11.3 字符串输出
三、字符串输出
C有3个标准库函数 用于打印字符串:put()、fputs() 和 printf()。
3.1 puts()函数
- puts() 在显示字符串时会自动在 其末尾添加一个换行符。
- puts() 函数在遇到空字符时就停止输出,所以 必须确保有空字符。
3.2 fputs()函数
-
fputs() 函数的第 2 个参数指明要写入数据的文件。如果要打印在显示器上,可以用定义在stdio.h中的stdout(标准输出)作为该参数。
-
gets() 丢弃输入中的换行符, puts() 在输出中添加换行符;
fgets() 保留输入中的换行符,fputs() 不在输出中添加换行符。
-
puts() 应与 gets() 配对使用,fputs() 应与 fgets() 配对使用。
3.3 printf()函数
- printf()不会自动在每个字符串末尾加上一个换行符,必须在参数中指明应该在哪里使用换行符。
- printf()的形式更复杂些,需要输入更多代码,而且计算机执行的时间也更长。
- 使用 printf()打印多个字符串更加简单。
作业
11.13.3& 11.13.4
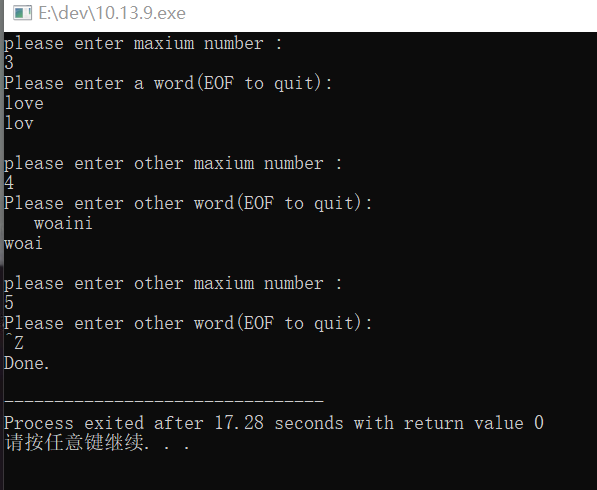
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h> //判断空白字符头文件
#define LEN 80
char * getword(char * str, int a);//定义存储字符的函数
int main(void)
{
char input[LEN];
int a;
printf("please enter maxium number :\n");//确定可读取的最大字符数
scanf("%d", &a);
printf("Please enter a word(EOF to quit):\n");
while (getword(input, a) != NULL)
{
puts(input);
printf("\n");
printf("please enter other maxium number :\n");//again
scanf("%d", &a);
printf("Please enter other word(EOF to quit):\n");
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
char * getword(char * str, int a)
{
char * orig = str;
int ch;
int n = 0;
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF && isspace(ch))//跳过第一个字符前的空白字符
continue;
if (ch == EOF) //退出程序
return NULL;
else
{
*str++ = ch;//赋值储存第一个字符
n++;
}
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF && !isspace(ch) && n < a)//储存范围内剩下的字符。
{
*str++ = ch;
n++;
}
*str = '\0';//添加单词字符串结尾空字符
if (ch == EOF)
return NULL;
else
{
while (ch != '\n')
ch = getchar(); //舍弃剩下的字符
return orig;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号