oop-实验5
task1
publisher.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<string> 5 6 //发行/出版物类:Publisher(抽象类) 7 class Publisher{ 8 public: 9 Publisher(const std::string &name_=""); //构造函数 10 virtual ~Publisher()=default; 11 12 public: 13 //两个纯虚函数,作为接口继承 14 virtual void publish() const=0; 15 virtual void use() const =0; 16 17 protected: 18 std::string name; //发行/出版物名称 19 }; 20 21 //图书类:Book 22 class Book:public Publisher{ 23 public: 24 Book(const std::string &name_="",const std::string &author_=""); 25 void publish() const override; 26 void use() const override; 27 private: 28 std::string author; //作者 29 }; 30 31 //电影类:Film 32 class Film:public Publisher{ 33 public: 34 Film(const std::string &name_="",const std::string &director_=""); 35 void publish() const override; 36 void use() const override; 37 private: 38 std::string director; //导演 39 }; 40 41 //音乐类:Music 42 class Music:public Publisher{ 43 public: 44 Music(const std::string &name_="",const std::string &artist_=""); 45 void publish() const override; 46 void use() const override; 47 private: 48 std::string artist; //音乐艺术家名称 49 };
publisher.cpp
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include"publisher.hpp" 4 5 //Publisher 6 Publisher::Publisher(const std::string &name_):name{name_}{} 7 8 //Book 9 Book::Book(const std::string &name_,const std::string &author_):Publisher{name_},author{author_}{} 10 void Book::publish() const{ 11 std::cout<<"Publishing book <<"<<name<<">> by"<<author<<"\n"; 12 } 13 void Book::use() const{ 14 std::cout<<"Reading book <<"<<name<<">> by"<<author<<"\n"; 15 } 16 17 //Film 18 Film::Film(const std::string &name_,const std::string &director_):Publisher(name_),director{director_}{} 19 void Film::publish() const{ 20 std::cout<<"Publishing film <"<<name<<"> directed by"<<director<<'\n'; 21 } 22 void Film::use() const{ 23 std::cout<<"Watching film <"<<name<<"> directed by"<<director<<'\n'; 24 } 25 26 //Music 27 Music::Music(const std::string &name_, const std::string &artist_):Publisher{name_},artist{artist_}{} 28 void Music::publish() const{ 29 std::cout << "Publishing music <" << name << "> by " << artist << '\n'; 30 } 31 void Music::use() const{ 32 std::cout << "Listening to music <" << name << "> by " << artist << '\n'; 33 }
task1.cpp
1 #include <memory> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include "publisher.hpp" 5 void test1(){ 6 std::vector<Publisher *> v; 7 v.push_back(new Book("Harry Potter", "J.K. Rowling")); 8 v.push_back(new Film("The Godfather", "Francis Ford Coppola")); 9 v.push_back(new Music("Blowing in the wind", "Bob Dylan")); 10 for(Publisher *ptr: v) { 11 ptr->publish(); 12 ptr->use(); 13 std::cout << '\n'; 14 delete ptr; 15 } 16 } 17 void test2() { 18 std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Publisher>> v; 19 v.push_back(std::make_unique<Book>("Harry Potter", "J.K. Rowling")); 20 v.push_back(std::make_unique<Film>("The Godfather", "Francis Ford Coppola")); 21 v.push_back(std::make_unique<Music>("Blowing in the wind", "Bob Dylan")); 22 for(const auto &ptr:v){ 23 ptr->publish(); 24 ptr->use(); 25 std::cout<<'\n'; 26 } 27 } 28 void test3() { 29 Book book("A Philosophy of Software Design", "John Ousterhout"); 30 book.publish(); 31 book.use(); 32 } 33 int main() { 34 std::cout << "运行时多态:纯虚函数、抽象类\n"; 35 std::cout << "\n测试1: 使用原始指针\n"; 36 test1(); 37 std::cout << "\n测试2: 使用智能指针\n"; 38 test2(); 39 std::cout << "\n测试3: 直接使用类\n"; 40 test3(); 41 }
运行截图:

回答问题
问题1:抽象类机制
(1)是什么决定了 Publisher 是抽象类?用一句话说明,并指出代码中的具体依据。
含有纯虚函数。
virtual void publish() const=0;
virtual void use() const =0;
(2)如果在 main.cpp 里直接写 Publisher p; 能否编译通过?为什么?
