33.2.NIO
4.1概述【理解】
-
BIO
Blocking IO,阻塞型IO
-
NIO
No Blocking IO,非阻塞型IO
-
阻塞IO的弊端
在等待的过程中,什么事也做不了
-
非阻塞IO的好处
不需要一直等待,当一切就绪了再去做
4.2NIO与BIO的区别【理解】
-
区别一
BIO是阻塞的,NIO是非阻塞的
-
区别二
BIO是面向流的,NIO是面向缓冲区的
BIO中数据传输是单向的,NIO中的缓冲区是双向的
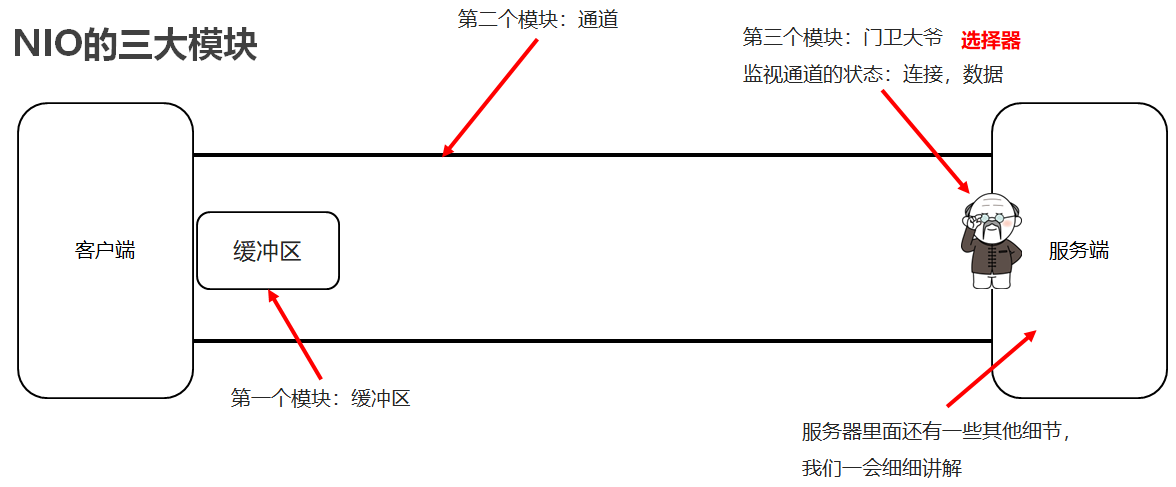
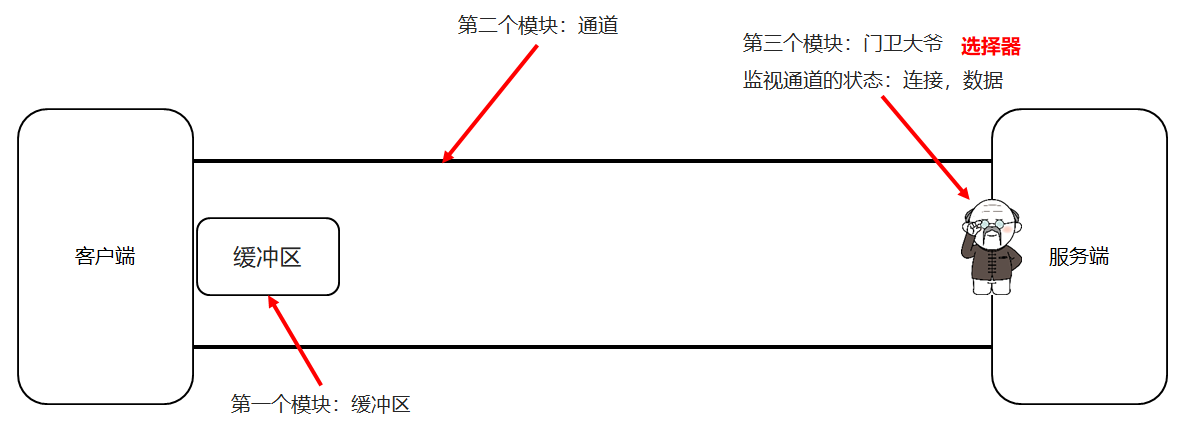
4.3NIO三大模块【理解】
-
缓冲区
用来存储数据
-
通道
用来建立连接和传输数据
-
选择器
监视通道状态
4.4NIO创建缓冲区对象【应用】
缓冲区其实就是一个数组
-
方法介绍
方法名 说明 static ByteBuffer allocate(长度) 创建byte类型的缓冲区 static ByteBuffer wrap(byte[] array) 创建一个有内容的byte类型缓冲区 -
代码示例
package com.itheima.mynio;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class CreateByteBufferDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//method1();
//method2();
method3();
}
public static void method3() {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer3 = ByteBuffer.wrap("aaa".getBytes());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println(byteBuffer3.get());
}
}
public static void method2() {
byte [] bytes={97,98,99};
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes);
//缓冲区的长度3
//缓冲区的内容就是字节数组的内容
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println(byteBuffer2.get());
}
}
public static void method1() {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1=ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
//get
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(byteBuffer1.get());
}
System.out.println(byteBuffer1.get());
}
}
4.5NIO缓冲区添加数据【应用】
缓冲区其实就是一个数组
两个功能:
读/写
问:我要把数据写到缓冲区中 使用缓冲读的功能
我要把缓冲区的数据读出来并打印 使用缓冲写的功能
- 如何用写?何时用读?
