实验2
实验任务1:
1.源代码

1 #include "T.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string> 4 const std::string T::doc{"a simple class sample"}; 5 const int T::max_cnt = 999; 6 int T::cnt = 0; 7 int T::get_cnt() { 8 return cnt; 9 } 10 11 T::T(int x, int y): m1{x}, m2{y} { 12 ++cnt; 13 std::cout << "T constructor called.\n"; 14 } 15 T::T(const T &t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { 16 ++cnt; 17 std::cout << "T copy constructor called.\n"; 18 } 19 T::T(T &&t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { 20 ++cnt; 21 std::cout << "T move constructor called.\n"; 22 } 23 T::~T() {--cnt; 24 std::cout << "T destructor called.\n"; 25 } 26 void T::adjust(int ratio) { 27 m1 *= ratio; 28 m2 *= ratio; 29 } 30 void T::display() const { 31 std::cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")" ; 32 } 33 34 void func() { 35 T t5(42); 36 t5.m2 = 2049; 37 std::cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); std::cout << '\n'; 38 }

1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <string> 4 5 6 class T { 7 8 public: 9 T(int x = 0, int y = 0); 10 T(const T &t); 11 T(T &&t); 12 ~T(); 13 14 void adjust(int ratio); 15 void display() const; 16 17 private: 18 int m1, m2; 19 20 21 public: 22 static int get_cnt(); 23 24 public: 25 static const std::string doc; 26 static const int max_cnt; 27 28 private: 29 static int cnt; 30 31 32 friend void func(); 33 }; 34 35 36 void func();

1 #include "T.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 void test_T(); 5 6 int main() { 7 std::cout << "test Class T: \n"; 8 test_T(); 9 10 std::cout << "\ntest friend func: \n"; 11 func(); 12 } 13 14 void test_T() { 15 using std::cout; 16 using std::endl; 17 18 cout << "T info: " << T::doc << endl; 19 cout << "T objects'max count: " << T::max_cnt << endl; 20 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl << endl; 21 22 T t1; 23 cout << "t1 = "; t1.display(); cout << endl; 24 25 T t2(3, 4); 26 cout << "t2 = "; t2.display(); cout << endl; 27 28 T t3(t2); 29 t3.adjust(2); 30 cout << "t3 = "; t3.display(); cout << endl; 31 32 T t4(std::move(t2)); 33 cout << "t4 = "; t4.display(); cout << endl; 34 35 cout << "test: T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl; 36 }
