[第三天 4h]学习deep learning ,有GPU的PC,win10 搭建开发环境
参考链接:
【Anaconda+pycharm+pytorch】超详细pytorch安装教程_pycharm,anconda,pytorch安装csdn-CSDN博客
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9B8pqo3juYQ1WSEwGAnYwg
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/7mryfMqJx0gHsuI4TK4iCw
AI开发环境一步到位:Anaconda + PyTorch + PyCharm 安装配置全攻略
1、安装anaconda,创建一个虚拟环境
2、CUDA与Cudnn的安装,官网速度快,直接下载
在「命令提示符 / Anaconda Prompt」中输入 nvidia-smi,查看“CUDA Version” 字段,记录支持的最高 CUDA 版本(后续安装需选择不高于此版本的 PyTorch-CUDA 对应版本)。
https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive
https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-archive
3、安装pytorch
https://pytorch.org/ 注意GPU版本,官网生成命令行:
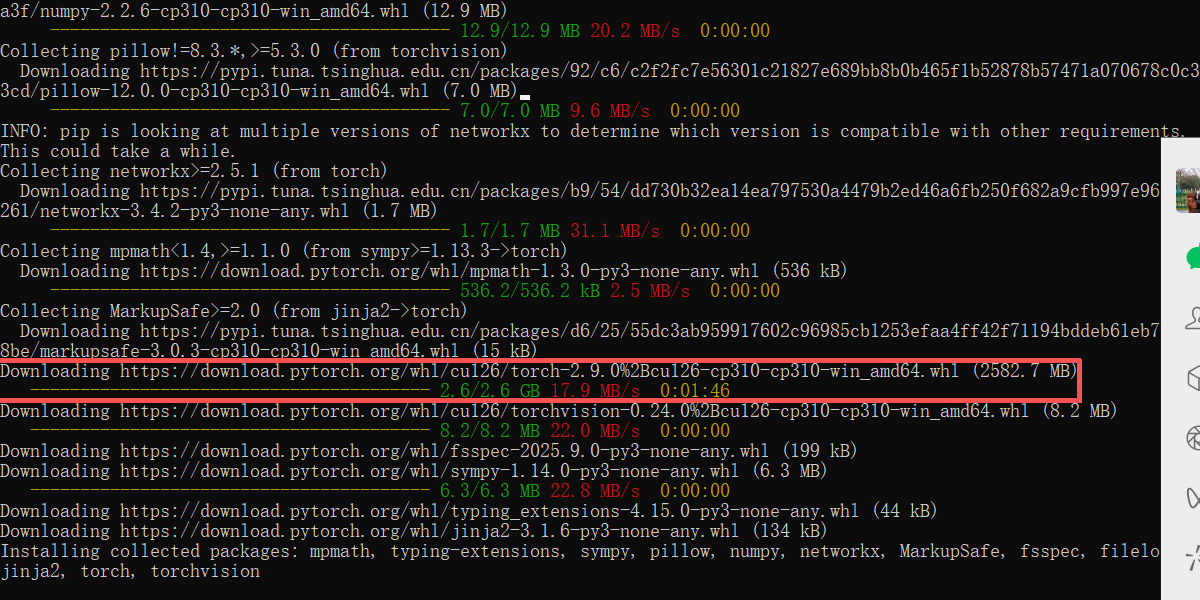
pip3 install torch torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126
若网速较慢,可添加国内源(如清华源)加速,命令如下:
pip3 install torch torchvision --index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple --trusted-host pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126
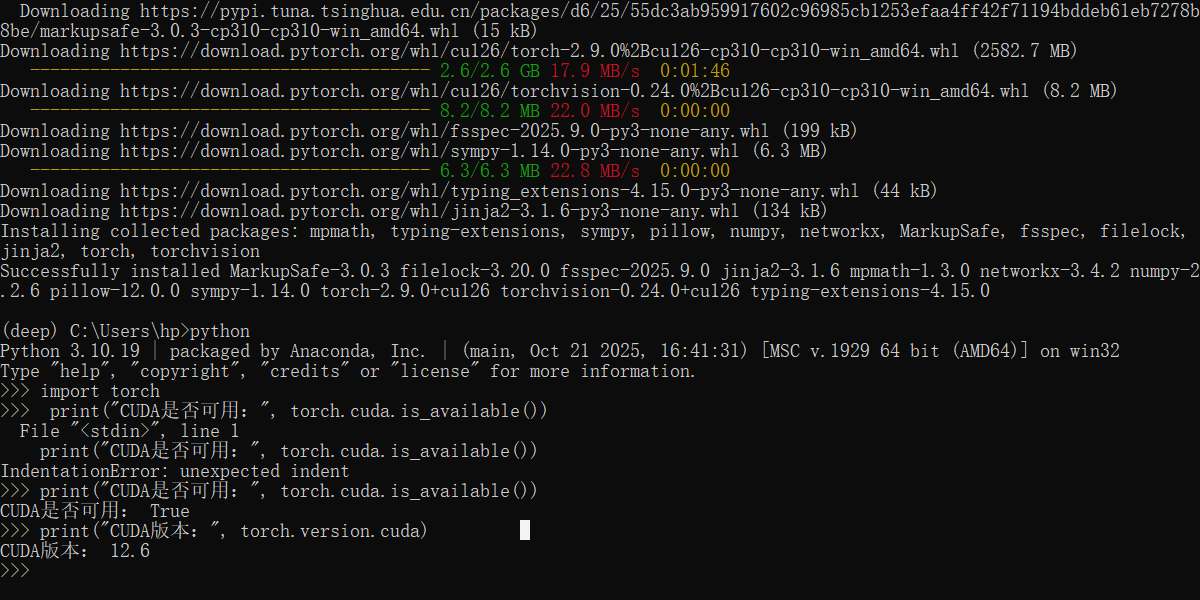
在命令提示符中输入以下命令,验证安装是否成功
python
>>> import torch
>>> print("CUDA是否可用:", torch.cuda.is_available()) # 返回True表示成功
>>> print("CUDA版本:", torch.version.cuda) # 应显示12.6(与CUDA Toolkit版本一致)
>>> exit()
4、安装pycharm
PyCharm professional 2023.1.4版本免费激活_pycharm2023激活-CSDN博客
5、安装vscode
配置conda的虚拟环境
首先在命令行中确认环境是否存在且能正常激活:
# 打开命令提示符或 Anaconda Prompt
conda info --envs
#应该能看到你的 deep 环境。然后激活测试:
conda activate deep
python --version
B、打开 VSCode,按 Ctrl+Shift+P 打开命令面板,输入Python: Select Interpreter配置。
也可以json文件配置。输入: Preferences: Open Settings (JSON)配置。例如:
{
"python.condaPath": "C:\\Users\\hp\\anaconda3\\Scripts\\conda.exe",
"python.defaultInterpreterPath": "C:\\Users\\hp\\anaconda3\\envs\\deep\\python.exe",
"python.terminal.activateEnvironment": true
}
6、测试例子
MNIST

import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim from torchvision import datasets, transforms from torch.utils.data import DataLoader # 确定设备 device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') # 定义模型 class SimpleCNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(SimpleCNN, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=3, padding=1) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1) self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2) self.fc1 = nn.Linear(64 * 7 * 7, 128) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 10) self.relu = nn.ReLU() self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5) def forward(self, x): x = self.pool(self.relu(self.conv1(x))) x = self.pool(self.relu(self.conv2(x))) x = x.view(-1, 64 * 7 * 7) x = self.relu(self.fc1(x)) x = self.dropout(x) x = self.fc2(x) return x # 加载本地数据 transform = transforms.Compose([ transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,)) ]) train_dataset = datasets.MNIST('./data', train=True, transform=transform) test_dataset = datasets.MNIST('./data', train=False, transform=transform) train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True, num_workers=0) test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=1000, shuffle=False, num_workers=0) # 初始化模型 model = SimpleCNN().to(device) criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001) # 训练循环 def train(): model.train() for epoch in range(3): for images, labels in train_loader: images = images.to(device) labels = labels.to(device) optimizer.zero_grad() outputs = model(images) loss = criterion(outputs, labels) loss.backward() optimizer.step() # 评估 def evaluate(): model.eval() correct = 0 total = 0 with torch.no_grad(): for images, labels in test_loader: images = images.to(device) labels = labels.to(device) outputs = model(images) _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1) total += labels.size(0) correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item() return 100 * correct / total # 运行 print("开始训练...") train() print(f"测试准确率: {evaluate():.2f}%")