- 必须站在缓冲区的角度思考问题。
- capacity:容量(长度)
- limit:界限(最多能读/写到哪里)
- posotion:位置(读/写哪个索引)
存三个字节
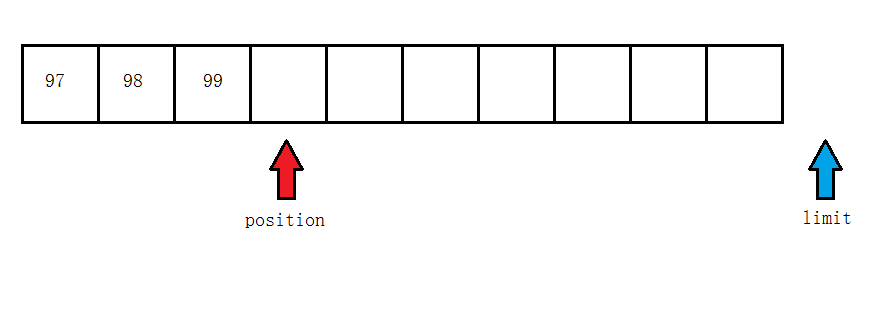
调用flip方法
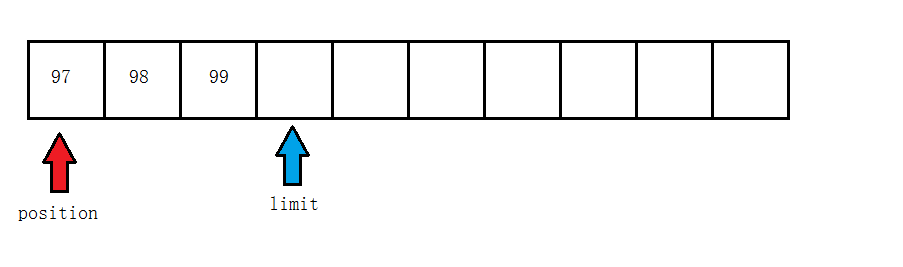
读一个字节后

读第一个数组后
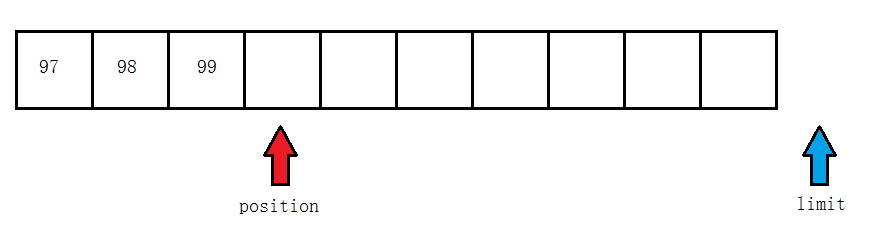
调用rewind后
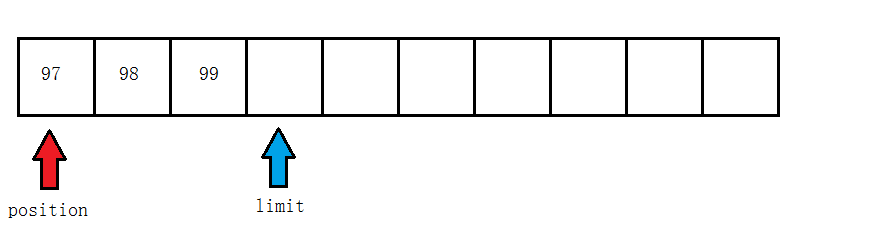
调用clear后
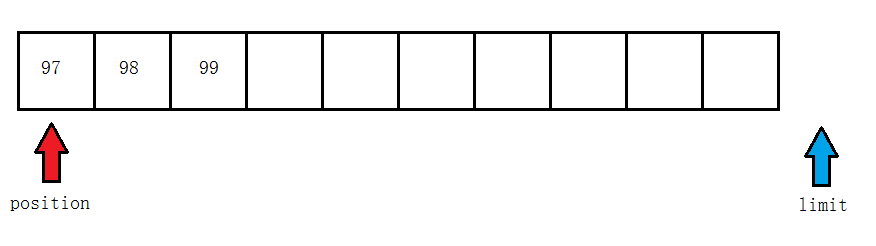
-
方法介绍
-
![]()
package com.itheima.mynio;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class ByteBufferDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int position() 当前要操作的索引
// int limit() 最多能操作到哪个索引
// int capacity() 缓冲区的总长度
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
// put(byte b) 一次添加一个字节
// byteBuffer.put((byte) 97);
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
// put(byte[] src) 一次添加一个字节数组
// byteBuffer.put("aaa".getBytes());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
// position(int newPosition) 修改position
// byteBuffer.position(1);
// limit(int newLimit) 修改limit
// byteBuffer.limit(5);
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
// System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
// int remaining() 还有多少能操作
byteBuffer.put("0123456789".getBytes());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.remaining());//10
System.out.println(byteBuffer.hasRemaining());//true
// boolean hasRemaining() 是否还有能操作的
}
}
4.6NIO缓冲区获取数据【应用】
-
方法介绍
方法名 介绍 flip() get() 读一个字节 get(byte[] dst) 读多个字节 get(int index) 读指定索引的字节 rewind() 将position设置为0,可以重复读 clear() 数据读写完毕(读->写) array() 将缓冲区转换成字节数组返回 -
代码示例
package com.itheima.mynio;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class ByteBufferDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
byteBuffer.put("abc".getBytes());
//flip() 切换读写模式(写->读)
byteBuffer.flip();
//get() 读一个字节
// while(byteBuffer.position()!=byteBuffer.limit()){
// System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());
// }
for (int i = 0; i < byteBuffer.limit(); i++) {
System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());
}
//get(byte[] dst) 读多个字节
// byte []bytes=new byte[byteBuffer.limit()];
// byteBuffer.get(bytes);
// System.out.println(new String(bytes));
//
//
// //get(int index) 读指定索引的字节
// System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get(0));
//rewind() 将position设置为0,可以重复读
// byteBuffer.rewind();
// for (int i = 0; i < byteBuffer.limit(); i++) {
// System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());
// }
//clear() 数据读写完毕(读->写)
byteBuffer.clear();
byteBuffer.put("qqq".getBytes());
//array() 将缓冲区转换成字节数组返回
byte[] bytes = byteBuffer.array();
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
}
4.7小结【理解】
-
需求:我要把数据写到缓冲区中。
数据是从外面进入到缓冲区的,所以缓冲区在做读数据的操作。
-
需求:我要把数据从缓冲区中读出来。
数据是从缓冲区里面到外面的。所以缓冲区在做写数据的操作。
-
capacity:容量(长度) limit: 界限(最多能读/写到哪里) posotion:位置(读/写哪个索引)
-
获取缓冲区里面数据之前,需要调用flip方法
-
再次写数据之前,需要调用clear方法,
但是数据还未消失,等再次写入数据,被覆盖了才会消失。
1.NIO
1.1 NIO通道客户端【应用】
客户端通道----------连接服务端
------------传递缓冲区---------------传递数据
服务端通道-----------建立连接
-
客户端实现步骤
-
打开通道---------------SocketChannel
-
指定IP和端口号--------InetSocketAddress
-
写出数据-------------------------write
-
释放资源----------------------释放资源
-
-
示例代码
package com.itheima.mynio2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. 打开通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//2. 指定IP和端口号
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10000));
//3. 写出数据
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
//4. 释放资源
socketChannel.close();
}
}
1.2 NIO通道服务端【应用】
-
NIO通道
-
服务端通道
只负责建立建立,不负责传递数据
-
客户端通道
建立建立并将数据传递给服务端
-
缓冲区
客户端发送的数据都在缓冲区中
-
服务端通道内部创建出来的客户端通道
相当于客户端通道的延伸用来传递数据
-
-
服务端实现步骤
-
打开一个服务端通道
-
绑定对应的端口号
-
通道默认是阻塞的,需要设置为非阻塞
-
此时没有门卫大爷,所以需要经常看一下有没有连接发过来没?
