Spring Amqp 五种工作模式
么是AMQP?
amqp(高级消息队列协议)是一种协议,类似http协议
amqp协议规定了,消息生产者和mq及消息消费者和mq通信的标准
什么是Spring AMQP?
Spring基于amqp协议定义的一套API规范(spring-amqp),并且由rabbitmq官方对这一套规范进行了实现(spring-rabbit);
SpringAMQP是基于RabbitMQ封装的一套模板,并且还利用SpringBoot对其实现了自动装配,使用起来非常方便。
SpringAMQP提供了三个功能
自动声明队列、交换机及其绑定关系
基于注解的监听器模式,异步接收消息
封装了RabbitTemplate工具,用于发送消息
工作模式
1.简单工作模式
2.工作队列模式
3.发布订阅模式
4.路由模式
5.通配符模式
模式使用如下:
1.简单工作模式
工作流程图:
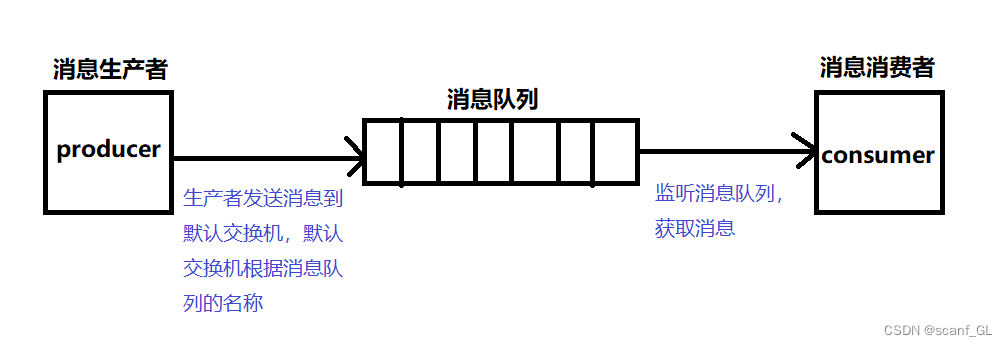
模式特点:生产者发送消息到默认交换机,默认交换机根据消息队列的名称,将消息转发到指定队列。
消费者监听消息队列,获取消息。
项目结构
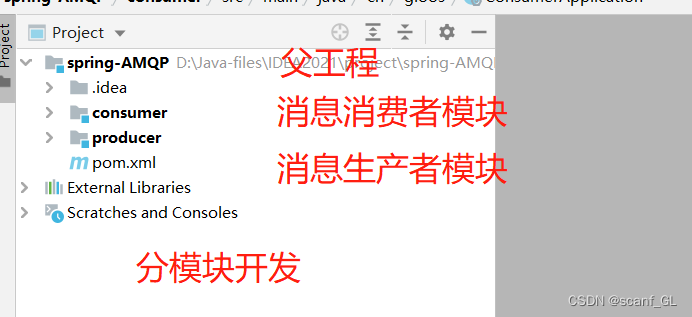
1.父工程的pom.xml
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.3.9.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
2. 消息生产者模块
2.1.消息生产者模块pom.xml,application.yml配置,并编写启动类
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!--AMQP依赖,包含RabbitMQ--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
application.yml配置
server: port: 8081 spring: rabbitmq: # 主机名 host: 192.168.220.131 # 端口 port: 5672 # 用户名和密码 username: guest password: guest # 虚拟主机 virtual-host: /
2.2.编写消息生产者的Controller方法,当访问sendMessage的方法时,向消息队列中发送hello world
@RestController @RequestMapping("/producer") public class ProducerController { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; @GetMapping("/sendMessage") public String sendMessage() { //RabbitTemplate实现消息发送 //参数一:默认的交换机空字符串 //参数二:路由到那个消息队列 //参数三:发送的消息内容 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("","simple.queue","hello world"); return "success"; } }
