【08-02、03】ssh的常用参数、用法和sshd的常用参数
ssh的常用参数,用法和sshd的常用参数
ssh和sshd的区别:
ssh是ssh的客户端,在远程系统时进行可验证的加密安全访问。
sshd是服务端
1.ssh常用参数、用法
1.1 ssh使用方法
#使用格式 ssh [user@]host [COMMAND] #ssh root@10.0.1.10 -p 9527 ssh [-l user] host [COMMAND] #ssh -l root 10.0.1.11 -p 9527 #选项参数 -p #远程服务器监听的端口 -b #指定连接的源IP -v #调试模式 -C #压缩方式 -X #支持x11转发 -t #强制伪tty分配,如:ssh -t 10.0.0.5 ssh -t 10.0.0.6 ssh 10.0.0.7 这个可以实现多跳中的逐级登陆,最后达到可以登录最后一个服务器的目的 -o #option 如:-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i #指定私钥路径,实现基于key验证,默认为: ~/.ssh/id_dsa,~/.ssh/id_ecdsa, ~/.ssh/id_ed25519,~/.ssh/id_rsa
1.2 ssh连接类型
简单来说:区别是公钥谁先发,密码方式服务器发公钥。公钥连接则是客户端发起公钥
1.2.1 使用密码进行连接
连接过程:
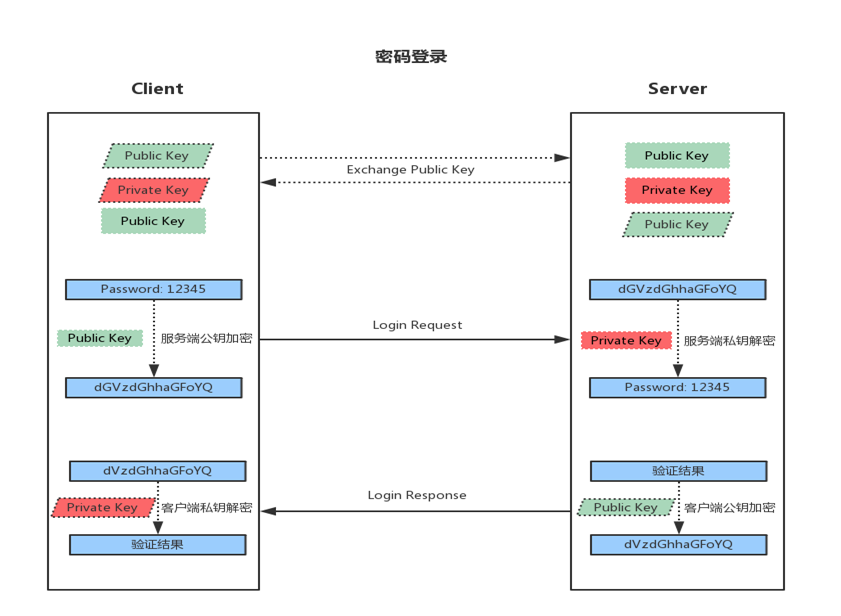
1. 客户端发起ssh请求,服务器会把自己的公钥发送给用户 2. 用户会根据服务器发来的公钥对密码进行加密 3. 加密后的信息回传给服务器,服务器用自己的私钥解密,如果密码正确,则用户登录成功
1.2.2 使用秘钥进行连接
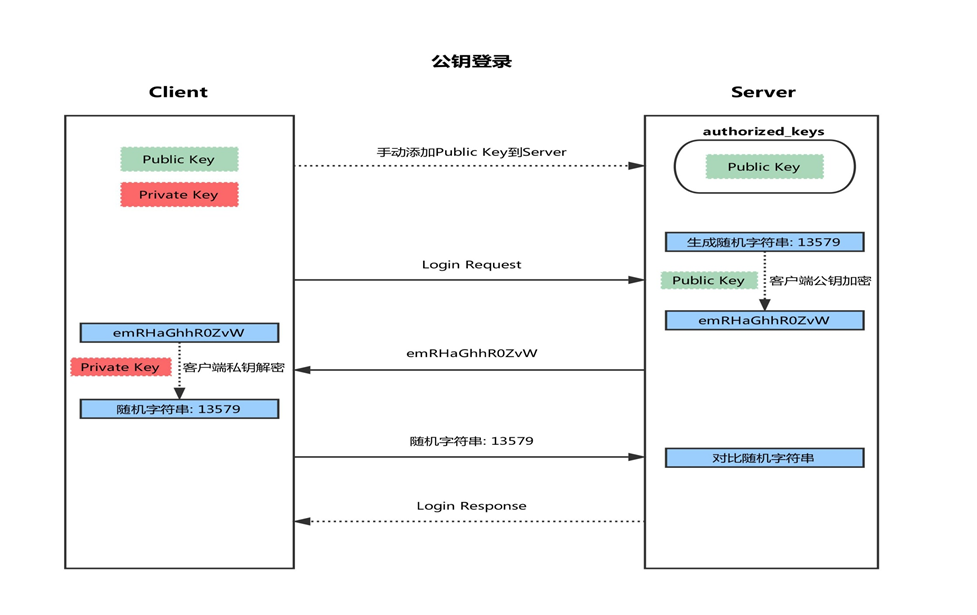
1. 首先在客户端生成一对密钥(ssh-keygen) 2. 并将客户端的公钥ssh-copy-id 拷贝到服务端 3. 当客户端再次发送一个连接请求,包括ip、用户名 4. 服务端得到客户端的请求后,会到authorized_keys中查找,如果有响应的IP和用户,就会随机生成一个字符串,例如:magedu 5. 服务端将使用客户端拷贝过来的公钥进行加密,然后发送给客户端 6. 得到服务端发来的消息后,客户端会使用私钥进行解密,然后将解密后的字符串发送给服务端 7. 服务端接受到客户端发来的字符串后,跟之前的字符串进行对比,如果一致,就允许免密码登录
1.3 ssh客户端配置文件
# Host * # ForwardAgent no #转发代理 # ForwardX11 no #X11转发 慎用 # PasswordAuthentication yes #密码认证 # HostbasedAuthentication no #yes的话开启主机认证 # GSSAPIAuthentication no #yes的时候登录速度会慢,可能因为GSS-API认证有问题 # GSSAPIDelegateCredentials no #yes的时候登录速度慢,GSS-API问题 # GSSAPIKeyExchange no #如果不启用GSSAPIDelegateCredentials的话可以启用该选项保证安全 # GSSAPITrustDNS no #似乎可以欺骗GSSAPI反向解析正确的主机名 # BatchMode no #yes的话密码查询被禁用 # CheckHostIP yes #yes的话会检查known_hosts文件中的IP地址 # AddressFamily any #连接时使用指定的地址,'any','inet','inet6' # ConnectTimeout 0 #连接超时时间单位'秒' 关闭或却是无法使用时候生效,而不是拒绝连接的 # StrictHostKeyChecking ask #如果为yes 不会自动将主机秘钥添加到~/.ssh/known_hosts文件,相对安全 [yes|no|ask] ask为询问 # IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa #1. 读取验证身份的文件位置protocol version 1(协议版本1)默认为~/.ssh/identity # IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_dsa #2. protocol version 2(协议版本2) ~/.ssh/id_rsa和~/.ssh/id_dsa # IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ecdsa #3. 目录转义: %d(本地用户主目录) %u(本地用户名) %I(本地主机名) %h(远程主机名) %r(远程用户名) # IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 # Port 22 #指定要在远程主机上连接的端口号 # Ciphers aes128-ctr,aes192-ctr,aes256-ctr,aes128-cbc,3des-cbc # MACs hmac-md5,hmac-sha1,umac-64@openssh.com # EscapeChar ~ #设置转义字符 默认为~ # Tunnel no #客户端与服务器之间的设备转发 参数 # TunnelDevice any:any #指定要在客户端(local_tun)和服务器(remote_tun) 上打开tun4设备 # PermitLocalCommand no #允许通过LocalCommand选项使用ssh中的命令转义序列 # VisualHostKey no #如果为yes登录时还会输出主机秘钥的ASCII码 # ProxyCommand ssh -q -W %h:%p gateway.example.com #用于链接服务器的命令 %h替换要连接主机名 %p为端口 # RekeyLimit 1G 1h #指定在重新协商会话密钥之前可以传输的最大数据量
参考文件:客户端配置文件
