angular学习进阶(十五)
resolve(解决守卫)
保证了数据获取后在进行路由跳转,防止因为数据延迟而出现的空组件情况
简单的理解成解决延迟守卫
创建一个接口
product/product.ts
ng g i product/product.ts
export interface Product {
id: number;
name: string;
price: number
}
创建一个服务
ng g s product/product
import {Injectable} from '@angular/core';
import {Observable, of} from 'rxjs';
import {Product} from './product';
import {delay} from 'rxjs/internal/operators/delay';
import {ActivatedRouteSnapshot, Resolve, RouterStateSnapshot} from '@angular/router';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class ProductService implements Resolve<Product[]> {
constructor() {
}
// 模拟请求
getList(): Observable<Product[]> {
return of([
{id: 12, name: 'sss', price: 124},
{id: 13, name: 'xxx', price: 1231},
{id: 14, name: 'bbb', price: 132},
]).pipe(delay(2000));
}
// 把请求放在延迟函数中
resolve(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, state: RouterStateSnapshot): Observable<Product[]> | Promise<Product[]> | Product[] {
return this.getList();// 可以对这个值进行二次加工
}
}
app-routing.module
{
path: 'three',
component: ThreeComponent,
resolve: {products: ProductService}
}
从其他页面跳转到three页面
<a [routerLink]="['three']">three</a>
ThreeComponent 页面拿到这个值