2.运行结果截图
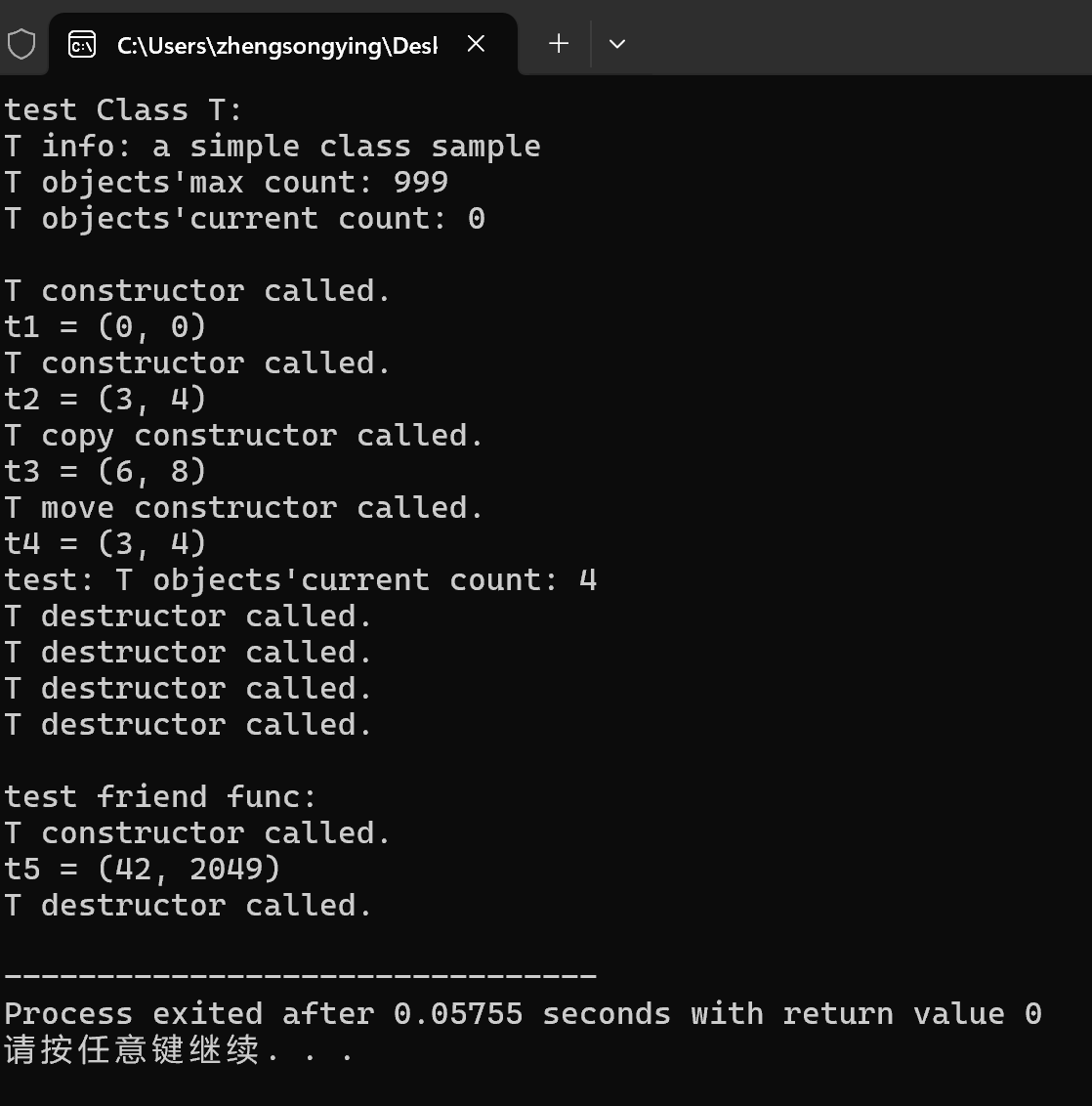
3.问题:
1.No 在作用域内未声明func函数, 因为 func() 是类外定义的友元函数,必须先声明.
![]()
2.普通构造函数的功能是为对象分配内存且为成员赋初值
调用时机:当创建一个新的 T 类对象,并显式提供整型参数时,会调用普通构造函数
复制构造函数的功能是拷贝构造函数,其形参是本类对象的引用
调用时机:用已经存在的对象初始化一个新对象时,复制构造函数会被调用
移动构造函数的功能是将资源从一个对象转移到另一个对象
调用时机:用一个右值初始化对象时会调用移动构造函数
析构函数的作用是释放对象所占的内存及完成相关的“清理”工作
调用时机:在对象生存期结束时由编译器自动调用
3.不能,静态成员变量必须在类外单独定义初始化,否则链接失败。
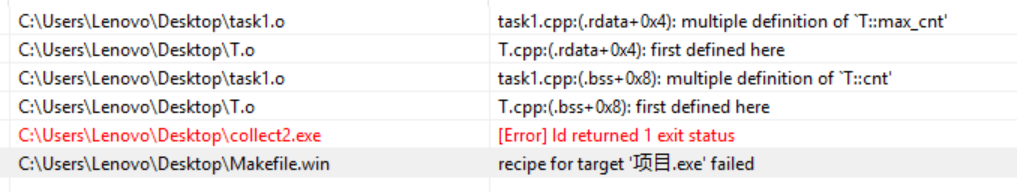
实验任务2:
1.源代码

1 #include "Complex.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cmath> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const string Complex::doc = "a simplified complex class"; 8 9 Complex::Complex() : real_(0.0), imag_(0.0) {} 10 11 Complex::Complex(double real) : real_(real), imag_(0.0) {} 12 13 Complex::Complex(double real, double imag) : real_(real), imag_(imag) {} 14 15 Complex::Complex(const Complex& other) : real_(other.real_), imag_(other.imag_) {} 16 17 double Complex::get_real() const { 18 return real_; 19 } 20 21 double Complex::get_imag() const { 22 return imag_; 23 } 24 25 void Complex::add(const Complex& other) { 26 real_ += other.real_; 27 imag_ += other.imag_; 28 } 29 30 void output(const Complex& c) { 31 cout << c.real_; 32 if (c.imag_ >= 0) { 33 cout << " + " << c.imag_ << "i"; 34 } else { 35 cout << " - " << -c.imag_ << "i"; 36 } 37 } 38 39 double abs(const Complex& c) { 40 return sqrt(c.real_ * c.real_ + c.imag_ * c.imag_); 41 } 42 43 Complex add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) { 44 return Complex(c1.real_ + c2.real_, c1.imag_ + c2.imag_); 45 } 46 47 bool is_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) { 48 return (c1.real_ == c2.real_) && (c1.imag_ == c2.imag_); 49 } 50 51 bool is_not_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) { 52 return !is_equal(c1, c2); 53 }

1 #ifndef COMPLEX_H 2 #define COMPLEX_H 3 4 #include <string> 5 6 class Complex { 7 public: 8 static const std::string doc; 9 10 Complex(); 11 Complex(double real); 12 Complex(double real, double imag); 13 Complex(const Complex& other); 14 double get_real() const; 15 double get_imag() const; 16 void add(const Complex& other); 17 18 