不可以,抽象类不能被实例化。
问题2:纯虚函数与接口继承
(1) Book 、 Film 、 Music 必须实现哪两个函数才能通过编译?请写出其完整函数声明。
virtual void publish() const=0;
virtual void use() const =0;
(2) 在 publisher.cpp 的 Film 类实现中,把两个成员函数实现里的 const 去掉(保持函数体不变),重新编译,报错信息是什么?
两个纯虚函数在Film这个类中未被正确override。
问题3:运行时多态与虚析构
(1)在 test1() 里, for (Publisher *ptr : v) 中 ptr 的声明类型是什么?
Publisher *,基类指针。
(2)当循环执行到 ptr->publish();时, ptr 实际指向的对象类型分别有哪些?(按循环顺序写出)
Book Film Music
(3)基类 Publisher 的析构函数为何声明为virtual ?若删除 virtual ,执行 delete ptr; 会出现什么问题?
确保用基类指针定义的派生类对象在删除时派生类的析构函数也能被正确调用。
如果删除,当执行delete ptr时无法调用派生类的析构函数,如果派生类对象新添的数据成员如(string)无法被销毁,会造成内存泄漏。
task2
book.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<string> 4 5 class Book{ 6 public: 7 Book(const std::string &name_,const std::string &author_,const std::string &translator_,const std::string &isbn_,double price); 8 9 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out,const Book &book); 10 11 private: 12 std::string name; //book name 13 std::string author; 14 std::string translator; //译者 15 std::string isbn; //isbn号 16 double price; //定价 17 };
book.cpp
1 #include<iomanip> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 #include"book.hpp" 5 6 //图书描述类信息Book的实现 7 Book::Book(const std::string &name_,const std::string &author_,const std::string &translator_,const std::string &isbn_,double price_):name(name_),author(author_),translator(translator_),isbn{isbn_},price{price_}{} 8 9 //运算符<<重载实现 10 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out,const Book &book){ 11 using std::left; 12 using std::setw; 13 14 out<<left; 15 out << setw(15) << "书名:" << book.name << '\n' 16 << setw(15) << "作者:" << book.author << '\n' 17 << setw(15) << "译者:" << book.translator << '\n' 18 << setw(15) << "ISBN:" << book.isbn << '\n' 19 << setw(15) << "定价:" << book.price; 20 21 return out; 22 }
booksale.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<string> 4 #include"book.hpp" 5 6 //图书销售基类BookSales:声明 7 class BookSale{ 8 public: 9 BookSale(const Book &rb_,double sales_price,int sales_amount); 10 int get_amount() const; //返回销售数量 11 double get_revenue() const; //返回营收 12 13 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out,const BookSale &item); 14 15 private: 16 Book rb; 17 double sales_price; //售价 18 int sales_amount; //销售数量 19 };
