工厂模式的几种形态
依赖抽象,而不要依赖具体类,要尽可能让事情保持抽象。
简单工厂(Simple Factory)模式:又称静态工厂方法(Static Factory Methord)模式。
工厂方法(Factory Method)模式:又称多态性工厂(Polymorphic Factory)模式或虚拟构造子(Virtual Constructor)模式。
抽象工厂(Abstract Factory)模式:又称工具箱(Kit或Toolkit)模式。
简单工厂模式
简单工厂模式是类的创建,又叫静态工厂方法(Static Factory Methord)模式。简单工厂模式是由一个工厂对象决定创造哪一种产品类的实例。
下图所示的就是简单工厂模式的简略类图。
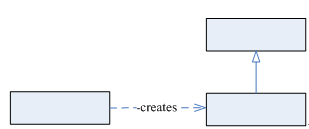
简单工厂模式,或称静态工厂方法模式,是不同工厂方法模式的一个特殊实现。在Java语言中,通常的工厂方法模式不能通过设计功能的退化给出静态工厂方法模式。
例子
比如有一个农场,生产各种水果,有苹果(Apple)、草莓(Strawberry)、葡萄(Grape);农场的园丁(FruitGardener)要根据客户的需求,提供相应的水果。下面看看是如何用简单工厂模式实现这个过程的,如下图:
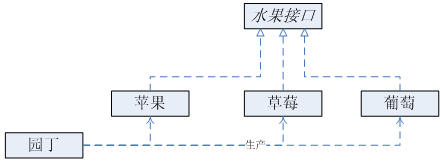
此模式的实现源码如下:
// 产品接口-水果接口:Fruit.java public interface Fruit { /** * 种植 */ void plant(); /** * 生长 */ void grow(); /** * 收获 */ void harvest(); }
// 产品-苹果类:Apple.java public class Apple implements Fruit { private int treeAge; /** * 种植 */ public void plant() { System.out.println("Apple has been planted."); } /** * 生长 */ public void grow() { System.out.println("Apple is growing..."); } /** * 收获 */ public void harvest() { System.out.println("Apple has been harvested."); } /** * @return 返回树龄 */ public int getTreeAge() { return treeAge; } /** * 设置树龄 */ public void setTreeAge(int treeAge) { this.treeAge = treeAge; } }
// 产品-草莓类:Strawberry.java public class Strawberry implements Fruit { /** * 生长 */ public void grow() { System.out.println("Strawberry is growing..."); } /** * 收获 */ public void harvest() { System.out.println("Strawberry has been harvested."); } /** * 种植 */ public void plant() { System.out.println("Strawberry has been planted."); } /** * 辅助方法 */ public static void log(String msg) { System.out.println(msg); } }
// 产品-葡萄类:Grape.java public class Grape implements Fruit { private boolean seedless; //是否有籽 /** * 种植 */ public void plant() { System.out.println("Grape has been planted."); } /** * 生长 */ public void grow() { System.out.println("Grape is growing..."); } /** * 收获 */ public void harvest() { System.out.println("Grape has been harvested."); } /** * @return 是否有籽 */ public boolean getSeedless() { return seedless; } /** * 有无籽的赋值方法 */ public void setSeedless(boolean seedless) { this.seedless = seedless; } /** * 辅助方法 */ public static void log(String msg) { System.out.println(msg); } }
// 工厂-园丁类:FruitGardener.java public class FruitGardener { /** * 静态工厂方法 * @param which :具体的产品名称 * @return 一个水果对象 * @throws BadFruitException */ public static Fruit factory(String which) throws BadFruitException { if (which.equalsIgnoreCase("apple")) { return new Apple(); } else if (which.equalsIgnoreCase("strawberry")) { return new Strawberry(); } else if (which.equalsIgnoreCase("grape")) { return new Grape(); } else { throw new BadFruitException("Bad fruit request"); } } }
// 工厂异常定义类:BadFruitException.java public class BadFruitException extends Exception { public BadFruitException(String msg) { super(msg); //调用父类的构造方法 } }
// 一般工厂模式的测试类 public class TestApp { /** * 测试方法 */ private void test(String fruitName) { try { Fruit f = FruitGardener.factory(fruitName); System.out.println("恭喜!生产了一个水果对象:" + fruitName); } catch (BadFruitException e) { System.out.println("对不起!工厂目前不能生产你所要的产品:" + fruitName); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); //输出异常信息 e.printStackTrace(); //输出异常堆栈信息 } } /** * 应用入口方法 */ public static void main(String args[]) { TestApp t = new TestApp(); t.test("apple"); t.test("grape"); t.test("strawberry"); t.test("car"); //此处会抛异常,水果工厂能生产car(轿车)吗!哈哈哈哈... } }
// 测试运行结果 恭喜!生产了一个水果对象:apple 恭喜!生产了一个水果对象:grape 恭喜!生产了一个水果对象:strawberry 对不起!工厂目前不能生产你所要的产品:car Bad fruit request com.lavasoft.patterns.simplefactory.ybgc.BadFruitException: Bad fruit request at com.lavasoft.patterns.simplefactory.ybgc.FruitGardener.factory(FruitGardener.java:28) at com.lavasoft.patterns.simplefactory.ybgc.TestApp.test(TestApp.java:19) at com.lavasoft.patterns.simplefactory.ybgc.TestApp.main(TestApp.java:37) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:585) at com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain.main(AppMain.java:90) Process finished with exit code 0
从结果看来,有异常,是因为输入了工厂不能生产的类型car(小汽车),哈哈哈哈,果园能生产汽车吗?让幼儿园的小朋友告诉你吧!
示例总结
总结一下,从上面的简单工厂模式的实现可以看到,简单工厂模式需要实现:
工厂角色:园丁
抽象产品:水果接口
具体产品:苹果、葡萄、草莓
另外还一般还需要实现:
工厂异常类
客户类
简单工厂模式的一般性结构图如下:
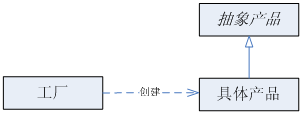
简单工厂模式的优缺点
优点
(1)简单工厂包含必要的判断逻辑,简单工厂实现了对象的创建和使用的分离。
(2)客户端无需知道所创建的具体产品类的类名,只需要具体产品类对应的参数即可
(3)在不修改任何客户端代码的情况下更换和增加新的具体产品类,在一定程度上提高了系统的灵活性
缺点
(1)工厂类的职责过重,从类图中可以看出简单工厂中包含所有的逻辑判断语句,它一旦有问题,整个系统都要出问题
(2)在添加新的类的时候,例如我添加了开根号运算,那么系统中的简单工厂类就要修改,违反了开放——封闭原则!这样及其不利于系统的扩展和维护
(3)简单工厂的静态方法,使得工厂角色无法形成基于继承的等级结构!
在Java中的应用
DateFormat与简单工厂模式
SAX2库中的XMLReaderFactory与简单工厂模式




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号