28.HashSet
4.HashSet集合
4.1HashSet集合概述和特点【应用】
-
底层数据结构是哈希表
-
不能保证存储和取出的顺序完全一致
-
不可以存储重复元素
-
没有索引,不能使用普通for循环遍历
4.2HashSet集合的基本应用【应用】
存储字符串并遍历
package com.itheima.myhashset;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class HashSetDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> hs=new HashSet<>();
hs.add("hello");
hs.add("world");
hs.add("java");
hs.add("java");
hs.add("java");
hs.add("java");
hs.add("java");
hs.add("java");
Iterator<String> it=hs.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String next = it.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
System.out.println("============");
for (String h : hs) {
System.out.println(h);
}
}
}
4.3哈希值【理解】
-
哈希值简介
是JDK根据对象的地址或者字符串或者数字算出来的int类型的整数
-
如何获取哈希值
Object类中的public int hashCode():返回对象的哈希码值
-
哈希值的特点
- 如果没有重写hashCode方法,那么时根据对象的地址值计算出的哈希值
-
-
同一个对象多次调用hashCode()方法返回的哈希值是相同的,
-
不同对象的哈希值时不一样的
-
- 如果重写了hashCode方法,一般都是通过对象的属性值计算出哈希值
-
如果不同的对象属性值时一样的,那么计算出来的哈希值也是一样的
package com.itheima.myhashset;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//我们可以对Object类中的hashCode方法进行重写
//在重写时,就一般是根据对象的属性值来计算哈希值的
//此时跟对象的地址值就没有任何关系了
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试类
package com.itheima.myhashset;
/*
*
* 计算哈希值
*
* */
public class HashSetDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student("xiaozhi",23);
Student s2=new Student("xiaomei",22);
//因为在Object类中,是根据对象的地址值计算出来的哈希值
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());//1060830840
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());//1060830840
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());//2137211482
}
}
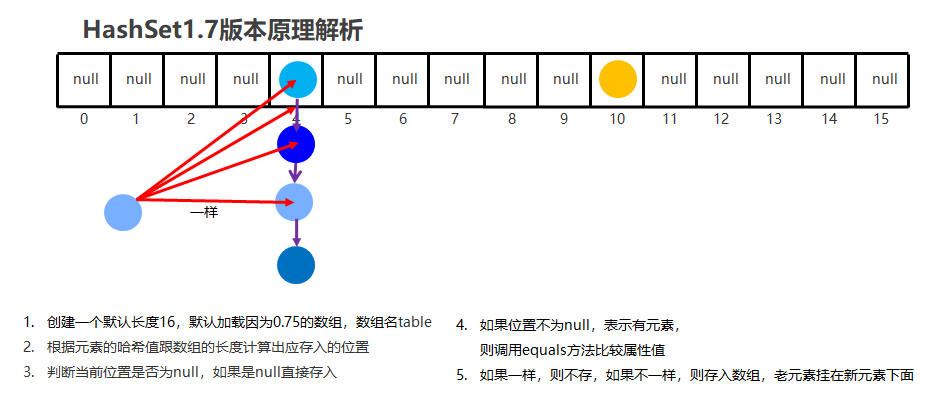
4.4哈希表结构【理解】
-
JDK1.8以前 不包括jdk8底层采用数组 + 链表
- 数组的长度默认为16,加载因子为0.75
- 首先会获取元素的哈希值,计算出在数组中应存入的索引
- 判断该索引处是否为null,如果时null,直接添加
- 如果不是null则与链表中所有的元素,通过equals方法比较属性值
- 只要有一个相同,就不存,如果都不一样,才会存入集合
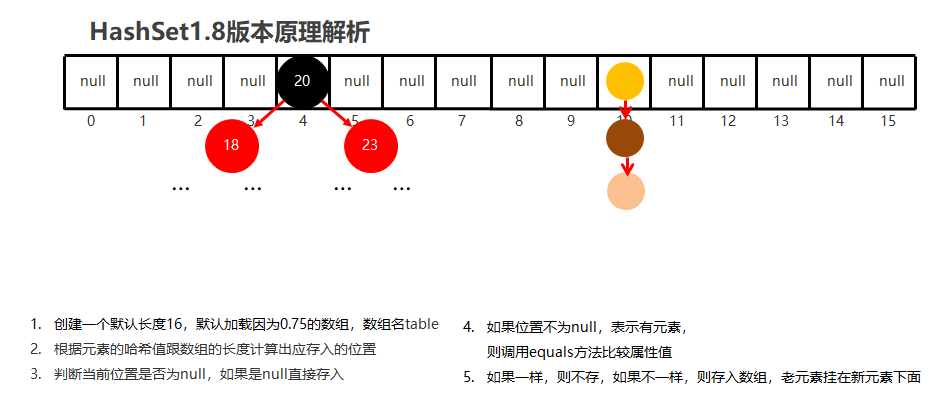
JDK1.8以后 底层进行了优化,由数组+链表+红黑树实现
-
数组 + 链表
-
节点个数多于8个
4.5HashSet集合存储学生对象并遍历【应用】
-
案例需求
-
创建一个存储学生对象的集合,存储多个学生对象,使用程序实现在控制台遍历该集合
-
要求:学生对象的成员变量值相同,我们就认为是同一个对象
-
-
代码实现
学生类
package com.itheima.hashsettest;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
if (age != student.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试类
没有重写hashCode方法,是根据对象的地址值计算的哈希值
哈希值不一样,那么计算出来应存入的索引就不一样
package com.itheima.hashsettest;
import java.util.HashSet;
/*
* - 创建一个存储学生对象的集合,存储多个学生对象,使用程序实现在控制台遍历该集合
- 要求:学生对象的成员变量值相同,我们就认为是同一个对象
*
*结论:
* 如果HashSet集合要存储自定义对象,那么必须重写hashCode和equals方法
* */
public class HashSetTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Student> hs=new HashSet<>();
Student s1=new Student("xiaohei",23);
Student s2=new Student("xiaohei",23);
Student s3=new Student("xiaomei",22);
hs.add(s1);
hs.add(s2);
hs.add(s3);
for (Student h : hs) {
System.out.println(h);
}
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号