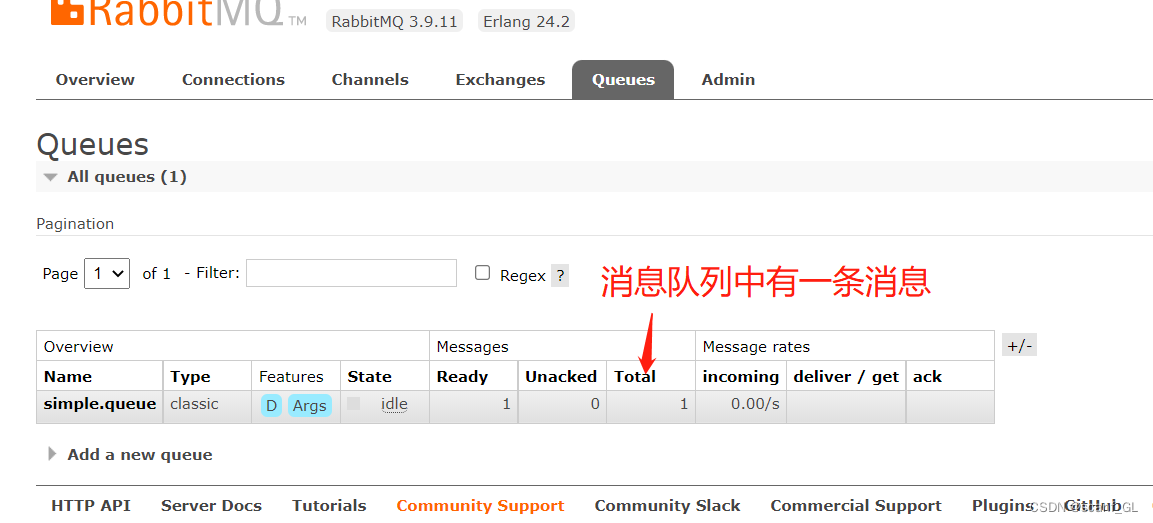
2.3.启动生产者服务,查看RabbitMQ中是否把消息存储到队列中,以及访问Controller方法是否成功
3.消息消费者
3.1.消息消费者模块pom.xml,application.yml配置,并编写启动类
代码和消息生产者的一样,但是application.yml记得修改一下端口
3.2.编写消息消费者的监听,监听消息队列,获取消息
@Component @Slf4j public class SimpleQueueLisener { //监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue") public void receiveMessage(String message) { //由于对消息不做如何操作,在日志打印一下 log.info("接受到的消息是--->{}",message); } }
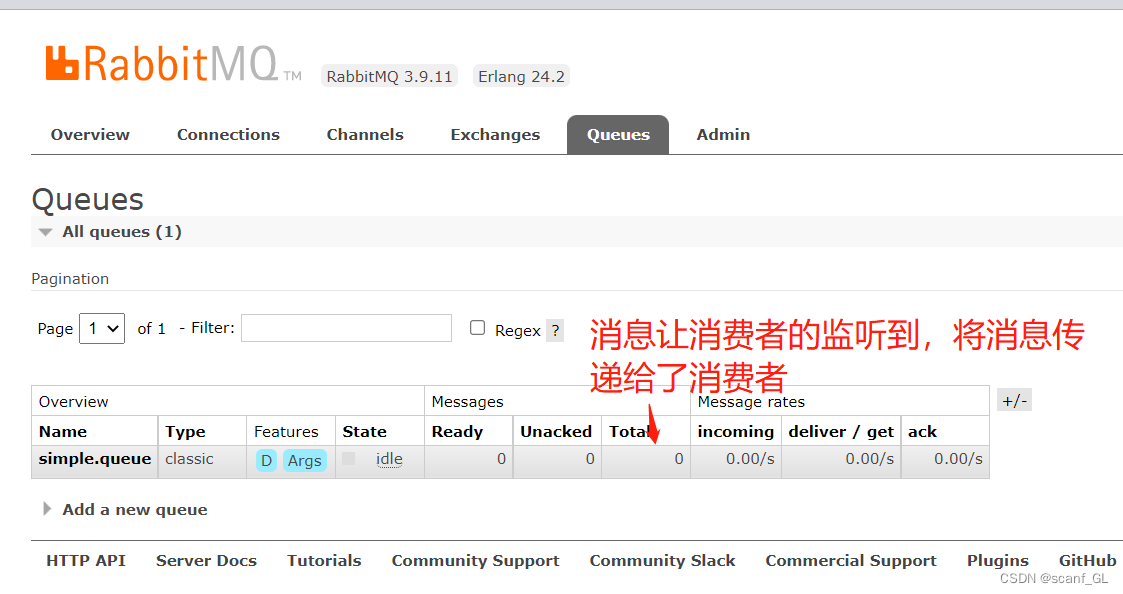
2.3.启动消费者服务,查看RabbitMQ中消息是否被取出,打印到控制台
2.工作队列模式
工作流程图:
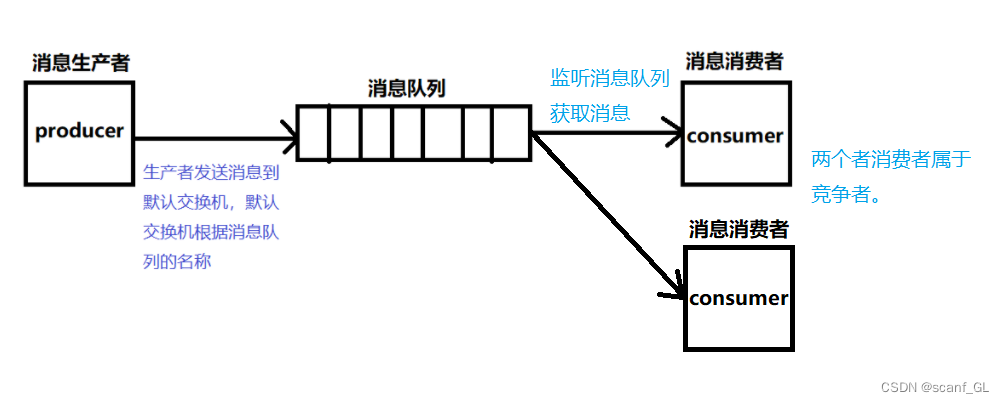
在简单模式的项目结构上,多启动一个消息消费者的主启动类。多个消费者去监听同一个消息队列。
当消息队列数据过多时,一个消费者无法跟上生产者的效率,很可能出现故障,如果还有一个消费者同时去抢消息,那么效率就会很快。
3.发布订阅模式(Fanout:广播,将消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列 )
工作流程图:
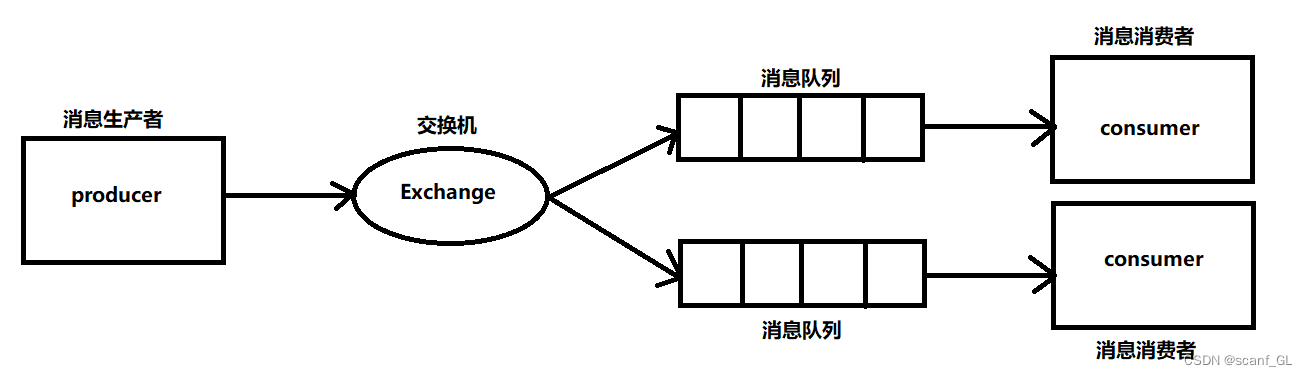
1.生产者发送消息到某个交换机(不能是默认交换机)
2.由交换机将消息转发给绑定它的所有消息队列
3.消费者可以从每一个消息队列中获取消息
1.项目结构同上一样
2.消息生产者模块(该配置类要在消息消费者来一份,由于部署不知道先是生产者还是消费者,防止消费者启动没有交换机和消息队列)
2.1.编写一个Config类,创建交换机,消息队列,并绑定交换机和消息队列
//配置类 @Configuration public class FanoutConfig { /** * 创建交换机 */ @Bean public Exchange createFanoutExchange(){ //参数一:交换机名称 //参数二:是否支持持久化 //参数三:是否自动删除 return new FanoutExchange("exchange",true,false); //构建者模式创建交换机 //return ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange("exchange").durable(true).build(); } /** *创建队列fqueue1 */ @Bean public Queue createFQueue1(){ return QueueBuilder.durable("fqueue1").build(); //队列名字,是否支持持久化 //return new Queue("fqueue1",true); } /** *创建队列fqueue2 */ @Bean public Queue createFQueue2(){ return QueueBuilder.durable("fqueue2").build(); //队列名字,是否支持持久化 //return new Queue("fqueue1",true); } /** *绑定交换机和队列 */ public Binding bindFqueuelToExchange(@Qualifier("createFanoutExchange") Exchange exchange, @Qualifier("createFQueue1") Queue queue){ //将队列1于交换机绑定,with是路由规则是绑定所有 return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("").noargs(); } /** *绑定交换机和队列 */ public Binding bindFqueue2ToExchange(@Qualifier("createFanoutExchange") Exchange exchange, @Qualifier("createFQueue2") Queue queue){ //将队列2于交换机绑定,with是路由规则是绑定所有 return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("").noargs(); } } 2.2.编写Controller方法向交换机发送消息 @GetMapping("/hh") public String sendMm(){ //将消息发送到exchange交换机,路由:路由到所有,默认为"",消息是:你好呀! rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange","","你好呀!"); return "OK"; }
3.消息消费者模块
3.1.创建一个C1模块,编写监听,监听消息
@Component @Slf4j public class C1Lisener { //监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "fqueue1") public void receiveMessage(String message) { //由于对消息不做如何操作,在日志打印一下 log.info("接受到的消息是--->{}",message); } }
3.2.创建一个C2模块,编写监听,监听消息
