第一章-微服务简介
第一章 微服务简介
微服务是一种软件架构风格,以专注于单一职责的很多小型项目为基础,组合出复杂的大型应用
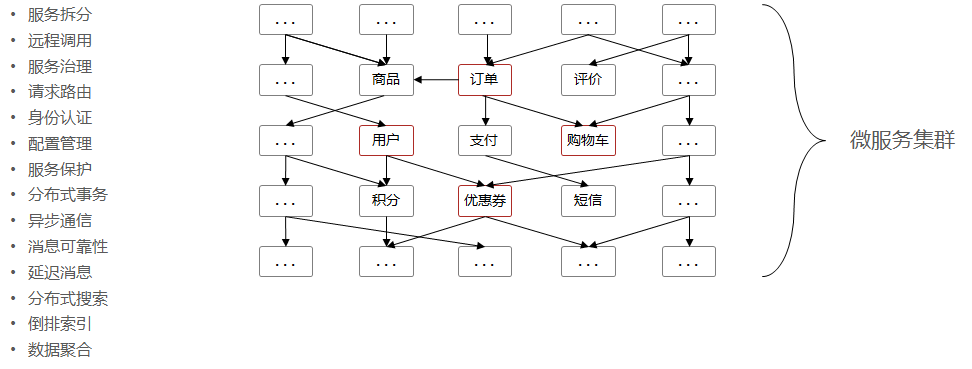
基于单体项目:黑马商城 演示单体架构到微服务架构的演变过程,分析其中存在的问题,以及微服务技术如何解决这些问题。
每一个微服务技术都是在解决服务化过程中产生的问题。
软件架构简介
单体架构
单体架构(Monolithic Structure):整个项目的所有模块在一个工程中开发,项目部署时所有模块一同编译、打包。项目的架构设计、开发模式都很简单。
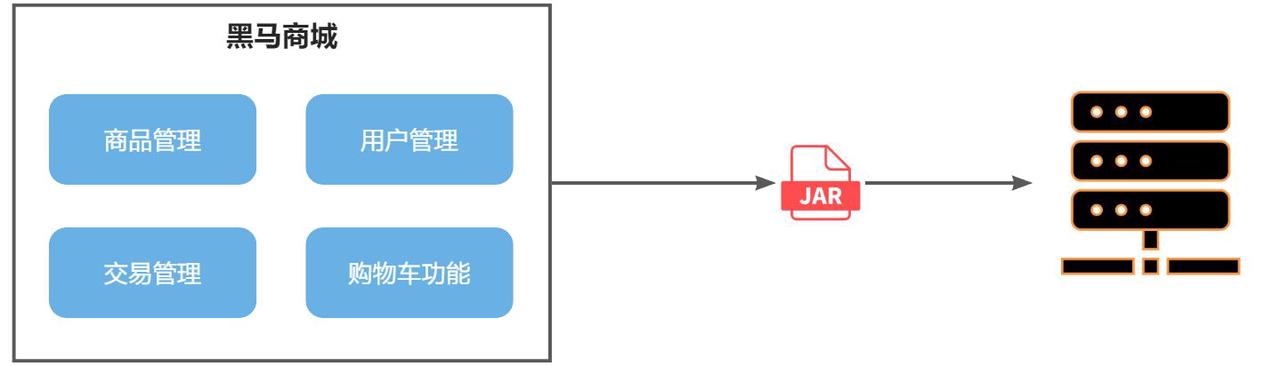
项目规模较小时,这种模式上手快,部署、运维都很方便,因此早期很多小型项目都采用这种模式,但随着业务规模越来越大,开发人员不断增多,单体架构的弊端逐渐显现:
-
团队协作成本高:一个团队数十人同时协作开发一个项目,所有模块都在一个项目中,不同模块的代码之间的物理边界越来越模糊。最终要将功能合并在一个分支中,一定会有很多分支冲突问题
-
系统发布效率低:任何模块的变动都需要重新发布整个系统,而系统发布的过程中需要多个模块之间制约较多,需要对比各种文件,任何一处出现问题都会导致发布失败,一次发布可能耗费数十分钟甚至数小时
-
系统可用性差:单体架构的各个功能模块作为一个服务部署,各个模块之间相互影响,热点功能会耗尽系统资源,导致其他服务低可用