friend void output(const Complex& c); 19 friend double abs(const Complex& c); 20 friend Complex add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); 21 friend bool is_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); 22 friend bool is_not_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); 23 24 private: 25 double real_; 26 double imag_; 27 }; 28 29 void output(const Complex& c); 30 double abs(const Complex& c); 31 Complex add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); 32 bool is_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); 33 bool is_not_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2); 34 35 #endif

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <iomanip> 3 #include <complex> 4 #include"Complex.h" 5 void test_Complex(); 6 void test_std_complex(); 7 int main() { 8 std::cout << "*******测试1: 自定义类Complex*******\n"; 9 test_Complex(); 10 std::cout << "\n*******测试2: 标准库模板类complex*******\n"; 11 test_std_complex(); 12 } 13 void test_Complex() { 14 using std::cout; 15 using std::endl; 16 using std::boolalpha; 17 cout << "类成员测试: " << endl; 18 cout << Complex::doc << endl << endl; 19 cout << "Complex对象测试: " << endl; 20 Complex c1; 21 Complex c2(3, -4); 22 Complex c3(c2); 23 Complex c4 = c2; 24 const Complex c5(3.5); 25 26 cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 27 cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl; 28 cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl; 29 cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 30 cout << "c5.real = " << c5.get_real() 31 << ", c5.imag = " << c5.get_imag() << endl << endl; 32 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 33 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 34 c1.add(c2); 35 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 36 cout << boolalpha; 37 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl; 38 cout << "c1 != c2 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c2) << endl; 39 c4 = add(c2, c3); 40 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 41 } 42 void test_std_complex() { 43 using std::cout; 44 using std::endl; 45 using std::boolalpha; 46 cout << "std::complex<double>对象测试: " << endl; 47 std::complex<double> c1; 48 std::complex<double> c2(3, -4); 49 std::complex<double> c3(c2); 50 std::complex<double> c4 = c2; 51 const std::complex<double> c5(3.5); 52 cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl; 53 cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl; 54 cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl; 55 cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl; 56 cout << "c5.real = " << c5.real() 57 << ", c5.imag = " << c5.imag() << endl << endl; 58 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 59 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 60 c1 += c2; 61 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl; 62 cout << boolalpha; 63 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2)<< endl; 64 cout << "c1 != c2 : " << (c1 != c2) << endl; 65 c4 = c2 + c3; 66 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl; 67 }
2.运行结果截图
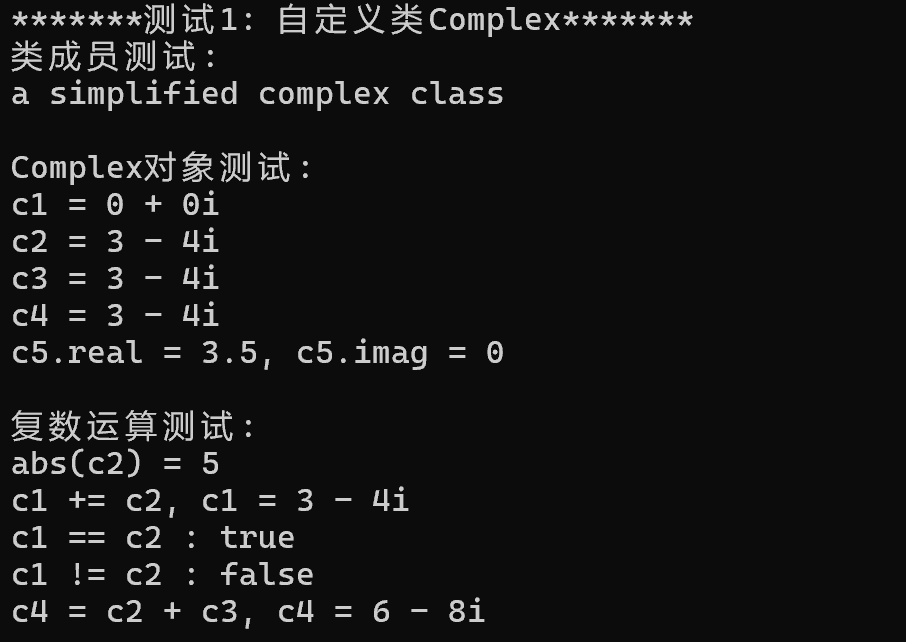
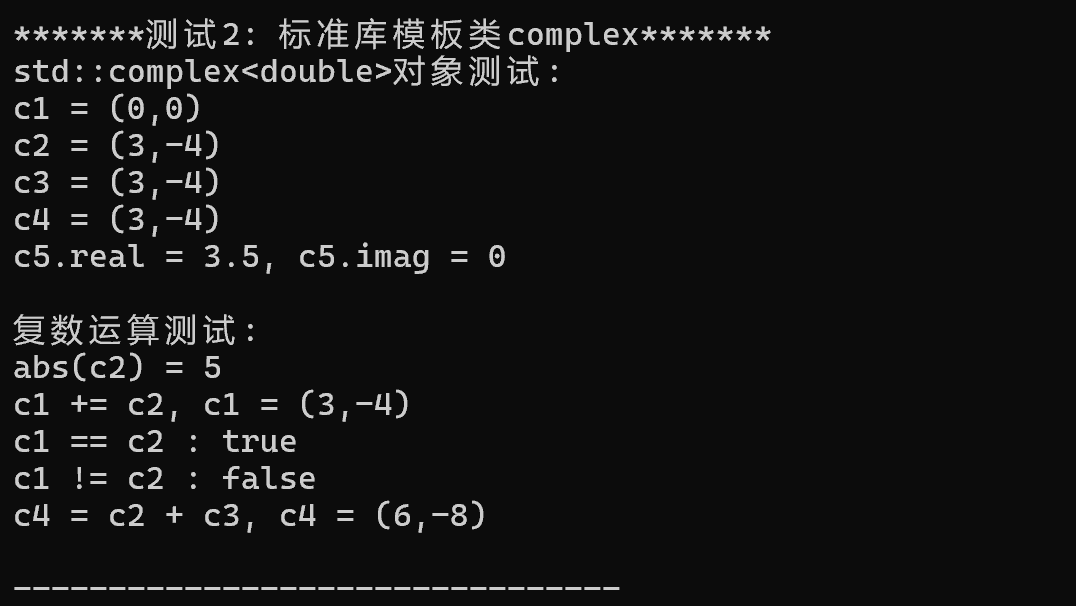
3.问题:
1.标准库模板类complex的使用形式更简洁
有关联,这两种不同的实现方式在数学运算方面本质上是相同的,只是接口设计不同。比如复数的加法这一运算中,都是执行实部+实部,虚部+虚部;又比如比较复数是否相等都是比较实部和虚部是否分别相等。
2.1 是,理由如下:
output 函数需要直接访问 real_ 和 imag_ 来格式化输出复数
abs 函数需要访问 real_ 和 imag_ 来计算模长
add 函数需要访问两个操作数的 real_ 和 imag_ 来执行加法运算
2.2 否,std::abs(std::complex) 是一个非成员函数,它通过公有成员函数 real() 和 imag() 来访问复数的实部和虚部,不需要友元关系。
2.3 当访问私有成员的非成员函数时或者当一个类私有成员需要频繁访问另一个类的私有成员时可以考虑使用friend,但我觉得应该尽量少用友元,因为它破坏了封装性。
3.调整方法:将拷贝函数声明为explicit,禁止编译器的拷贝初始化
实验任务3:
1.源代码

1 #include "PlayerControl.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 int PlayerControl::total_cnt = 0; 5 PlayerControl::PlayerControl() {} 6 7 std::string to_lower(const std::string& str) { 8 std::string result; 9 for (char c : str) { 10 result += std::tolower(static_cast<unsigned char>(c)); 11 } 12 return result; 13 } 14 15 ControlType PlayerControl::parse(const std::string& control_str) { 16 std::string lower_str = to_lower(control_str); 17 ControlType result = ControlType::Unknown; 18 if (lower_str == "play") { 19 result = ControlType::Play; 20 } else if (lower_str == "pause") { 21 result = ControlType::Pause; 22 } else if (lower_str == "next") { 23 result = ControlType::Next; 24 } else if (lower_str == "prev") { 25 result = ControlType::Prev; 26 } else if (lower_str == "stop") { 27 result = ControlType::Stop; 28 } 29 if (result != ControlType::Unknown) { 30 total_cnt++; 31 } 32 33 return result; 34 } 35 36 void PlayerControl::execute(ControlType cmd) const { 37 switch (cmd) { 38 case ControlType::Play: std::cout << "[play] Playing music...\n"; break; 39 case ControlType::Pause: std::cout << "[Pause] Music paused\n"; break; 40 case ControlType::Next: std::cout << "[Next] Skipping to next track\n"; break; 41 case ControlType::Prev: std::cout << "[Prev] Back to previous track\n"; break; 42 case ControlType::Stop: std::cout << "[Stop] Music stopped\n"; break; 43 default: std::cout << "[Error] unknown control\n"; break; 44 } 45 } 46 int PlayerControl::get_cnt() { 47 return total_cnt; 48 }

1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 enum class ControlType {Play, Pause, Next, Prev, Stop, Unknown}; 4 class PlayerControl { 5 public: 6 PlayerControl(); 7 8 static int get_cnt(); 9 ControlType parse(const std::string& control_str); 10 void execute(ControlType cmd) const; 11 private: 12 static int total_cnt; 13 };

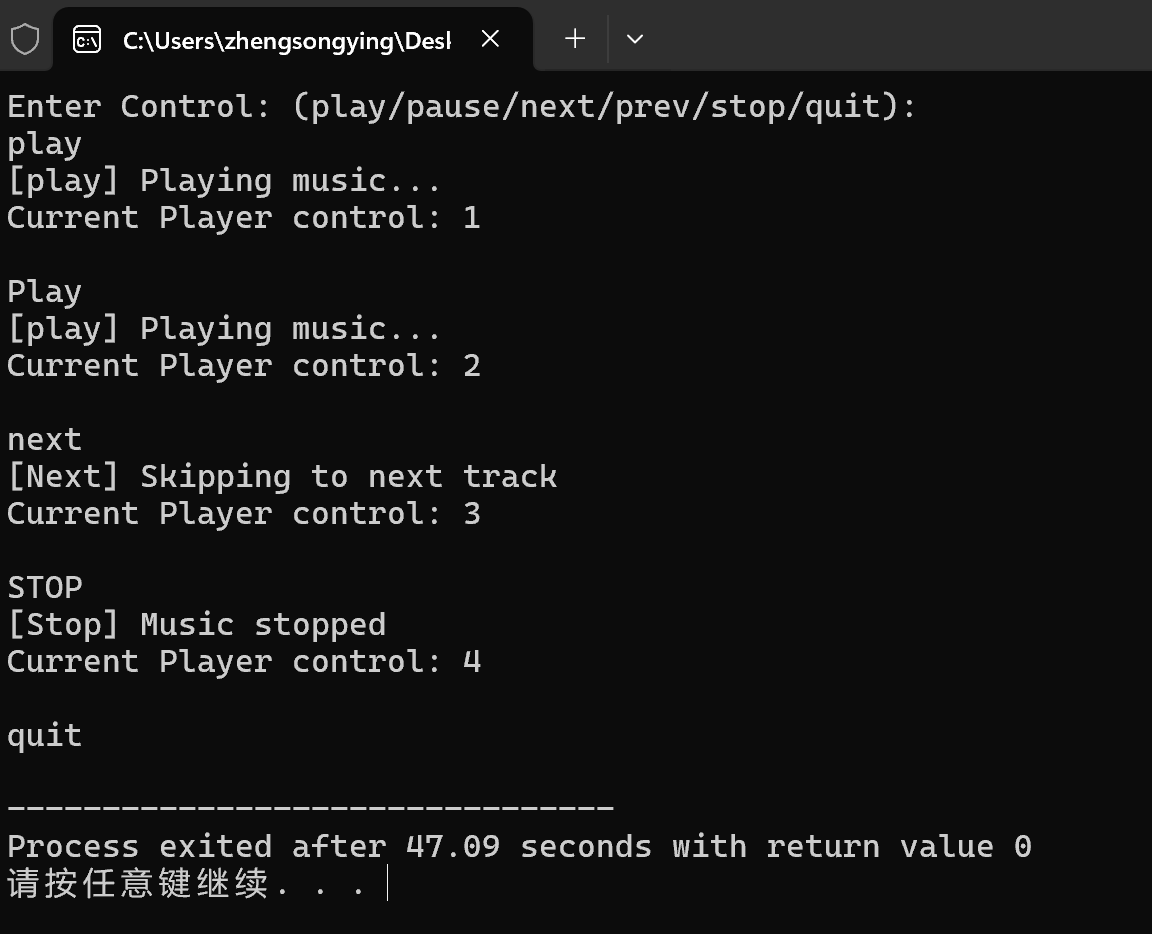
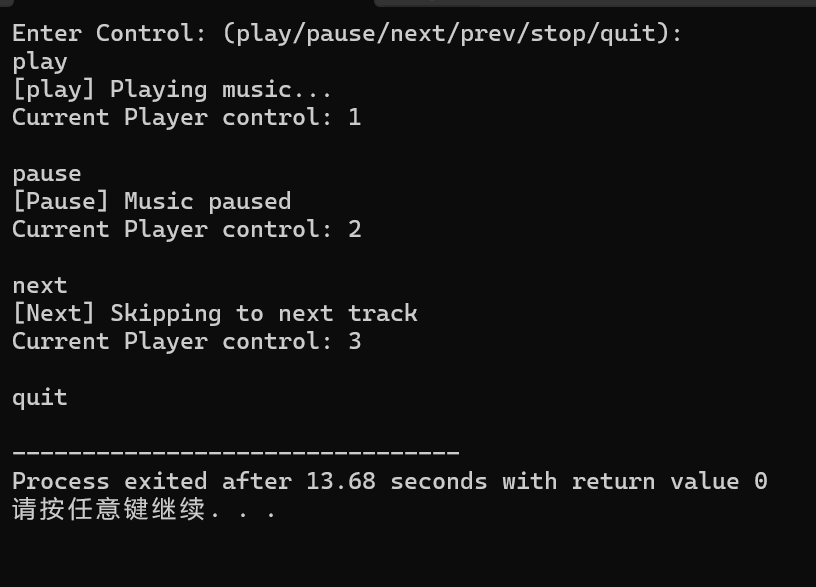
1 #include "PlayerControl.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 void test() { 4 PlayerControl controller; 5 std::string control_str; 6 std::cout << "Enter Control: (play/pause/next/prev/stop/quit):\n"; 7 while(std::cin >> control_str) { 8 if(control_str == "quit") 9 break; 10 11 ControlType cmd = controller.parse(control_str); 12 controller.execute(cmd); 13 std::cout << "Current Player control: " << PlayerControl::get_cnt() << "\n\n"; 14 } 15 16 } 17 int main() { 18 test(); 19 }
2.运行结果截图
3.思考
源代码:

1 #include "PlayerControl.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 int PlayerControl::total_cnt = 0; 5 PlayerControl::PlayerControl() {} 6 7 std::string to_lower(const std::string& str) { 8 std::string result; 9 for (char c : str) { 10 result += std::tolower(static_cast<unsigned char>(c)); 11 } 12 return result; 13 } 14 15 ControlType PlayerControl::parse(const std::string& control_str) { 16 std::string lower_str = to_lower(control_str); 17 ControlType result = ControlType::Unknown; 18 if (lower_str == "play") { 19 result = ControlType::Play; 20 } else if (lower_str == "pause") { 21 result = ControlType::Pause; 22 } else if (lower_str == "next") { 23 result = ControlType::Next; 24 } else if (lower_str == "prev") { 25 result = ControlType::Prev; 26 } else if (lower_str == "stop") { 27 result = ControlType::Stop; 28 } 29 if (result != ControlType::Unknown) { 30 total_cnt++; 31 } 32 33 return result; 34 } 35 36 void PlayerControl::execute(ControlType cmd) const { 37 switch (cmd) { 38 case ControlType::Play: std::cout << "[play] Playing music...\n"; break; 39 case ControlType::Pause: std::cout << "[Pause] Music paused\n"; break; 40 case ControlType::Next: std::cout << "[Next] Skipping to next track\n"; break; 41 case ControlType::Prev: std::cout << "[Prev] Back to previous track\n"; break; 42 case ControlType::Stop: std::cout << "[Stop] Music stopped\n"; break; 43 default: std::cout << "[Error] unknown control\n"; break; 44 } 45 } 46 int PlayerControl::get_cnt() { 47 return total_cnt; 48 }
由于电脑系统原因我无法把emoji插入所以用[play][pause]等替代
运行结果截图
实验任务4:
1.源代码

1 #include "Fraction.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <stdexcept> 4 #include <cmath> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 const string Fraction::doc = "Fraction类 v 0.01版。\n目前仅支持分数对象的构造、输出、加/减/乘/除运算。"; 9 10 int Fraction::gcd(int a, int b) { 11 a = abs(a); 12 b = abs(b); 13 while (b != 0) { 14 int temp = b; 15 b = a % b; 16 a = temp; 17 } 18 return a; 19 } 20 21 void Fraction::simplify() { 22 if (down_ == 0) { 23 return; 24 } 25 26 if (down_ < 0) { 27 up_ = -up_; 28 down_ = -down_; 29 } 30 31 int common = gcd(up_, down_); 32 if (common != 0) { 33 up_ /= common; 34 down_ /= common; 35 } 36 } 37 38 39 Fraction::Fraction(int up, int down) : up_(up), down_(down) { 40 if (down_ == 0) { 41 return; 42 } 43 simplify(); 44 } 45 46 47 Fraction::Fraction(const Fraction& other) : up_(other.up_), down_(other.down_) { 48 49 } 50 51 int Fraction::get_up() const { 52 return up_; 53 } 54 55 int Fraction::get_down() const { 56 return down_; 57 } 58 59 Fraction Fraction::negative() const { 60 return