我的世界1.12.2Forge模组开发笔记——方块
第一章 方块
1 什么是方块
方块是Minecraft世界的重要组成部分。它们构成了所有的地形、结构和机器。如果你对制作模组感兴趣,那么你可能会想添加一些方块,这篇文章将会带你了解如何添加新的方块。
1.1基本方块
对于不需要特殊功能的简单方块(比如圆石、木板等),不需要自定义类。只需实例化Block类并调用一些setter方法,就可以创建出多种不同类型的方块。例如:setHardness //控制破坏方块所需的时间。这是一个任意值。以供参考,石头的硬度为1.5,泥土的硬度为0.5。如果方块应该是不可破坏的,则提供了一个方便的方法setBlockUnbreakable。
setResistance // 控制方块的爆炸抗性。这与硬度是分开的,但如果爆炸抗性低于硬度的5倍,则setHardness也会将爆炸抗性设置为硬度的5倍。
setSoundType // 控制当方块被击打、破坏或放置时发出的声音。需要一个SoundType参数
setLightLevel // 控制方块的发光度。注意:此方法接受的值是从0到1,而不是从0到15。要计算此值,请取你希望方块发出的光亮度并除以16。例如,一个发出5级光的方块应该向此方法传递5 / 16f。
setLightOpacity // 控制光穿过此方块时的减弱量。与setLightLevel不同,此值的范围是0到15。例如,将此值设置为3将每次光线穿过此类方块时降低3级亮度。
setUnlocalizedName // 主要是自解释的,设置方块的非本地化名称。出于本地化目的,这个名称前面会添加“tile.”,后面会添加“.name”。例如,setUnlocalizedName("foo") 会导致该方块的实际本地化键为“tile.foo.name”。对于更高级的本地化控制,需要自定义项目。
setCreativeTab // 控制这个方块将属于哪个创造模式物品栏。如果方块应显示在创造模式物品栏中,则必须调用此方法。可以在 CreativeTabs 类中找到物品栏选项。
所有这些方法都是可链接的,这意味着您可以连续调用它们。
1.2高级方块
以上内容仅允许使用极其基础的方块。如果您想添加功能,如玩家交互,则需要自定义类。
2 注册方块
方块必须先注册才可以使用。
2.1方块的特性
(1) 世界中的方块
世界中的方块由IBlockState表示,其行为由Block的实例定义。
(2) 物品栏中的方块
库存中的物品是ItemStack,由Item控制。
(3) ItemBlock类
作为Block和Item两个不同世界之间的桥梁,存在ItemBlock类。ItemBlock是Item的子类,它有一个名为block的字段,该字段保存了对它所表示的Block的引用。ItemBlock定义了一些“方块”作为物品时的行为,比如右键单击会放置方块。有可能存在一个Block而没有ItemBlock。(例如,minecraft:water存在方块,但没有物品。因此,无法将其作为一个物品放入库存中。)
(4) IProperty
每个数据块都有一组零个或多个这样的对象,毫不奇怪,它们描述了数据块的属性。这方面的例子包括颜色(IProperty
例如,对于相应的示例属性,我们可以有值EnumDyeColor.WHITE、EnumFacing.EAST、1或false。
现在,与其使用“minecraft:stone_button meta 9”,我们可以使用“minecraft:stone_button[facing=east,powered=true]”。猜猜哪个更有意义?我们对这些三元组有一个非常特殊的名字——它们被称为IBlockState。
在你的方块类中,为你的方块所具有的每一个属性创建static final IProperty<> 对象。Vanilla 提供了几种方便的实现方式:
PropertyInteger //实现了 IProperty<Integer>。通过调用 PropertyInteger.create(“name”, minValue, maxValue) 创建。
PropertyBool //实现了 IProperty<Boolean>。通过调用 PropertyBool.create(“name”) 创建。