# CIFAR-10 :是一个用于小图像分类的数据集,包含10个类别的60000张32x32彩色图像, # 每个类别有6000张图片。这个数据集对于理解卷积神经网络(CNN)等更高级的图像处理技术非常有用。 # 使用pytorch+cuda python代码 import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim import torch.nn.functional as F import torchvision import torchvision.transforms as transforms import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import time from tqdm import tqdm class CIFAR10Trainer: def __init__(self, batch_size=128, learning_rate=0.001): self.device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') self.batch_size = batch_size self.learning_rate = learning_rate self.classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck') print(f"使用设备: {self.device}") self.setup_data() self.setup_model() def setup_data(self): """设置数据加载和预处理""" # 数据增强和预处理 transform_train = transforms.Compose([ transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4), transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)), ]) transform_test = transforms.Compose([ transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)), ]) # 加载数据集 self.trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10( root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform_train) self.trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( self.trainset, batch_size=self.batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=2) self.testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10( root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform_test) self.testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( self.testset, batch_size=self.batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=2) print(f"训练集大小: {len(self.trainset)}") print(f"测试集大小: {len(self.testset)}") def setup_model(self): """初始化模型""" self.model = CIFAR10CNN().to(self.device) self.criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.model.parameters(), lr=self.learning_rate, weight_decay=1e-4) self.scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(self.optimizer, step_size=15, gamma=0.1) print("模型初始化完成") print(f"模型参数量: {sum(p.numel() for p in self.model.parameters()):,}") def train(self, epochs=30): """训练模型""" print(f"开始训练,共{epochs}个epochs...") train_losses = [] test_accuracies = [] best_accuracy = 0.0 for epoch in range(epochs): start_time = time.time() self.model.train() running_loss = 0.0 correct = 0 total = 0 # 使用tqdm显示进度条 pbar = tqdm(self.trainloader, desc=f'Epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs}') for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(pbar): inputs, targets = inputs.to(self.device), targets.to(self.device) self.optimizer.zero_grad() outputs = self.model(inputs) loss = self.criterion(outputs, targets) loss.backward() self.optimizer.step() running_loss += loss.item() _, predicted = outputs.max(1) total += targets.size(0) correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item() # 更新进度条 pbar.set_postfix({ 'Loss': f'{running_loss / (batch_idx + 1):.3f}', 'Acc': f'{100. * correct / total:.2f}%' }) # 计算训练准确率 train_accuracy = 100. * correct / total avg_loss = running_loss / len(self.trainloader) # 在测试集上评估 test_accuracy = self.evaluate() test_accuracies.append(test_accuracy) train_losses.append(avg_loss) # 学习率调度 self.scheduler.step() epoch_time = time.time() - start_time print(f'Epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs} - Time: {epoch_time:.2f}s') print(f'训练损失: {avg_loss:.4f}, 训练准确率: {train_accuracy:.2f}%, 测试准确率: {test_accuracy:.2f}%') print('-' * 