剑指offer
1、判断栈的压入弹出序列
关键:模拟,借用一个辅助栈,每次按照入栈顺序压入元素,并判断栈顶元素是否与出栈序列元素相等,若相等则循环出栈,最后若辅助栈为空则该出栈序列合理

class Solution:
def validateStackSequences(self, pushed: List[int], popped: List[int]) -> bool:
stack=[]
j=0
for i in range(len(pushed)):
stack=append(pushed[i])
while stack and stack[-1]==popped[j]:
stack.pop()
j+=1
return not stack
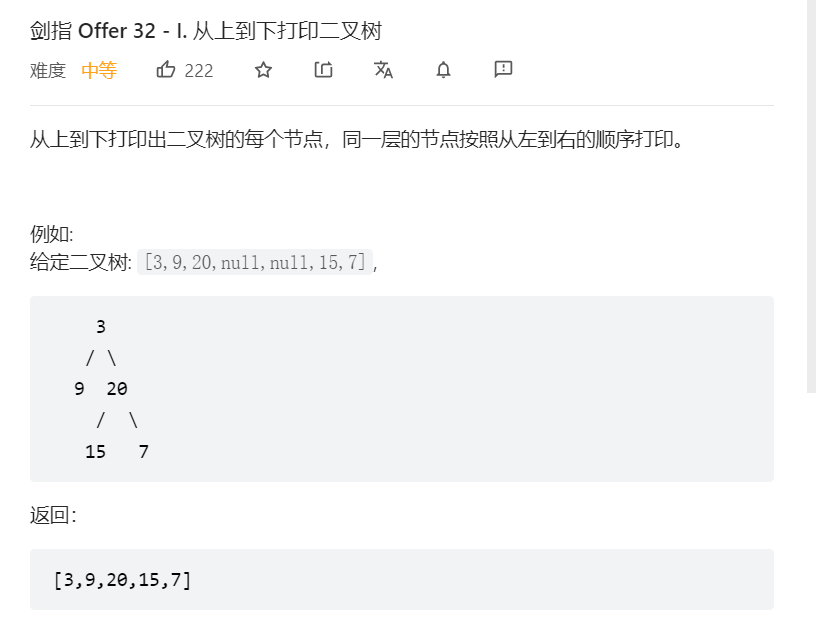
2、二叉树的层序遍历
关键:使用数据结构队列,collections.deque(),广度优先遍历
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
s=[]
queue=collections.deque()
queue.append(root)
while queue:
t=queue.popleft()
if t:
s.qppend(t.val)
else:
continue
queue.append(t.left)
queue.append(t.right)
return s
#扩展:要求按层输出
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
queue=collections.deque()
queue.append(root)
r=[]
while queue:
l=len(queue)
level=[]
for i in range(l):
t=queue.popleft()
if t:
level.append(t.val)
else:
continue
queue.append(t.left)
queue.append(t.right)
if level:
r.append(level)
return r
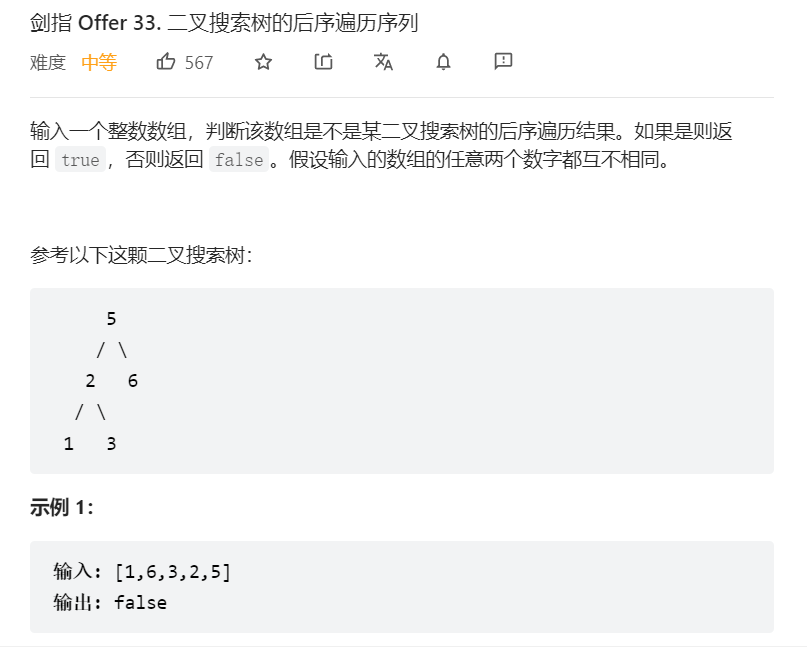