PropertyEnum<E extends Enum<>> //实现了 IProperty<E>,定义了一个属性,该属性可以接受一个枚举类的值。通过调用 PropertyEnum.create(“name”, EnumClass.class) 创建。
//你也可以只使用枚举值的一个子集(例如,要获取一个表示基本方向的属性,通过调用PropertyDirection.create("<name>", EnumFacing.Plane.HORIZONTAL)获取方向)
//您可以自由创建自己的 IProperty<> 实现
如果你的模组有一个API或者意味着可以从其他模组与之交互,那么强烈建议你将你的IProperty(以及任何用作值的类)放在你的API中。这样,人们就可以使用属性和值来设置你的世界中的方块,而不是像以前那样忍受任意的数字。
创建完IProperty<>对象后,请在您的Block类中覆盖createBlockState方法。在该方法中,只需编写返回new BlockState()的代码。首先,将BlockState的构造函数传递给您的Block(即this),然后跟随您想要声明的每个IProperty。
您可以通过调用getValue(
如果您想获取具有不同值集的IBlockState,只需如上所述调用withProperty("<"PROPERTY">","<"NEW_VALUE">")。这将返回另一个具有您请求值的预生成的IBlockState。
您可以使用setBlockState()和getBlockState()在世界中获取和放置IBlockState。
第二章 创建方块
1 方块类
所有方块的类型都是net.minecraft.block.Block类的实例。所以也需要继承这个类,实现自己的方块。
1.1 创建方块类
新建一个fktg.test.block(fktg.test是自定义的路径)的子包,然后在新建的子包下新建一个BlockExample类(例子方块类)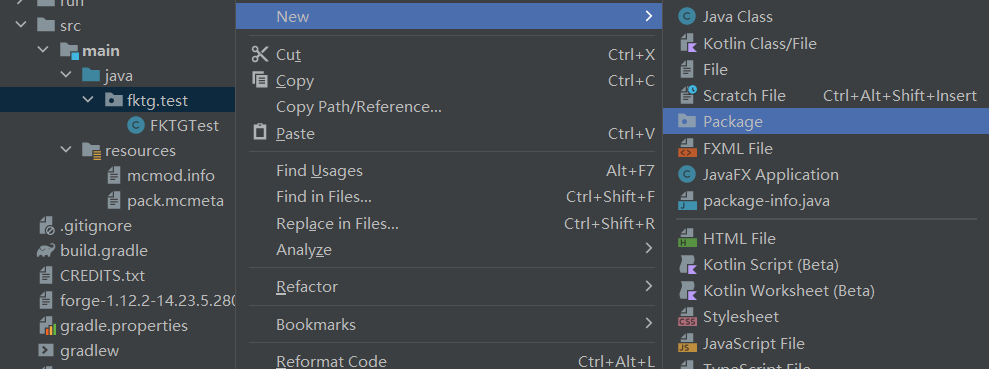
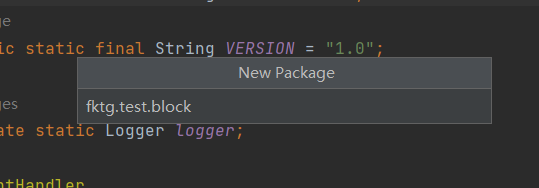
(1) 新建包
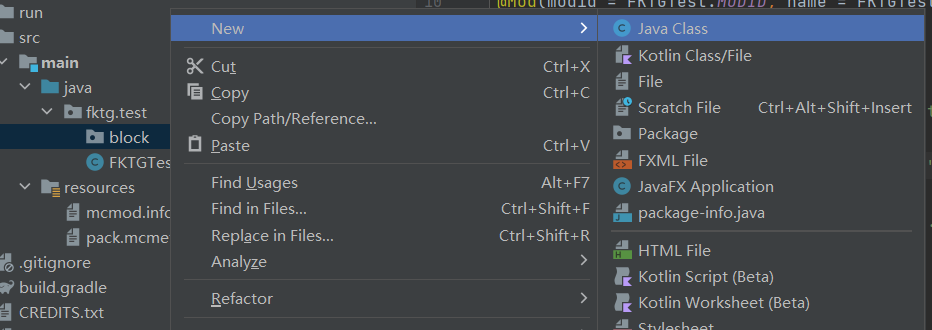
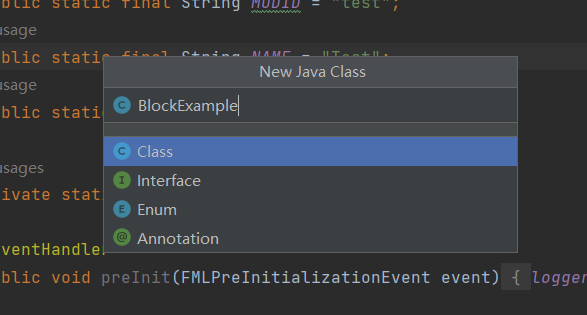
(2) 新建类
在类中写入以下代码,注意类名要与文件名一致:package fktg.test.block;
import fktg.test.FKTGTest;
import net.minecraft.block.Block;
import net.minecraft.block.material.Material;
public class BlockExample extends Block {
public BlockExample() {
super(Material.GOURD);
this.setUnlocalizedName(FKTGTest.MODID + ".example");
this.setRegistryName("example");
this.setHarvestLevel("shovel",0); //挖掘工具(pickaxe、shovel、axe等)和挖掘等级(0是木质工具)
this.setHardness(0.5F); //方块的硬度,即挖掘所需的时间和防爆强度
}
}
(3) 方块类代码
1.2 注册方块
新建一个fktg.test.block.BlockRegistryHandler类,并填写代码
(1) 新建BlockRegistryHandler类
将以下代码写入BlockRegisterHandler类中,注意class文件格式:package fktg.test.block;
import net.minecraft.block.Block;