单体架构的可用性比较低,功能之间的影响很大。
即便对系统进行水平扩展(加服务器),资源同样会被热点功能占用,从而影响到其他的接口,这也是单体架构扩展性差的原因。
微服务架构
微服务架构的核心是服务化,将单体架构的功能模块拆分出来,独立部署为多个服务,多个独立的项目,特点:
-
单一职责:一个微服务负责一部分业务功能,核心数据不依赖于其他模块
-
粒度小
-
团队自治:每个微服务都有自己独立的开发、测试、发布、运维人员,团队的规模不超过10人。
-
服务自治:每个微服务独立打包、部署。访问自己的数据库。服务之间相互隔离,避免对其他服务产生影响。
对于当前的单体项目黑马商城来说:

就可以将 交易、商品、用户、购物车等模块拆分,交给不同的团队进行开发,并独立部署:
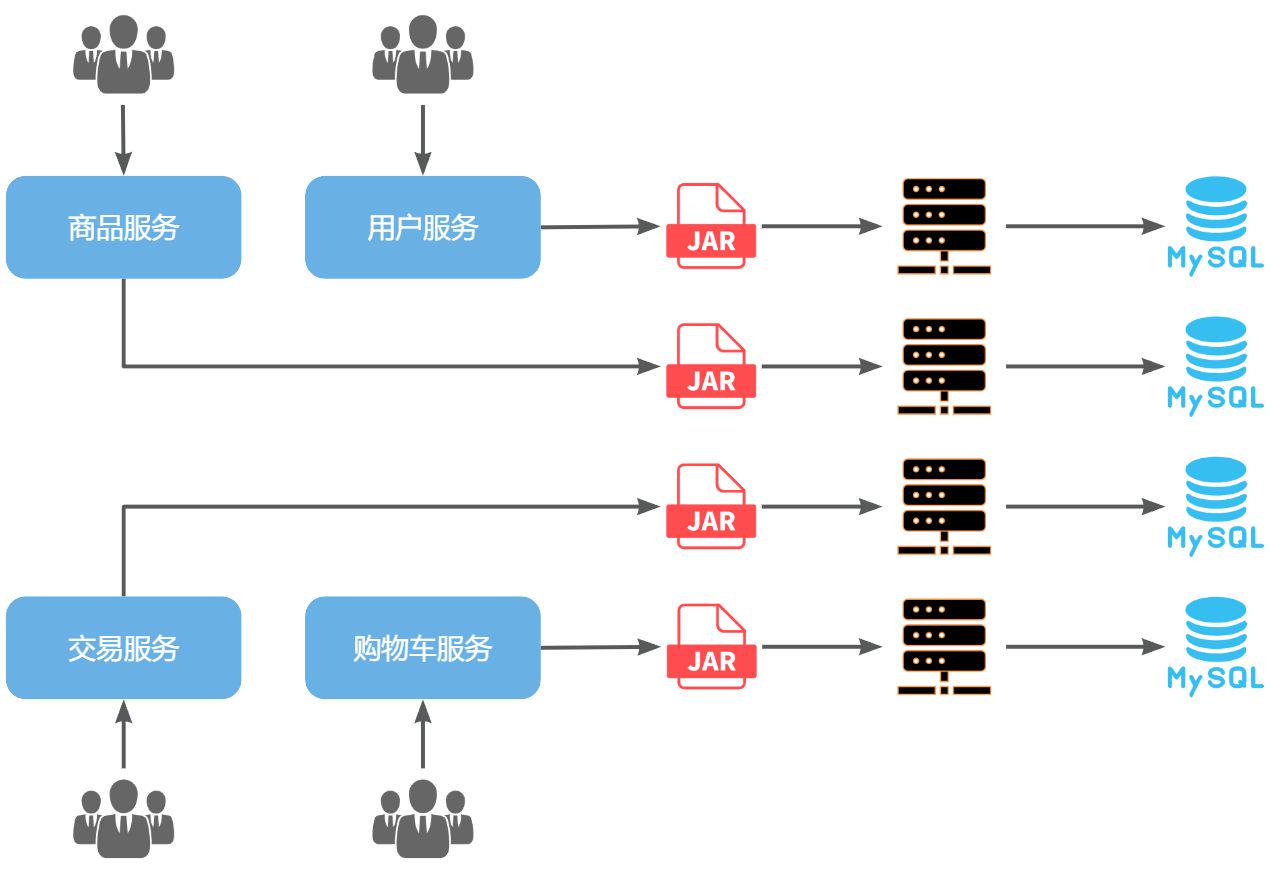
单体架构存在的三个问题都得到了解决:
-
解决团队协作成本高:服务拆分后代码量大大减少,参与开发的后台人员在1 - 3名,协作成本低。
-
解决系统发布效率低:每个服务独立部署,当一个服务的代码变更后,仅需要打包部署该服务即可。
-
解决系统可用性差:每个服务独立部署,进行了服务隔离,使用自己的服务器资源,不会影响到其他服务
微服务解决了单体架构的各种问题,但是在服务拆分的过程中,还会面临其他问题:
-
跨服务的业务如何处理?