export class ThreeComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(private route:ActivatedRoute) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
// 拿到获取的数据
console.log(this.route.snapshot.data['products']);
}
}
rxjs 中的map和switchMap区别
switchMap 创建一个内部课观察对象,进行订阅并发出其值为可观察者
of(1, 2, 3, 4).pipe(
map(v => v * 2),
toArray()
).subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res);
//[2, 4, 6, 8]
})
of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).pipe(
switchMap(val => of(val * 2)),
toArray()
).subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res);
// [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
})
点击按钮,每1s发送一个值,再次点击,取消之前的订阅重新开始发送值
<button #button>click</button>
@ViewChild('button') button;
ngAfterViewInit(): void {
fromEvent(this.button.nativeElement,'click').pipe(
switchMap(()=>interval(1000))
).subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res);
})
}
比如拿到xxx/:id
this.activateRoute.paramMap.pipe(
switchMap(params=>params.get('id'))
).subscribe(res=>{
console.log(id)
})
from表单触发某个值,提交请求
this.mainForm.get("productCode").valueChanges
.pipe(
debounceTime(700),
switchMap(val => {
return this.queryDepositData();
})
)
.subscribe(data => {
this.product=data;
})
Rxjs 学习原理图
看着原理图学习,会印象深刻一些
angular的相关命令细节
--flat 强制修改创建文件的位置
ng g c --f fix/hello
在app的fix/hello位置下创建一个hello组件
-export 添加到对应模块的exports
ng g c home --export
// 会添加到对应模块的exports
--prefix 添加组件选择器前缀
ng g c --p=d hello
// 选择器的名称 d-hello
selector: 'd-hello',
--selector 替换组件选择器
ng g c fix/hello-e --selector=hello-g
selector: 'hello-g',// 而不是hello-e
创建一个class 文件
ng g class xxx
创建模块
ng g m south //会创建一个south模块
ng g m south --routing // 同时创建模块和路由
如果创建了模块没有没有创建路由,可以使用下面的命令
ng g m -f south --routing
模板字符串规范
不好
{{num/60}}
推荐
{{num}}
get num(){
return this.total/60
}
父子组件传递
不好
{{getOffer(amount)}}
@Input() amount:number
getOffer(amount:number){
if(amount > 3500 && amount < 4999)
return `You will get 20% off on 5k purchase`;
else if (amount > 5000)
return `You will get 30% off on 7k purchase`;
else
return `5% off on your existing purchase.`;
}
推荐
{{offerMessage}}
offerMessage: string;
@Input() set amount(value: number) {
let message: string = '';
if (value > 5000)
message = `You will get 30% off on 7k purchase`;
else if (value > 3500 && value < 4999)
message = `You will get 20% off on 5k purchase`;
else