import net.minecraftforge.event.RegistryEvent.Register;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.common.Mod;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.common.eventhandler.SubscribeEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.registries.IForgeRegistry;
@Mod.EventBusSubscriber
public class BlockRegistryHandler {
public static final BlockExample Block_Example = new BlockExample();
@SubscribeEvent
public static void onRegistry(Register<Block> event) //方块注册器
{
IForgeRegistry<Block> registry = event.getRegistry();
registry.register(Block_Example);
}
}
(2) BlockRegistryHandler类代码
1.3 注册方块对应的物品
对绝大多数方块来说,它们都有对应的物品,这类物品在右键一个方块时,会在该方块旁边被放置,其对应的类就是net.minecraft.item.ItemBlock类。
首先新建一个fktg.test.item包(有就不用新建),然后在该包中新建一个ItemRegistryHandler类,写入相应代码
(1) 新建fktg.test.item包
随后新建ItemRegistryHandler类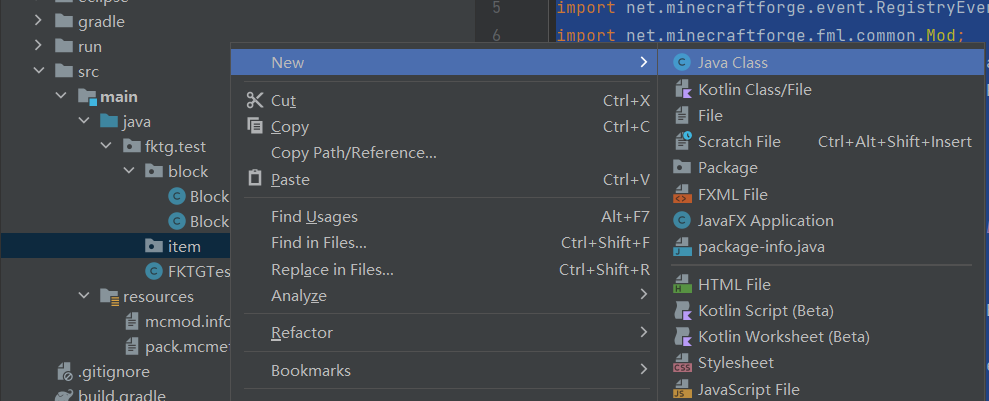
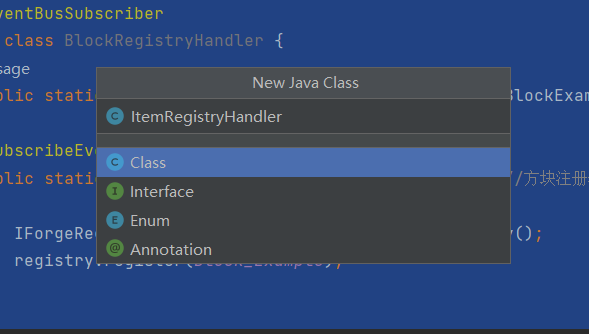
(2) 新建ItemRegistryHandler类
将以下代码写入ItemRegistryHandler类:package fktg.test.item;
import fktg.test.block.BlockRegistryHandler;
import net.minecraft.client.renderer.block.model.ModelResourceLocation;
import net.minecraft.item.Item;
import net.minecraft.item.ItemBlock;
import net.minecraftforge.client.event.ModelRegistryEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.client.model.ModelLoader;
import net.minecraftforge.event.RegistryEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.common.Mod;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.common.eventhandler.SubscribeEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.relauncher.Side;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.relauncher.SideOnly;
import net.minecraftforge.registries.IForgeRegistry;
@Mod.EventBusSubscriber
public class ItemRegistryHandler {
public static final ItemBlock ITEM_EXAMPLE = withRegistryName(new ItemBlock(BlockRegistryHandler.Block_Example));
@SubscribeEvent