@Component @Slf4j public class C1Lisener { //监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "fqueue2") public void receiveMessage(String message) { //由于对消息不做如何操作,在日志打印一下 log.info("接受到的消息是--->{}",message); } }
4.查看控制台,消息是否被监听到
4.路由模式(directExchange)
工作流程图:
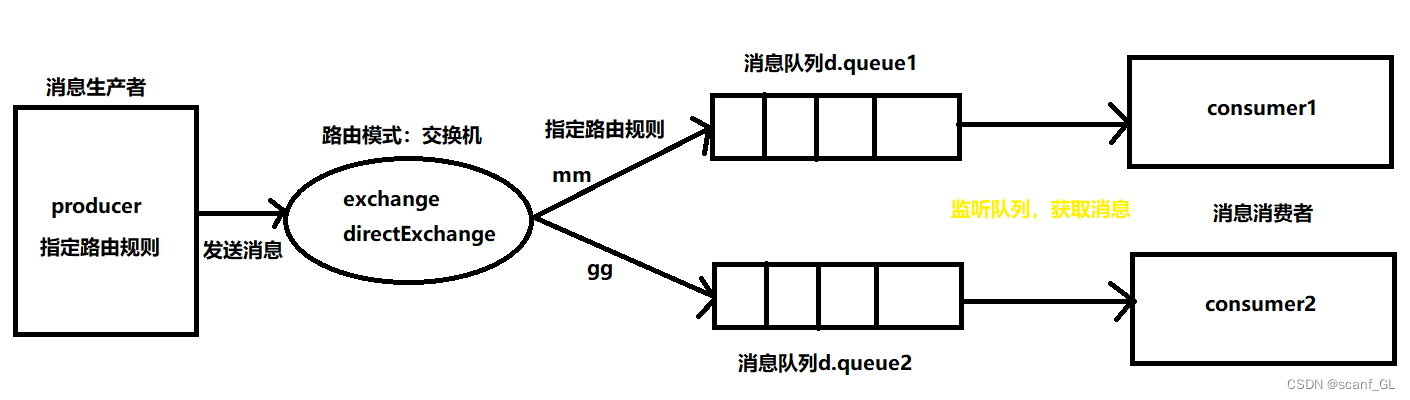
1.生产者发送消息时,需指定交换机名称(directExchange),还要指定路由规则,然后发送到交换机
2.交换机事先通过不同的路由规则和消息队列进行绑定,当交换机拿到消息后,通过路由规则路由到指定队列
3.消费者通过监听获取消息
1.项目结构同上一样
2.消息生产者模块(该配置类要在消息消费者来一份,由于部署不知道先是生产者还是消费者,防止消费者启动没有交换机和消息队列)
2.1.编写一个Config类,创建交换机,消息队列,并绑定交换机和消息队列
@Configuration public class DirectConfig { /** * 创建交换机 */ @Bean public Exchange createDirect(){ return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("dirct.exchange").durable(true).build(); } /** * 创建队列 */ @Bean public Queue Dqueue1(){ return QueueBuilder.durable("d.queue1").build(); } /** * 创建队列 */ @Bean public Queue Dqueue2(){ return QueueBuilder.durable("d.queue2").build(); } /** * 绑定 */ @Bean public Binding bindDQueue1ToExchange(@Qualifier("createDirect") Exchange exchange, @Qualifier("Dqueue1") Queue queue){ return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("mm").noargs(); } /** * 绑定 */ @Bean public Binding bindDQueue2ToExchange(@Qualifier("createDirect") Exchange exchange, @Qualifier("Dqueue2") Queue queue){ return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("gg").noargs(); } }
2.2.编写Controller方法向交换机发送消息
@GetMapping("/mm")
public String sendMm(){
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("dirct.exchange","mm","大美女");
