vue- 脚手架和组件
5.脚手架
基于vue+vue-router单文件开发,可以完成小规模的页面的开发,但如果项目大+组件多+依赖多,开发起来就非常不方便。
此时,脚手架 vue cli (vue cli - Vue Command Line Interface )是一个基于 Vue.js 进行快速开发的完整系统。
官方的说法:
Vue CLI 致力于将 Vue 生态中的工具基础标准化。它确保了各种构建工具能够基于智能的默认配置即可平稳衔接,这样你可以专注在撰写应用上,而不必花好几天去纠结配置的问题。
通俗的说法:
他帮助我们构内置了很多组件来帮助我们更便捷的的开发vue.js项目。
-
第一步:想用脚手架 得安装node.js
Vue CLI 4.x+ 需要 Node.js v8.9 或更高版本 (推荐 v10 以上)。
https://nodejs.org/en/download/![]()
=======如果想要更新node.js的版本=======
1.先查看本机node.js版本:
node -v
2.清除node.js的cache:
sudo npm cache clean -f
3.安装 n 工具,这个工具是专门用来管理node.js版本的,别怀疑这个工具的名字,是他是他就是他,他的名字就是 "n"
sudo npm install -g n
4.安装最新版本的node.js
sudo n stable
5.再次查看本机的node.js版本:
node -v -
第二步:关于npm(node.js是一门变成语言 类似于python)
安装上node之后,自带了npm包管理工具,类似于Python中的pip。
如果想要更新npm到最新版,可以执行命令:
sudo npm install npm@latest -g![]()
-
第三步:npm淘宝源,以后基于npm安装包就会快了(相当于豆瓣的pip源)
npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org -
第四步:全局安装脚手架 vue-cli
# 安装(最新版)
sudo npm install -g @vue/cli
# 安装(指定版本)
sudo npm install -g @vue/cli@4.5.14
# 卸载
sudo npm uninstall -g @vue/cli![]()
cd /Users/wupeiqi/WebstormProjects // 打开终端 进入需要存放项目的文件
vue create mysite // 执行命令 项目名mysite
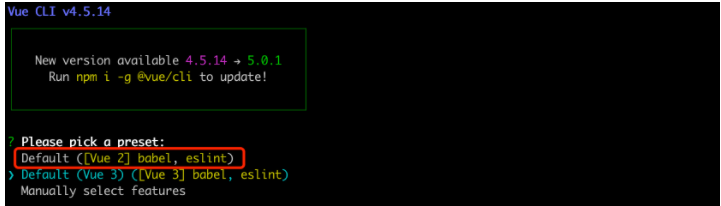
提示:babel是一个将ES6语法转化成ES5的工具,eslint是做语法检查。
a few moments later...
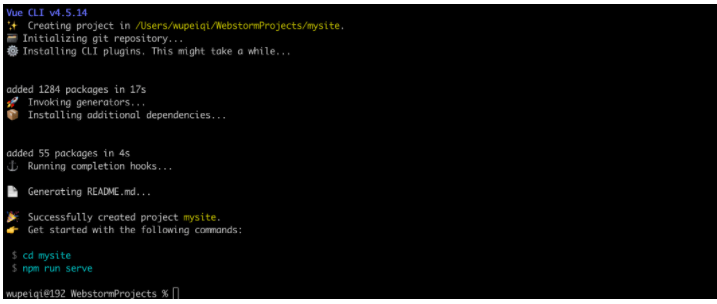
按照提示执行如下命令,脚手架就会给我们大家一个Web服务去运行编写的vue项目(便于开发测试)。
cd mysite
npm run serve
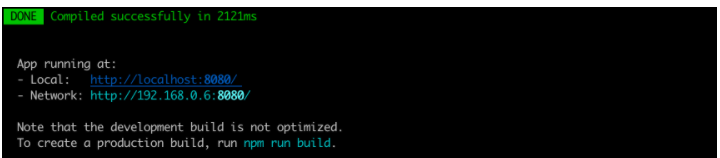
项目创建完,脚手架会默认会生成如下文件(包含项目依赖、配置文件、默认代码)。
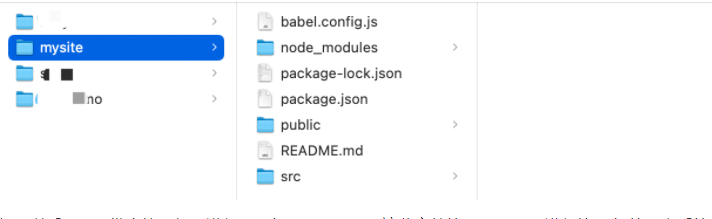
如果以后项目开发完毕,想要进行项目部署,是不需要这些文件的,需要npm进行编译 把编译之后的东西放到服务器上
执行命令:
cd 项目目录
npm run build // 编译当前项目
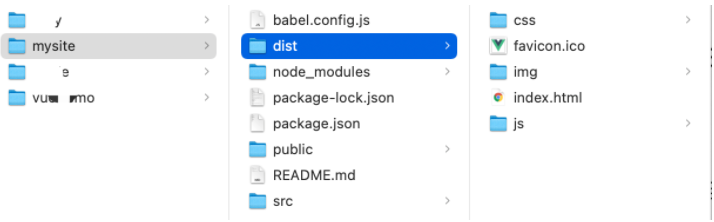
build会将项目中的依赖和代码自动编译成HTML、CSS、JavaScript代码,后续只需要将此代码上传至服务器部署即可。

