设计模式 - 策略模式(strategy pattern/policy pattern)【摘自 wikipedia】
策略模式是一种在运行时选择算法的行为软件设计模式,代码不是直接实现单个算法,而是接收关于在一系列算法中使用哪个的运行时指令。策略让算法独立于使用它的客户端而变化。
普及了使用设计模式来描述如何设计灵活且可重用的面向对象软件的概念。将关于使用哪种算法的决定 推迟到 运行时,允许调用代码更加灵活和可重用。
UML 类和序列图
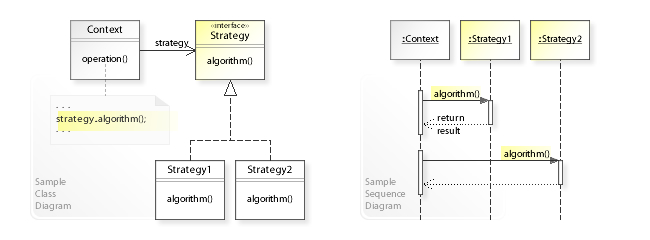
在上面的 UML 类图中,Context 该类没有直接实现算法。相反,Context 指向的是 Strategy 用于执行算法的接口。
示例 1
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
interface BillingStrategy {
// Use a price in cents to avoid floating point round-off error
int getActPrice(int rawPrice);
// Normal billing strategy (unchanged price)
static BillingStrategy normalStrategy() {
return new BillingStrategy() {
@Override
public int getActPrice(int rawPrice) {
return rawPrice;
}
};
}
// Strategy for Happy hour (50% discount)
static BillingStrategy happyHourStrategy() {
return new BillingStrategy() {
@Override
public int getActPrice(int rawPrice) {
return rawPrice / 2;
}
};
}
}
class CustomerBill {
private final List<Integer> drinks = new ArrayList<>();
private BillingStrategy strategy;
public CustomerBill(BillingStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public void add(int price, int quantity) {
this.drinks.add(this.strategy.getActPrice(price*quantity));
}
// Payment of bill
public void print() {
int sum = this.drinks.stream().mapToInt(v -> v).sum();
System.out.println("Total due: " + sum);
this.drinks.clear();
}
// Set Strategy
public void setStrategy(BillingStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
}
public class StrategyPattern {
public static void main(String[] arguments) {
// Prepare strategies
BillingStrategy normalStrategy = BillingStrategy.normalStrategy();
BillingStrategy happyHourStrategy = BillingStrategy.happyHourStrategy();
CustomerBill firstCustomer = new CustomerBill(normalStrategy);
// Normal billing
firstCustomer.add(100, 1);
// Start Happy Hour
firstCustomer.setStrategy(happyHourStrategy);
firstCustomer.add(100, 2);
// New Customer
CustomerBill secondCustomer = new CustomerBill(happyHourStrategy);
secondCustomer.add(80, 1);
// The Customer pays 200
firstCustomer.print();
// End Happy Hour 550
secondCustomer.setStrategy(normalStrategy);
secondCustomer.add(130, 2);
secondCustomer.add(250, 1);
secondCustomer.print();
}
}
策略和开放/封闭原则
策略模式,类的行为不应该被继承,应该使用接口进行封装。符合开闭原则。
策略模式使用组合而不是继承,行为被定义成单独的接口和实现这些接口的特定类。这允许在行为和使用该行为的类之间更好地解耦。
可以在不破坏使用它的类的情况下更改行为,并且类可以通过更改所使用的特定实现而在行为之间切花,而不需要任何重大的代码更改;行为也可以在运行时和设计时更改。
For instance, a car object's brake behavior can be changed from BrakeWithABS() to Brake() by changing the brakeBehavior member to:
/* Encapsulated family of Algorithms * Interface and its implementations */ public interface IBrakeBehavior { public void brake(); } public class BrakeWithABS implements IBrakeBehavior { public void brake() { System.out.println("Brake with ABS applied"); } } public class Brake implements IBrakeBehavior { public void brake() { System.out.println("Simple Brake applied"); } } /* Client that can use the algorithms above interchangeably */ public abstract class Car { private IBrakeBehavior brakeBehavior; public Car(IBrakeBehavior brakeBehavior) { this.brakeBehavior = brakeBehavior; } public void applyBrake() { brakeBehavior.brake(); } public void setBrakeBehavior(IBrakeBehavior brakeType) { this.brakeBehavior = brakeType; } } /* Client 1 uses one algorithm (Brake) in the constructor */ public class Sedan extends Car { public Sedan() { super(new Brake()); } } /* Client 2 uses another algorithm (BrakeWithABS) in the constructor */ public class SUV extends Car { public SUV() { super(new BrakeWithABS()); } } /* Using the Car example */ public class CarExample { public static void main(final String[] arguments) { Car sedanCar = new Sedan(); sedanCar.applyBrake(); // This will invoke class "Brake" Car suvCar = new SUV(); suvCar.applyBrake(); // This will invoke class "BrakeWithABS" // set brake behavior dynamically suvCar.setBrakeBehavior( new Brake() ); suvCar.applyBrake(); // This will invoke class "Brake" } }
以下仅供参考,个人梳理,方便记忆
* 定义 接口 IBrakeBehavior 、刹车方法
* 接口不同实现类
* 抽象类,构造器注入,变更注入方法
* 继承抽象类,通过注入的接口实现类调用方法


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号