public static void onRegistry(RegistryEvent.Register<Item> event) //注册物品
{
IForgeRegistry<Item> registry = event.getRegistry();
//ITEM_EXAMPLE.setRegistryName(ITEM_EXAMPLE.getBlock().getRegistryName()); //为了防止重复造轮子,将重复的部分封装成了方法
registry.register(ITEM_EXAMPLE);
}
@SubscribeEvent
@SideOnly(Side.CLIENT)
public static void onModelRegistry(ModelRegistryEvent event) //注册物品材质
{
registerModel(ITEM_EXAMPLE);
}
private static ItemBlock withRegistryName(ItemBlock item)
{
item.setRegistryName(item.getBlock().getRegistryName());
return item;
}
@SideOnly(Side.CLIENT)
private static void registerModel(Item item)
{
ModelResourceLocation modelResourceLocation = new ModelResourceLocation(item.getRegistryName(),
"inventory");
ModelLoader.setCustomModelResourceLocation(item, 0, modelResourceLocation);
}
}
(3) ItemRegistryHandler类代码
如果以上步骤没问题,那么你就可以在游戏中使用看到紫红色光芒的物品如果你不会启动游戏,可以去看看我之前的笔记一切的开始
打开游戏,输入:
/give @a test:example (注意:test是模组id,example是setRegistryName方法注册的名称)
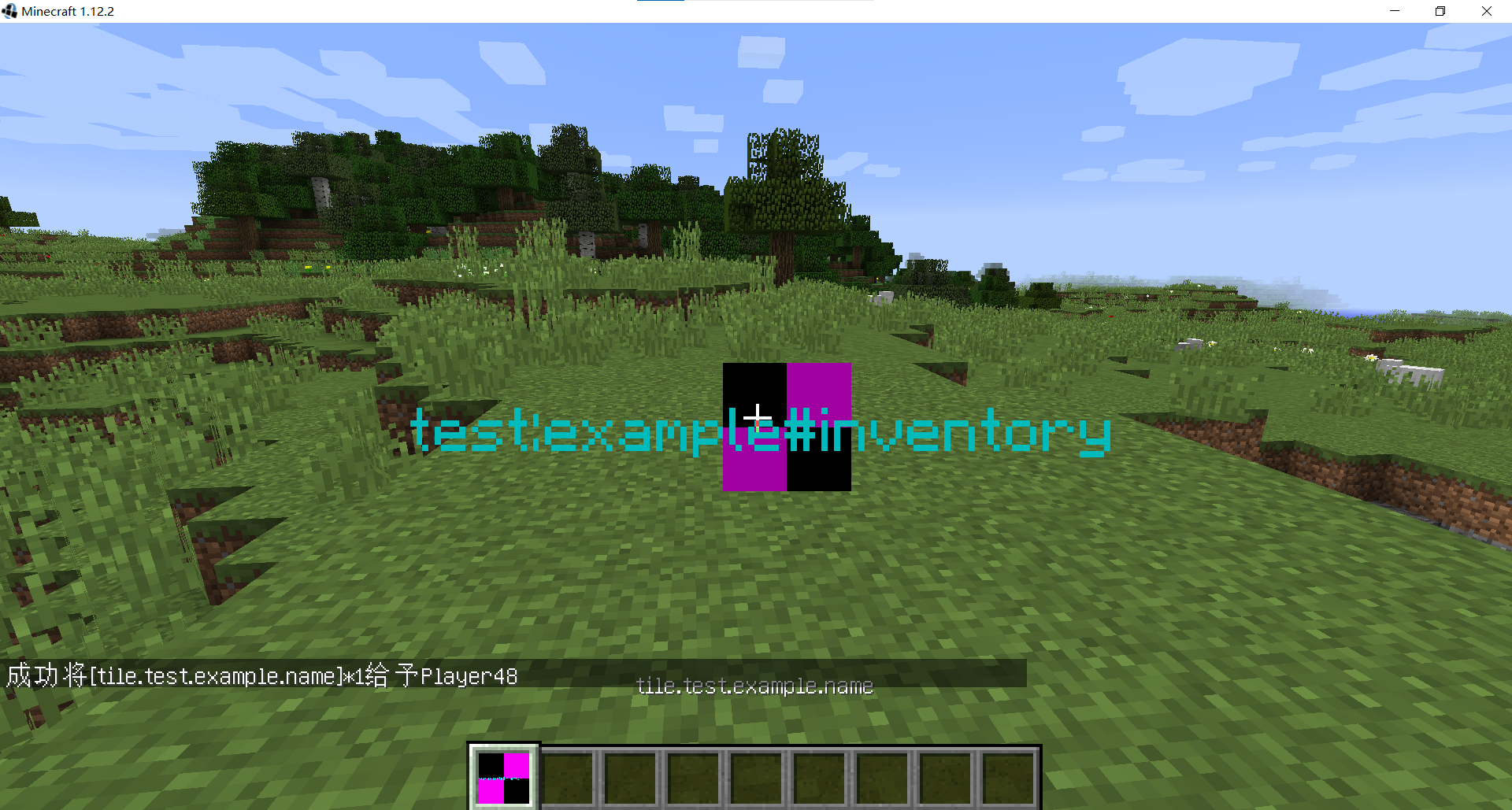
(4) 游戏中该方块的物品
将获取到的物品右键放置在地面,就会得到紫红色的方块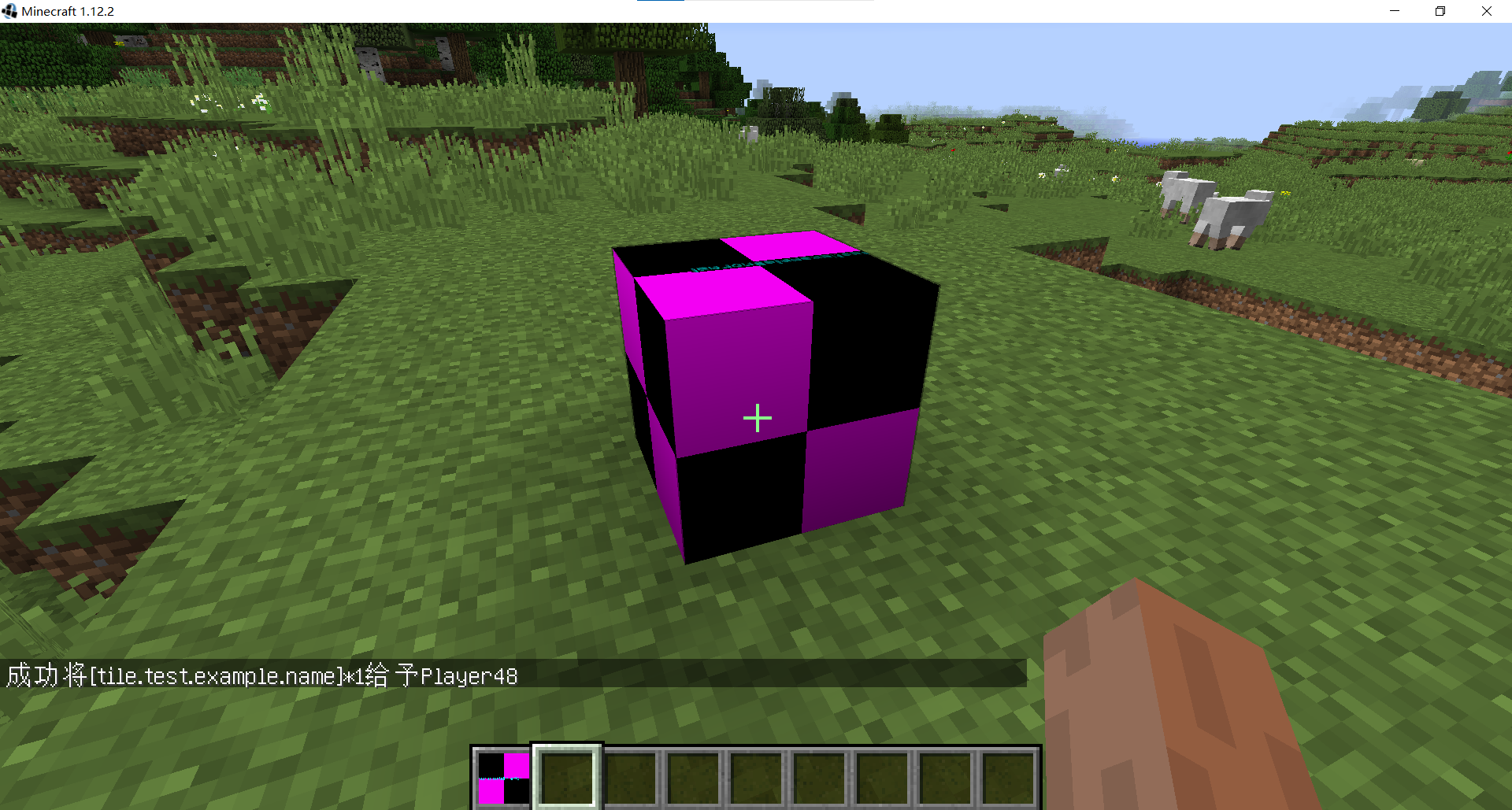
(5) 游戏中的该方块
1.4 语言文件和方块材质
语言文件能够让方块在游戏中的名称标准化,方块的前缀为title
首先在resources目录中新建一个assets.test.lang包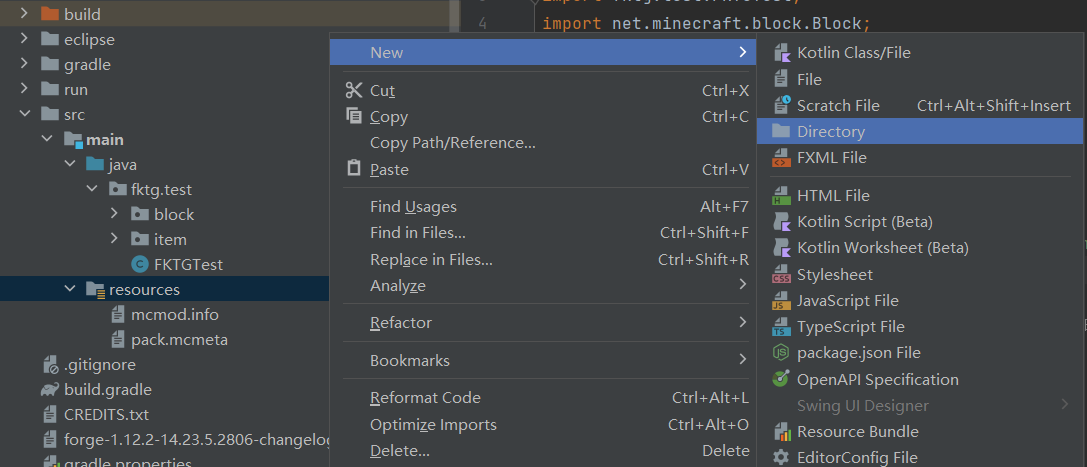
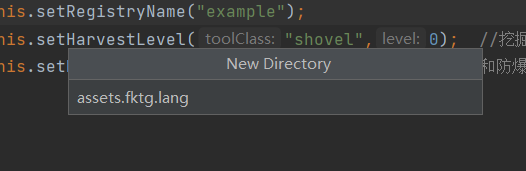
(1) 新建lang包
然后在该包下新建一个en_us.lang的File文件,在该文件中写入:tile.test.example.name=example
(2) en_us.lang内容
之后在该包下新建一个zh_cn.lang的File文件,在该文件中写入:tile.test.example.name=样例
(3) zh_cn.lang内容
然后在resources目录中新建一个assets.test.blockstates包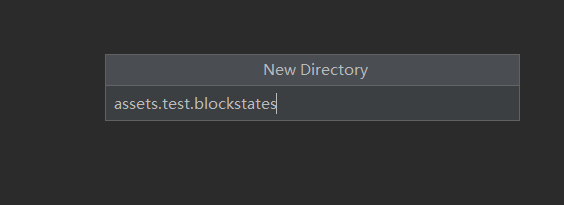
(4) 创建blockstates包
在blockstates包中创建example.json文件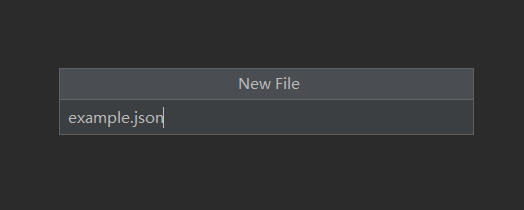
(5) 创建example.json文件
在其中写入以下内容:{
"forge_marker": 1,
"defaults": {
"model": "minecraft:cube_all",
"textures": {"all": "test:blocks/example"}
},
"variants": {
"normal": [{}],