-
如果有客户端来连接了,则在服务端通道内部,再创建一个客户端通道,相当于是客户端通道的延伸
-
获取客户端传递过来的数据,并把数据放在byteBuffer1这个缓冲区中
- 服务端创建一个空的缓冲区装数据并输出
-
给客户端回写数据
-
释放资源
-
-
示例代码
package com.itheima.mynio2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. 打开通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//2. 指定IP和端口号
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10000));
//3. 写出数据
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("一点汗毛献辞".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
//4. 释放资源
socketChannel.close();
}
}
1.3 NIO通道练习【应用】
需求:利用NIO的非阻塞通道与缓冲区完成下面的需求
客户端发送数据给服务端
服务端接收后回写一个数据给客户端
-
客户端
-
实现步骤
-
打开通道
-
指定IP和端口号
-
写出数据
-
读取服务器写回的数据
-
释放资源
-
-
示例代码
-
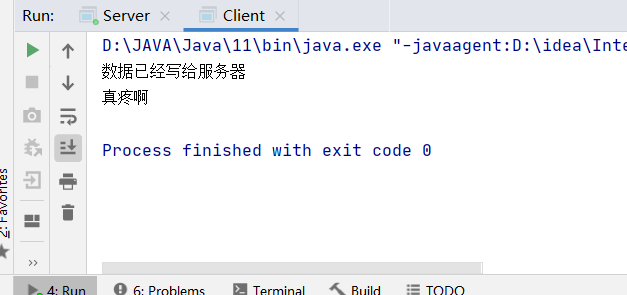
Client
package com.itheima.mynio3;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10001));
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.wrap("吃俺老孙一棒".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer1);
System.out.println("数据已经写给服务器");
socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len;
while((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer2))!=-1){
byteBuffer2.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer2.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer2.clear();
}
socketChannel.close();
}
}
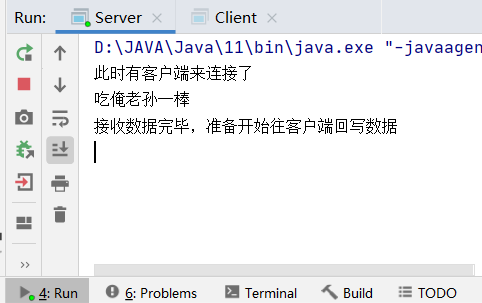
Server
package com.itheima.mynio3;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10001));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
while(true){
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if (socketChannel != null) {
System.out.println("此时有客户端来连接了");
//获取客户端传递过来的数据,并把数据放在byteBuffer1这个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1);
int len;
//针对于缓冲区来讲
//如果 从添加数据---->获取数据 flip
//如果 从获取数据---->添加数据 clear
while((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1))!=-1){
byteBuffer1.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer1.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer1.clear();
}
System.out.println("接收数据完毕,准备开始往客户端回写数据");
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap("真疼啊".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer2);
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
}
1.4 NIO通道练习优化【应用】
-
存在问题
服务端内部获取的客户端通道在读取时,如果读取不到结束标记就会一直阻塞
-
解决方案
- 1.给一个结束标记
-
//结束标记
// socketChannel.shutdownOutput(); -
2.将服务端内部获取的客户端通道设置为非阻塞的
-
示例代码
Client
package com.itheima.mynio3;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10001));
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.wrap("吃俺老孙一棒".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer1);
System.out.println("数据已经写给服务器");
//结束标记
// socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len;
while((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer2))!=-1){
System.out.println("客户端接收回写数据");
byteBuffer2.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer2.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer2.clear();
}
socketChannel.close();
}
}
Server
package com.itheima.mynio3;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10001));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
while(true){
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if (socketChannel != null) {
System.out.println("此时有客户端来连接了");
//把延伸端的非阻塞关闭 !!!!!!
