JAVA基础
基本类型包装类
常见的操作
基本类型和字符串之间的相互转换
/*静态方法获取对象:
public static Integer valueOf(int i);返回表示指定int值得Integer实例
public static Integer valueOf(String i);返回一个保存指定值得对象Integer对象String
*/
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer num1 = Integer.valueOf(100);
System.out.println(num1);
Integer num2 = Integer.valueOf("100");
System.out.println(num2);
}
}
自动装箱/拆箱
/*
装箱:基本数据类型转换为对应的包装类型
拆箱:包装类型转换为对应的基本数据类型
*/
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer num1 = Integer.valueOf(100);//手动装箱
Integer num2 = 100;//自动装箱,功能同上
num2 = num1.intValue()+200;//.intValue()手动拆箱
num2 += 200;//自动装箱,功能同上
}
}
日期类
时间
/*
long getTime();获取的日期对象从1970年1月1日00:00:00到现在的毫秒值
void setTime();设置时间,给的是毫秒值;
*/
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d = new Date();
System.out.println(d.getTime()*1.0/1000/60/60/24/365+"年");//返回78.6577327295789年
System.out.println(d);//输出当前时间
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
d.setTime(time);
System.out.println(d);//输出当前时间
//日期格式化
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyy年mm月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
String s = sdf.format(d);
System.out.println(s);//输出xxx年xx月xx日 xx:xx:xx
//String 到Date
String s = "2021-07-28 11:11:23";//此格式必须和下面的日期格式一致
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyy-mm-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date dd = sdf.parse(s);
System.out.println(dd);
}
}
日历
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
//int get(int field)返回给定日历字段的值
int year = c.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = c.get(Calendar.MONTH);
int date = c.get(Calendar.DATE);
System.out.println(year+"年"+month+"月"+date+"日");
//abstract void add(int field,int amount)根据日历的规则,将指定的时间量添加或减去给定的日历字段
c.add(Calendar.YEAR,-3);//-3:表示3年前;3:表示3年后
c.add(Calendar.DATE,5);//-5:表示5天前;5:表示5天后
c.set(2025,11,23);//设置当前日历为2025/12/23
}
异常处理
异常处理格式:
try{
可能出现异常的代码;
}catch(异常类名 变量名){
异常的处理代码;
}
自定义异常
//定义一个异常
public class SocoreExceptin extends Exception{
public SocoreExceptin(){}
public SocoreExceptin(String message){
super(message);
}
}
//调用自定义异常类
public class test{
public void checkScore(int score) throws ScoreException{
if (score<0 || score>100){
throw new ScoreException("Error!")
}else{
System.out.println("normal!")
}
}
}
throws和throw的区别

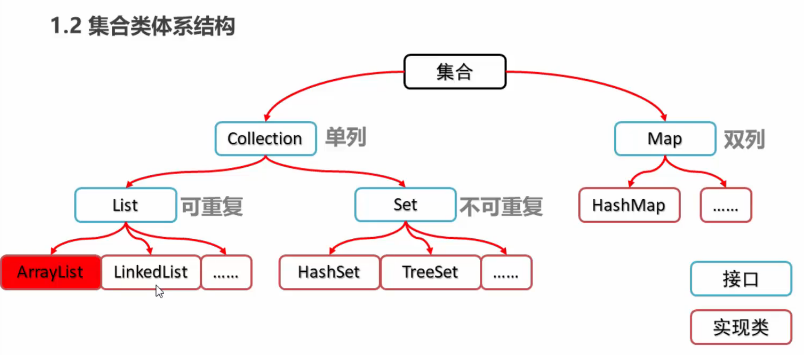
-集合
集合的划分:
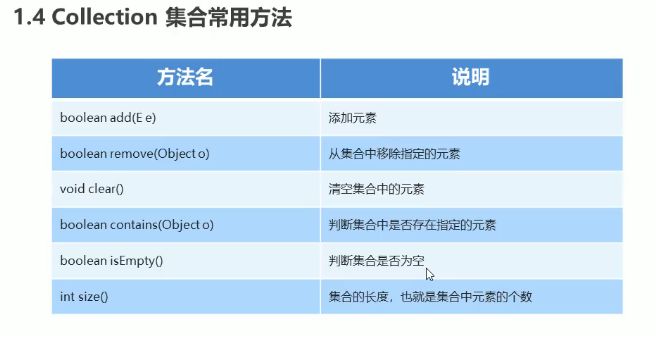
Collection集合常用方法
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<String>();
c.add("Eric");//为集合添加元素
}
}
集合的遍历
Iterator:迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式;
Iterator
Iterator中常用方法:

public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<String>();
c.add("Eric");//为集合添加元素
Iterator<String> it = c.iterator();
System.out.println(it.next());//返回迭代中的下一个元素
if (it.hasNext()){//hasNext():如果迭代具有更多的元素,则返回true
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
列表迭代器
ListIterator:列表迭代器:
-
通过list集合的listIterator()方法得到,是list集合特有的
-
可以沿任一方向遍历列表,在迭代期间修改列表,获取列表中迭代器的当前位置
-
listIterator中的常用方法:

public class ListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> li = new ArrayList<String>();
li.add("Eric");
//通过list集合的listIterator()方法得到
ListIterator<String> lit = li.listIterator();
while(lit.hasNext()){
String s = lit.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
//逆向遍历
while (lit.hasPrevious()){
String s = lit.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
//获取列表迭代器
ListIterator<String> lit = list.listIterator();
while (lit.hasNext()){
String s = lit.next();
if (s.equals("Eric")){
lit.add("THD");
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
}
增强for语句:
-
格式:
for(元素数据类型 变量名:数组或者Collection集合){
//使用变量,该变量就是元素
}
-
示范:
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4}; for(int i:arr){ System.out.println(i); }
打乱顺序集合:Collections.shuffle(集合)
list集合
list集合特有的方法
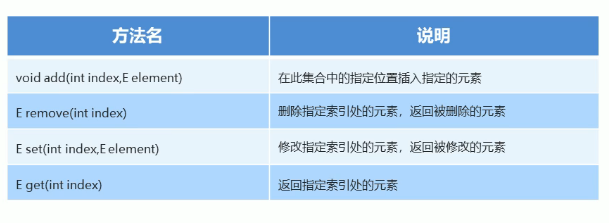
//与Collection集合差不多,但还是有些许不同
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> c = new ArrayList<String>();
c.add("Eric");//为列表添加元素
Iterator<String> it = c.iterator();
System.out.println(it.next());//返回迭代中的下一个元素
if (it.hasNext()){//hasNext():如果迭代具有更多的元素,则返回true
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
list集合子类特点
list集合常用子类:ArrayList,LinkedList(这两种的使用是一样的)
- ArrayList:底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢;
- LinkedList:底层数据结构是链表,查询慢,增删块;
LinkedList集合
- LinkedList集合的特有功能:
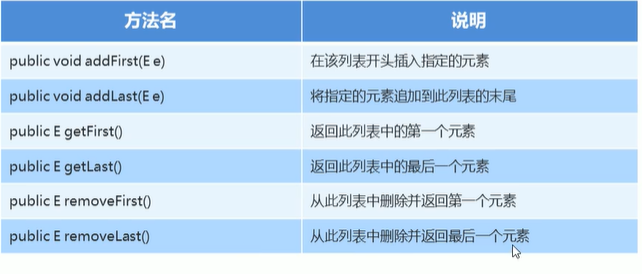
*示范:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("Eric");
//追加插入列表头
list.addFirst("Thd");
//追加插入列表尾
list.addLast("thd");
// 返回此列表中的第一个元素
System.out.println(list.getFirst());
//返回此列表中的最后一个元素
System.out.println(list.getLast());
//删除此列表中的第一个元素并返回元素
System.out.println(list.removeFirst());
//删除此列表中的最后一个元素并返回
System.out.println(list.removeLast());
}
set集合
数据结构之哈希表:黑马程序员视频讲解
-
hash值:
public static void main(String[] args) { Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(); set.add("eric"); //同一个对象多次调用hashCode()方法返回的哈希值相同 Student s = new Student(); System.out.println(s.hashCode); //默认情况下,不同对象的哈希值是不相同的 //而重写hashCode()方法可以让不同对象的哈希值相同 Student v = new Student(); System.out.println(v.hashCode); } -
LinkedHashSet集合:
/*linkedHashSet集合特点: 1:哈希表和链表实现的set接口,具有可预测的迭代次序; 2:由链表保证有序,也就是元素的存储和取出顺序一样; 3:有哈希表保证元素唯一,没有重复的元素; */ LinkedHashSet<String> linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<String>(); linkedHashSet.add("Eric"); linkedHashSet.add("the"); for (String s:linkedHashSet){ System.out.println(s); } -
TreeSet集合:

public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<>();
ts.add(123);
ts.add(2);
for(int i:ts){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
- comparable 接口:强行对实现它的每个类对象进行整体排序。
实现它的类要实现的int compareTo(T o)方法
返回:负整数、零、正整数:根据此对象是大于、等于、小于指定对象,进行排序 - Comparator是比较接口,我们如果需要控制某个类的次序,而该类本身不支持排序(即没有实现Comparable接口),那么我们就可以建立一个“该类的比较器”来进行排序,这个“比较器”只需要实现Comparator接口即可。
案例
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取 10个1-20之间的随机数,要求随机数不能重复
// HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();//方式一
HashSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>();//方式二
Random r = new Random();
while (set.size()<10){
int number = r.nextInt(20) + 1;
set.add(number);
}
}
Map集合
Map集合的基本功能
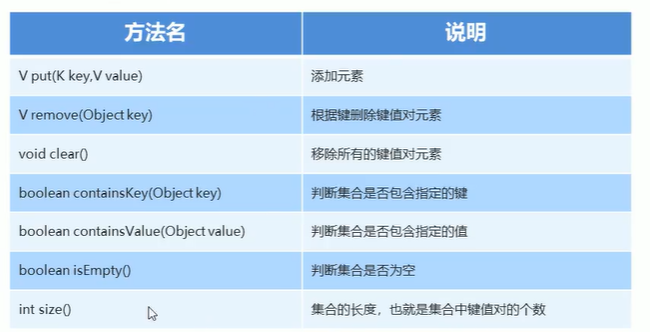
代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("ERic","THD");
map.remove("Eric");
map.containsKey("Eric");//判断是否包含指定的键
map.containsValue("THD");//判断是否包含指定的值
map.isEmpty();//判断是否为空
map.size();//集合的长度,也就是键值对的个数
map.clear();//清空map集合
}
Map集合的获取功能
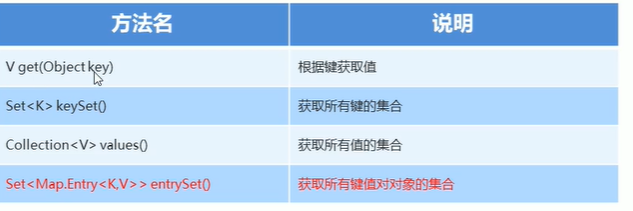
代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println(map.get("Eric"));//根据键获取值
Set<String> keyset = map.keySet();//获取所有键的集合
Collection<String> values = map.values();//获取所有值得集合
}
Map集合的遍历
-
方式一:根据键获取值
-
方式二:
public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for(Map.Entry<String, String> me:entrySet){ String key = me.getKey(); String value = me.getValue(); System.out.println(key+","+value); } }
-泛型
泛型定义格式:

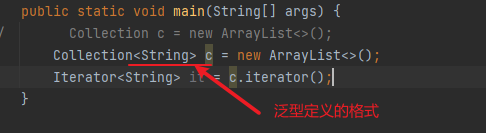
泛型类
泛型类的定义格式:

代码:
//创建一个泛型类
package com.eric;
public class Generic<T>{
private T t;
public T getT() {
return t;
}
public void setT(T t) {
this.t = t;
}
}
//测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用同一个泛型类就可以解决不同数据类型的问题
Generic<String> g1 = new Generic<>();
g1.setT("Eric");
Generic<Integer> g2 = new Generic<>();
g2.setT(233);
Generic<Boolean> g3 = new Generic<>();
g3.setT(true);
}
泛型方法
泛型方法的定义格式:

代码:
//1创建一个泛型类
package com.eric;
public class Generic<T>{
public void show(T t){
System.out.println(t);
}
}
//2泛型类改进
public class Generic<T>{
public T show(T t){
System.out.println(t);
}
}
//1测试类、
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用泛型方法,可以做到同一个类的方法,可以接受不同数据类型的参数
Generic<String> g1 = new Generic<>();
g1.show("Eric");
Generic<Integer> g2 = new Generic<>();
g2.show(233);
Generic<Boolean> g3 = new Generic<>();
g3.show(true);
}
//2测试类改进
public static void main(String[] args) {
Generic g = new Generic();
g.show("Eric");
g.show(233);
g.show(true);
}
泛型接口
泛型接口的定义格式:

代码:
//创建一个泛型接口类
public interface Generic<T> {
void show(T t);
}
//新建一个实现泛型接口的实现类
public class GenericImp<T> implements Generic<T>{
@Override
public void show(T t){
System.out.println(t);
}
}
//测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Generic<String> g1 = new GenericImp<String>();
g1.show("Eric");
Generic<Integer> g2 = new GenericImp<Integer>();
g2.show("19");
}
类型通配符
为了表示各种泛型list的父类,可以使用类型通配符
-
类型通配符:<?>
List<?>:表示元素类型位置的List,他的元素可以匹配任何的类型;
这种带通配符的List仅表示他是各种泛型List的父类,并不能把元素添加到其中;
-
类型通配符的上限:<?extends 类型>
List<?extends Number>:他表示类型是Number或者其子类型
-
类型通配符下限:<?super 类型>
List<?super Number>:他表示类型是Number或者其父类型
代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 类型通配符:<?>
List<?> list1 = new ArrayList<Object>();
List<?> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 类型通配符上限<? extends 类型>
// List<? extends Number> list3 = new ArrayList<Object>();//报错
List<? extends Number> list4 = new ArrayList<Number>();
List<? extends Number> list5 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 类型通配符下限<? super 类型>
List<? super Number> list6 = new ArrayList<Object>();
List<? super Number> list7 = new ArrayList<Number>();
// List<? super Number> list8 = new ArrayList<Integer>();//报错
}
可变参数
可变参数:

代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(sum(1,3));
System.out.println(sum(12,45,8,8,4));
System.out.println(sum(1,5,7,8,9,0,78));
}
//如果sum有多个参数,则可变参数要放在末尾位置
public static int sum(int... a){
int sum = 0;
for(int i:a){
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
可变参数的使用
Array工具类中的一个静态方法:
- public static
List aslist(T...a):返回指定数组支持的固定大小的列表 - 返回的集合不能做增删操作,只可以修改
List接口中的一个静态方法:
- public static
list of(E...elements):返回包含任意数量元素的不可变列表 - 返回的集合不能做增删改操作
Set接口转中有一个静态方法:
- public static
Set of(E...elements):返回一个包含任意数量元素的不可变集合 - 不能有重复的元素
- 返回的集合不能租增删操作,也没有修改的方法;
File类
File:他是文件好目录的路径的抽象表示
File的构造方法:
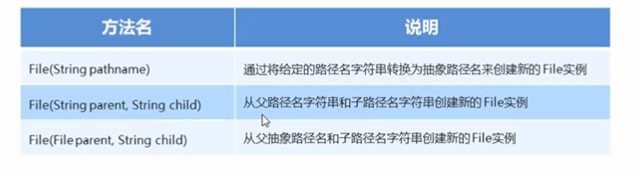
File类的创建功能
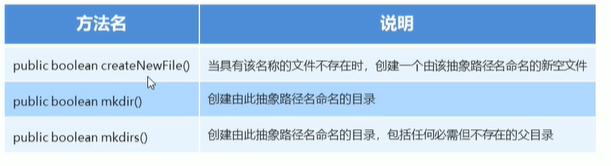
File类判断和获取功能
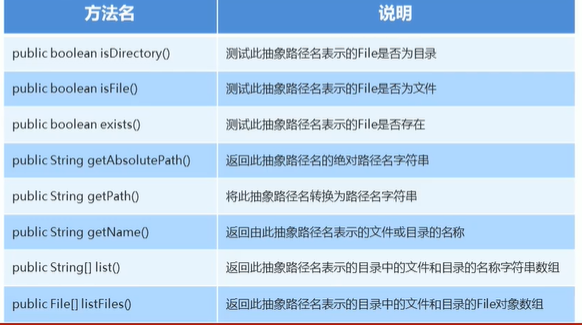
File类删除功能

