9.28 线段树 / 树状数组专项测试 题解
9.28 线段树 / 树状数组专项测试 题解
A. 谜一样的牛(树状数组 + 二分)
题意
有一列数 \(H_1,H_2,\dots,H_n\) 为 \(1\sim n\) 的排列,给定 \(A_i(2\le i\le n)\) 表示第 \(i\) 个数前面有 \(A_i\) 个数比 \(i\) 小,求原数列。
\(1\le n\le10^5\)。
思路
对于这种起始时无从下手的问题,我们可以先考虑边界情况。
考虑如何求 \(H_n\),显然 \(H_n=A_n+1\),即 \(H_n\) 是可选的数的集合中第 \(A_n+1\) 大的数。
那么如何求 \(H_{n-1}\) 呢?由于已经确定 \(H_n\),那么从可选的数的集合即 \(\{1,2,\dots,n\}\) 中把 \(H_n\) 删去,剩下的数中的第 \(A_{n-1}+1\) 大的数即为 \(H_{n-1}\)。
以此类推,每次把所取的数删去,重复在剩下的数中取第 \(A_i+1\) 大的数。
暴力算法很好实现,只需要用 bool 数组维护是否可选,然后遍历一遍即可。但是这样无疑会 T。
考虑用数据结构维护是否可选,并快速查询可选的第 \(x\) 个数。
我们把可选设为 \(1\),不可选设为 \(0\),不难发现数组的前缀和 \(s_i\) 即为 \(i\) 前面(包括 \(i\))有几个数可以选。
所以用支持修改和查询的树状数组维护 bool 数组的前缀和。
并且由于前缀和是单调增加的,我们可以用二分查找到前缀和为 \(A_i+1\) 的位置。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log^2n)\)。
代码
#include <iostream>
#define f(x, y, z) for (int x = (y); (x) <= (z); ++(x))
#define g(x, y, z) for (int x = (y); (x) >= (z); --(x))
#define lowbit(x) x & (-x)
using namespace std;
int const N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
int c[N], a[N], h[N];
void modify(int x, int y) {
while (x <= n) {
c[x] += y;
x += lowbit(x);
}
return;
}
int query(int x) {
int res = 0;
while (x > 0) {
res += c[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return res;
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
modify(1, 1);
f(i, 2, n) cin >> a[i], modify(i, 1);
g(i, n, 1) {
int l = 0, r = n + 1;
while (l + 1 < r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (query(mid) > a[i]) r = mid;
else l = mid;
}
h[i] = r;
modify(r, -1);
}
f(i, 1, n) cout << h[i] << '\n';
return 0;
}
B. Flowers(线段树 / 树状数组)
区间增加 + 离散化 模板题。
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#define f(x, y, z) for (int x = (y); (x) <= (z); ++(x))
#define lson (u << 1)
#define rson (u << 1 | 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int const N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m, q[N];
pair<int, int> a[N];
int raw[N << 1], tot;
map<int, int> val;
struct Node{
int l, r, add;
ll sum;
} tr[N << 3];
void pushup(int u) {
tr[u].sum = tr[lson].sum + tr[rson].sum;
return;
}
void pushdown(int u) {
if (tr[u].add) {
Node &rt = tr[u], &ls = tr[lson], &rs = tr[rson];
ls.add += rt.add, ls.sum += 1ll * rt.add * (raw[ls.r] - raw[ls.l] + 1);
rs.add += rt.add, rs.sum += 1ll * rt.add * (raw[rs.r] - raw[rs.l] + 1);
rt.add = 0;
}
return;
}
void build(int u, int l, int r) {
tr[u].l = l, tr[u].r = r;
if (l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(lson, l, mid);
build(rson, mid + 1, r);
pushup(u);
return;
}
void modify(int u, int l, int r) {
if (l <= tr[u].l && tr[u].r <= r) {
tr[u].add ++;
tr[u].sum += raw[tr[u].r] - raw[tr[u].l] + 1;
return;
}
pushdown(u);
int mid = (tr[u].l + tr[u].r) >> 1;
if (l <= mid) modify(lson, l, r);