1 脚手架本地开发的文件 2 3 ``` 4 - babel.config.js babel是ES6转换ES5的组件,这是他所需的配置文件(一般不需要动)。 5 - package.json 项目所需的包的版本信息。 6 - package-lock.json 保存项目所需的包细节以及包的依赖等信息。 7 - node-modules 项目安装依赖包的文件保存的地方。例如:npm install axios 8 axios包会保存在此目录、信息也会写在 package.json、package-lock.json中 9 - src 10 - main.js 项目的启动 npm run serve ,用户访问时程序的入门。 11 - App.vue 主组件(老父亲 由他来调用其他组件的 ) 12 - components 子组件(以后写的组件都写在这里) 13 - assets 静态文件(自己的静态文件,会被压缩和合并) 14 - public 【此目录下的文件直接被复制到dist/目录下,一般放不动的数据,引入第三方】 15 - index.html 主HTML文件(模板引擎) 16 - favicon.icon 图标 17 - README.md 项目说明文档 18 ``` 19 20 ``` 21 cd 项目 22 npm install // 联合开发时候 只需要下载下来就可以开发别人的代码 23 ``` 24 25 本质上,其实就是将原来的代码做了拆分来进行开发,开发完毕之后再编译整合起来。 26 27 ```html 28 <!DOCTYPE html> 29 <html lang="en"> 30 <head> 31 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 32 <title>Title</title> 33 <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script> 34 </head> 35 <body> 36 37 <div id="app"> 38 <h1>欢迎学习Vue.js</h1> 39 <div>我叫{{name}},微信{{wechat}}</div> 40 </div> 41 42 <script> 43 44 45 var app = new Vue({ 46 el: '#app', 47 data: { 48 name: '武沛齐', 49 wechat: 'wupeiqi888' 50 }, 51 methods: { 52 clickMe: function () { 53 this.name = "alex"; 54 this.wechat = "wupeiqi666"; 55 } 56 } 57 }) 58 </script> 59 </body> 60 </html> 61 ```
需要安装两个组件在脚手架里
Axios是一个基于 promise 的 HTTP 库,简单的讲就是可以发送get、post请求。
安装: ``` cd 项目目录 npm install axios npm install vue-axios ``` 导入 (main.js): ``` main.js import Vue from 'vue' import axios from 'axios' import VueAxios from 'vue-axios' Vue.use(VueAxios, axios) // 这两个东西挂载到vue对象里 ``` 使用: ``` Vue.axios.get(api).then((response) => { console.log(response.data) }) // 或 this.axios.get(api).then((response) => { // this 就是当前vue对象 console.log(response.data) }) // 或 this.$http.get(api).then((response) => { console.log(response.data) }) ```