"inventory": [{"transform": "forge:default-block"}]
}
}
(6) example.json文件内容
然后在resources目录中创建assets.test.textures.blocks包,准备将材质图片放进去
(7) 创建blocks包
在作图软件里制作一张材质图,要求大小必须是2的n次方
(8) 制作方块材质
最后将图存放进blocks目录中,注意图片名称为example.png
(9) assets目录
打开游戏查看材质和名字是否正确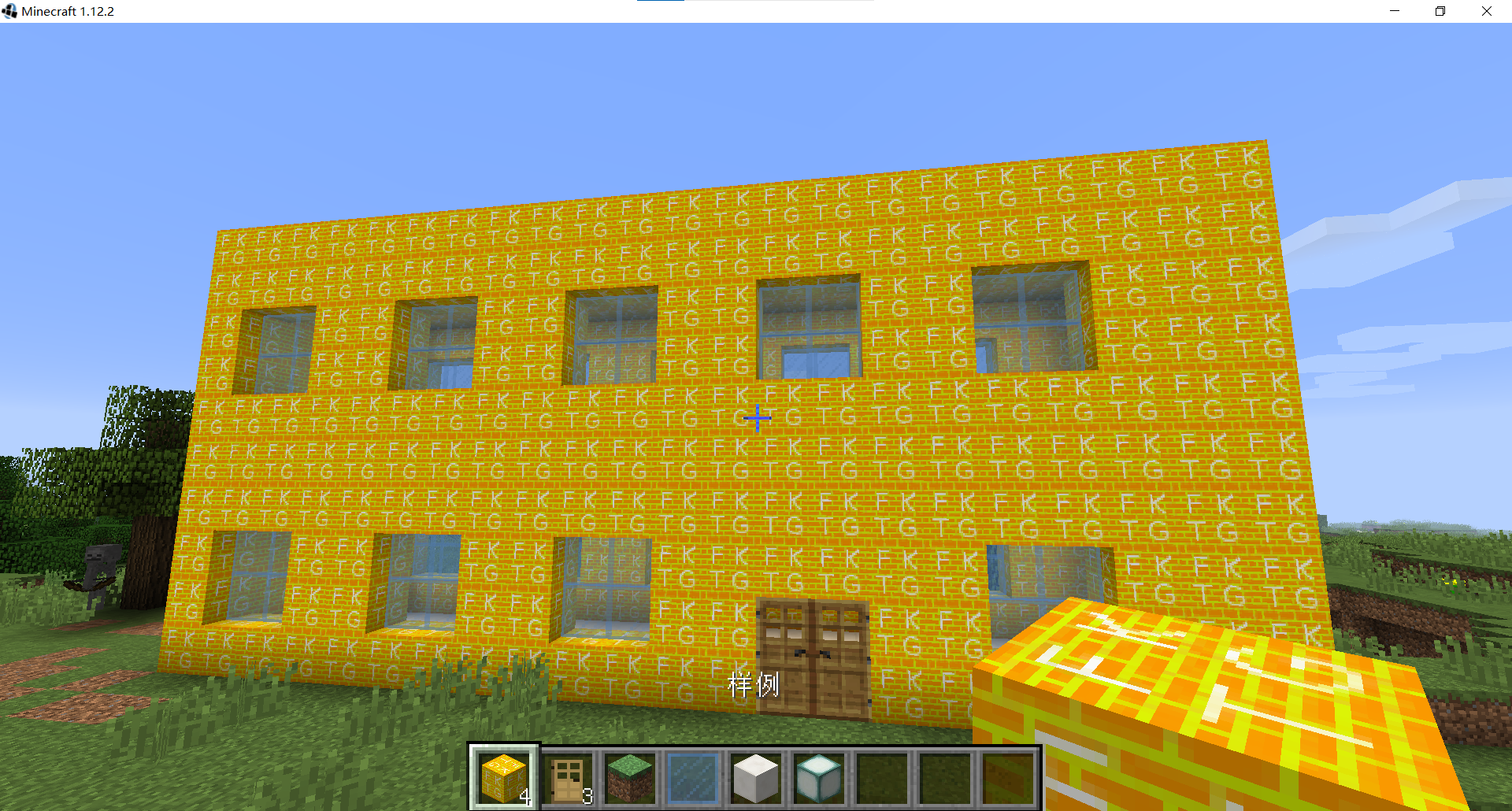 目前为止,添加一个自己的方块已经完成了
目前为止,添加一个自己的方块已经完成了
第三章 修改方块的属性
1 方块的方法
public Block setUnlocalizedName(String name) //设置本地名称
//this.setUnlocalizedName(FKTGTest.MODID + ".example");
public final T setRegistryName(String name) //设置名称
//this.setRegistryName("example");
public void setHarvestLevel(String toolClass, int level) //设置挖掘工具和挖掘等级
//this.setHarvestLevel("shovel",0);
//shovel - 铲 axe - 斧 pickaxe - 镐 sword - 剑 hoe - 锄
// 0-木、金 1-石 2-铁 3-钻石
public Block setHardness(float hardness) //设置方块的硬度、防爆等级
//this.setHardness(0.5F);
// 泥土-0.5
public Block setBlockUnbreakable() //设置方块为不可破坏
//this.setBlockUnbreakable();
protected Block setSoundType(SoundType sound) //设置方块音效类型
// this.setSoundType(SoundType.STONE);
// SoundType在Minecraft的代码中有 WOOD、GROUND、PLANT、STONE、METAL、GLASS、CLOTH、SAND、SNOW、LADDER、ANVIL、SLIME
public Block setLightLevel(float value) //控制方块的发光度
//this.setLightLevel(2/16F);
//注意:此方法接受的值是从0到1,而不是从0到15。要计算此值,请取你希望方块发出的光亮度并除以16。
//例如,一个发出5级光的方块应该向此方法传递5 / 16f。
public Block setLightOpacity(int opacity) //控制光穿过此方块时的减弱量
//this.setLightOpacity(3);
//与setLightLevel不同,此值的范围是0到15。例如,将此值设置为3将每次光线穿过此类方块时降低3级亮度。
public Block setCreativeTab(CreativeTabs tab) //控制这个方块将属于哪个创造模式物品栏
//setCreativeTab(CreativeTabs.BUILDING_BLOCKS);
//物品栏有: BUILDING_BLOCKS(建筑方块)、DECORATIONS(装饰方块)、REDSTONE(红石)、TRANSPORTATION(交通)、MISC(杂项)、SEARCH(搜索栏)、FOOD(食物)、TOOLS(工具)、COMBAT(武器)、BREWING(药水)、HOTBAR(玩家底部物品槽)
//物品栏也可以进行自定义
public Block setResistance(float resistance) //设定方块的爆炸抗性
//this.setResistance(10.0f);
//如果一个方块的爆炸阻力为 0,则它会在任何爆炸中被直接破坏。
