20243310《Python程序设计》实验四报告
课程:《Python程序设计》实验四报告
班级: 2433
姓名: 倪昊
学号:20243310
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2025年6月8日
必修/选修: 公选课
1.实验内容
设计一个基于历史天气数据的天气预测程序,主要实现以下功能:
天气数据管理:
存储每日天气数据(日期、最高温、最低温、天气状况)
添加和管理历史天气记录
天气预测算法:
使用加权移动平均法预测温度
基于最近天气模式预测天气状况
考虑温度趋势进行预测调整
预测可视化:
生成明日天气预报
展示预测结果与实际天气对比
- 实验过程及结果
实验过程:
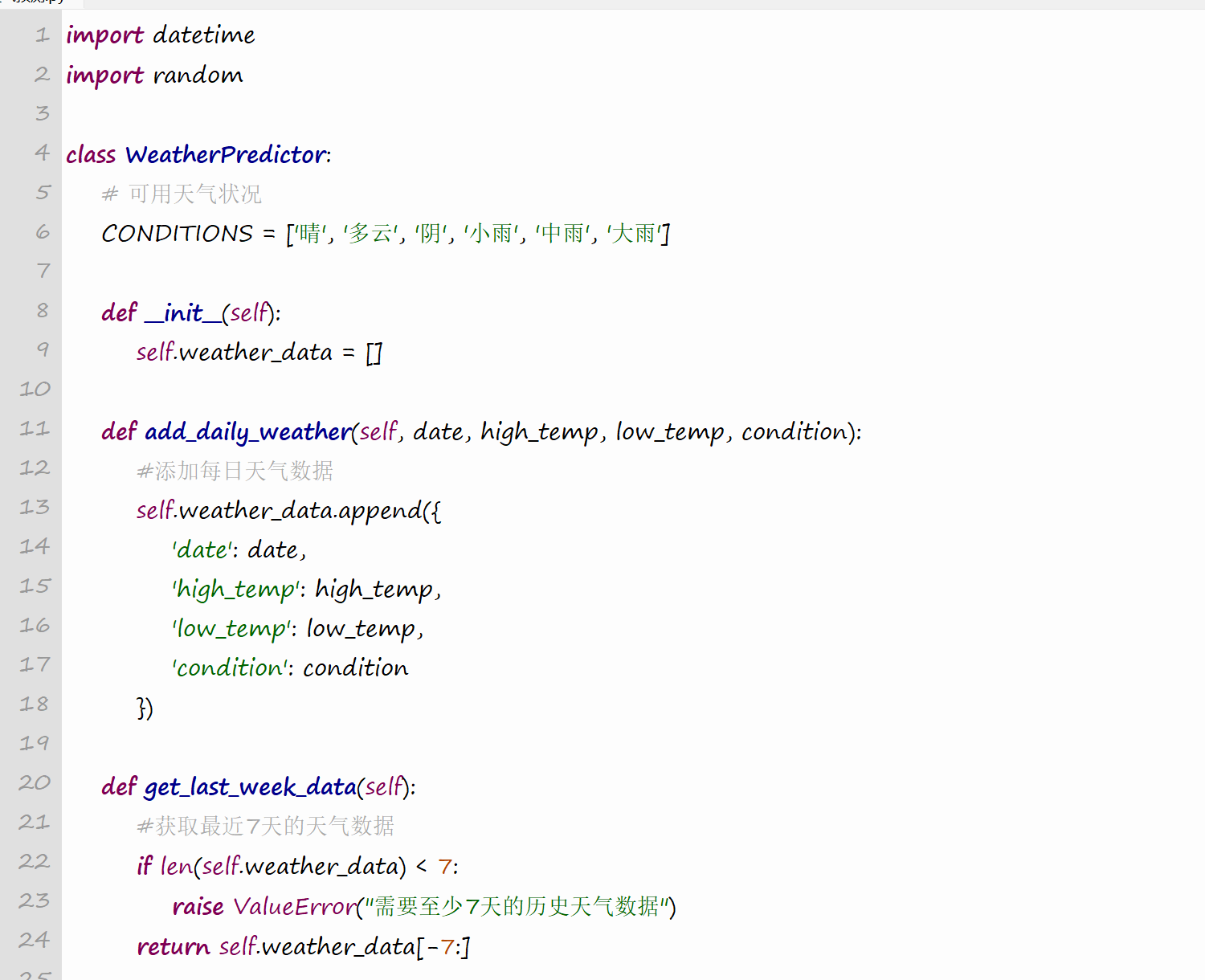
(1) 设计天气数据代码
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import datetime
import random
class WeatherPredictor:
# 可用天气状况
CONDITIONS = ['晴', '多云', '阴', '小雨', '中雨', '大雨']
def __init__(self):
self.weather_data = []
def add_daily_weather(self, date, high_temp, low_temp, condition):
#添加每日天气数据
self.weather_data.append({
'date': date,
'high_temp': high_temp,
'low_temp': low_temp,
'condition': condition
})
def get_last_week_data(self):
#获取最近7天的天气数据
if len(self.weather_data) < 7:
raise ValueError("需要至少7天的历史天气数据")
return self.weather_data[-7:]
def predict_tomorrow(self):
#预测明天的天气
last_week = self.get_last_week_data()
# 温度预测 - 加权平均(最近日期权重更大)
weights = [0.1, 0.1, 0.15, 0.15, 0.2, 0.2, 0.25]
avg_temp = sum((d['high_temp'] + d['low_temp'])/2 * w
for d, w in zip(last_week, weights)) / sum(weights)