-
页面请求应该访问哪个服务?
-
如何实现服务之间的隔离?
Spring Cloud
微服务拆分时产生的各种问题都有对应的解决方案和微服务组件,Spring Cloud框架是Java领域最全面的微服务组件集合。
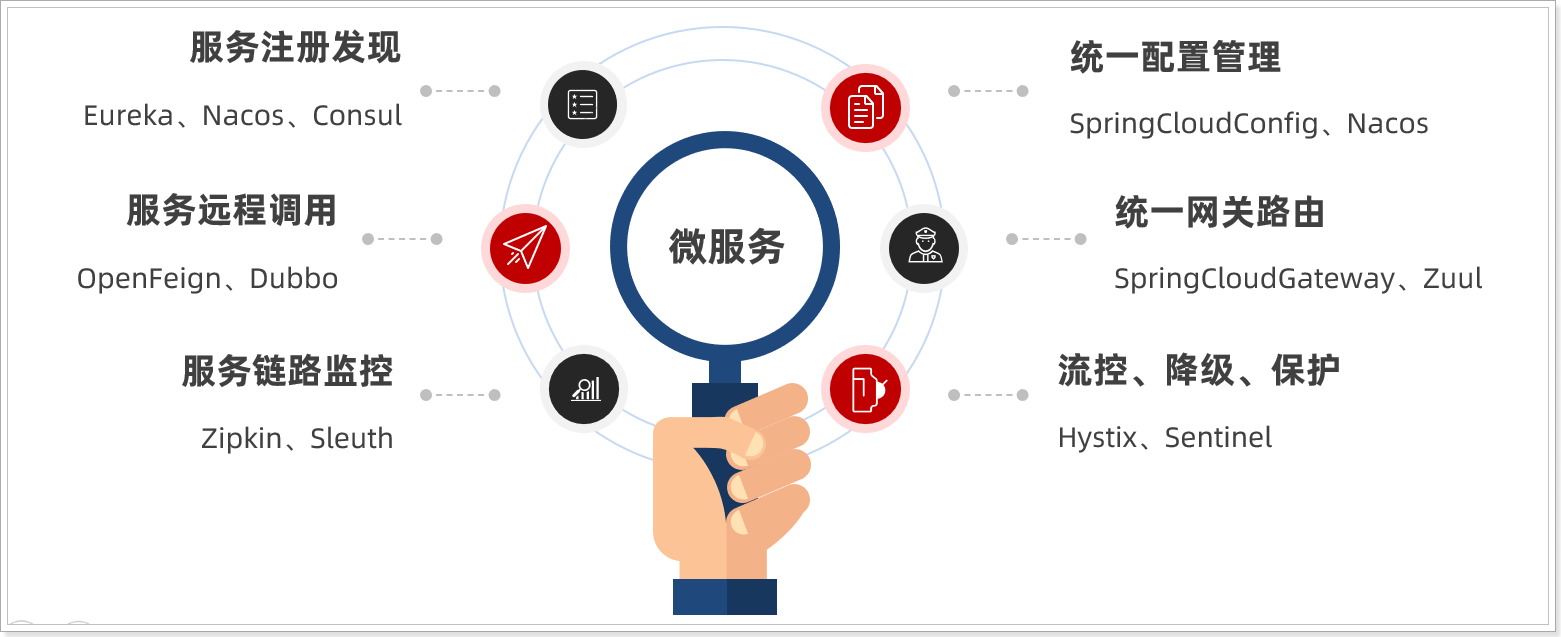
Spring Cloud 依托于Spring Boot的自动装配能力,大大降低了项目搭建、组件使用的成本。
Spring Cloud 是基于Spring Boot的、微服务系统架构的一站式解决方案。
版本
目前SpringCloud的最新版本是2023.0.x,对应SpringBoot的版本是3.2.x,但是2022及其后续版本全部依赖于JDK17,目前企业中使用相对较少。
Spring Boot 3.x 新变化
- 要求JDK17 +
- 要求Spring 6.0 +
- JavaEE迁移为JakartaEE
- IntelliJ IDEA 2022.2 之后才完全支持Spring Boot 3.x 和 Spring 6.0
- Maven最低3.9.0
JDK免费/收费版本
自2019年开始:
- JDK8之前版本仍然免费,JDK8至8u202免费,8u211收费
- JDK9、JDK10全版本免费
- JDK12、JDK13、JDK14、JDK15、JDK16,全版本商用收费
- JDK11,免费版本至11.0.2,从11.0.3开始商用收费
- JDK17、JDK18、JDK19、JDK20,全版本(二进制版本)免费
Spring Cloud版本
| SpringCloud版本 | SpringBoot版本 |
|---|---|
| 2023.0.x aka Leyton | 3.2.x |
| 2022.0.x aka Kilburn | 3.0.x |
| 2021.0.x aka Jubilee | 2.6.x, 2.7.x (Starting with 2021.0.3) |
| 2020.0.x aka Ilford | 2.4.x, 2.5.x (Starting with 2020.0.3) |
| Hoxton | 2.2.x, 2.3.x (Starting with SR5) |
| Greenwich | 2.1.x |
| Finchley | 2.0.x |
| Edgware | 1.5.x |
| Dalston | 1.5.x |
2022.x 分支
适配 Spring Boot 3.0,Spring Cloud 2022.x 版本及以上的 Spring Cloud Alibaba 版本按从新到旧排列如下表(最新版本用 * 标记): (注意,该分支 Spring Cloud Alibaba 版本命名方式进行了调整,未来将对应 Spring Cloud 版本,前三位为 Spring Cloud 版本,最后一位为扩展版本,比如适配 Spring Cloud 2022.0.0 版本对应的 Spring Cloud Alibaba 第一个版本为:2022.0.0.0,第个二版本为:2022.0.0.1,依此类推)
| Spring Cloud Alibaba Version | Spring Cloud Version | Spring Boot Version |
|---|---|---|
| 2022.0.0.0* | Spring Cloud 2022.0.0 | 3.0.2 |
| 2022.0.0.0-RC2 | Spring Cloud 2022.0.0 | 3.0.2 |
| 2022.0.0.0-RC1 | Spring Cloud 2022.0.0 | 3.0.0 |
| 我们学习的是2022.0.0.0-RC2 |
2021.x 分支
适配 Spring Boot 2.4,Spring Cloud 2021.x 版本及以上的 Spring Cloud Alibaba 版本按从新到旧排列如下表(最新版本用* 标记):
| Spring Cloud Alibaba Version | Spring Cloud Version | Spring Boot Version |
|---|---|---|
| 2021.0.5.0* | Spring Cloud 2021.0.5 | 2.6.13 |
| 2021.0.4.0 | Spring Cloud 2021.0.4 | 2.6.11 |
| 2021.0.1.0 | Spring Cloud 2021.0.1 | 2.6.3 |
| 2021.1 | Spring Cloud 2020.0.1 | 2.4.2 |
推荐使用 Spring Cloud 2021.0.x,对应了Spring Boot 2.7.x