message = `5% off on your existing purchase.`;
this.offerMessage = message;
}
正常情况下这样也行
{{getGrade(student)}}
getGrade(marks: number) {
let grade: string = 'F';
if (marks >= 85)
grade = 'S'
else if (marks > 60 && marks < 85)
grade = 'A'
return grade;
}
在使用ngFor 绑定数据的时候
<tr *ngFor="let student of students; trackBy:trackByFn">
<td>{{student.name}}</td>
<td>{{student.grade}}</td>
</tr>
trackByFn(index, item) {
return item.id;
}
RXjs 具体api的实际运用
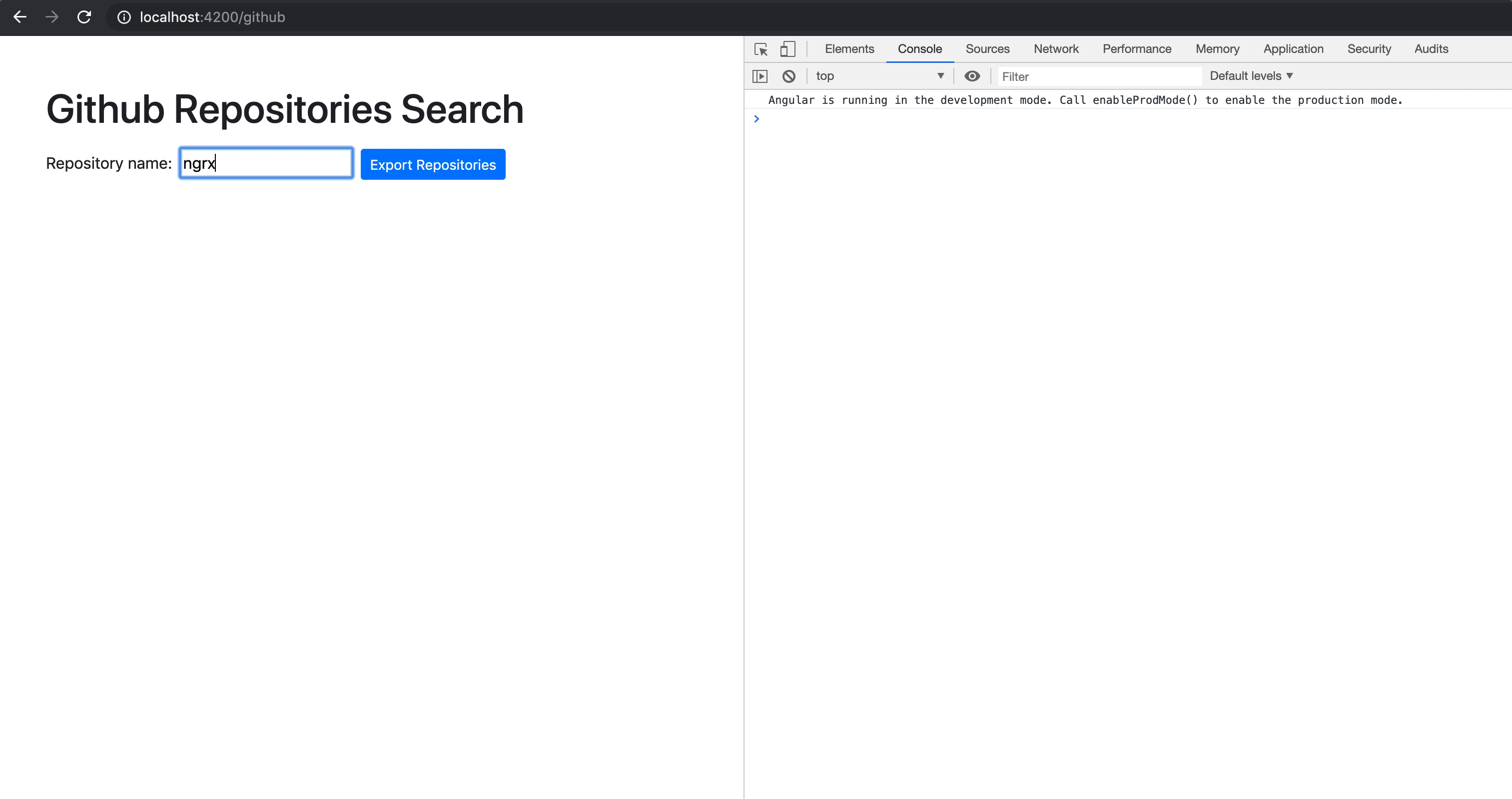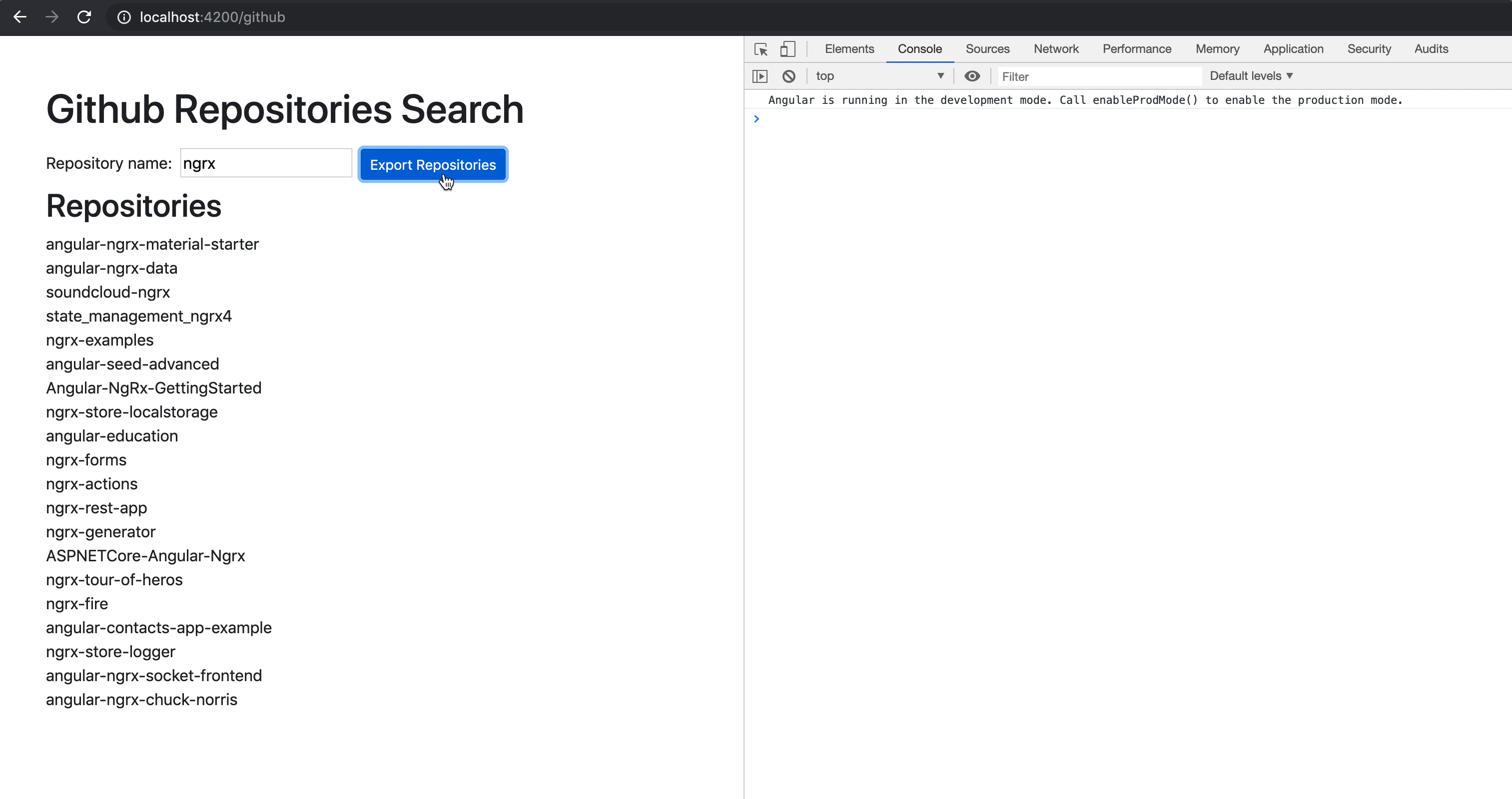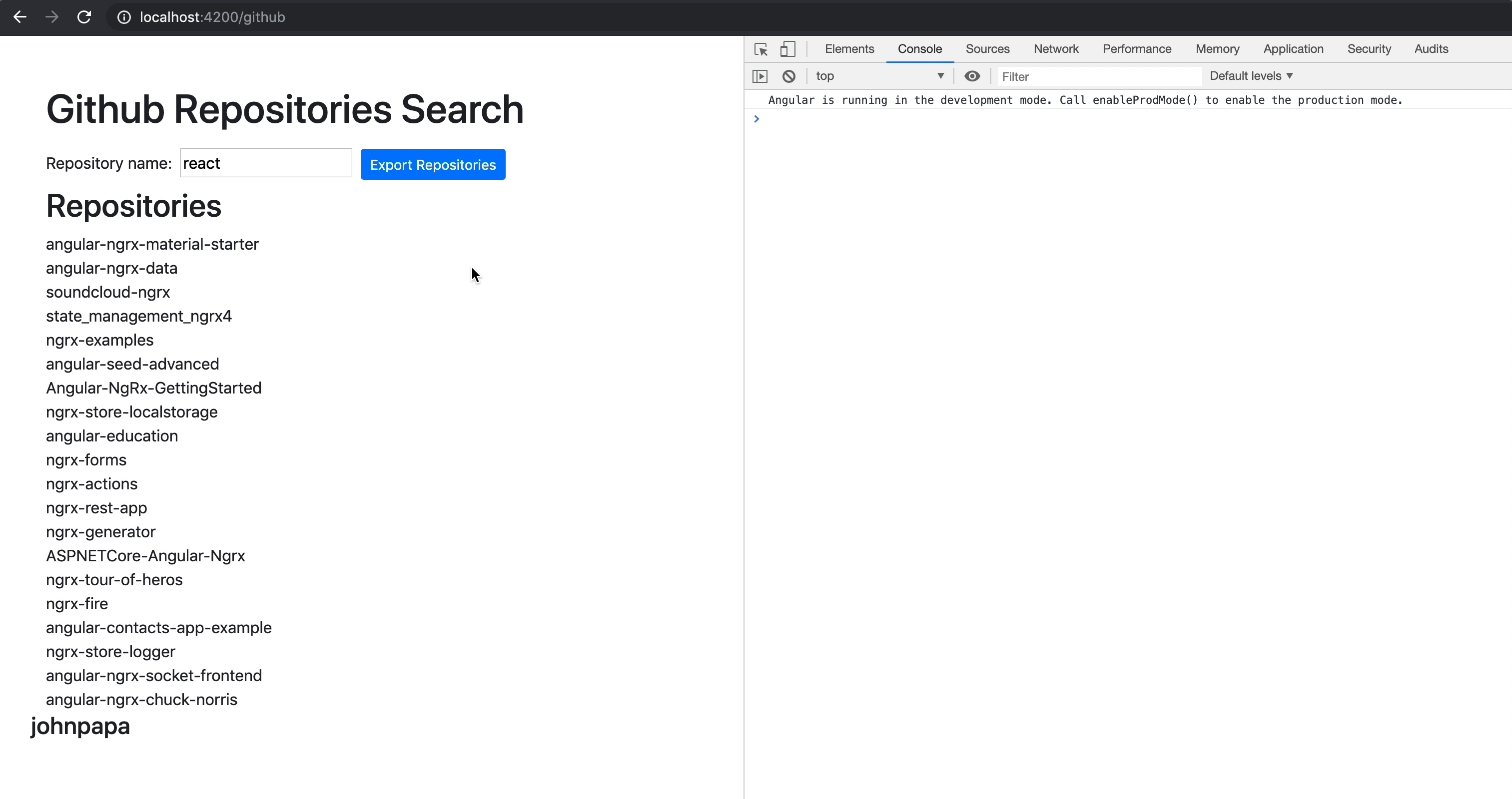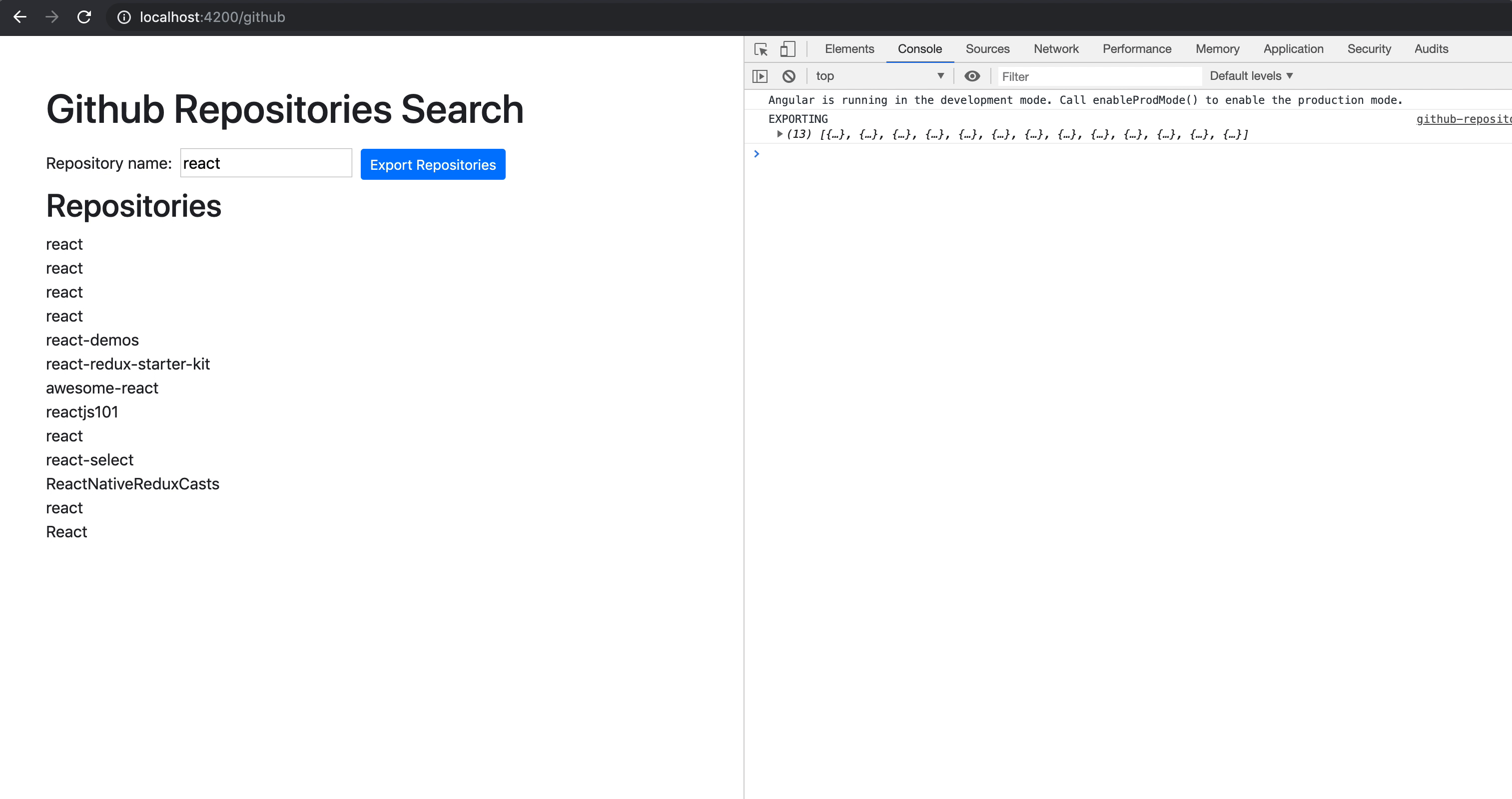
debounceTime
输入数据搜索资料的时候,而不按搜索的数据按钮,请求下拉框
我们发现当修改一个的时候回立刻请求值,所以我们可以加上,在一段时间内,修改只会发一次请求
this.from.get('xxx').valueChanges.pipe(
debounceTime(300),
switchMap(key=>this.http.get('xxx',key))
)
distinctUntilChanged
当当前值和之前值有变化才会发送订阅
<form [formGroup]="myForm">
<input formControlName="firstName">
</form>
constructor(private fb: FormBuilder,) {
}
myForm = this.fb.group({
firstName: ['']
}
);
ngOnInit(): void {
this.myForm.get('firstName').valueChanges.pipe(
debounceTime(300),// 当300ms没有新资料,才会运行
distinctUntilChanged()// 当[内容真正有修改]时,才运行搜索
).subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res);