2.sshd服务常用参数
2.1 sshd常用参数及使用方式
#修改配置后需要重启服务 systemctl restart sshd systemctl reload sshd 重新加载配置文件 vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config Port 9527 #默认端口,建议修改为10000<=65535重启sshd后生效 PasswordAuthentication no #建议关闭 使用公钥登录 关闭前先创建好公钥登录方式 PermitRootLogin no #建议关闭 不要使用root用户来登录服务器 StrictModes yes #检查.ssh/文件的所有者,权限等 MaxAuthTries 6 #指定每个连接允许的最大尝试次数,失败次数超过一般则记录进日志,默认为6 MaxSessions 10 #指定每个网络连接允许的最大打开会话数 默认为10 PubkeyAuthentication yes #是否允许公钥认证 默认为yes PermitEmptyPasswords no #是否允许空密码的用户登录 默认为no GatewayPorts no #指定是否允许远程主机连接到为客户端转发的端口 ClientAliveInterval 10 #当几秒没收到客户端数据则向客户端发送alive消息并等候应答 0为不发送 ClientAliveCountMax 3 #发送alive的次数,发送到上限后会强制断开连接 alive比TCPKeepAlive更加安全,如果值为15 则会在45秒后强制断开 UseDNS no #不使用DNS查询客户端 关闭可提高速度 GSSAPIAuthentication no #是否允许使用基于 GSSAPI 的用户认证。默认值为"no" 关闭可提高链接速度 MaxStartups 10:30:100 #未验证机器连接数,后续丢弃,直到验证成功或断开 #用户黑白名单 Denyusers user1 #设定用户黑名单,添加后无法使用ssh进行登录 Allowusers user2 user3 #设定用户白名单,默认不在白名单的用户无法登录
SSH服务注意事项
- 建议使用非默认端口
- 禁止使用protocol version 1
- 限制可登录用户
- 设定空闲会话超时时长
- 利用防火墙设置ssh访问策略
- 仅监听特定的IP地址
- 基于口令认证时,使用强密码策略,比如:tr -dc A-Za-z0-9_ < /dev/urandom | head -c 12|xargs
- 使用基于密钥的认证
- 禁止使用空密码
- 禁止root用户直接登录
- 限制ssh的访问频度和并发在线数
- 经常分析日志
2.2 sshd默认配置文件详解
[root@rhel011 ~]# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
#Port 22 #默认端口,建议修改为10000<=65535重启sshd后生效 #AddressFamily any #指定使用地址[any|inet|inet6] #ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #监听本机IPv4地址 #ListenAddress :: #监听本机IPv6地址 HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key #设置包含私人秘钥的文件 HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key # Ciphers and keying 密码和秘钥↓ #RekeyLimit default none # Logging #SyslogFacility AUTH #有人登录ssh登录系统 记录的信息类型[AUTH|AUTHPRIV] SyslogFacility AUTHPRIV #LogLevel INFO #日志信息级别[QUIET|FATAL|ERROR|INFO|VERBOSE|DEBUG|DEBUG1|DEBUG2|DEBUG3] DEBUG级别会侵犯隐私 # Authentication: #LoginGraceTime 2m #如果没有登录成功,将会断开连接 默认为120秒 PermitRootLogin yes #是否允许root登录 默认允许 建议为no 使用秘钥登录 #StrictModes yes #ssh在接受登录前是否检查home和rhosts文件的权限和所有权,建议为yes 因为新手会把自己的目录和文件设置成任何人都有权限 #MaxAuthTries 6 #指定每个连接允许的最大尝试次数,失败次数超过一般则记录进日志,默认为6 #MaxSessions 10 #指定每个网络连接允许的最大打开会话数 默认为10 #PubkeyAuthentication yes #是否允许公钥认证 默认为yes # The default is to check both .ssh/authorized_keys and .ssh/authorized_keys2 # but this is overridden so installations will only check .ssh/authorized_keys AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys #用户身份验证默认存储位置 #AuthorizedPrincipalsFile none #AuthorizedKeysCommand none #指定脚本查找用户的公钥文件做认证,登录认证层面调用,可以调用指定参数进行认证 通过相关配置 AuthorizedKeysCommandUser 指定脚本的执行用户 #在 8.x 之前的版本,优先使用 AuthorizedKeysCommand 进行认证,如果认证失败,继续使用 AuthorizedKeysFile 认证 #AuthorizedKeysCommandUser nobody # For this to work you will also need host keys in /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hosts #HostbasedAuthentication no #指定是否允许 rhosts 或 /etc/hosts.equiv 身份验证以及公钥客户端主机身份验证(基于主机的身份验证) # Change to yes if you don't trust ~/.ssh/known_hosts for # HostbasedAuthentication #IgnoreUserKnownHosts no # Don't read the user's ~/.rhosts and ~/.shosts files #IgnoreRhosts yes #指定.rhosts和.shosts文件不会在RhostsRSAAuthentication或HostbasedAuthentication中使用 # To disable tunneled clear text passwords, change to no here! #要禁用隧道明文密码,请在此处更改为 no #PasswordAuthentication yes #PermitEmptyPasswords no #是否允许空密码的用户登录 默认为no PasswordAuthentication yes #是否使用密码验证。设置为no后会转而使用秘钥登录 # Change to no to disable s/key passwords #ChallengeResponseAuthentication yes ChallengeResponseAuthentication no #是否允许质疑 应答(challenge-response)认证 # Kerberos options #KerberosAuthentication no #是否允许Kerberos(秘钥)认证登录 #KerberosOrLocalPasswd yes #如果Kerberos验证失败,那么还会通过其他机制认证比如(/etc/passwd) #KerberosTicketCleanup yes #如果用户在退出登录后会自动销户 #KerberosGetAFSToken no #如果使用了 AFS 并且该用户有一个 Kerberos 5 TGT,那么开启该指令后,将会在访问用户的家目录前尝试获取一个 AFS token #KerberosUseKuserok yes #是否查看.k5login文件中的用户别名 # GSSAPI options GSSAPIAuthentication yes #是否允许使用基于 GSSAPI 的用户认证。默认值为"no" GSSAPICleanupCredentials no #是否在用户退出登录后自动销毁用户凭证缓存。默认值是"yes" #GSSAPIStrictAcceptorCheck yes #是否对客户端进行严格的身份认证.若为”yes”,则客户端会在服务端被验证主机名 #GSSAPIKeyExchange no #指定是否允许基于 GSSAPI的密钥交换 #GSSAPIEnablek5users no # Set this to 'yes' to enable PAM authentication, account processing, # and session processing. If this is enabled, PAM authentication will # be allowed through the ChallengeResponseAuthentication and # PasswordAuthentication. Depending on your PAM configuration, # PAM authentication via ChallengeResponseAuthentication may bypass # the setting of "PermitRootLogin without-password". # If you just want the PAM account and session checks to run without # PAM authentication, then enable this but set PasswordAuthentication # and ChallengeResponseAuthentication to 'no'. # WARNING: 'UsePAM no' is not supported in Fedora and may cause several # problems. UsePAM yes #AllowAgentForwarding yes #指定是否允许ssh-agent转发 #AllowTcpForwarding yes #指定是否允许 TCP 转发 #GatewayPorts no #指定是否允许远程主机连接到为客户端转发的端口 X11Forwarding yes #指定是否允许 X11 转发 #X11DisplayOffset 10 #指定X11转发的第一个可用的显示区(display)数字。