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//获取客户端传递过来的数据,并把数据放在byteBuffer1这个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1);
int len;
//针对于缓冲区来讲
//如果 从添加数据---->获取数据 flip
//如果 从获取数据---->添加数据 clear
while((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1))>0){
System.out.println("服务端接收发送数据");
byteBuffer1.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer1.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer1.clear();
}
System.out.println("接收数据完毕,准备开始往客户端回写数据");
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap("真疼啊".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer2);
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
}
1.5NIO选择器【理解】
-
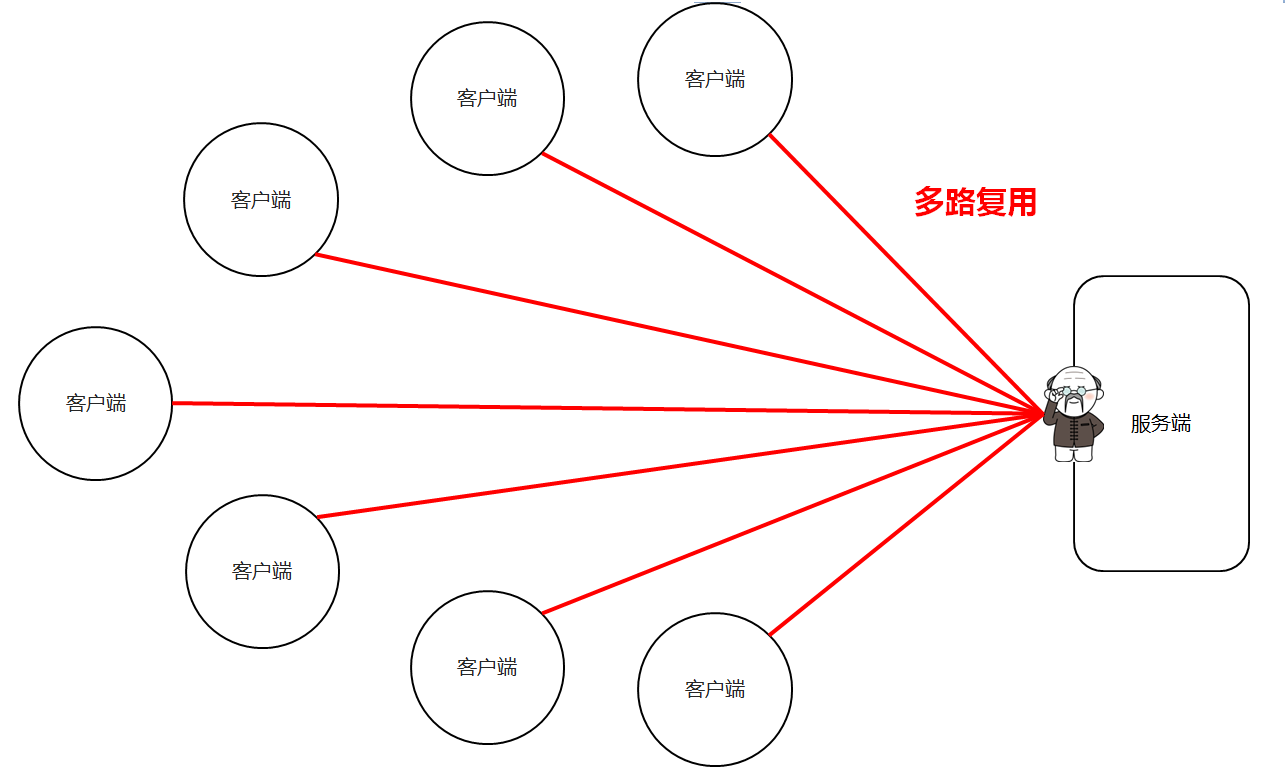
概述
选择器可以监视通道的状态,多路复用
-
Selector
选择器对象
-
SelectionKey
绑定的通道后返回的key
-
SelectableChannel
能使用选择器的通道
-
SocketChannel
-
-
1.6NIO选择器改写服务端【应用】
当有客户端连接时,选择器会看哪个服务端通道准备好了,谁准备好了,就让谁去连
-
实现步骤
-
打开一个服务端通道(open)
-
绑定对应的端口号
-
通道默认是阻塞的,需要设置为非阻塞
-
打开一个选择器(门卫大爷) 以上步骤中,服务端通道和门卫大爷还没有任何关系
-
将选择器绑定服务端通道,并监视服务端是否准备好
-
如果有客户端来连接了,大爷会遍历所有的服务端通道,谁准备好了,就让谁来连接 连接后,在服务端通道内部,再创建一个客户端延伸通道
-
如果客户端把数据传递过来了,大爷会遍历所有的延伸通道,谁准备好了,谁去接收数据
-
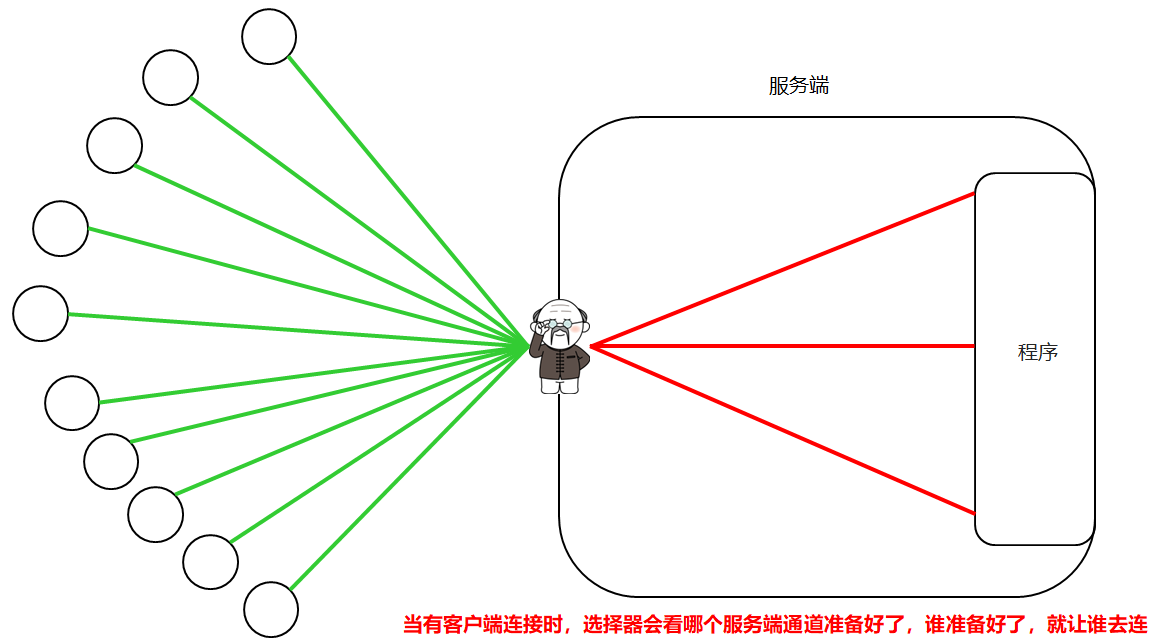
选择器监视客户端通道
选择器监视服务端通道
选择器监视客户端延伸通道
Client
package com.itheima.mynio5;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10001));
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.wrap("吃俺老孙一棒".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer1);
System.out.println("数据已经写给服务器");
//结束标记
// socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len;
while((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer2))!=-1){
System.out.println("客户端接收回写数据");
byteBuffer2.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer2.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer2.clear();
}
socketChannel.close();
}
}
Server
package com.itheima.mynio5;
import jdk.swing.interop.SwingInterOpUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.打开服务端通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2.让这个通道绑定一个端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10001));
//3.设置通道为非阻塞状态
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//4.打开一个选择器
//selector ---选择器
//SelectionKey ----绑定通道后返回的令牌
//SelectableChannel ---可以使用选择器的通道
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//5.绑定选择器和服务端通道
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while(true){
//6.选择器会监视客户端通道的状态
//返回值就表示此时有多少个客户端来连接。
int count = selector.select();
if (count != 0) {
System.out.println("有客户端来连接了");
//7.会遍历所有的服务端通道,看谁准备好了,谁准备好了,就让谁去连接
//获取所有服务端通道的令牌,并将它们放到一个集合中,将集合返回
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
//selectionKey 依次表示每一个服务端通道的令牌
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
//可以通过令牌来获取到了一个已经就绪的服务器通道
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
//客户端的延伸通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc.accept();
//将客户端的延伸通道设置为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//当客户端来连接的时候,所有的步骤已经全部执行完毕
}else if (selectionKey.isReadable()){
//当前通道已经做好了读取的准备(延伸通道)
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len;
while((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1))>0){
byteBuffer1.flip();
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer1.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer1.clear();
}
//给客户端的回写数据
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("好疼啊!".getBytes()));
socketChannel.close();
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
}
2.HTTP协议
非阻塞的HTTP服务器
非阻塞的服务器:就是刚刚写的NIO服务器
HTTP:互联网传输数据的一种规则