if (r > mid) modify(rson, l, r);
pushup(u);
}
int query(int u, int x) {
if (tr[u].l == x && tr[u].r == x) return tr[u].sum;
pushdown(u);
int mid = (tr[u].l + tr[u].r) >> 1;
if (x <= mid) return query(lson, x);
else return query(rson, x);
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
// freopen("test0.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("test0.out", "w", stdout);
cin >> n >> m;
f(i, 1, n) {
cin >> a[i].first >> a[i].second;
raw[++tot] = a[i].first, raw[++tot] = a[i].second;
}
f(i, 1, m) {
cin >> q[i];
raw[++tot] = q[i];
}
sort(raw + 1, raw + tot + 1);
tot = unique(raw + 1, raw + tot + 1) - raw - 1;
f(i, 1, tot) val[raw[i]] = i;
// f(i, 1, tot) cout << i << ' ' << raw[i] << '\n';
build(1, 1, tot);
f(i, 1, n) modify(1, val[a[i].first], val[a[i].second]);
f(i, 1, m) cout << query(1, val[q[i]]) << '\n';
return 0;
}
C. 线段覆盖 4(线段树区间覆盖)
题意
有一根长度为 \(L\) 的白色条状物。有两种操作:
- 用一条长度为 \(T\) 的黑布盖住条状物的 \([a, a+T]\) 这个区间;
- 把某条黑布拿走。
输入 \(L\) 和 \(n\) 次操作,要你输出每次操作之后:
- 条状物上有多少个黑区间;
- 条状物上黑区间的总长度。
思路
线段树区间覆盖问题。具体看代码。
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#define f(x, y, z) for (int x = (y); (x) <= (z); ++(x))
#define lson (u << 1)
#define rson (u << 1 | 1)
using namespace std;
int const N = 2e5 + 10;
int L, n, m, tot;
struct Node{
int l, r, len;
bool l1, r1; //左右端点是否被黑区间覆盖
int cnt, sum; //cnt: 黑区间数 sum: 黑区间长度
int tag; //区间被整个覆盖的层数
} tr[N << 2];
void pushup(int u) {
if (tr[u].tag) { //区间被覆盖至少一层
tr[u].l1 = tr[u].r1 = true;
tr[u].cnt = 1, tr[u].sum = tr[u].len;
return;
}
tr[u].l1 = tr[lson].l1, tr[u].r1 = tr[rson].r1;
tr[u].sum = tr[lson].sum + tr[rson].sum;
tr[u].cnt = tr[lson].cnt + tr[rson].cnt;
if (tr[lson].r1 && tr[rson].l1) tr[u].cnt--; //lson的右端和rson的左端合并
return;
}
void build(int u, int l, int r) {
tr[u].l = l, tr[u].r = r, tr[u].len = r - l + 1;
if (l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(lson, l, mid);
build(rson, mid + 1, r);
return;
}
void modify(int u, int l, int r, int x) {
if (l <= tr[u].l && tr[u].r <= r) {
tr[u].tag += x;
if (tr[u].len == 1) {
if (tr[u].tag)
tr[u].l1 = tr[u].r1 = tr[u].cnt = tr[u].sum = 1;
else
tr[u].l1 = tr[u].r1 = tr[u].cnt = tr[u].sum = 0;
} else pushup(u);
return;
}
int mid = (tr[u].l + tr[u].r) >> 1;
if (l <= mid) modify(lson, l, r, x);
if (r > mid) modify(rson, l, r, x);
pushup(u);
return;
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
// freopen("xdfg5.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("xdfg5.out", "w", stdout);
cin >> L >> n;
build(1, 0, L);
int m, a, t;
f(i, 1, n) {
cin >> m >> a >> t;
if (m == 1) {
modify(1, a, a + t - 1, 1);
cout << tr[1].cnt << ' ' << tr[1].sum << '\n';
} else if (m == 2) {
modify(1, a, a + t - 1, -1);