Fraction(-up_, down_); 61 } 62 63 void output(const Fraction& f) { 64 if (f.get_down() == 0) { 65 cout << "分母不能为0"; 66 return; 67 } 68 69 int up = f.get_up(); 70 int down = f.get_down(); 71 72 if (down == 1) { 73 74 cout << up; 75 } else if (up == 0) { 76 77 cout << "0"; 78 } else { 79 80 cout << up << "/" << down; 81 } 82 } 83 84 Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { 85 if (f1.get_down() == 0 || f2.get_down() == 0) { 86 return Fraction(0, 0); 87 } 88 89 int new_up = f1.get_up() * f2.get_down() + f2.get_up() * f1.get_down(); 90 int new_down = f1.get_down() * f2.get_down(); 91 return Fraction(new_up, new_down); 92 } 93 94 Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { 95 if (f1.get_down() == 0 || f2.get_down() == 0) { 96 return Fraction(0, 0); 97 } 98 99 int new_up = f1.get_up() * f2.get_down() - f2.get_up() * f1.get_down(); 100 int new_down = f1.get_down() * f2.get_down(); 101 return Fraction(new_up, new_down); 102 } 103 104 Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { 105 if (f1.get_down() == 0 || f2.get_down() == 0) { 106 return Fraction(0, 0); 107 } 108 109 int new_up = f1.get_up() * f2.get_up(); 110 int new_down = f1.get_down() * f2.get_down(); 111 return Fraction(new_up, new_down); 112 } 113 114 Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { 115 if (f1.get_down() == 0 || f2.get_down() == 0 || f2.get_up() == 0) { 116 return Fraction(0, 0); 117 } 118 119 int new_up = f1.get_up() * f2.get_down(); 120 int new_down = f1.get_down() * f2.get_up(); 121 return Fraction(new_up, new_down); 122 }

1 #ifndef FRACTION_H 2 #define FRACTION_H 3 4 #include <string> 5 6 class Fraction { 7 public: 8 static const std::string doc; 9 10 11 Fraction(int up = 0, int down = 1); 12 Fraction(const Fraction& other); 13 14 int get_up() const; 15 int get_down() const; 16 Fraction negative() const; 17 18 private: 19 int up_; 20 int down_; 21 22 void simplify(); 23 static int gcd(int a, int b); 24 }; 25 26 void output(const Fraction& f); 27 Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 28 Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 29 Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 30 Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 31 32 #endif