60) # 保存最佳模型 if test_accuracy > best_accuracy: best_accuracy = test_accuracy self.save_model('best_cifar10_model.pth') print(f'新的最佳模型已保存,准确率: {best_accuracy:.2f}%') self.train_losses = train_losses self.test_accuracies = test_accuracies return train_losses, test_accuracies def evaluate(self): """评估模型在测试集上的表现""" self.model.eval() correct = 0 total = 0 with torch.no_grad(): for inputs, targets in self.testloader: inputs, targets = inputs.to(self.device), targets.to(self.device) outputs = self.model(inputs) _, predicted = outputs.max(1) total += targets.size(0) correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item() accuracy = 100. * correct / total return accuracy def evaluate_per_class(self): """评估每个类别的准确率""" self.model.eval() class_correct = list(0. for _ in range(10)) class_total = list(0. for _ in range(10)) with torch.no_grad(): for inputs, targets in self.testloader: inputs, targets = inputs.to(self.device), targets.to(self.device) outputs = self.model(inputs) _, predicted = outputs.max(1) c = predicted.eq(targets) for i in range(targets.size(0)): label = targets[i] class_correct[label] += c[i].item() class_total[label] += 1 print("\n各类别准确率:") for i in range(10): accuracy = 100 * class_correct[i] / class_total[i] print(f'{self.classes[i]:10s}: {accuracy:.2f}%') return class_correct, class_total def visualize_predictions(self, num_images=12): """可视化预测结果""" self.model.eval() # 获取一批测试数据 dataiter = iter(self.testloader) images, labels = next(dataiter) images, labels = images.to(self.device), labels.to(self.device) # 预测 with torch.no_grad(): outputs = self.model(images[:num_images]) _, predicted = outputs.max(1) # 转换图像用于显示 images = images.cpu() imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(images[:num_images])) # 打印结果 print('预测结果: ', ' '.join(f'{self.classes[predicted[j]]:5s}' for j in range(num_images))) print('真实标签: ', ' '.join(f'{self.classes[labels[j]]:5s}' for j in range(num_images))) # 计算这批图像的准确率 correct = predicted.eq(labels[:num_images]).sum().item() print(f'这批图像的准确率: {100. * correct / num_images:.1f}%') def plot_training_history(self): """绘制训练历史""" plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4)) plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.plot(self.train_losses) plt.title('训练损失') plt.xlabel('Epoch') plt.ylabel('Loss') plt.grid(True) plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.plot(self.test_accuracies) plt.title('测试准确率') plt.xlabel('Epoch') plt.ylabel('Accuracy (%)') plt.grid(True) plt.tight_layout() plt.show() def save_model(self, filename): """保存模型""" torch.save({ 'model_state_dict': self.model.state_dict(), 'optimizer_state_dict': self.optimizer.state_dict(), 'test_accuracy': self.test_accuracies[-1] if hasattr(self, 'test_accuracies') else 0 }, filename) def load_model(self, filename): """加载模型""" checkpoint = torch.load(filename) self.model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict']) self.optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer_state_dict']) print(f"模型已加载,测试准确率: {checkpoint['test_accuracy']:.2f}%") class CIFAR10CNN(nn.Module): """CIFAR-10 CNN模型""" def __init__(self): super(CIFAR10CNN, self).