组件版本关系
每个 Spring Cloud Alibaba 版本及其自身所适配的各组件对应版本如下表所示(注意,Spring Cloud Dubbo 从 2021.0.1.0 起已被移除出主干,不再随主干演进):
| Spring Cloud Alibaba Version | Sentinel Version | Nacos Version | RocketMQ Version | Dubbo Version | Seata Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022.0.0.0 | 1.8.6 | 2.2.1 | 4.9.4 | ~ | 1.7.0 |
| 2022.0.0.0-RC2 | 1.8.6 | 2.2.1 | 4.9.4 | ~ | 1.7.0-native-rc2 |
| 2021.0.5.0 | 1.8.6 | 2.2.0 | 4.9.4 | ~ | 1.6.1 |
| 2.2.10-RC1 | 1.8.6 | 2.2.0 | 4.9.4 | ~ | 1.6.1 |
| 2022.0.0.0-RC1 | 1.8.6 | 2.2.1-RC | 4.9.4 | ~ | 1.6.1 |
| 2.2.9.RELEASE | 1.8.5 | 2.1.0 | 4.9.4 | ~ | 1.5.2 |
| 2021.0.4.0 | 1.8.5 | 2.0.4 | 4.9.4 | ~ | 1.5.2 |
| 2.2.8.RELEASE | 1.8.4 | 2.1.0 | 4.9.3 | ~ | 1.5.1 |
| 2021.0.1.0 | 1.8.3 | 1.4.2 | 4.9.2 | ~ | 1.4.2 |
| 2.2.7.RELEASE | 1.8.1 | 2.0.3 | 4.6.1 | 2.7.13 | 1.3.0 |
| 2.2.6.RELEASE | 1.8.1 | 1.4.2 | 4.4.0 | 2.7.8 | 1.3.0 |
| 2021.1 or 2.2.5.RELEASE or 2.1.4.RELEASE or 2.0.4.RELEASE | 1.8.0 | 1.4.1 | 4.4.0 | 2.7.8 | 1.3.0 |
| 2.2.3.RELEASE or 2.1.3.RELEASE or 2.0.3.RELEASE | 1.8.0 | 1.3.3 | 4.4.0 | 2.7.8 | 1.3.0 |
| 2.2.1.RELEASE or 2.1.2.RELEASE or 2.0.2.RELEASE | 1.7.1 | 1.2.1 | 4.4.0 | 2.7.6 | 1.2.0 |
| 2.2.0.RELEASE | 1.7.1 | 1.1.4 | 4.4.0 | 2.7.4.1 | 1.0.0 |
| 2.1.1.RELEASE or 2.0.1.RELEASE or 1.5.1.RELEASE | 1.7.0 | 1.1.4 | 4.4.0 | 2.7.3 | 0.9.0 |
| 2.1.0.RELEASE or 2.0.0.RELEASE or 1.5.0.RELEASE | 1.6.3 | 1.1.1 | 4.4.0 | 2.7.3 | 0.7.1 |
微服务环境准备
参照SpringCloud官网引入Spring Cloud依赖
Spring Cloud Alibaba 2022.0.0.0-RC2 对应的Spring Cloud 版本为 2022.0.0
<properties>
<spring-cloud.version>2022.0.0</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
参照SpringCloud官网引入Spring Cloud Alibaba依赖
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>{project-version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
引入后的pom文件:
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2022.0.0</spring-cloud.version>
<spring-cloud-alibaba.version>2022.0.0.0-RC2</spring-cloud-alibaba.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-alibaba.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
