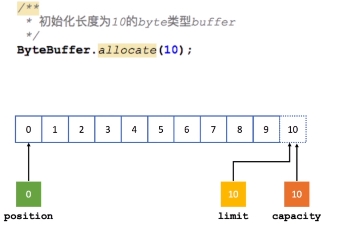
Capacity:容量。作用是标明数组最大可以容纳多少字节,一旦写入的字节数超过最大容量,需要将其清空后才能继续往里写入数据。
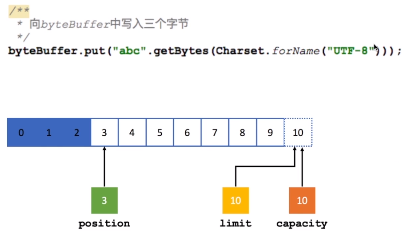
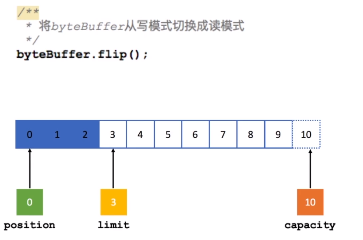
Position:位置。当你写数据时,Position表示当前的位置,初始的Position为0,当一个byte写入到Buffer后,Position会向后移动到下一个可播入数据的Buffer单元,Position最大可为Capacity-1,相当于这个数组的下标最大值。当读取数据时,Buffer会从写模式切换到写模式,这个就是Buffer完成读写切换的模式,此时Position会被重置为0,当从Buffer的Position处读取数据时,Position会向后移动到下一个可读的位置。
Limit:上限。在写模式下,Buffer的Limit表示最多能往Buffer中写多少数据,此模式下,Limit等于Position。当切换到读模式时,Limit表示最多能从Buffer中读取多少数据,此时,Limit会被设置成写模式下的Position值。
Mark:标记。Mark存储一个特定的Position位置,之后可以通过调用Buffer的reset方法,可以恢复到这个Position位置,依然可以从这个位置处理数据。
3).Buffer使用
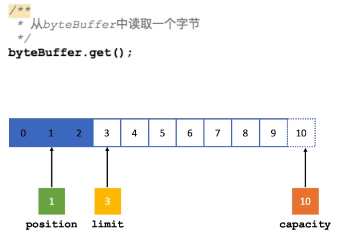
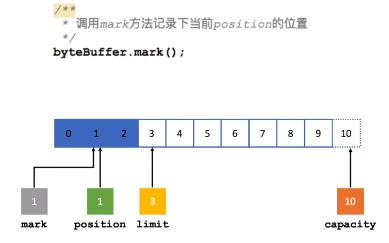
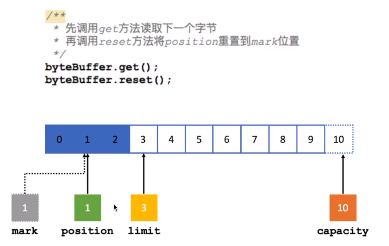
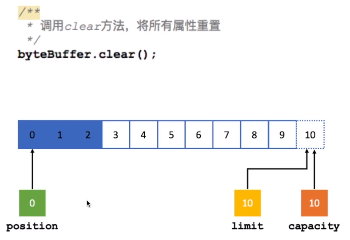
另外,NIO为Buffer类提供了很多基础实现类,基本类型中除了Boolean类型外,其余所有类型都对应有Buffer类型的实现。但在网络编程中,使用最多的还是基于字节的ByteBuffer类。
3.NIO核心类之Selector
1).Selector简介
Selector叫选择器,或者叫多路复用器,它是NIO网络编程的基础。
作用:I/O就绪选择
地位:NIO网络编程的基础
在这里需重点强调一下:整个NIO网络编程,就是构建在非阻塞IO和Selector多路复用器之上的。Selector是Java NIO中能够检测1到多个NIO通道并能够知晓通道是否为注入读写事件做好准备的组件,通过它,一个单独的线程就可以管理多个Channel,从而管理多个网络连接。
2).Selector使用

代码片段3的selector.select()方法,此方法内部根据不同操作系统底层针对IO的支持来实现的,目的就是检测注册到selector对象上的Channel,希望监听的事件是否已就绪,如果存在已就绪的,就会返回已就绪Channel个数,如果没有,就会一直阻塞。
3).SelectionKey简介
四种就绪状态常量,分别是CONNECT连接就绪,ACCEPT接收就绪,READ读就绪,WRITE写就绪,再调用selector.selectedKeys方法时,会返回一个SelectionKey的集合,可以通过selectKeys集合获取到当前的Channel,获取Selector对象,获取该Channel已就绪事件集合和所关心事件集合,这就是SelectionKey对象一些有价值的属性。
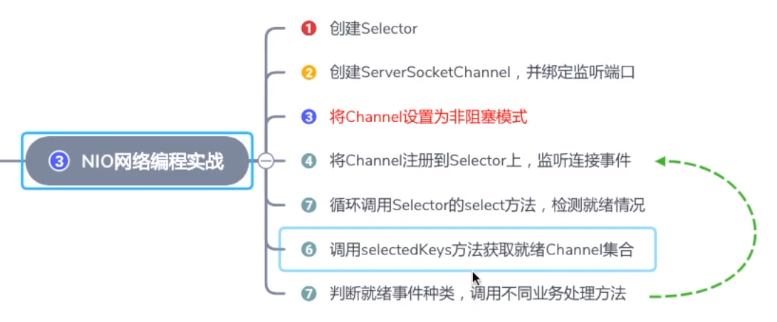
4.NIO编程实现步骤
第一步:创建Selector
第二步:创建ServerSocketChannel,并绑定监听端口
第三步:将Channel设置为非阻塞模式
第四步:将Channel注册到Selector上,监听连接事件
第五步:循环调用Selector的select方法,检测就绪情况
第六步:调用selectedKeys方法获取就绪channel集合
第七步:判断就绪事件种类,调用业务处理方法
第八步:根据业务需要决定是否再次注册监听事件,重复执行第三步操作
三.NIO网络编程实战
利用NIO编程知识,实现多人聊天室。
NioServer.java
package com.bijian; import com.sun.security.ntlm.Server; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.*; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; /** * NIO服务器端 */ public class NioServer { /** * 启动服务器端方法 */ public void start() throws IOException { /** * 1.创建Selector */ Selector selector = Selector.open(); /** * 2.通过ServerSocketChannel创建channel通道 */ ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); /** * 3.为channel通道绑定监听端口 */ serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8000)); /** * 4.设置channel为非阻塞模式 */ serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); /** * 5.将channel注册到selector上,监听连接事件 */ serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); System.out.println("服务器启动成功!"); /** * 6.循环等待新接入的连接 */ for(;;) { /** * 获取可用channel数量 */ int readyChannels = selector.select(); /** * 为什么要这样? */ if(readyChannels == 0) continue; /** * 获取可用channel的集合 */ Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator iterator = selectionKeys.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { /** * selectionKey实例 */ SelectionKey selectionKey = (SelectionKey)iterator.next(); /** * 移除Set中的当前selectionKey,这是重点 */ iterator.remove(); /** * 7.