return "OK";
}
@GetMapping("/gg")
public String sendDm(){
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("dirct.exchange","gg","大哥哥");
return "OK OK";
3.消息消费者模块
3.1.创建一个C1模块,编写监听,监听消息
@Component @Slf4j public class C1Lisener { //监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "d.queue1") public void receiveMessage(String message) { //由于对消息不做如何操作,在日志打印一下 log.info("接受到的消息是--->{}",message); } }
3.2.创建一个C2模块,编写监听,监听消息
@Component @Slf4j public class C2Lisener { //监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "d.queue2") public void receiveMessage(String message) { //由于对消息不做如何操作,在日志打印一下 log.info("接受到的消息是--->{}",message); } }
4.查看控制台,消息是否被监听到
5.通配符模式(topicExchange),和路由模式非常像,路由规则不同
工作流程图:
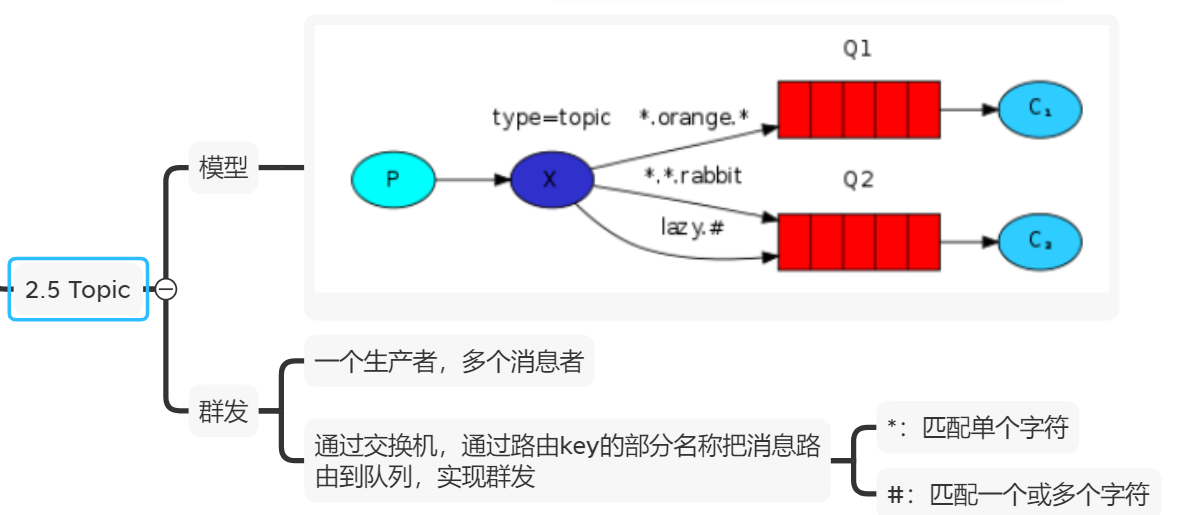
1.生产者发送消息时,需指定交换机名称(topicExchange),还要指定路由规则,然后发送到交换机
通配模式的路由规则:
#:统配0~多个单词,单词之间用.分隔
*:统配一个任意单词
2.交换机事先通过不同的路由规则和消息队列进行绑定,当交换机拿到消息后,通过路由规则路由到指定队列
3.消费者通过监听获取消息
1.项目结构同上一样
2.消息生产者模块(该配置类要在消息消费者来一份,由于部署不知道先是生产者还是消费者,防止消费者启动没有交换机和消息队列)
2.1.编写一个Config类,创建交换机,消息队列,并绑定交换机和消息队列
@Configuration public class TopicConfig { /** * 创建交换机 */ @Bean public Exchange topicExchange(){ return ExchangeBuilder.topicExchange("topic.exchange").durable(true).build(); } /** * 创建消息队列 */ @Bean public Queue queue1(){ return QueueBuilder.durable("t.queue1").build(); } @Bean public Queue queue2(){ return