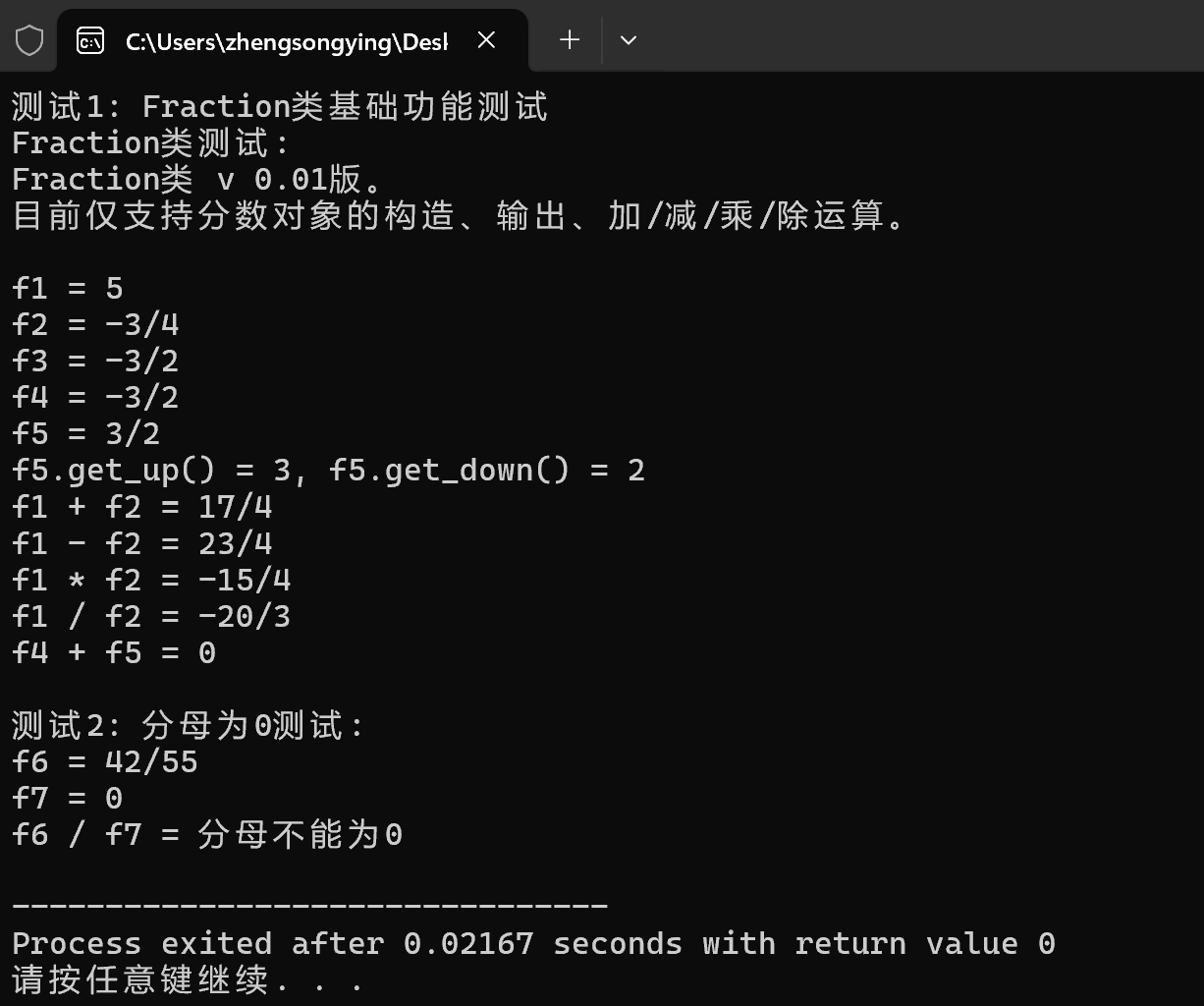
1 #include "Fraction.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 void test1(); 4 void test2(); 5 int main() { 6 std::cout << "测试1: Fraction类基础功能测试\n"; 7 test1(); 8 std::cout << "\n测试2: 分母为0测试: \n"; 9 test2(); 10 } 11 void test1() { 12 using std::cout; 13 using std::endl; 14 cout << "Fraction类测试: " << endl; 15 cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl; 16 Fraction f1(5); 17 Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12); 18 Fraction f4(f3); 19 cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl; 20 cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl; 21 cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl; 22 cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl; 23 const Fraction f5(f4.negative()); 24 cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl; 25 cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up() 26 << ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl; 27 cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 28 cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 29 cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 30 cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 31 cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl; 32 } 33 void test2() { 34 using std::cout; 35 using std::endl; 36 Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3); 37 cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl; 38 cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl; 39 cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl; 40 }
2.运行结果截图
3.问题
在代码中,我选择了将 output、add、sub、mul、div 等函数实现为自由函数(非成员函数)。
决策理由:
1. 友元方案的缺点是破坏了封装性,增加了类之间的耦合度。所以对于分数运算,通过公有接口 get_up() 和 get_down() 已经能够完成所有操作,不需要破坏封装
2. 静态成员函数方案适用于当函数与类紧密相关,但不依赖于特定对象实例时
这些工具函数虽然与 Fraction 类相关,但逻辑上更适合作为独立的操作函数,而不是类的静态成员
3.选择自由函数的理由:
保持了类的封装性 - 内部实现细节对用户隐藏
接口清晰 ,可以让用户清楚地知道哪些是核心功能,哪些是工具函数
总结:
本次实验让我深入理解了C++面向对象编程的核心概念。通过四个任务,我掌握了类的封装设计、构造函数/析构函数的调用机制、静态成员的使用场景。特别是在设计分数类和复数类时,学会了在数据共享与保护之间寻找平衡,理解了友元函数的适用场景。实验过程中,多文件组织代码的实践提升了我的工程化思维,而异常处理机制则让我认识到健壮代码的重要性。这些收获为后续更复杂的C++编程打下了坚实基础。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号