根据就绪状态,调用对应方法处理业务逻辑 */ /** * 如果是接入事件 */ if(selectionKey.isAcceptable()) { acceptHandler(serverSocketChannel, selector); } /** * 如果是可读事件 */ if(selectionKey.isReadable()) { readHandler(selectionKey, selector); } } } } /** * 接入事件处理器 */ private void acceptHandler(ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel, Selector selector) throws IOException { /** * 如果要是接入事件,创建socketChannel */ SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); /** * 将socketChannel设置为非阻塞工作模式 */ socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); /** * 将channel注册到selector上,监听可读事件 */ socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); /** * 回复客户端提示信息 */ socketChannel.write(Charset.forName("UTF-8").encode("你与聊天室里其他人都不是朋友关系,请注意隐私安全")); } /** * 可读事件处理器 */ private void readHandler(SelectionKey selectionKey, Selector selector) throws IOException { /** * 要从selectionKey中获取到已经就绪的channel */ SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); /** * 创建buffer */ ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); /** * 循环读取客户端请求信息 */ String request = ""; while(socketChannel.read(byteBuffer) > 0) { /** * 切换buffer为读模式 */ byteBuffer.flip(); /** * 读取buffer中的内容 */ request += Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(byteBuffer); } /** * 将channel再次注册到selector上,监听他的可读事件 */ socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); /** * 将客户端发送的请求信息,广播给其他客户端 */ if(request.length() > 0) { //广播给其他客户端 System.out.println("::" + request); broadCast(selector, socketChannel, request); } } /** * 广播给其他客户端 */ private void broadCast(Selector selector, final SocketChannel sourceChannel, final String request) { /** * 获取到所有已接入的客户端channel */ Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeySet = selector.keys(); /** * 循环向所有channel广播信息 */ selectionKeySet.forEach(selectionKey -> { Channel targetChannel = selectionKey.channel(); //剔除发消息的客户端 if(targetChannel instanceof SocketChannel && targetChannel != sourceChannel) { try { //将信息发送到targetChannel客户端 ((SocketChannel) targetChannel).write(Charset.forName("UTF-8").encode(request)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); } /** * 主方法 * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { NioServer nioServer = new NioServer(); nioServer.start(); } }
NioClient.java
package com.bijian; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.Scanner; /** * NIO客户端 */ public class NioClient { /** * 启动 */ void start(String nickName) throws IOException { /** * 连接服务器端 */ SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8000)); /** * 接收服务器端响应 */ //新开线程,专门负责来接收服务器端的响应数据 Selector selector = Selector.open(); socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); new Thread(new NioClientHandler(selector)).start(); /** * 向服务器端发送数据 */ Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while(scanner.hasNextLine()) { String request = scanner.nextLine(); if(request != null && request.length() > 0) { socketChannel.write(Charset.forName("UTF-8").encode(nickName + " : " + request)); } } } }