#emm,这里大概就是把前几天的温度进行一个加权的计算,我就按照
#距离今天的远近来当权重,不算很合理
# 温度变化趋势预测
temp_changes = [d['high_temp'] - last_week[i-1]['high_temp']
for i, d in enumerate(last_week) if i > 0]
temp_trend = sum(temp_changes[-3:]) / 3 if temp_changes else 0
# 天气状况预测
# 优先考虑连续相同天气的趋势
recent_conditions = [d['condition'] for d in last_week[-3:]]
if all(c == recent_conditions[0] for c in recent_conditions):
condition = recent_conditions[0]
else:
# 否则选择本周最常见的天气
condition_counts = {c: 0 for c in self.CONDITIONS}
for d in last_week:
condition_counts[d['condition']] += 1
condition = max(condition_counts, key=condition_counts.get)
# 根据温度趋势调整温度预测
predicted_high = round(avg_temp + temp_trend * 0.7 + random.uniform(-1, 1), 1)
predicted_low = round(avg_temp - 5 + random.uniform(-1, 1), 1)
return {
'date': last_week[-1]['date'] + datetime.timedelta(days=1),
'high_temp': predicted_high,
'low_temp': predicted_low,
'condition': condition
}
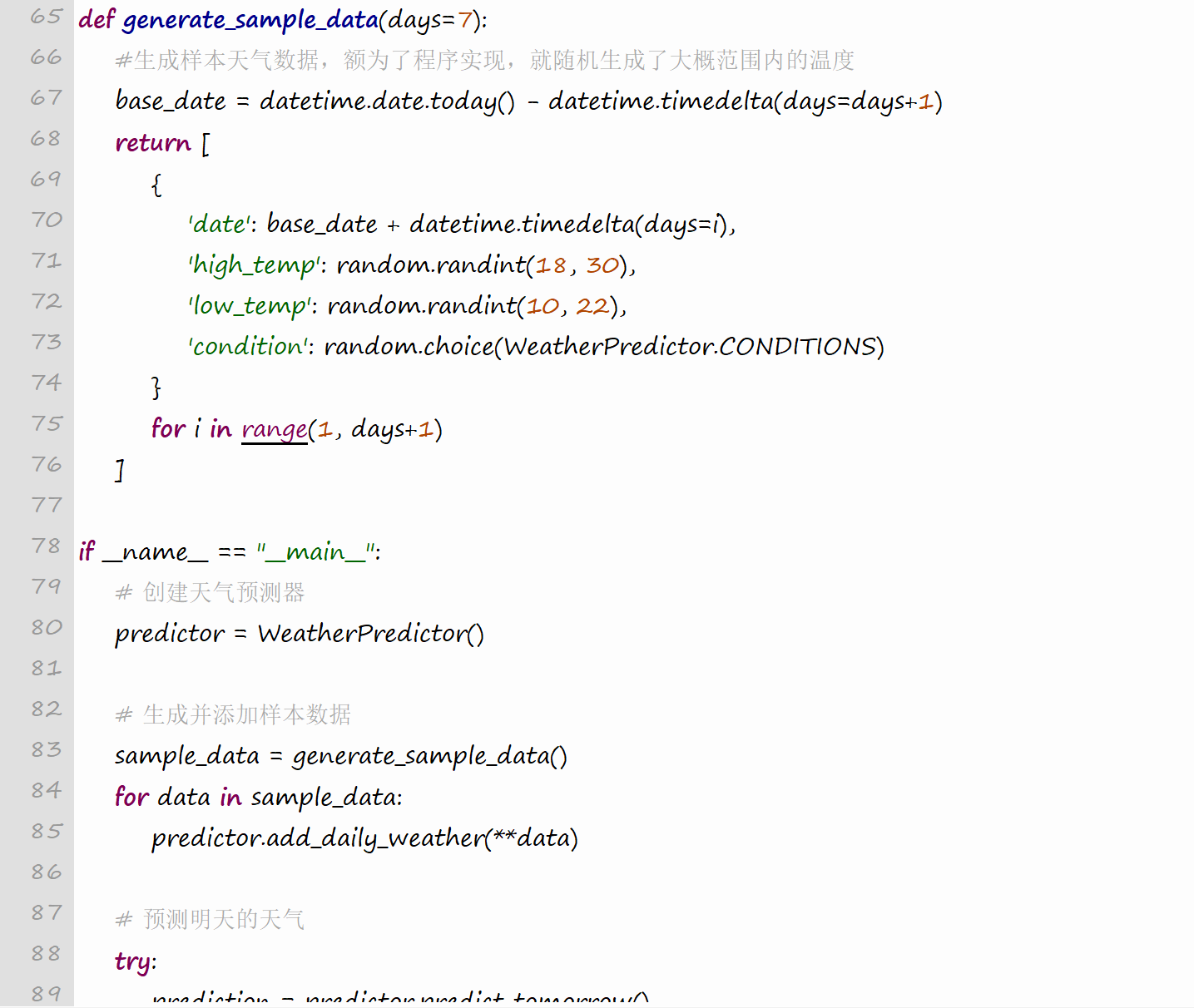
def generate_sample_data(days=7):
#生成样本天气数据,额为了程序实现,就随机生成了大概范围内的温度
base_date = datetime.date.today() - datetime.timedelta(days=days+1)
return [
{
'date': base_date + datetime.timedelta(days=i),