字节流

字节流写数据
//方式一
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test\\fox.txt");
//将指定的字节写入此文件输出流
fos.write(97);
//关闭文件输出流,释放资源
fos.close();
}
//方式二
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test\\fox.txt");
//将指定的字节写入此文件输出流
byte[] bts = {97,23,12,21};//byte[] bts = "abcs".getBytes();
fos.write(bts);
//关闭文件输出流,释放资源
fos.close();
}
//方式三
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test\\fox.txt");
//将指定的字节写入此文件输出流
byte[] bts = "abcs".getBytes();
fos.write(bts,1,3);//写入bcs
//关闭文件输出流,释放资源
fos.close();
}
字节流写数据换行
/* 写完数据后换行:
三种换行方式:window:"\r\n";linux:"\n":mac:"\r"
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象,参数true表示追加写入
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test\\fox.txt",true);
//将指定的字节写入此文件输出流
byte[] bts = "abcs".getBytes();
fos.write(bts,1,3);//写入bcs
fos.write("\r\n".getBytes());//写入换行
//关闭文件输出流,释放资源
fos.close();
}
字节流读数据
//方式一
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输入流对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test\\fos.txt");
//调用字节输入流对象的读数据方法
int by = fis.read();//从改输入流读取一个字节的数据,文件末尾是-1
//关闭文件输出流,释放资源
fis.close();
}
//方式二
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输入流对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test\\fos.txt");
//调用字节输入流对象的读数据方法
//一次读取一个数组数据
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=fis.read(bys))!=1){
System.out.println(new String(bys,0,len));
}
//关闭文件输出流,释放资源
fis.close();
}
字节缓冲流
//字节缓冲输出流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节缓冲输出流对象
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test\\bos.txt"));
bos.write(243);//同字节输出流对象的操作相同
//关闭文件输出流,释放资源
bos.close();
}
//字节缓冲输入流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节缓冲输出流对象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("test\\bis.txt"));
//一次读取一个字节数组数据
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=bis.read(bys))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(bys,0,len));
}
//关闭文件输出流,释放资源
bis.close();
}
案例
字节流复制图片
字节流复制视频
为什么出现字节流
一个汉字存储:
如果是GBK编码:占用2个字节
如果是UTF-8编码:占用3个字节
字符流
编码/解码
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String s = "照顾共";
byte[] bys = s.getBytes("GBK");//编码
String gbk = new String(bys, "GBK");//解码
}
未完成待续........
并发修改异常
对象序列化
//创建一个实现Serializable的类
public class Students implements Serializable {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
//对象序列化流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test\\oos.txt"));
Students s = new Students("Eric");
oos.writeObject(s);
oos.close();
}
//对象反序列化流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("test\\oos.txt"));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
Students s = (Students) obj;
System.out.println(s.getName());
ois.close();
}
网络编程
InetAddress的使用
为了方便对IP地址的获取和操作,java提供了一个类InetAddress供我们使用
InetAddress:该类表示Ineternet协议地址
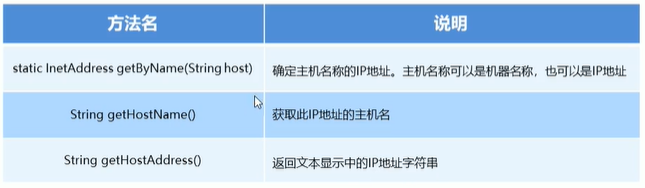
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("机器名/ip地址");
String name = address.getHostName();
String ip = address.getHostAddress();
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(ip);
}
UDP发送数据
发送数据的步骤:
- 创建发送端的Socket对象(DatagramSocket)
- 创建数据,并把数据打包
- 调用DatagramSocket对象的方法发送数据
- 关闭发送端
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// DatagramSocket()构造数据包套接字并将其绑定到本地主机上的任何可用端口
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
// 创建数据,并把数据打包
byte[] bys = "Hello Eric".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
int length = bys.length;
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("172.27.128.1");
int port = 10086;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys,length,address,port);
// 调用DatagramSocket对象方法发送数据
ds.send(dp);
// 关闭发送端
ds.close();
}
UDP接收数据
接收数据的步骤:
- 创建接收端的Socket对象(DatagramSocket);