3、二叉搜索树的后序遍历
关键:递归,二叉搜索树节点为其左子树的上限,其右子树的下限,递归判断每棵子树是否符合条件
class Solution:
def verifyPostorder(self, postorder: List[int]) -> bool:
def func(i,j):
if i>=j:
return True
p=i
while postoerder[p]<postorder[j]:p+=1
m=p
while postorder[p]>postorder[j]:p+=1
return p==j and func(i,m-1) and func(m,j-1)
return func(0,len(postorder)-1)
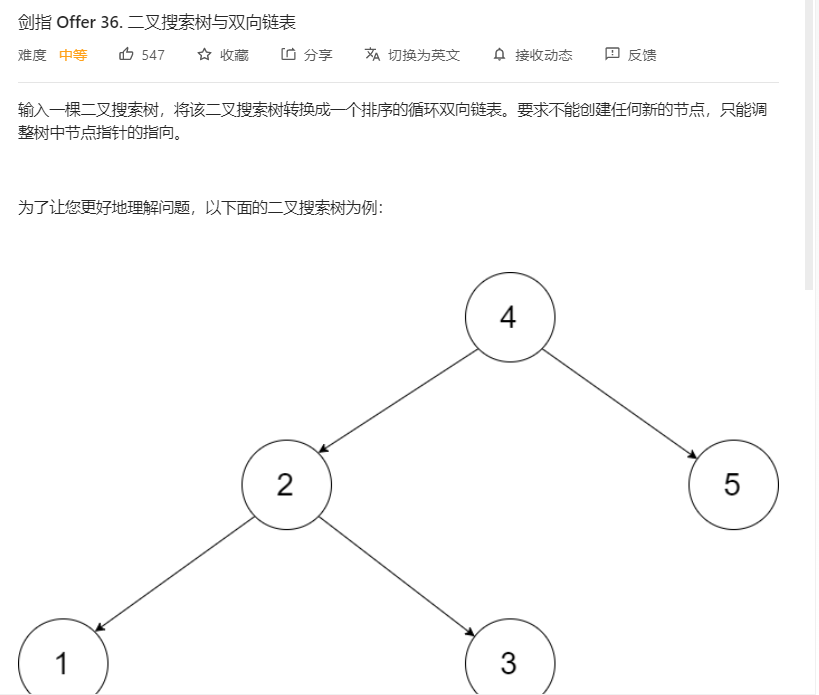
4、二叉搜索树与双向链表
关键:排序链表则需要中序遍历二叉树,并在修改每个节点的指针指向
class Solution:
def treeToDoublyList(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
def dfs(root):
if not root:
return
dfs(root.left)
if self.pre:
self.pre.right,root.left=root,self.pre
else:
self.head=root
self.pre=root
dfs(root.right)
if not root:
return
self.pre=None
dfs(root)
self.head.left,self.pre.right=slef.pre,self.head
5、连续子数组最大和
关键:将数组每个元素的值更新为前序和,最后输出最大前序和

class Solution:
def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
for i in range(1,len(nums)):
nums[i]+=max(nums[i-1],0)
return max(nums)6、最长不含重复字符的子字符串