'high_temp': random.randint(18, 30),
'low_temp': random.randint(10, 22),
'condition': random.choice(WeatherPredictor.CONDITIONS)
}
for i in range(1, days+1)
]
if name == "main":
# 创建天气预测器
predictor = WeatherPredictor()
# 生成并添加样本数据
sample_data = generate_sample_data()
for data in sample_data:
predictor.add_daily_weather(**data)
# 预测明天的天气
try:
prediction = predictor.predict_tomorrow()
print("\n明日天气预报:")
print(f"日期: {prediction['date']}")
print(f"最高温度: {prediction['high_temp']}°C")
print(f"最低温度: {prediction['low_temp']}°C")
print(f"天气状况: {prediction['condition']}")
# 生成可能的实际天气进行比较
actual = {
'high_temp': prediction['high_temp'] + random.uniform(-3, 3),
'low_temp': prediction['low_temp'] + random.uniform(-2, 2),
'condition': random.choice(WeatherPredictor.CONDITIONS)
}
actual['high_temp'] = round(max(actual['high_temp'], prediction['low_temp'] + 2), 1)
actual['low_temp'] = round(min(actual['low_temp'], prediction['high_temp'] - 2), 1)
print("\n可能的实际天气:")
print(f"最高温度: {actual['high_temp']}°C")
print(f"最低温度: {actual['low_temp']}°C")
print(f"天气状况: {actual['condition']}")
except ValueError as e:
print(f"错误: {e}")
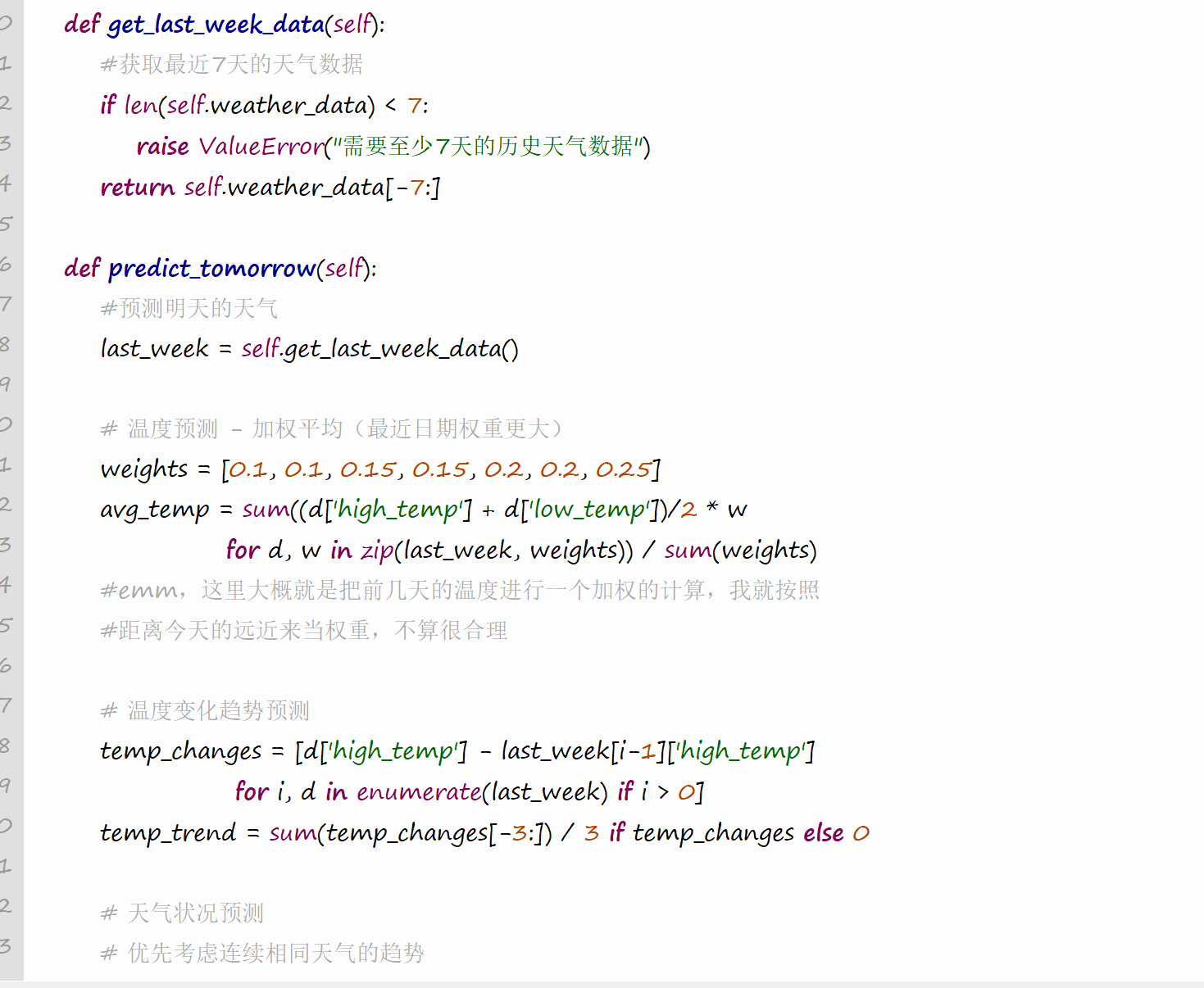
(2)算法核心逻辑