默认值是10.这个可以用于防止sshd占用了真实的X11服务器显示区,从而发生混淆 #X11UseLocalhost yes #是否应当将X11转发服务器绑定到本地loopback地址。默认值是"yes"。 #PermitTTY yes #指定是否允许设备转发 # It is recommended to use pam_motd in /etc/pam.d/sshd instead of PrintMotd, # as it is more configurable and versatile than the built-in version. PrintMotd no #PrintLastLog yes #指定 sshd(8) 是否在每一次交互式登录时打印最后一位用户的登录时间。默认值是"yes" #TCPKeepAlive yes #指定系统是否向客户端发送 TCP keepalive 消息。默认值是"yes"。可以检测到死连接、连接不当关闭、客户端崩溃等异常 #PermitUserEnvironment no #指定是否允许 sshd(8) 处理 ~/.ssh/environment 以及 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys 中的 environment= 选项。 #默认值是"no"。如果设为"yes"可能会导致用户有机会使用某些机制(比如 LD_PRELOAD)绕过访问控制,造成安全漏洞。 #Compression delayed #是否对通信数据进行加密,还是延迟到认证成功之后再对通信数据加密。[yes|delayed] #ClientAliveInterval 0 #当几秒没收到客户端数据则向客户端发送alive消息并等候应答 0为不发送 #ClientAliveCountMax 3 #发送alive的次数,发送到上限后会强制断开连接 alive比TCPKeepAlive更加安全,如果值为15 则会在45秒后强制断开 #UseDNS no #指定 sshd(8) 是否应该对远程主机名进行反向解析,以检查此主机名是否与其IP地址真实对应。默认值为"yes"。 #PidFile /var/run/sshd.pid #指定在哪个文件中存放SSH守护进程的进程号,默认为 /var/run/sshd.pid 文件 #MaxStartups 10:30:100 #未验证机器连接数,后续丢弃,直到验证成功或断开 #PermitTunnel no #指定是否允许设备转发 #ChrootDirectory none #指定认证后chroot(2)的路径。此路径及其所有组件必须是任何其他用户或组不可写的根目录。在chroot之后sshd(8) 将工作目录更改为用户的主目录。 #VersionAddendum none # no default banner path #Banner none #将这个指令指定的文件中的内容在用户进行认证前显示给远程用户。 # Accept locale-related environment variables #语言环境变量 AcceptEnv LANG LC_CTYPE LC_NUMERIC LC_TIME LC_COLLATE LC_MONETARY LC_MESSAGES AcceptEnv LC_PAPER LC_NAME LC_ADDRESS LC_TELEPHONE LC_MEASUREMENT AcceptEnv LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_ALL LANGUAGE AcceptEnv XMODIFIERS # override default of no subsystems Subsystem sftp /usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server #sfpt的目录 # Example of overriding settings on a per-user basis #Match User anoncvs # X11Forwarding no #指定是否允许 X11 转发 # AllowTcpForwarding no #指定是否允许 TCP 转发 # PermitTTY no #指定是否允许tun (4)设备转发 # ForceCommand cvs server #强制执行这里指定的命令而忽略客户端提供的任何命令。
参考文件:https://www.cnblogs.com/zqifa/p/ssh-2.html2.2 Linux下SSHD各配置项解释

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号