1 安装: 2 3 ``` 4 cd 项目目录 5 npm install vue-router@3 //vue2的项目建议用vue-router@3 6 ``` 7 8 引入:(components组件都写在这里router路由都写到这里) 9 10 ```javascript 11 // router/index.js 12 13 // 第一步 14 import Vue from 'vue' 15 import VueRouter from 'vue-router' 16 17 18 import Home from '../components/Home' // 导入组件 19 20 21 Vue.use(VueRouter) // 让VueRouter挂载到vue对象里 22 23 // 第二步编写路由对象 24 const router = new VueRouter({ 25 routes: [ 26 { 27 path: '/home', 28 name: "Home", 29 component: Home //组件 30 }, 31 ] 32 }) 33 // 第三步 导出 外部就可以引入router对象了 34 export default router 35 ``` 36 37 ```javascript 38 // main.js 39 import Vue from 'vue' 40 import axios from 'axios' 41 import VueAxios from 'vue-axios' 42 43 44 import App from './App.vue' // 引入App.vue组件 45 46 // 第四步 导入router文件(加载了router生成了对象) 47 import router from "./router" 48 49 50 Vue.use(VueAxios, axios) 51 52 Vue.config.productionTip = true 53 54 55 new Vue({ // 实例化对象 56 // 第五步 57 router: router,// router对象放在这里 58 render: h => h(App), // 用来做渲染的 render里返回的是什么 页面上就是什么 App是个组件 59 }).$mount('#app')//$mount进行挂载 也可以用 el:‘app’ 60 ``` 61 62 使用:App.vue(路由的切换 都写这里router-link router-view) 63 64 ``` 65 // 最后一步router-link router-view 项目就可以运行起来了 66 67 <router-link to="/home">点我</router-link> 68 <router-view></router-view> 69 ```
基于vue-cli快速开发:路飞学城(第一版)( 对照着没用脚手架的第一版)
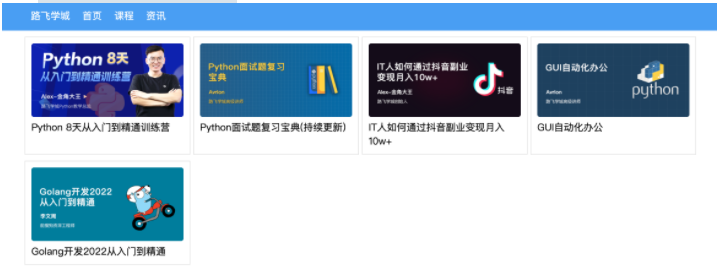
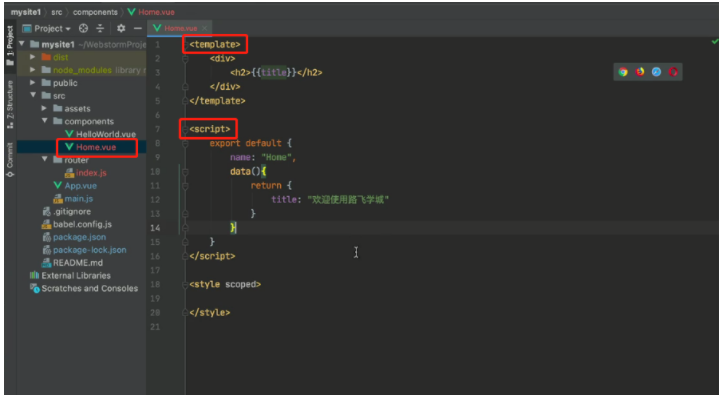
home组件:
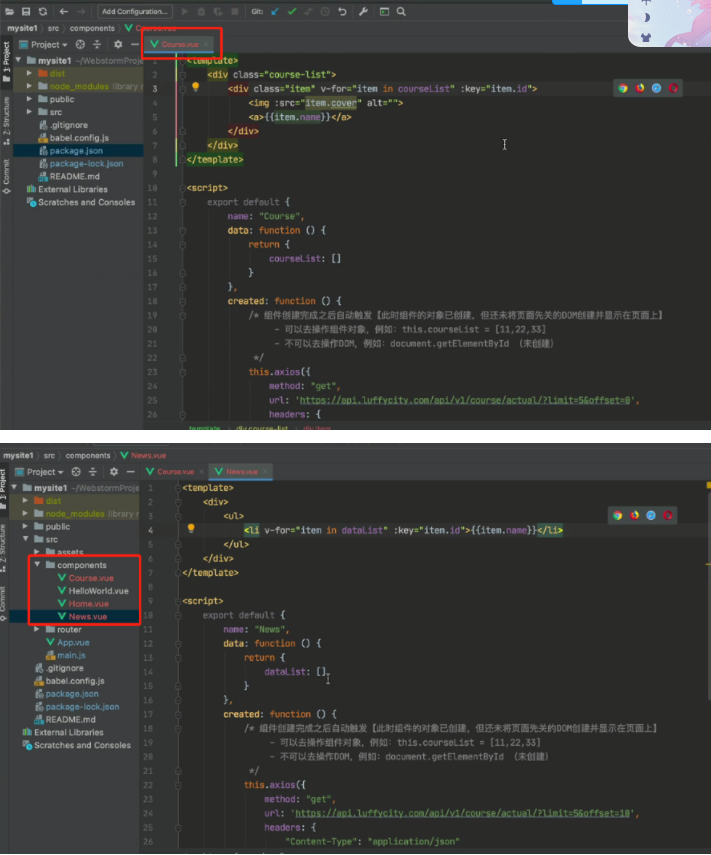
course组件:
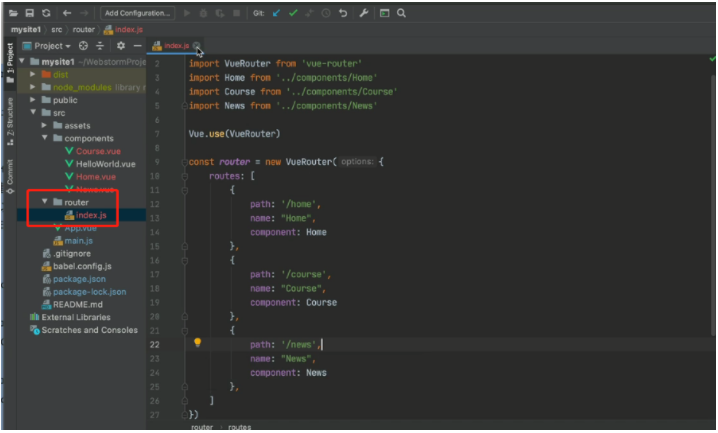
路由:
应用:
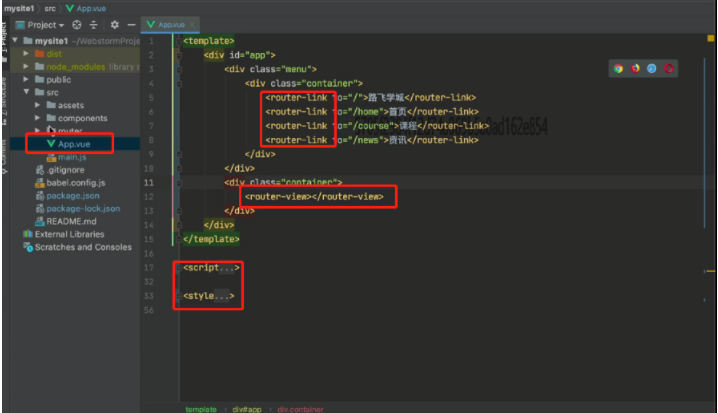
-
npm run build -
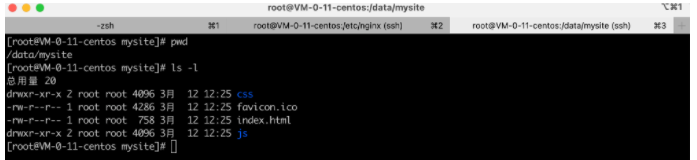
第二步:将编译后的代码dist文件上传到服务器(阿里云、腾讯云)
![]()
-
第三步:安装nginx + 配置 + 启动
yum install nginx
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf (修改配置)