超文本传输协议(关于超文本的概念JavaWeb在进行学习),是建立在TCP/IP协议基础上,是网络应用层的协议。
由请求和响应构成,是一个标准的客户端和服务器模型
是互联网传输数据的一种规则
是基于TCP/IP协议
由请求和响应组成
2.2URL【理解】
-
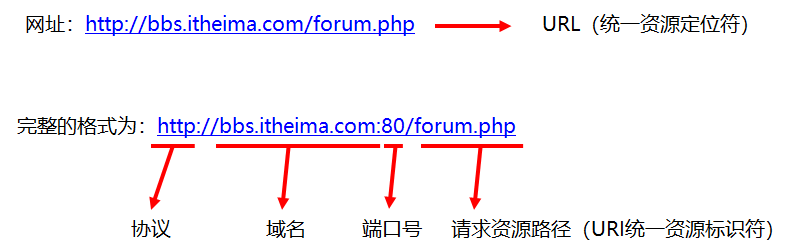
概述
统一资源定位符,常见的如http://bbs.itheima.com/forum.php
-
详解
2.3抓包工具的使用【应用】
-
使用步骤
-
在谷歌浏览器网页中按F12 或者网页空白处右键,点击检查,可以调出工具
-
点击network,进入到查看网络相关信息界面
-
这时在浏览器中发起请求,进行访问,工具中就会显示出请求和响应相关的信息
-
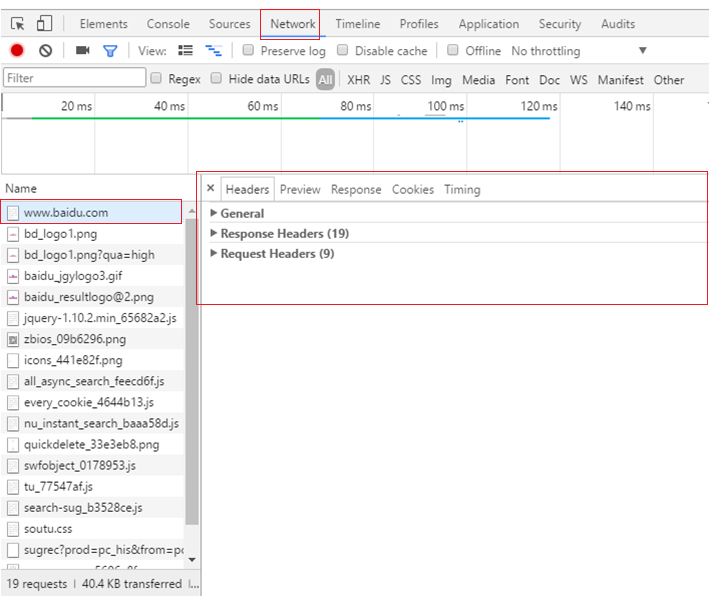
Request Headers 请求数据
Response Headers 响应数据
2.4请求信息【理解】
Request Headers 请求
-
组成
-
请求行
-
请求头
-
请求空行
-
请求体
-
-
请求行
-
格式
-

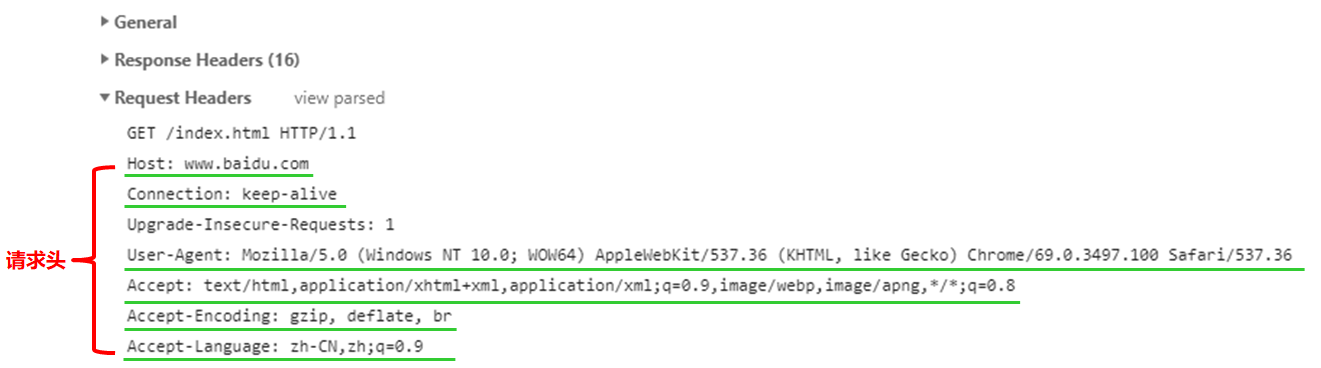
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
使用GET方式请求数据是没有请求体的
-
GET,POST,HEAD,PUT,DELETE,CONNECT,OPTIONS,TRACE,PATCH
其中用的比较多的是GET和POST
-
URI
![]()
-
HTTP1.0: 每次请求和响应都需要建立一个单独的连接
-
-
-
Host: 用来指定请求的服务端地址
-
Connection: 取值为keep-alive表示需要持久连接
-
User-Agent: 客户端的信息
-
Accept: 指定客户端能够接收的内容类型
-
Accept-Encoding: 指定浏览器可以支持的服务器返回内容压缩编码类型
-
小结

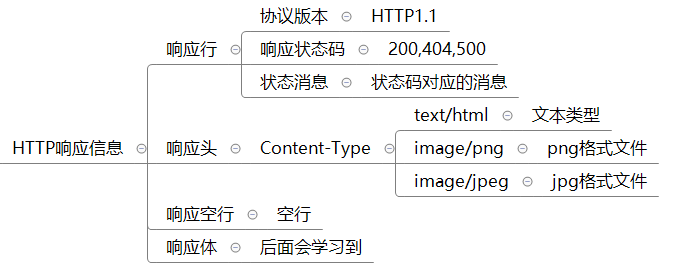
2.5响应信息【理解】
-
组成
-
响应行
-
响应头
-
响应空行
-
响应体
-
-
响应行
-
格式
-

Http/1.1 200 OK
-
-
-
HTTP1.0: 每次请求和响应都需要建立一个单独的连接
-
HTTP1.1: 支持长连接
-
-
响应状态码
-
1xx: 指示信息(表示请求已接收,继续处理)
-
2xx: 成功(表示请求已被成功接收、理解、接受)
-
3xx: 请求重定向(要完成请求必须进行更进一步的操作)
-
4xx: 客户端错误(请求有语法错误或请求无法实现)
-
5xx: 服务器端错误(服务器未能实现合法的请求)
-
-
状态信息
-
200 ok
-
404 Not Found
-
500 Internal Server Error
-
-
-
响应头
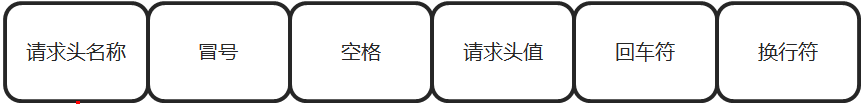
- 响应头名称 冒号 空格 响应头值 回车符 换行符
-
-
响应头名称
-
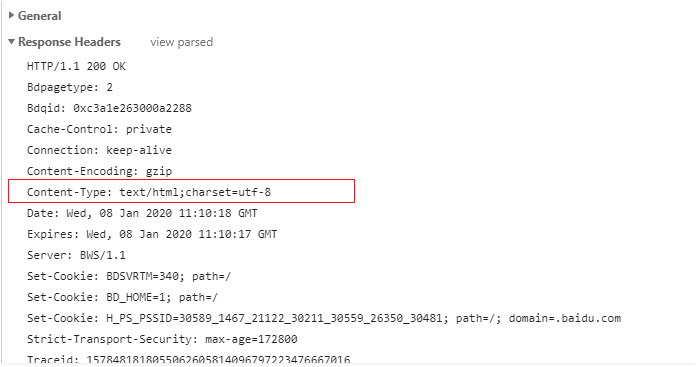
Content-Type: 告诉客户端实际返回内容的网络媒体类型(互联网媒体类型,也叫做MIME类型)
-
-
响应头值
-
text/html ----> 文本类型
-
image/png ----> png格式文件
-
-
-
小结
3.HTTP服务器
3.1需求【理解】
-
编写服务器端代码,实现可以解析浏览器的请求,给浏览器响应数据
-
实现步骤
-
编写HttpServer类,实现可以接收浏览器发出的请求
-
其中获取连接的代码可以单独抽取到一个类中
-
-
代码实现
服务端代码HttpServer
package com.itheima.mynio6;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class HttpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.打开服务端通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2.让这个通道绑定一个端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10001));
//3.设置通道为非阻塞状态
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//4.打开一个选择器
//selector ---选择器
//SelectionKey ----绑定通道后返回的令牌
//SelectableChannel ---可以使用选择器的通道
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//5.绑定选择器和服务端通道
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while(true){
//6.选择器会监视客户端通道的状态
//返回值就表示此时有多少个客户端来连接。
int count = selector.select();
if (count != 0) {
System.out.println("有客户端来连接了");
//7.会遍历所有的服务端通道,看谁准备好了,谁准备好了,就让谁去连接
//获取所有服务端通道的令牌,并将它们放到一个集合中,将集合返回
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
//selectionKey 依次表示每一个服务端通道的令牌
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
//获取连接
AcceptHandler acceptHandler=new AcceptHandler();
acceptHandler.connSocketChannel(selectionKey);
//当客户端来连接的时候,所有的步骤已经全部执行完毕
}else if (selectionKey.isReadable()){
//当前通道已经做好了读取的准备(延伸通道)
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len;
//循环读取
while((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1))>0){
byteBuffer1.flip();
sb.append(new String(byteBuffer1.array(),0,len));
//System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer1.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer1.clear();
}
System.out.println(sb);
//给客户端的回写数据
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("好疼啊!".getBytes()));
socketChannel.close();
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
}
// 将获取连接的代码抽取到这个类中
package com.itheima.mynio6;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
/*
* 接受连接的任务处理类
*
* */
public class AcceptHandler {
public SocketChannel connSocketChannel(SelectionKey selectionKey){