此时微服务环境就准备完毕了
案例一:简单provider、consumer
01-provider-8081:服务提供者
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/provider/depart")
public class DepartController {
@Resource
private DepartService departService;
@PostMapping
public ResponseResult<Boolean> postDepart(@RequestBody Depart depart){
departService.save(depart);
return ResponseResult.success();
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseResult<Boolean> deleteHandler(@PathVariable Long id){
departService.removeById(id);
return ResponseResult.success();
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseResult<Depart> getHandler(@PathVariable Long id){
return ResponseResult.success(departService.getById(id));
}
@GetMapping("/list")
public ResponseResult<List<Depart>> listHandler(){
return ResponseResult.success(departService.lambdaQuery().list());
}
}
01-consumer-8080:服务消费者
问题在于:如何实现跨服务的调用?
我们其实遇到过类似的远程查询功能,从前端向服务端查询数据,其实就是从浏览器远程查询服务器端数据。
前端向服务器端发起的请求是HTTP请求,不仅可以实现远程查询,还可以实现新增、删除等远程操作,而服务器向服务器发起的请求也是HTTP请求
使用RestTemplate发起HTTP请求。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/consumer/depart")
public class DepartController {
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
public static final String SERVICE_PROVIDER = "http://localhost:8081/provider/depart";
@PostMapping
public ResponseResult<Boolean> saveHandle(@RequestBody Depart depart){
ResponseResult<Boolean> responseResult = restTemplate.postForObject(SERVICE_PROVIDER, depart, ResponseResult.class);
return responseResult;
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseResult<Depart> getHandler(@PathVariable Long id){
String url = SERVICE_PROVIDER + "/" + id;
ResponseResult<Depart> result = restTemplate.getForObject(url, ResponseResult.class, id);
return result;
}
@GetMapping("/list")
public ResponseResult<List<Depart>> listHandler(){
String url = SERVICE_PROVIDER + "/list";
ResponseResult<List<Depart>> result = restTemplate.getForObject(url, ResponseResult.class);
return result;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号