__init__() self.conv_layers = nn.Sequential( # 第一层卷积 nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 3, padding=1), nn.BatchNorm2d(32), nn.ReLU(), nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(), nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2), nn.Dropout(0.25), # 第二层卷积 nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, padding=1), nn.BatchNorm2d(64), nn.ReLU(), nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(), nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2), nn.Dropout(0.25), # 第三层卷积 nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3, padding=1), nn.BatchNorm2d(128), nn.ReLU(), nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(), nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2), nn.Dropout(0.25), ) self.fc_layers = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(128 * 4 * 4, 512), nn.BatchNorm1d(512), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5), nn.Linear(512, 256), nn.BatchNorm1d(256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5), nn.Linear(256, 10) ) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv_layers(x) x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) x = self.fc_layers(x) return x def imshow(img): """显示图像""" img = img / 2 + 0.5 # 反标准化 npimg = img.numpy() plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8)) plt.imshow(np.transpose(npimg, (1, 2, 0))) plt.axis('off') plt.show() def main(): """主函数""" # 创建训练器实例 trainer = CIFAR10Trainer(batch_size=128, learning_rate=0.001) # 训练模型 trainer.train(epochs=30) # 绘制训练历史 trainer.plot_training_history() # 评估每个类别的表现 trainer.evaluate_per_class() # 可视化一些预测结果 print("\n可视化预测结果:") trainer.visualize_predictions(num_images=12) # 最终测试准确率 final_accuracy = trainer.evaluate() print(f"\n最终测试准确率: {final_accuracy:.2f}%") # 保存最终模型 trainer.save_model('final_cifar10_model.pth') print("模型已保存为 'final_cifar10_model.pth'") if __name__ == "__main__": main()
IMDB情感分析 - 简化版本(不依赖nltk)

# IMDB情感分析 - 简化版本(不依赖nltk) import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim import torch.nn.functional as F from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader import re import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tqdm import tqdm import time from collections import Counter import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') class IMDBDataset(Dataset): """IMDB数据集类""" def __init__(self, reviews, labels, vocab, max_length=200): self.reviews = reviews self.labels = labels self.vocab = vocab self.max_length = max_length def __len__(self): return len(self.reviews) def __getitem__(self, idx): review = self.reviews[idx] label = self.labels[idx] # 将文本转换为索引序列 words = review.split()[:self.max_length] indices = [self.vocab.get(word, self.vocab['<UNK>']) for word in words] # 填充或截断到固定长度 if len(indices) < self.max_length: indices += [self.vocab['<PAD>']] * (self.max_length - len(indices)) else: indices = indices[:self.max_length] return torch.tensor(indices, dtype=torch.long), torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.float) class TextProcessor: """文本预处理类(不依赖nltk)""" def __init__(self): # 简单的英文停用词列表 self.stop_words = set([ 'i', 'me', 'my', 'myself', 'we', 'our', 'ours', 'ourselves', 'you', "you're", "you've", "you'll", "you'd", 'your', 'yours', 'yourself', 'yourselves', 'he', 'him', 'his', 'himself', 'she', "she's", 'her', 'hers', 'herself', 'it', "it's", 'its', 'itself', 'they', 'them', 'their', 'theirs', 'themselves', 'what', 'which', 'who', 'whom', 'this', 'that', "that'll", 'these', 'those', 'am', 'is', 'are', 'was', 'were', 'be', 'been', 'being', 'have', 'has', 'had', 'having', 'do', 'does', 'did', 'doing', 'a', 'an', 'the', 'and', 'but', 'if', 'or', 'because', 'as', 'until', 'while', 'of', 'at', 'by', 'for', 'with', 'about', 'against', 'between', 'into', 'through', 'during', 'before', 'after', 'above', 'below', 'to', 'from', 'up', 'down', 'in', 'out', 'on', 'off', 'over', 'under', 'again', 'further', 'then', 'once', 'here', 'there', 'when', 'where', 'why', 'how', 'all', 'any', 'both', 'each', 'few', 'more', 'most', 'other', 'some', 'such', 'no', 'nor', 'not', 'only', 'own', 'same', 'so', 'than', 'too', 