QueueBuilder.durable("t.queue2").build(); } /** * 绑定交换机和消息队列 */ @Bean public Binding bindQ1ToTopic(@Qualifier("topicExchange") Exchange exchange, @Qualifier("queue1") Queue queue){ return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("*.gao.*").noargs(); } /** * 绑定交换机和消息队列 */ @Bean public Binding bindQ2ToTopic(@Qualifier("topicExchange") Exchange exchange, @Qualifier("queue2") Queue queue){ return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("da.#").noargs(); } }
2.2.编写Controller方法向交换机发送消息
@GetMapping("/hh")
public String send1(){
//指定交换机的名称
//通配符模式的路由规则
//消息内容
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topic.exchange","da.gao.aaa","这人牛逼");
return "GLgoodMan";
}
@GetMapping("/dd")
public String send2(){
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topic.exchange","da.hh","hhhhh");
return "hellow";
}
3.消息消费者模块
3.1.创建一个C2模块,编写监听,监听消息
@Component @Slf4j public class TopLisener { @RabbitListener(queues = "t.queue1") public void receiveMessage(String message){ //由于对消息不做如何操作,在日志打印一下 log.info("接受到的消息是--->{}",message); } }
3.2.创建一个C2模块,编写监听,监听消息
@Component @Slf4j public class TopLisener { @RabbitListener(queues = "t.queue2") public void receiveMessage(String message){ //由于对消息不做如何操作,在日志打印一下 log.info("接受到的消息是--->{}",message); } }
4.查看控制台,消息是否被监听到
本文部分资料来源网上,用于做学习笔记.
posted on 2023-09-15 19:17 face-world 阅读(241) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号