try {
//可以通过令牌来获取到了一个已经就绪的服务器通道
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
//客户端的延伸通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc.accept();
//将客户端的延伸通道设置为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//把socketChannel注册到选择器上
socketChannel.register(selectionKey.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ);
return socketChannel;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
3.3获取请求信息并解析【理解】
-
实现步骤
-
将请求信息封装到HttpRequest类中
-
在类中定义方法,实现获取请求信息并解析
-
-
代码实现
HttpRequest
package com.itheima.mynio6;
import javax.naming.ldap.PagedResultsControl;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
/*
* 用来封装请求数据的类
* */
public class HttpRequest {
private String method;//请求方式
private String requestURI;//请求的URI
private String version;//http的协议版本
private HashMap<String,String> hm=new HashMap<>();//所有的请求头
//parse ----获取请求数据,并解析
public void parse(SelectionKey selectionKey){
try {
//当前通道已经做好了读取的准备(延伸通道)
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len;
//循环读取
while((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer1))>0){
byteBuffer1.flip();
sb.append(new String(byteBuffer1.array(),0,len));
//System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer1.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer1.clear();
}
//System.out.println(sb);
parseHttpRequest(sb);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//解析http请求协议中的数据
private void parseHttpRequest(StringBuilder sb) {
//1.需要把StringBuilder先变成一个字符串
String httpRequeststr=sb.toString();
//2.获取每一行数据
String[] split = httpRequeststr.split("\r\n");
//3.获取请求行
String httpRequestLine = split[0];//GET / HTTP/1.1
//4.再按照空格进行切割,得到请求行中的三部分
String[] httpRequestInfo = httpRequestLine.split(" ");
this.method=httpRequestInfo[0];
this.requestURI=httpRequestInfo[1];
this.version=httpRequestInfo[2];
//5.操作每一个请求头
for (int i = 1; i < split.length; i++) {
String httpRequestHeaderInfo = split[i];
String[] httpRequestHeaderInfoArr = httpRequestHeaderInfo.split(": ");
hm.put(httpRequestHeaderInfoArr[0],httpRequestHeaderInfoArr[1]);
}
}
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
public void setMethod(String method) {
this.method = method;
}
public String getRequestURI() {
return requestURI;
}
public void setRequestURI(String requestURI) {
this.requestURI = requestURI;
}
public String getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(String version) {
this.version = version;
}
public HashMap<String, String> getHm() {
return hm;
}
public void setHm(HashMap<String, String> hm) {
this.hm = hm;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HttpRequest{" +
"method='" + method + '\'' +
", requestURI='" + requestURI + '\'' +
", version='" + version + '\'' +
", hm=" + hm +
'}';
}
}
3.4给浏览器响应数据【理解】
-
实现步骤
-
将响应信息封装HttpResponse类中
-
定义方法,封装响应信息,给浏览器响应数据
-
-
代码实现
package com.itheima.mynio6;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectableChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class HttpResponse {
private String version;//协议版本
private String status;//响应状态码
private String desc;//状态码的描述信息
//响应头数据
private HashMap<String,String> hm=new HashMap<>();
private HttpRequest httpRequest;//我们后面要根据请求的信息,来进行一些判断
//给浏览器响应数据的方法
public void sendstaticResource(SelectionKey selectionKey){
//1.给相应行赋值
this.version="HTTP/1.1";
this.status="200";
this.desc="ok";
//2.将响应行拼接成一个单独的字符串 //HTTP/1.1 200 ok
String responseLine=this.version+" "+this.status+" "+this.desc+"\r\n";
//3.给响应头赋值
hm.put("Content-Type","text/html;charset=UTF-8");