'very', 's', 't', 'can', 'will', 'just', 'don', "don't", 'should', "should've", 'now', 'd', 'll', 'm', 'o', 're', 've', 'y', 'ain', 'aren', "aren't", 'couldn', "couldn't", 'didn', "didn't", 'doesn', "doesn't", 'hadn', "hadn't", 'hasn', "hasn't", 'haven', "haven't", 'isn', "isn't", 'ma', 'mightn', "mightn't", 'mustn', "mustn't", 'needn', "needn't", 'shan', "shan't", 'shouldn', "shouldn't", 'wasn', "wasn't", 'weren', "weren't", 'won', "won't", 'wouldn', "wouldn't" ]) def clean_text(self, text): """清洗文本""" # 转换为小写 text = text.lower() # 移除HTML标签 text = re.sub(r'<.*?>', '', text) # 移除标点符号和特殊字符,但保留基本标点 text = re.sub(r'[^a-zA-Z\s!?]', '', text) # 移除多余空格 text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text).strip() return text def simple_tokenize(self, text): """简单分词并移除停用词""" tokens = text.split() tokens = [token for token in tokens if token not in self.stop_words and len(token) > 1] return ' '.join(tokens) class LSTMSentiment(nn.Module): """LSTM情感分析模型""" def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim=128, hidden_dim=256, output_dim=1, n_layers=2, dropout=0.3): super(LSTMSentiment, self).__init__() self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, padding_idx=0) self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim, n_layers, batch_first=True, dropout=dropout, bidirectional=True) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim * 2, output_dim) self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid() def forward(self, x): embedded = self.embedding(x) lstm_out, (hidden, _) = self.lstm(embedded) # 使用双向LSTM的最后一个隐藏状态 out = self.dropout(torch.cat((hidden[-2, :, :], hidden[-1, :, :]), dim=1)) out = self.fc(out) return self.sigmoid(out).squeeze() class IMDBSentimentTrainer: """IMDB情感分析训练器""" def __init__(self, batch_size=32, max_length=200, vocab_size=10000): self.device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') self.batch_size = batch_size self.max_length = max_length self.vocab_size = vocab_size self.text_processor = TextProcessor() print(f"使用设备: {self.device}") print(f"批大小: {batch_size}, 最大序列长度: {max_length}, 词汇表大小: {vocab_size}") def load_and_preprocess_data(self): """加载和预处理数据""" print("正在加载IMDB数据集...") try: from torchtext.datasets import IMDB from torchtext.data.utils import get_tokenizer from torchtext.vocab import build_vocab_from_iterator # 获取数据 print("下载数据中...") train_iter = IMDB(split='train') test_iter = IMDB(split='test') train_data = list(train_iter) test_data = list(test_iter) except Exception as e: print(f"加载IMDB数据集失败: {e}") print("使用模拟数据进行测试...") return self._create_dummy_data() print(f"训练集大小: {len(train_data)}") print(f"测试集大小: {len(test_data)}") # 预处理文本 print("预处理文本...") train_texts = [] train_labels = [] for text, label in tqdm(train_data, desc="处理训练数据"): cleaned = self.text_processor.clean_text(text) tokenized = self.text_processor.simple_tokenize(cleaned) train_texts.append(tokenized) train_labels.append(label - 1) # 将标签从[1,2]转换为[0,1] test_texts = [] test_labels = [] for text, label in tqdm(test_data, desc="处理测试数据"): cleaned = self.text_processor.clean_text(text) tokenized = self.text_processor.simple_tokenize(cleaned) test_texts.append(tokenized) test_labels.append(label - 1) # 构建词汇表 print("构建词汇表...") all_words = [] for text in train_texts: all_words.extend(text.split()) word_freq = Counter(all_words) common_words = word_freq.most_common(self.vocab_size - 2) vocab = {'<PAD>': 0, '<UNK>': 1} for i, (word, freq) in enumerate(common_words): vocab[word] = i + 2 print(f"词汇表大小: {len(vocab)}") # 创建数据集 self.train_dataset = IMDBDataset(train_texts, train_labels, vocab, self.max_length) self.test_dataset = IMDBDataset(test_texts, test_labels, vocab, self.max_length) self.vocab = vocab return train_texts, train_labels, test_texts, test_labels, vocab def _create_dummy_data(self): """创建模拟数据用于测试""" print("创建模拟数据...") dummy_texts = [ "this movie is great and wonderful I love it", "terrible film waste of time horrible", "amazing acting and story fantastic", "boring and disappointing movie bad", "fantastic cinematography and direction excellent", "poor script and bad acting awful", "excellent performance by all actors superb", "awful storyline and characters terrible", "beautiful photography and music nice", "horrible editing and pacing disgusting" ] dummy_labels = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0] # 构建词汇表 all_words = [] for text in dummy_texts: words = self.text_processor.clean_text(text).split() all_words.extend(words) word_counts = Counter(all_words) vocab = {'<PAD>': 0, '<UNK>': 1} for i, (word, count) in enumerate(word_counts.most_common(self.vocab_size - 2)): vocab[word] = i + 2 self.train_dataset = IMDBDataset(dummy_texts, dummy_labels, vocab, self.max_length) self.test_dataset = IMDBDataset(dummy_texts, dummy_labels, vocab, self.max_length) self.vocab = vocab return dummy_texts, dummy_labels, dummy_texts, dummy_labels, vocab def setup_model(self, model_type='lstm'): """设置模型""" if model_type == 'lstm': self.model = LSTMSentiment( vocab_size=len(self.vocab), embedding_dim=128, hidden_dim=256, n_layers=2, dropout=0.3 ).to(self.device) self.criterion = nn.BCELoss() self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.model.parameters(), lr=0.001) self.scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(self.optimizer, patience=2) print(f"使用模型: {model_type}") print(f"模型参数量: {sum(p.numel() for p in self.model.parameters()):,}") def train(self, epochs=5): """训练模型""" print("开始训练...") train_loader = DataLoader(self.train_dataset, batch_size=self.batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=0) train_losses = [] train_accuracies = [] val_accuracies = [] best_accuracy = 0.0 for epoch in range(epochs): start_time = time.time() self.model.train() running_loss = 0.0 correct = 0 total = 0 pbar = tqdm(train_loader, desc=f'Epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs}') for batch_idx, (data, targets) in enumerate(pbar): data, targets = data.to(self.device), targets.to(self.device) self.optimizer.zero_grad() outputs = self.model(data) loss = self.criterion(outputs, targets) loss.backward() # 梯度裁剪防止梯度爆炸 torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0) self.optimizer.step() running_loss += loss.item() predicted = (outputs > 0.5).float() total += targets.size(0) correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item() # 更新进度条 pbar.set_postfix({ 'Loss': f'{running_loss / (batch_idx + 1):.4f}', 'Acc': f'{100. * correct / total:.2f}%' }) # 计算训练准确率 train_accuracy = 100. * correct / total avg_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader) # 在测试集上评估 val_accuracy = self.evaluate() val_accuracies.append(val_accuracy) train_losses.append(avg_loss) train_accuracies.append(train_accuracy) # 学习率调度 self.scheduler.step(avg_loss) epoch_time = time.time() - start_time print(f'Epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs} - 耗时: {epoch_time:.2f}s') print(f'训练损失: {avg_loss:.4f}, 训练准确率: {train_accuracy:.2f}%, 测试准确率: {val_accuracy:.2f}%') print('-' * 60) # 保存最佳模型 if val_accuracy > best_accuracy: best_accuracy = val_accuracy self.save_model('best_imdb_model.pth') print(f'新的最佳模型已保存,准确率: {best_accuracy:.2f}%') self.train_losses = train_losses self.train_accuracies = train_accuracies self.val_accuracies = val_accuracies return train_losses, train_accuracies, val_accuracies