//常见方块的爆炸阻力:草块(0.6)、木板(2.0)、木头(2.0)、石头(3.0)、铁块(30)、黑曜石(6000)
protected final void setDefaultState(IBlockState state) //设置方块的默认状态
/*import net.minecraft.block.Block;
import net.minecraft.block.material.Material;
import net.minecraft.block.properties.IProperty;
import net.minecraft.block.properties.PropertyBool;
import net.minecraft.block.state.BlockStateContainer;
import net.minecraft.block.state.IBlockState;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.common.registry.GameRegistry;
public class MyCustomBlock extends Block {
// 定义一个布尔属性,表示方块是否处于“激活”状态
public static final PropertyBool ACTIVE = PropertyBool.create("active");
public MyCustomBlock() {
super(Material.ROCK); // 设置材料类型为石头
setUnlocalizedName("my_custom_block"); // 设置方块的名称
setHardness(5.0f); // 设置方块的硬度
setResistance(10.0f); // 设置方块的爆炸阻力
//设置默认状态为未激活状态
this.setDefaultState(this.blockState.getBaseState().withProperty(ACTIVE, Boolean.FALSE));
}
@Override
protected BlockStateContainer createBlockState() {
return new BlockStateContainer(this, new IProperty[]{ACTIVE});
}
@Override
public IBlockState getStateFromMeta(int meta) {
return this.getDefaultState().withProperty(ACTIVE, (meta & 1) == 1);
}
@Override
public int getMetaFromState(IBlockState state) {
return state.getValue(ACTIVE) ? 1 : 0;
}
public static void registerBlock() {
GameRegistry.registerBlock(new MyCustomBlock(), "my_custom_block");
}
}*/
public boolean removedByPlayer(IBlockState state, World world, BlockPos pos, EntityPlayer player, boolean willHarvest) //处理当玩家移除方块时的行为
/*@Override
public void removedByPlayer(World worldIn, BlockPos pos, IBlockState state, EntityPlayer player, boolean willHarvest) {
super.removedByPlayer(worldIn, pos, state, player, willHarvest);
// 在方块被移除时执行特定逻辑
if (!worldIn.isRemote) {
// 逻辑,比如播放音效