1 user nginx; 2 worker_processes auto; 3 error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; 4 pid /run/nginx.pid; 5 6 # Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic. 7 include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf; 8 9 events { 10 worker_connections 1024; 11 } 12 13 http { 14 log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' 15 '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' 16 '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; 17 18 access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; 19 20 sendfile on; 21 tcp_nopush on; 22 tcp_nodelay on; 23 keepalive_timeout 65; 24 types_hash_max_size 4096; 25 26 include /etc/nginx/mime.types; 27 default_type application/octet-stream; 28 29 include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; 30 31 server { 32 listen 80; 33 listen [::]:80; 34 server_name _; 35 # 项目目录 修改的地方 36 root /data/mysite; 37 38 # Load configuration files for the default server block. 39 include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; 40 41 error_page 404 /404.html; 42 location = /404.html { 43 } 44 45 error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; 46 location = /50x.html { 47 } 48 } 49 50 51 }
服务器上启动命令
>>>systemctl start nginx
第四步:访问
6.vuex
https://next.vuex.vuejs.org/zh/index.html
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的 状态管理模式 store。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态,以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
Vuex 的思想
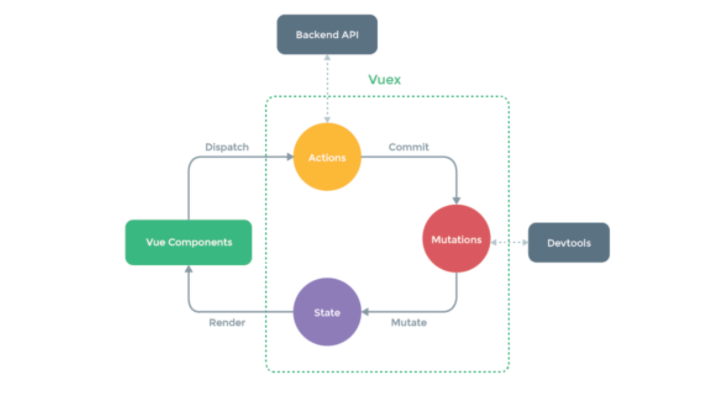
当我们在页面上点击一个按钮,它会处发(dispatch)一个action, action 随后会执行(commit)一个mutation, mutation 立即会改变state, state 改变以后,我们的页面会state 获取数据,页面发生了变化。
Store 对象,包含了我们谈到的所有内容,action, state, mutation,所以是核心了
vuex的使用:
初始化store.js
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 实例化一个vuex存储库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {// 数据存储位置,相当于组件中的data
test: 'x'
},
mutations: {// 操作数据的方法,相当于methods