- 创建一个数据包,用于接收数据;
- 调用DatagramSocket对象的方法接收数据;
- 解析数据包,并把数据在控制台显示;
- 关闭接收端;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// DatagramSocket()构造数据包套接字并将其绑定到本地主机上的指定端口
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10086);
// 创建一个数据包,接收数据
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int length = bys.length;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys,length);
// 调用DatagramSocket对象方法接收数据
ds.receive(dp);
// 解析数据包,并显示
byte[] datas = dp.getData();
String datastring = new String(datas,0,dp.getLength());
System.out.println(datastring);
// 关闭发送端
ds.close();
}
TCP通信程序
TCP发送数据
发送数据的步骤:
- 创建客户端的Socket对象(Socket);
- 获取输出流,写数据;
- 释放资源
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建客户端的Socket对象
// Socket(InetAddress address,int port)创建流套接字并将其连接到指定的IP地址的指定端口号
// Socket(String host,int port)
// 和上面一样的功能:Socket socket = new Socket("172.29.160.1", 10086);
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("172.29.160.1"), 10086);
// 获取输出流,写数据
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("Hello Eric".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 接收服务器数据反馈
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len = is.read(bys);
String data = new String(bys,0,len);
System.out.println("反馈给客户端的数据:"+data);
// 释放资源
socket.close();
}
TCP接收数据
接收数据的步骤:
- 创建服务端的Socket对象(ServerSocket);
- 获取输入流,读数据,并把数据显示在控制台;
- 释放资源;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建服务端的Socket对象(ServerSocket)
// ServerSocket(int port)创建绑定到指定端口的服务器套接字
ServerSocket sst = new ServerSocket(10086);
// Socket accept侦听要连接到此套接字并接受他
Socket s = sst.accept();
// 获取输入流,读数据并显示在控制台
InputStream ins = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len = ins.read(bys);
String data = new String(bys, 0, len);
System.out.println("数据:"+data);
// 接收客户端反馈的数据
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
os.write("数据以接收".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 释放资源
s.close();
}
练习:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-----客户端-----");
Socket socket = new Socket("172.29.160.1", 10086);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
//封装输出流对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
String line;
while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){
if ("886".equals(line)){
break;
}
// 获取输出流
// OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
// os.write(line.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
// 释放资源
socket.close();
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-----服务端-----");
// 创建服务器Socket对象
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(10086);
// 监听客户端的连接,返回一个对应的Socket对象
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
// 获取输入流
// InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
// 释放资源
serverSocket.close();
}
------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ##将接收到的数据写入文本文件##
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-----服务端-----");
ServerSocket sst = new ServerSocket(10086);
// 监听客户端连接,返回一个对应的Socket对象
Socket accept = sst.accept();
// 接收数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(accept.getInputStream()));
// 把数据写入文本文件
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("spring-boot\\Eric.txt"));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
// 释放资源
bw.close();
sst.close();
}
------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ##客户端从文本文件读取数据##
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-----客户端-----");
Socket socket = new Socket("172.29.160.1", 10086);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\文档\\Eric.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
br.close();
socket.close();
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号