9.2 数论测试 B. 方程 题解
答案取模无高精度非毒瘤版:P1445 [Violet] 樱花
题目描述
给定一个正整数 \(n\),找到符合下面方程的正整数解 \((x,y)\) 的数量:
其中,\(n!\) 表示 \(n\) 的阶乘,即 \(n!=1\times 2\times 3\times \ldots \times n\)。
数据范围
对于 \(30\%\) 的数据,满足 \(n\le 100\),数据不超过 10 组;
对于 \(50\%\) 的数据,满足:\(n\le 10^3\),数据组数不超过 20 组;
对于 \(100\%\) 的数据,满足:\(n\le 10^4\),数据组数不超过 30 组。
分析
一波大力推导式子:
来自数学大佬 Raymin 的神奇因式分解:
于是得到
由于每一组不同的解 \((x,y)\) 都对应一个 \(x\),每一个 \(x\) 都对应一个 \(x-n!\),而不同的 \((x-n!)\) 的个数即为 \((n!)^2\) 的因数个数,所以求出 \((n!)^2\) 的因数个数即为答案。
设 \(n!=p_1^{\alpha_1}p_2^{\alpha_2}\dots p_k^{\alpha_k}\),则 \((n!)^2=p_1^{2\alpha_1}p_2^{2\alpha_2}\dots p_k^{2\alpha_k}\)。
所以
那么,对于每一个质因子 \(p_i\),如何求出对应的 \(\alpha_i\) 呢?
下面是举例子环节:
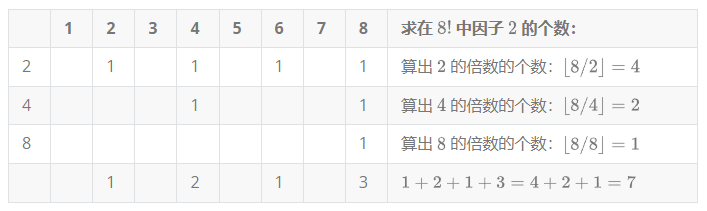
比如求 \(8!\) 中 \(2\) 的个数:
\(4+2+1=7\),所以一共 \(7\) 个 \(2\) 出现了。
于是我们得到:\(\alpha_i=\left\lfloor\dfrac n{p_i^1}\right\rfloor+\left\lfloor\dfrac n{p_i^2}\right\rfloor+\left\lfloor\dfrac n{p_i^3}\right\rfloor+\dots\)
直到 \(p_i\) 的幂大于 \(n\) 停止循环。
到这里我们可以发现:我们平时求的方法是一列一列求的(就是每一个数算一遍),而这个方法我们一行一行地求,虽然效果一样,但求起来速度很快。值得学习。
写成代码就是:
get_pri(); //线性筛n以内的素数
ll ans = 1; //(n!)^2的因子个数
int tmp = n; //存一下n
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt && pri[i] <= n; i++) {
int nw = 0; //相当于alpha_i
while (n) {
nw += n / pri[i];
n /= pri[i];
}
//注意求的是n!的平方的因子个数,所以alpha_i需要*2之后再+1
ans = ans * (nw << 1 | 1);
}
上面代码中的 ans 即为答案。
注意
- 多组数据;
- 不写高精度只有 10pts。。。高精度模板:OI Wiki。
总结
大力推式子得到答案为 \((n!)^2\) 的约数个数;- 快速求出 \(n!\) 的每个质因子的次数,由此求出 \((n!)^2\) 的约数个数;
- 高精度。
代码
(高精度模板和线性筛模板省略)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <bitset>
#define f(x, y, z) for (register int x = (y); (x) <= (z); (x)++)
#define g(x, y, z) for (register int x = (y); (x) >= (z); (x)--)
using namespace std;
int const N = 10010;
int pri[1600], cnt;
bitset<N> ck;
void get_pri() { ... }
#define MAXN 9999
#define MAXSIZE 10024
struct Big {
int a[MAXSIZE], len;
bool flag; // 标记符号'-'
Big() {
len = 1;
memset(a, 0, sizeof a);
flag = 0;
}
Big(const int);
Big& operator=(const Big&);
Big operator*(const Big&) const;
};
Big::Big(const int b) { ... }
Big& Big::operator=(const Big& T) { ... }
Big Big::operator*(const Big& T) const { ... }
inline void print(const Big& s) { ... }
signed main() {
int n;
get_pri();
while (cin >> n, n) {
Big ans(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt && pri[i] <= n; i++) {
int tmp = n, nw = 0;
while (tmp) {
nw += tmp / pri[i];
tmp /= pri[i];
}
ans = ans * (nw << 1 | 1);
}
print(ans);
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号