changetest(state, xxx) {
state.test = xxx
}
},
actions: {
changetest(context, xxx) {
context.commit('changetest', xxx)
}
},
getters: {
test2: state => state.test
}
})
export default store;
state:相当于Vue的data state为单一状态树,在state中需要定义我们所需要管理的数组、对象、字符串等等,只有在这里定义了,在vue.js的组件中才能获取你定义的这个对象的状态。
mutations:类似于事件,每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的事件类型 (type)和 一个回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数
更改store中state状态的唯一方法就是提交mutation,就很类似事件。每个mutation都有一个字符串类型的事件类型和一个回调函数,我们需要改变state的值就要在回调函数中改变。我们要执行这个回调函数,那么我们需要执行一个相应的调用方法:store.commit。
actions: Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态,Action 可以包含任意异步操作
action可以提交mutation,在action中可以执行store.commit,而且action中可以有任何的异步操作。
getters:可以认为是 store 的计算属性,就像计算属性一样,getter 的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算,接受 state 作为其第一个参数
好了,就这么简单可以用了
使用Vuex
打开main.js,导入,然后用
import Vue from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
import store from "./store";
new Vue({
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount("#app");
好了,你可以在所有App所有子组件里面使用Vuex了
如何使用 state
子组件能通过 this.$store 访问到
this.$store.state.test
// x
如何使用 mutations
子组件能通过 this.$store.commit 访问到
this.$store.commit('changetest',xxx)
它会去把 changetest 提交到 mutation 执行 ,第二个是载荷(可以理解为参数),大多数载荷应该是一个对象,这样可以包含多个字段并且记录的 mutation 会更易读
如何使用 actions
子组件能通过 this.$store.dispatch 访问到
this.$store.dispatch('changetest'xxx)
它会去把 changetest 分发到 actions 在通过 actions 提交到 mutation 执行
如何使用 getters
子组件能通过 this.$store.getters 访问到
this.$store.getters.test2
//x
说人话:将组件中需要共享的数据交给vuex来帮我们进行管理,例如:用户登录状态、加入购物车。

### ``` vue create vxdemo // 创建项目vxdemo ``` ``` npm install vue-router@3 // 需要路由 所以装vue-router ``` ``` npm install vuex@3 // 状态管理 用户登录成功后 改变登录的状态 ```
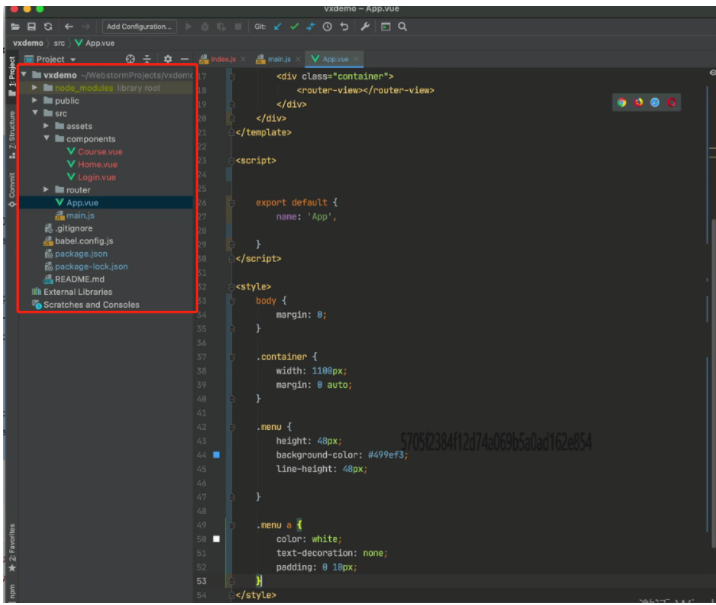