关键:滑动窗口,注意窗口设置的细节,初始值设为1,且从数组第二个数开始遍历,最后更新start时要加上原来的start

class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
if not s:
return 0
max_l=1
start=0
for end in range(1,len(s)):
if s[end] not in s[start:end]:
max_l=max(max_l,end-start+1)
else:
start+=s[start:end].index(s[end])+1
return max_l
7、树的子结构
关键:先在A中寻找与节点B相同的节点,找到后再依次判断B是否为该节点子结构

class Solution:
def isSubStructure(self, A: TreeNode, B: TreeNode) -> bool:
def recur(A,B):
if not B: return True
if not A or A.val!=B.val:return False
return recur(A.left,B.left) and recur(A.right,B.right)
return bool(A and B) and (recur(A,B) or self.isSubStructure(A.left,B) or self.isSubStructure(A.right,B))
#判断B是否为A的子树或者B是否为A左子树的子树或B是否为A右子树的子树
8、二叉树的后序遍历
关键:遍历找出根节点,根节点为左子树上限,右子树下限
class Solution:
def verifyPostorder(self, postorder: List[int]) -> bool:
def recur(i,j):
if i>=j:
return True
p=i
while postorder[p]<postorder[j]:
p+=1
m=p
while postorder[p]>postorder[j]:
p+=1
return p==j and recur(i,m-1) and recur(m,j-1)