worldIn.playSound(null, pos, SoundEvents.BLOCK_STONE_BREAK, SoundCategory.BLOCKS, 1.0F, 1.0F);
// 可能执行其他操作,例如掉落物品
// ItemStack stack = new ItemStack(Items.DIAMOND, 1);
// spawnAsEntity(worldIn, pos, stack);
}
}*/
public void updateTick(World worldIn, BlockPos pos, IBlockState state, Random rand) //用于处理方块的定期更新逻辑
//public class MyCustomBlock extends Block {
// public MyCustomBlock() {
// super(Material.ROCK);
// setUnlocalizedName("my_custom_block");
// setTickRandomly(true); // 启用随机更新
// }
//@Override
// public void updateTick(World worldIn, BlockPos pos, IBlockState state, Random rand) {
// 确保代码只在服务端执行
// if (!worldIn.isRemote) {
// // 生成一个随机数
// if (rand.nextInt(10) == 0) { // 10% 的几率
// // 将当前方块变为金块
// worldIn.setBlockState(pos, Blocks.GOLD_BLOCK.getDefaultState());
// }
// }
// }
//}
public Item getItemDropped(IBlockState state, Random rand, int fortune) //用于定义当方块被破坏时掉落的物品
@Override
public Item getItemDropped(IBlockState state, Random rand, int fortune) {
return Items.DIAMOND; //设置掉落物为钻石
}
public int quantityDropped(Random random) //定义方块被破坏时掉落的物品数量
@Override
public int quantityDropped(Random random) {
return 1 + random.nextInt(3); // 随机掉落1到3个物品
}
public int quantityDroppedWithBonus(int fortune, Random random) //根据玩家使用的工具的时运(Fortune)效果掉落的物品数量
@Override
public int quantityDroppedWithBonus(int fortune, Random random) {
int baseDrop = this.quantityDropped(random); // 获取基础掉落数量
if (fortune > 0) {
int extraDrops = random.nextInt(fortune + 2); // 根据时运等级随机计算额外掉落
return baseDrop + extraDrops; // 返回基础掉落加上额外掉落
} else {
return baseDrop; // 如果没有时运,直接返回基础掉落
}
}
public int damageDropped(IBlockState state) //控制方块掉落物品的具体子类型,特别是当方块有多种变体或状态时
@Override
public int damageDropped(IBlockState state) {
// 获取方块的颜色属性,并返回对应的染料损伤值
return state.getValue(COLOR_PROPERTY).getMetadata();
}