def evaluate(self): """评估模型""" self.model.eval() test_loader = DataLoader(self.test_dataset, batch_size=self.batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=0) correct = 0 total = 0 with torch.no_grad(): for data, targets in test_loader: data, targets = data.to(self.device), targets.to(self.device) outputs = self.model(data) predicted = (outputs > 0.5).float() total += targets.size(0) correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item() accuracy = 100. * correct / total return accuracy def predict_sentiment(self, text): """预测单个文本的情感""" self.model.eval() # 预处理文本 cleaned_text = self.text_processor.clean_text(text) tokenized_text = self.text_processor.simple_tokenize(cleaned_text) tokens = tokenized_text.split()[:self.max_length] # 转换为索引 indices = [self.vocab.get(word, self.vocab['<UNK>']) for word in tokens] if len(indices) < self.max_length: indices += [self.vocab['<PAD>']] * (self.max_length - len(indices)) else: indices = indices[:self.max_length] # 预测 with torch.no_grad(): data = torch.tensor(indices, dtype=torch.long).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device) output = self.model(data) probability = output.item() sentiment = "正面" if probability > 0.5 else "负面" return sentiment, probability def plot_training_history(self): """绘制训练历史""" if not hasattr(self, 'train_losses'): print("没有训练历史数据") return plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4)) plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.plot(self.train_losses) plt.title('训练损失') plt.xlabel('Epoch') plt.ylabel('Loss') plt.grid(True) plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.plot(self.train_accuracies, label='训练准确率') plt.plot(self.val_accuracies, label='测试准确率') plt.title('准确率') plt.xlabel('Epoch') plt.ylabel('Accuracy (%)') plt.legend() plt.grid(True) plt.tight_layout() plt.show() def save_model(self, filename): """保存模型""" torch.save({ 'model_state_dict': self.model.state_dict(), 'vocab': self.vocab, 'max_length': self.max_length, }, filename) print(f"模型已保存为: {filename}") def load_model(self, filename, model_type='lstm'): """加载模型""" checkpoint = torch.load(filename) self.vocab = checkpoint['vocab'] self.max_length = checkpoint['max_length'] # 重新初始化模型 self.setup_model(model_type) self.model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict']) print(f"模型已从 {filename} 加载") def main(): """主函数""" # 创建训练器(使用较小的批大小和词汇表) trainer = IMDBSentimentTrainer(batch_size=32, max_length=150, vocab_size=8000) # 加载数据 trainer.load_and_preprocess_data() # 设置模型 trainer.setup_model(model_type='lstm') # 训练模型(减少epochs以快速测试) trainer.train(epochs=3) # 绘制训练历史 trainer.plot_training_history() # 最终评估 final_accuracy = trainer.evaluate() print(f"\n最终测试准确率: {final_accuracy:.2f}%") # 保存模型 trainer.save_model('final_imdb_model.pth') # 测试一些示例 print("\n情感预测示例:") test_reviews = [ "This movie is absolutely fantastic! The acting was brilliant.", "Terrible movie. Waste of time. Poor acting.", "I loved this film! The plot was engaging.", "This is the worst movie I have ever seen.", "Amazing cinematography and great performances." ] for review in test_reviews: sentiment, probability = trainer.predict_sentiment(review) print(f"评论: {review[:60]}...") print(f"情感: {sentiment} (置信度: {probability:.4f})") print("-" * 50) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
方法一:使用 Pip 安装(推荐,最简单)
# 使用清华镜像
pip install ultralytics -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
当你第一次运行 YOLOv8 时,它会自动下载模型文件。默认存储位置是:
C:\Users\hp\AppData\Roaming\Ultralytics\yolov8n.pt
或
C:\Users\hp\.cache\torch\hub\ultralytics_yolov8_master





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号