booksale.cpp
1 #include<iomanip> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 #include"booksale.hpp" 5 6 //图书销售记录类 Booksales实现 7 BookSale::BookSale(const Book &rb_,double sales_price_,int sales_amount_): rb{rb_}, sales_price{sales_price_},sales_amount{sales_amount_} {} 8 9 int BookSale::get_amount() const{ 10 return sales_amount; 11 } 12 13 double BookSale::get_revenue() const{ 14 return sales_amount * sales_price; 15 } 16 17 18 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out,const BookSale&item){ 19 using std::left; 20 using std::setw; 21 22 out<<left; 23 out << item.rb << '\n' 24 << setw(15) << "售价:" << item.sales_price << '\n' 25 << setw(15) << "销售数量:" << item.sales_amount << '\n' 26 << setw(15) << "营收:" << item.get_revenue(); 27 return out; 28 }
task2.cpp
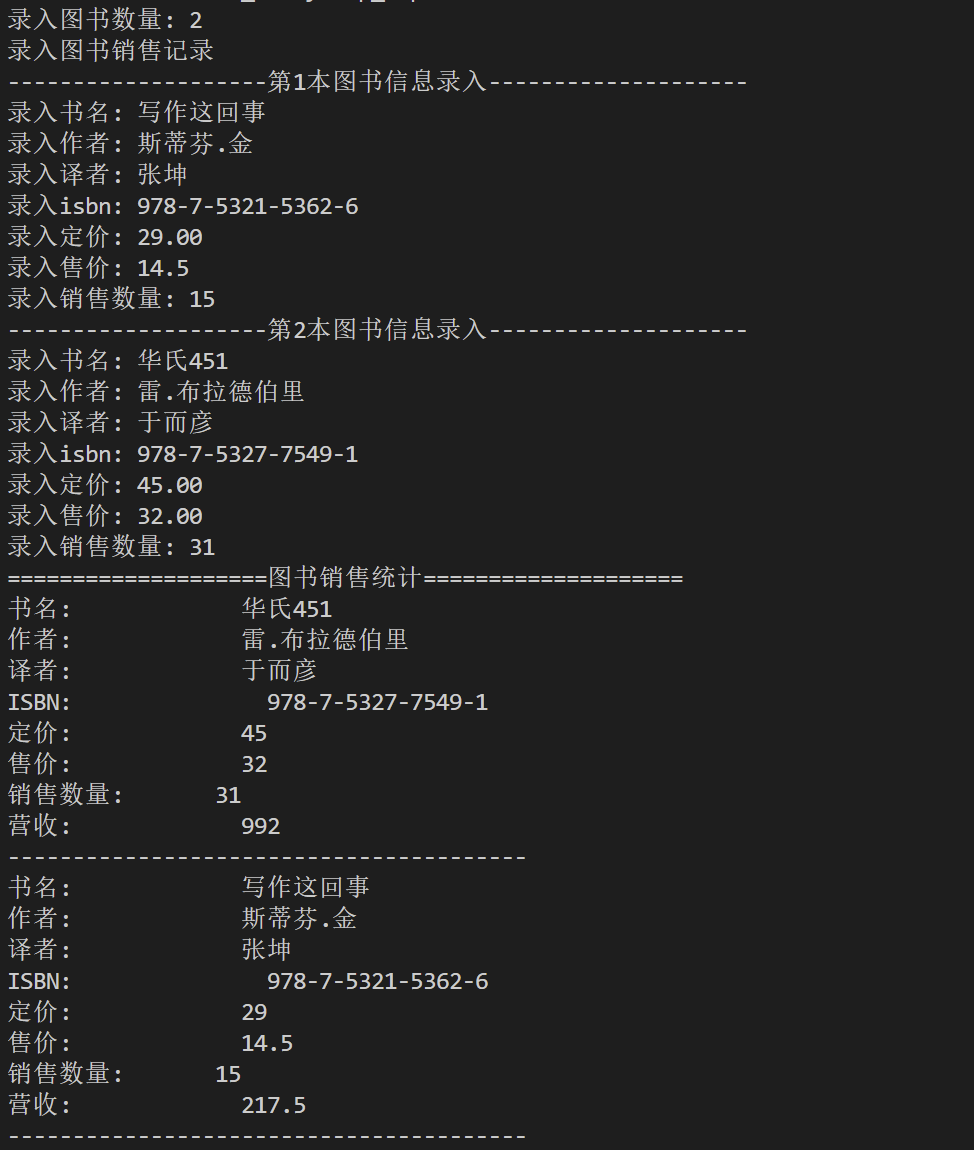
#include "booksale.hpp" #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> //按图书销售数额比较 bool compare_by_amount(const BookSale &x1, const BookSale &x2) { return x1.get_amount() > x2.get_amount(); } void test() { using namespace std; vector<BookSale> sales_lst; // 存放图书销售记录 int books_number; cout << "录入图书数量: "; cin >> books_number; cout << "录入图书销售记录" << endl; for(int i = 0; i < books_number; ++i) { string name, author, translator, isbn; float price; cout << string(20, '-') << "第" << i+1 << "本图书信息录入" << string(20, '-') <<endl; cout << "录入书名: "; cin >> name; cout << "录入作者: "; cin >> author; cout << "录入译者: "; cin >> translator; cout << "录入isbn: "; cin >> isbn; cout << "录入定价: "; cin >> price; Book book(name, author, translator, isbn, price); float sales_price; int sales_amount; cout << "录入售价: "; cin >> sales_price; cout << "录入销售数量: "; cin >> sales_amount; BookSale record(book, sales_price, sales_amount); sales_lst.push_back(record); } // 按销售册数排序 sort(sales_lst.begin(), sales_lst.end(), compare_by_amount); // 按销售册数降序输出图书销售信息 cout << string(20, '=') << "图书销售统计" << string(20, '=') << endl; for(auto &t: sales_lst) { cout << t << endl; cout << string(40, '-') << endl; } } int main() { test(); }
运行结果
回答问题
问题1:重载运算符<<
(1)找出运算符 << 被重载了几处?分别用于什么类型?