cout << tr[1].cnt << ' ' << tr[1].sum << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
D. 矩形周长并(扫描线)
题意
给定平面上一些矩形的左下顶点和右上顶点的坐标,求这些矩形的并的周长。
样例说明:
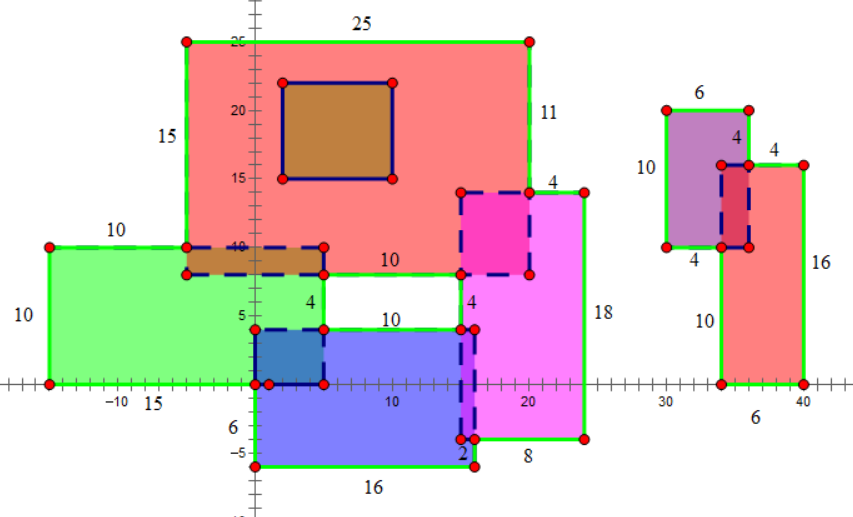
绿边围成的图形为矩形的并,绿边的长度之和即为周长。
思路
https://blog.csdn.net/codeswarrior/article/details/81079942
从左到右进行扫描,用线段树维护区间中线段的段数 \(num\),区间整个被覆盖的次数 \(cnt\),区间被覆盖的长度 \(len\)。
答案由横边和竖边两部分组成。
竖边的计算方式为:这一次扫描到的总覆盖长度 与 上一次扫描到的总覆盖长度 的差的绝对值,即这一次的 tr[1].len 与上一次的 tr[1].len 的差的绝对值。
横边的计算方式为:这一次扫描到的区间内线段数量 乘 这一次扫描与下一次扫描的横坐标的差值 乘二,即 tr[1].num * (q[i + 1].x - q[i].x) * 2。
最后别忘了加上最后一条竖边。
注意:在对修改操作按 x 排序的时候,x 相同时(即左侧的长方形的右边和右侧的长方形的左边重合)要把 1 放在前面,-1 放在后面,因为这条边是不算在周长内的,所以不可以在过程中有这段区间变为 0 的时刻。
代码
不知道为什么 HDU 评测 WA 80,POJ、 Luogu 和码创都能过。。。求大佬纠错
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#define abs(x) (((x) < 0) ? (-(x)) : (x))
#define f(x, y, z) for (int x = (y); (x) <= (z); ++(x))
#define lson (u << 1)
#define rson (u << 1 | 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int const N = 1e4 + 10;
int n, ans;
int raw[N], cnt;
map<int, int> val;
struct question {
int x, y1, y2, k;
question() {}
question(int a, int b, int c, int d): x(a), y1(b), y2(c), k(d) {}
bool operator<(question const &o) const { return x == o.x ? k > o.k : x < o.x; }
} q[N];
struct node {
int l, r;
int cnt; //这个区间被覆盖了几次
int num; //区间内线段的个数
int len; //区间内被线段覆盖的长度(离散之前)
bool lbd, rbd;
} tr[N << 2];
void pushup(int u) {
if (tr[u].cnt) {
tr[u].lbd = tr[u].rbd = true;
tr[u].len = raw[tr[u].r + 1] - raw[tr[u].l];
tr[u].num = 1;
return;
}
tr[u].len = tr[lson].len + tr[rson].len;
tr[u].num = tr[lson].num + tr[rson].num;
tr[u].lbd = tr[lson].lbd, tr[u].rbd = tr[rson].rbd;
if (tr[lson].rbd && tr[rson].lbd) tr[u].num--;
return;
}
void build(int u, int l, int r) {
tr[u].l = l, tr[u].r = r;
if (l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(lson, l, mid);
build(rson, mid + 1, r);
return;
}
void modify(int u, int l, int r, int x) {
if (l <= tr[u].l && tr[u].r <= r) {
tr[u].cnt += x;
pushup(u);
return;
}
int mid = (tr[u].l + tr[u].r) >> 1;
if (l <= mid) modify(lson, l, r, x);
if (r > mid) modify(rson, l, r, x);
pushup(u);
return;
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
f(i, 1, n) {
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
q[(i << 1) - 1] = question(x1, y1, y2, 1);
q[i << 1] = question(x2, y1, y2, -1);
raw[++cnt] = y1, raw[++cnt] = y2;
}
sort(raw + 1, raw + cnt + 1);
cnt = unique(raw + 1, raw + cnt + 1) - raw - 1;
f(i, 1, cnt) val[raw[i]] = i;
n <<= 1;
sort(q + 1, q + n + 1);
build(1, 1, n);
int lst = 0;
f(i, 1, n - 1) {
modify(1, val[q[i].y1], val[q[i].y2] - 1, q[i].k);
ans += abs(tr[1].len - lst);
lst = tr[1].len;
ans += (q[i + 1].x - q[i].x) * 2 * tr[1].num;
}
ans += lst;
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号