//4.将所有的响应头拼接成一个单独的字符串
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {
sb.append(entry.getKey()).append(": ").append(entry.getValue()).append("\r\n");
}
//5.响应空行
String emptyLine="\r\n";
//6.相应行,响应头,相应空行拼接成一个大的字符串
String reponseLineStr=responseLine+sb.toString()+emptyLine;
try {
//7.将上面三个写给浏览器
SocketChannel socketchannel = (SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.wrap(reponseLineStr.getBytes());
socketchannel.write(byteBuffer1);
//8.单独操作响应体
//因为在以后的响应体不一定是一个字符串
//有可能是一个文件,所以单独操作
String s="哎呀妈呀";
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2=ByteBuffer.wrap(s.getBytes());
socketchannel.write(byteBuffer2);
//9.释放资源
socketchannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(String version) {
this.version = version;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
public HashMap<String, String> getHm() {
return hm;
}
public void setHm(HashMap<String, String> hm) {
this.hm = hm;
}
public HttpRequest getHttpRequest() {
return httpRequest;
}
public void setHttpRequest(HttpRequest httpRequest) {
this.httpRequest = httpRequest;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HttpResponse{" +
"version='" + version + '\'' +
", status='" + status + '\'' +
", desc='" + desc + '\'' +
", hm=" + hm +
", httpRequest=" + httpRequest +
'}';
}
}
3.5代码优化【理解】
-
实现步骤
-
根据请求资源路径不同,响应不同的数据
-
服务端健壮性处理
-
访问不存在的资源处理
-
-
代码实现
/*
* 接受连接的任务处理类
*
package com.itheima.mynio9;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
/*
* 接受连接的任务处理类
*
* */
public class AcceptHandler {
public SocketChannel connSocketChannel(SelectionKey selectionKey){
try {
//可以通过令牌来获取到了一个已经就绪的服务器通道
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
//客户端的延伸通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc.accept();
//将客户端的延伸通道设置为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//把socketChannel注册到选择器上
socketChannel.register(selectionKey.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ);
return socketChannel;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
HttpResponse
package com.itheima.mynio9;
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class HttpResponse {
private String version; //协议版本
private String status; //响应状态码
private String desc; //状态码的描述信息
//响应头数据
private HashMap<String, String> hm = new HashMap<>();
private HttpRequest httpRequest; //我们后面要根据请求的数据,来进行一些判断
//给浏览器响应数据的方法
public void sendStaticResource(SelectionKey selectionKey) {
//1.给响应行赋值
this.version = "HTTP/1.1";
this.status = "200";
this.desc = "ok";
//3.给响应头赋值
//先获取浏览器请求的URI
String requestURI = this.getHttpRequest().getRequestURI();
if(requestURI != null){
File file = new File(WEB_APP_PATH + requestURI);
//判断这个路径是否存在
if(!file.exists()){
this.status = "404";
this.desc = "NOT FOUNG";
}
if("200".equals(this.status)){
if("/".equals(requestURI)){
hm.put("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8");
}else if("/favicon.ico".equals(requestURI)){
hm.put("Content-Type", "image/x-icon");
}else if("/a.txt".equals(requestURI)){
hm.put("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8");
}else if("/1.jpg".equals(requestURI)){
hm.put("Content-Type", "image/jpeg");
}else if("/1.png".equals(requestURI)){
hm.put("Content-Type", "image/png");
}
}else{
hm.put("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8");
}
}
//2.将响应行拼接成一个单独的字符串 // HTTP/1.1 200 ok
String responseLine = this.version + " " + this.status + " " + this.desc + "\r\n";
//4.将所有的响应头拼接成一个单独的字符串
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {
sb.append(entry.getKey()).append(": ").append(entry.getValue()).append("\r\n");
}
//5.响应空行
String emptyLine = "\r\n";
//6.响应行,响应头,响应空行拼接成一个大字符串
String responseLineStr = responseLine + sb.toString() + emptyLine;
try {
//7.将上面三个写给浏览器
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.wrap(responseLineStr.getBytes());
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer1);
//8.单独操作响应体
//因为在以后响应体不一定是一个字符串
//有可能是一个文件,所以单独操作
// String s = "哎哟,妈呀,终于写完了.";
byte [] bytes = getContent();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes);
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer2);
//9.释放资源
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static final String WEB_APP_PATH = "internetmodel\\webapp";
private byte[] getContent() {
try {
//1.获取浏览器请求的URI
String requestURI = this.getHttpRequest().getRequestURI();
if(requestURI != null){
if("200".equals(this.status)){
//2.判断一下请求的URI,根据不同的URI来响应不同的东西
if("/".equals(requestURI)){
String s = "哎哟,妈呀,终于写完了.";
return s.getBytes();
}else/* if("/favicon.ico".equals(requestURI))*/{
//获取一个ico文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(WEB_APP_PATH + requestURI);
//把ico文件变成一个字节数组返回
return IOUtils.toByteArray(fis);
}
}else{
return "访问的资源不存在".getBytes();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new byte[0];
}
public String getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(String version) {
this.version = version;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
public HashMap<String, String> getHm() {
return hm;
}
public void setHm(HashMap<String, String> hm) {
this.hm = hm;
}
public HttpRequest getHttpRequest() {
return httpRequest;
}
public void setHttpRequest(HttpRequest httpRequest) {
this.httpRequest = httpRequest;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HttpResponse{" +
"version='" + version + '\'' +
", status='" + status + '\'' +
", desc='" + desc + '\'' +
", hm=" + hm +
", httpRequest=" + httpRequest +
'}';
}
}
HttpServer
package com.itheima.mynio9;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class HttpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.打开服务端通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2.让这个通道绑定一个端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10000));
//3.设置通道为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//4.打开一个选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//5.绑定选择器和服务端通道
serverSocketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while(true){
//6.选择器会监视通道的状态.
int count = selector.select();
if(count != 0){
//7.会遍历所有的服务端通道.看谁准备好了,谁准备好了,就让谁去连接.
//获取所有服务端通道的令牌,并将它们都放到一个集合中,将集合返回.
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
//selectionKey 依次表示每一个服务端通道的令牌
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
if(selectionKey.isAcceptable()){
//获取连接
AcceptHandler acceptHandler = new AcceptHandler();
acceptHandler.connSocketChannel(selectionKey);
}else if(selectionKey.isReadable()){
//读取数据
HttpRequest httpRequest = new HttpRequest();
httpRequest.parse(selectionKey);
System.out.println("http请求的数据为 ---->" + httpRequest);
if(httpRequest.getRequestURI() == null || "".equals(httpRequest.getRequestURI())){
selectionKey.channel();
continue;
}
System.out.println("...数据解析完毕,准备响应数据....");
//响应数据
HttpResponse httpResponse = new HttpResponse();
httpResponse.setHttpRequest(httpRequest);
httpResponse.sendStaticResource(selectionKey);
}
//任务处理完毕以后,将SelectionKey从集合中移除
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
}
------------恢复内容结束------------





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号