public void getDrops(NonNullList<ItemStack> drops, IBlockAccess world, BlockPos pos, IBlockState state, int fortune) //让一个方块在被破坏时掉落多种物品,或者掉落多个物品
@Override
public void getDrops(NonNullList<ItemStack> drops, IBlockAccess world, BlockPos pos, IBlockState state, int fortune) {
super.getDrops(drops, world, pos, state, fortune); // 调用父类方法,通常用于初始化drops列表
drops.add(new ItemStack(Item.getItemFromBlock(this), 3, 0)); // 添加3个钻石
drops.add(new ItemStack(Item.getByNameOrId("minecraft:redstone"), 5)); // 添加5个红石
}
1.2 动手实现
下面的例子利用了getDrops方法使方块拥有多个掉落物
package fktg.testmod.block;
import fktg.testmod.TestMod;
import net.minecraft.block.Block;
import net.minecraft.block.material.Material;
import net.minecraft.block.state.IBlockState;
import net.minecraft.creativetab.CreativeTabs;
import net.minecraft.item.Item;
import net.minecraft.item.ItemStack;
import net.minecraft.util.NonNullList;
import net.minecraft.util.math.BlockPos;
import net.minecraft.world.IBlockAccess;
public class BlockGoldWall extends Block {
public BlockGoldWall() {
super(Material.GOURD);
this.setUnlocalizedName(TestMod.MODID + ".goldWall");
this.setRegistryName("gold_wall");
this.setHarvestLevel("shovel",0); //挖掘工具(pickaxe、shovel、axe等)和挖掘等级(0是木质工具)
this.setHardness(0.5F); //方块的硬度,即挖掘所需的时间和防爆强度
this.setCreativeTab(CreativeTabs.BUILDING_BLOCKS);
}
@Override
public Item getItemDropped(IBlockState state, Random rand, int fortune) {
return null; //设置本身不会掉落
}
@Override
public void getDrops(NonNullList<ItemStack> drops, IBlockAccess world, BlockPos pos, IBlockState state, int fortune) {
super.getDrops(drops, world, pos, state, fortune); // 调用父类方法,通常用于初始化drops列表
drops.add(new ItemStack(Item.getByNameOrId("minecraft:gold_ingot"), 1)); // 添加1个金锭
drops.add(new ItemStack(Item.getByNameOrId("minecraft:cobblestone"), 8)); // 添加8个圆石
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号