return recur(0,len(postorder)-1)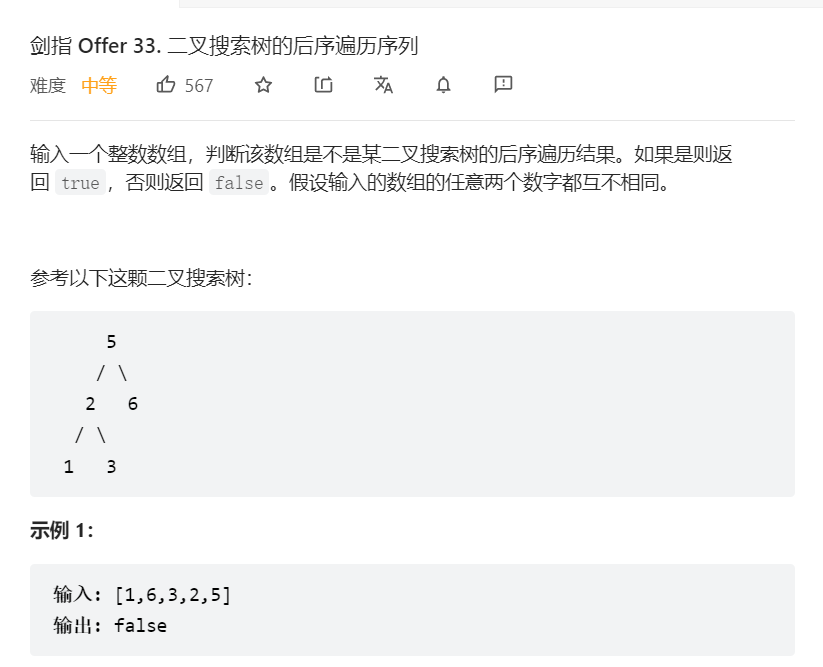
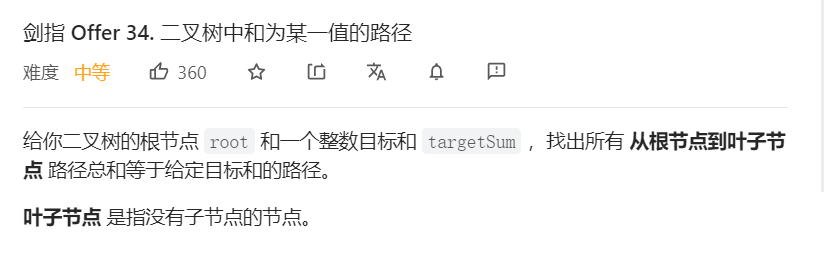
9、二叉树中和为某一值的路径
关键:先序遍历+路径记录
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res,path=[],[]
def recur(root,tar):
if noot root:return
path.append(root.val)
tar-=root.val
if tar==0 and not root.left and not root.right:
res.append(list(path))
recur(root.left,tar)
recur(root.right,tar)
path.pop()
recur(root,target)
return res
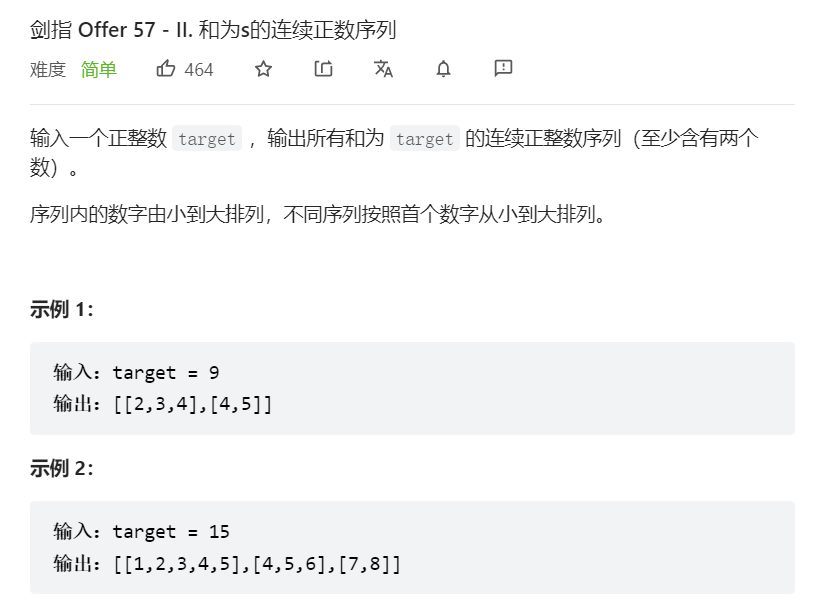
10、和为target的全部整数序列
class Solution:
def findContinuousSequence(self, target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
r=[]
i,j=1,1
s=0
while i<=target//2:
if s<target:
s+=j
j+=1
elif s>target:
s-=i
i+=1
else:
r.append(list(range(i,j)))
s-=i
i+=1
return r
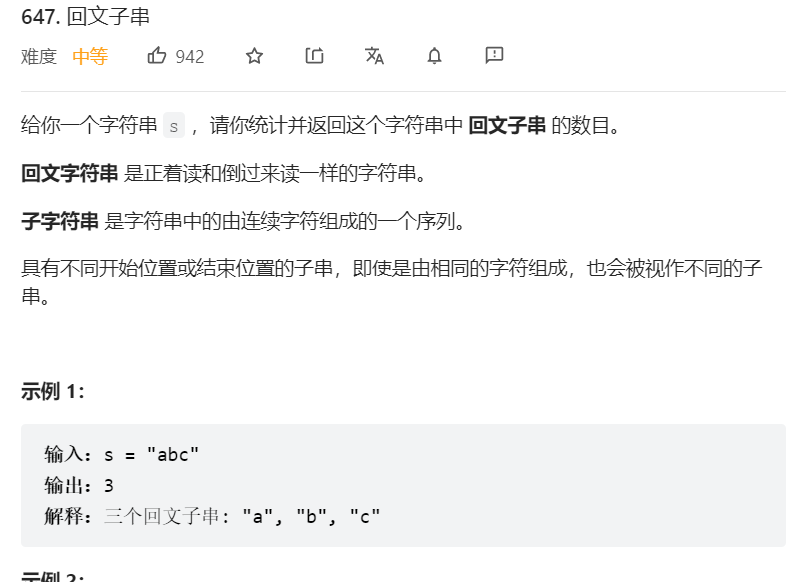
11、回文子串个数
关键:枚举
class Solution:
def countSubstrings(self, s: str) -> int:
c=0
for i in range(len(s)):
for j in range(i+1,len(s)+1):
if s[i:j]==s[i:j][::-1]:
c+=1
return c


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号