两处,都是用于友元函数
(2)找出使用重载 << 输出对象的代码,写在下面。
out << item.rb
cout << t << endl;
问题2:图书销售统计
(1)图书销售记录"按销售数量降序排序",代码是如何实现的?
bool compare_by_amount(const BookSale &x1, const BookSale &x2) {
return x1.get_amount() > x2.get_amount();
}
(2)拓展(选答*):如果使用lambda表达式,如何实现"按销售数量降序排序"?
sort(sales_lst.begin(), sales_lst.end(),[](const BookSale &x1, const BookSale &x2){
return x1.get_amount() > x2.get_amount();
}
);
task3
task3_1.cpp
1 #include<iostream> 2 3 //类A定义 4 class A{ 5 public: 6 A(int x0,int y0); 7 void display() const; 8 private: 9 int x,y; 10 }; 11 12 A::A(int x0,int y0):x{x0},y{y0}{} 13 14 void A::display() const{ 15 std::cout<<x<<","<<y<<"\n"; 16 } 17 18 class B{ 19 public: 20 B(double x0,double y0); 21 void display() const; 22 private: 23 double x,y; 24 }; 25 26 B::B(double x0,double y0):x{x0},y{y0}{} 27 28 void B::display() const{ 29 std::cout << x << ", " << y << '\n'; 30 } 31 32 void test(){ 33 std::cout << "测试类A: " << '\n'; 34 A a(3, 4); 35 a.display(); 36 std::cout << "\n测试类B: " << '\n'; 37 B b(3.2, 5.6); 38 b.display(); 39 } 40 int main(){ 41 test(); 42 }

task3_2.cpp
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 4 //定义类模板 5 template<typename T> 6 class X{ 7 public: 8 X(T x0,T y0); 9 void display(); 10 private: 11 T x,y; 12 }; 13 14 template<typename T> 15 X<T>::X(T x0,T y0):x{x0},y{y0}{} 16 17 template<typename T> 18 void X<T>::display(){ 19 std::cout<<x<<","<<y<<'\n'; 20 } 21 22 void test(){ 23 std::cout<<"测试1:用int实例化类模板X"<<'\n'; 24 X<int> x1(3,4); 25 x1.display(); 26 27 std::cout << "\n测试2: 用double实例化类模板X" << '\n'; 28 X<double> x2(3.2, 5.6); 29 x2.display(); 30 31 std::cout << "\n测试3: 用string实例化类模板X" << '\n'; 32 X<std::string> x3("hello", "oop"); 33 x3.display(); 34 } 35 36 int main(){ 37 test(); 38 }

task4
pet.hpp
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 4 //抽象类MachinePet 5 class MachinePet{ 6 public: 7 MachinePet(const std::string &name):nickname{name}{}; 8 const std::string& get_nickname() const{ return nickname; }; 9 virtual std::string talk() const=0; 10 virtual ~MachinePet()=default; 11 private: 12 std::string nickname; //昵称 13 }; 14 15 class PetCat:public MachinePet{ 16 public: 17 PetCat(const std::string& name):MachinePet(name){} 18 std::string talk() const override{ 19 return "miao wu~"; 20 } 21 }; 22 23 class PetDog:public MachinePet{ 24 public: 25 PetDog(const std::string& name):MachinePet(name){} 26 std::string talk() const override{ 27 return "wang wang~"; 28 } 29 };
task4.cpp
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <memory> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include "pet.hpp" 5 void test1() { 6 std::vector<MachinePet *> pets; 7 pets.push_back(new PetCat("miku")); 8 pets.push_back(new PetDog("da huang")); 9 for(MachinePet *ptr: pets) { 10 std::cout << ptr->get_nickname() << " says " << ptr->talk() << '\n'; 11 delete ptr; // 须手动释放资源 12 } 13 } 14 void test2() { 15 std::vector<std::unique_ptr<MachinePet>> pets; 16 pets.push_back(std::make_unique<PetCat>("miku")); 17 pets.push_back(std::make_unique<PetDog>("da huang")); 18 for(auto const &ptr: pets) 19 std::cout << ptr->get_nickname() << " says " << ptr->talk() << '\n'; 20 } 21 void test3() { 22 // MachinePet pet("little cutie"); // 编译报错:无法定义抽象类对象 23 const PetCat cat("miku"); 24 std::cout << cat.get_nickname() << " says " << cat.talk() << '\n'; 25 const PetDog dog("da huang"); 26 std::cout << dog.get_nickname() << " says " << dog.talk() << '\n'; 27 } 28 int main() { 29 std::cout << "测试1: 使用原始指针\n"; 30 test1(); 31 std::cout << "\n测试2: 使用智能指针\n"; 32 test2(); 33 std::cout << "\n测试3: 直接使用类\n"; 34 test3(); 35 }
运行结果

task5
Complex.hpp
1 /* 2 问题场景描述 3 自定义简化版类模板 Complex , 实现类似C++标准库类模板 complex ,支持对类型的参数化。具体要求如下: 4 支持实例化类模板与各种构造 5 如 Complex<double> c1; Complex<double> c2(1.0, 2.0); Comlex<double>c3(c2); 6 提供接口 get_real() , get_imag() 返回实部和虚部 7 对类模板重载运算符,支持如下操作: c1 += c2 , c1 + c2 , c1 == c2 , cin >> c1 >> c2 , cout 8 << c1 << c2 9 */ 10 #include<iostream> 11 12 template<typename T> class Complex; 13 14 template<typename T> 15 std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, Complex<T>& c); 16 17 template<typename T> 18 class Complex{ 19 public: 20 Complex()=default; 21 Complex(T real_,T imag_):real{real_},imag{imag_}{} 22 T get_real() const{ return real; } 23 T get_imag() const{ return imag; } 24 Complex& operator+=(const Complex<T>& c){ 25 this->real+=c.real; 26 this->imag+=c.imag; 27 return *this; 28 } 29 friend std::istream& operator>> <T>(std::istream& in,Complex<T> &c); 30 private: 31 T real,imag; 32 }; 33 34 template<typename T> 35 Complex<T> operator+(const Complex<T>& c1,const Complex<T>& c2){ 36 return Complex<T>(c1.get_real()+c2.get_real(),c1.get_imag()+c2.get_imag()); 37 } 38 39 template<typename T> 40 bool operator==(const Complex<T>& c1,const Complex<T>& c2){ 41 if(c1.get_real()==c2.get_real()&&c1.get_imag()==c2.get_imag()) return true; 42 return false; 43 } 44 45 template<typename T> 46 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out,const Complex<T>& c){ 47 out << c.get_real(); 48 out << (c.get_imag() >= 0 ? "+" : "") << c.get_imag() << "i"; 49 return out; 50 } 51 52 template<typename T> 53 std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in,Complex<T>& c){ 54 in>>c.real>>c.imag; 55 return in; 56 }
task5.cpp
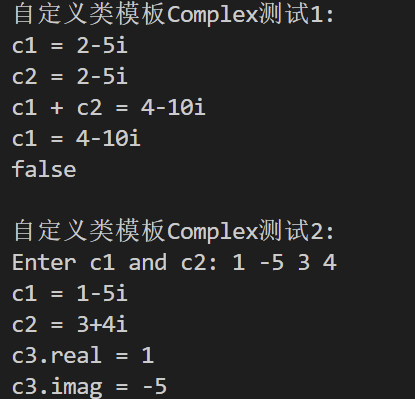
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "Complex.hpp" 3 void test1() { 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::boolalpha; 6 Complex<int> c1(2, -5), c2(c1); 7 cout << "c1 = " << c1 << '\n'; 8 cout << "c2 = " << c2 << '\n'; 9 cout << "c1 + c2 = " << c1 + c2 << '\n'; 10 c1 += c2; 11 cout << "c1 = " << c1 << '\n'; 12 cout << boolalpha << (c1 == c2) << '\n'; 13 } 14 void test2() { 15 using std::cin; 16 using std::cout; 17 Complex<double> c1, c2; 18 cout << "Enter c1 and c2: "; 19 cin >> c1 >> c2; 20 cout << "c1 = " << c1 << '\n'; 21 cout << "c2 = " << c2 << '\n'; 22 const Complex<double> c3(c1); 23 cout << "c3.real = " << c3.get_real() << '\n'; 24 cout << "c3.imag = " << c3.get_imag() << '\n'; 25 } 26 int main() { 27 std::cout << "自定义类模板Complex测试1: \n"; 28 test1(); 29 std::cout << "\n自定义类模板Complex测试2: \n"; 30 test2(); 31 }
运行结果




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号