def predict_tomorrow(self):
last_week = self.get_last_week_data()
# 温度预测 - 加权平均(最近日期权重更大)
weights = [0.1, 0.1, 0.15, 0.15, 0.2, 0.2, 0.25]
avg_temp = sum((d['high_temp'] + d['low_temp'])/2 * w
for d, w in zip(last_week, weights)) / sum(weights)
# 温度变化趋势预测
temp_changes = [d['high_temp'] - last_week[i-1]['high_temp']
for i, d in enumerate(last_week) if i > 0]
temp_trend = sum(temp_changes[-3:]) / 3 if temp_changes else 0
实验结果:
明日天气预测:

- 实验中遇到的问题和解决过程
问题1:温度预测不准确
问题描述:初始版本仅使用简单平均法,导致预测温度与实际偏差较大
解决方案:
采用加权移动平均法,给近期数据更高权重(目前改动的)
添加温度趋势分析,考虑近期温度变化方向(AI说的我不会)
引入随机波动因子,模拟实际天气变化(更不会了)
问题2:天气状况预测模式单一
问题描述:最初只使用最常见天气状况预测,未考虑天气连续性
解决方案:
增加"连续相同天气检测"逻辑,如果最近3天天气相同则预测延续
引入天气状况转移概率模型,添加特殊天气模式检测(如连续阴雨后可能转晴)(AI说的,写不出来,临时AI一段程序加进去很多错)
- 其他(感悟、思考等)
算法选择的重要性:
天气预测需要平衡历史数据的权重和近期趋势的时效性
简单算法经过精心调优也能获得较好的预测效果
数据质量的关键作用:
发现历史数据中的异常值会显著影响预测准确性
考虑添加季节因素、地理位置等额外维度可提升模型表现
工程实践的收获:
从初始版本到最终产品经历多次迭代优化
进一步改进方向:
接入实时天气API获取更全面的数据
添加可视化图表展示温度变化趋势
实现7天天气预报功能
增加降雨量、湿度等更多气象参数预测
感悟::::::::::::
通过本次实验,我深刻理解了时间序列预测的基本原理和实践方法。虽然天气预测是一个复杂问题,但合理的特征选择和算法优化可以在小数据集上取得较好的结果。未来希望将这个程序扩展为完整的天气预报应用。
感谢老师一个学期以来的教导。师傅领进门,修行在个人,老师让我发现了python的乐趣,未来我会继续努力的!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号