NioClientHandler.java
package com.bijian; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; /** * 客户端线程类,专门接收服务器端响应信息 */ public class NioClientHandler implements Runnable{ private Selector selector; public NioClientHandler(Selector selector) { this.selector = selector; } @Override public void run() { try { for (; ; ) { int readyChannels = selector.select(); if (readyChannels == 0) continue; /** * 获取可用channel的集合 */ Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator iterator = selectionKeys.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { /** * selectionKey实例 */ SelectionKey selectionKey = (SelectionKey) iterator.next(); /** * 移除Set中的当前selectionKey,这是重点 */ iterator.remove(); /** * 根据就绪状态,调用对应方法处理业务逻辑 */ /** * 如果是可读事件 */ if (selectionKey.isReadable()) { readHandler(selectionKey, selector); } } } }catch(IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 可读事件处理器 */ private void readHandler(SelectionKey selectionKey, Selector selector) throws IOException { /** * 要从selectionKey中获取到已经就绪的channel */ SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); /** * 创建buffer */ ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); /** * 循环读取服务器端响应信息 */ String response = ""; while(socketChannel.read(byteBuffer) > 0) { /** * 切换buffer为读模式 */ byteBuffer.flip(); /** * 读取buffer中的内容 */ response += Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(byteBuffer); } /** * 将channel再次注册到selector上,监听他的可读事件 */ socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); /** * 将服务器端响应信息打印到本地 */ if(response.length() > 0) { System.out.println(response); } } }
AClient.java
package com.bijian; import java.io.IOException; public class AClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { new NioClient().start("AClient"); } }
BClient.java
package com.bijian; import java.io.IOException; public class BClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { new NioClient().start("BClient"); } }
CClient.java
package com.bijian; import java.io.IOException; public class CClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { new NioClient().start("CClient"); } }
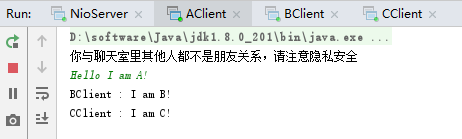
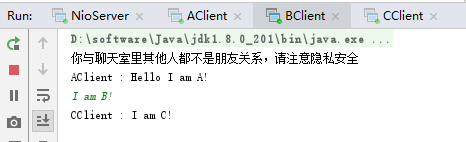
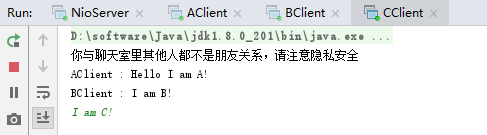
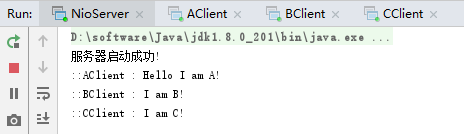
先后启动NioServer.java、AClient.java、BClient.java、CClient.java,测试效果如下:
四.NIO网络编程缺陷
麻烦:NIO类库和API繁杂
心累:可靠性能力补齐,工作量和难度都非常大
有坑:Selector空轮询,导致CPU100%。原生NIO有一个BUG,一直都没有改好,就是比较著名的epoll BUG,主要出现在类Linux系统上,问题是这样的:根据API规定,如果在调用selector的select方法时,如果没有准备就绪的channel,它应该阻塞在selector调用上,但Linux下的selector使用的是epoll IO事件通知工具,操作系统使用这一高性能的技术,与网络协议栈异步工作,从而导致就算没有准备就绪的channel,select方法也不会阻塞,最终造成CPU利用率100%现象。这个问题官方声称在JDK1.6版本的修复补丁里已经修复,但实际证明该问题在JDK1.8仍然存在,只不过发生的概率低了一些而已。如果程序需要兼容不同的操作系统、不同的环境,需要小心。
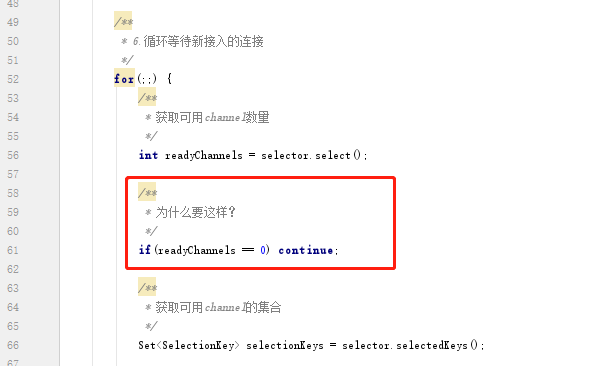
如上代码就是为了防止它的空轮询【当然,如果仅仅是continue这样做的话,还是会导致CPU 100%】。
五.课程总结

posted on 2019-06-16 21:32 bijian1013 阅读(1124) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号