})
}
filter
this.myForm.get('firstName').valueChanges.pipe(
debounceTime(300),// 当300ms没有新资料,才会运行
distinctUntilChanged(),// 当[内容真正有修改]时,才运行搜索
filter(key =>key.length>4)// 当之大于4的是偶,才会进行搜索
).subscribe(res => {
console.log(res);
});
完整版
public todos;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.todos= this.myForm.get('firstName').valueChanges.pipe(
map((query: string) => query ? query.trim() : ''),
filter(v => v.length > 3),
debounceTime(300),
distinctUntilChanged(),// 内容有修改
switchMap(query => of('111' + query)), //模拟发请求
shareReplay(1)// 避免重复载入
);
}
Subject
public sub = new Subject();
sub.subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res); //2,3,5,6
})
this.sub.next(2);
this.sub.next(3);
this.sub.subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res); //5,6
})
this.sub.next(5)
this.sub.next(6)
ReplaySubject
// 指定记录次数
public subject = new ReplaySubject(2);
ngOnInit(): void {
this.subject.next(1);
this.subject.subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res); //1,2,3,4
})
this.subject.next(2)
this.subject.next(3)
this.subject.subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res);//2,3,4 (2,3是最近2次重播的值)
})
this.subject.next(4)
}
asyncSubject
只有在
complete()才会被呼叫,订阅到[最后一次next()]的内容
public asySub = new AsyncSubject();
ngOnInit(): void {
this.asySub.subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res); //3
})
this.asySub.next(1)
this.asySub.next(2)
this.asySub.next(3)
this.asySub.complete()
}
处理错误
subject.subscribe(
res=>{
// 成功
},error=>{
// 失败
})
修改,记录错误类似于try...catch
this.http.get('....').pipe(
catchError(err=>{
console.log(err)
return of([])
})
)
模拟
throwError('xxx').pipe(
catchError(err=>of(1))
).subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res);//1
})
of(throwError('xxx')) 如果这样是就是of()了一个流,所以的是一个流,应该是上面的那种写法
如果想主动抛出错误
this.http.get('....').pipe(
tap(data=>{ //但是你要记得 tap 是不会影响流的
if(data.length==0){
throwError('no data')
}
}),
catchError(err=>{
console.log(err)
return of([])
})
)
finalize 放置到最后执行的程式,这样this.lading=false 就不用subscribe里面了
this.http.get('...').subscribe(res=>{
this.loading=false;
},error=>{
this.loading=false;
})
修改
this.http.get('...').pipe(
finalize(()=>{
// 不管出现什么错误等等等,都一定会进入finalize里面
this.loading=false
})
)
决定自己的高度的是你的态度,而不是你的才能
记得我们是终身初学者和学习者
总有一天我也能成为大佬




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号