1 - main.js 2 3 ```javascript 4 import Vue from 'vue' 5 import App from './App.vue' 6 import router from "./router" 7 import store from "./store" 8 9 Vue.config.productionTip = false 10 11 new Vue({ 12 router: router, 13 store: store, 14 render: h => h(App), 15 }).$mount('#app') 16 ``` 17 18 - App.vue 19 20 ```vue 21 <template> 22 <div id="app"> 23 <div class="menu"> 24 <div class="container"> 25 <router-link to="/home">首页</router-link> 26 <router-link to="/course">课程</router-link> 27 28 <div style="float: right"> 29 <a v-if="this.$store.state.isLogin"> // 如果state状态是True 30 {{this.$store.state.userInfo.username}} //显示用户名 31 </a> 32 <router-link v-else to="/login">登录</router-link> 33 34 </div> 35 </div> 36 </div> 37 <div class="container"> 38 <router-view></router-view> 39 </div> 40 </div> 41 </template> 42 <script> 43 export default { 44 name: 'App', 45 data() { 46 return {} 47 }, 48 components: {}, 49 } 50 </script> 51 52 <style> 53 body { 54 margin: 0; 55 } 56 .container { 57 width: 1100px; 58 margin: 0 auto; 59 } 60 .menu { 61 height: 48px; 62 background-color: #499ef3; 63 line-height: 48px; 64 65 } 66 .menu a { 67 color: white; 68 text-decoration: none; 69 padding: 0 10px; 70 } 71 </style> 72 ``` 73 74 - store/index.js(vuex代码相关逻辑) 75 76 ```javascript 77 import Vue from 'vue' 78 import Vuex from 'vuex' 79 80 Vue.use(Vuex) 81 82 83 export default new Vuex.Store({ // 实例化对象并导出 84 state: { // 存储的数据 状态 其他页面可以调用state 85 isLogin: false, //是否登录 86 userInfo: null //用户信息 87 }, 88 mutations: { // 改状态 更改Vuex的store中的状态的唯一方法是提交mutation 89 login: function (state, info) { 90 state.userInfo = info; // info 是个对象里面有用户名和密码 91 state.isLogin = true; 92 }, 93 94 }, 95 actions: {} 96 }) 97 98 ``` 99 100 - router/index.js 101 102 ```javascript 103 // router/index.js 104 105 import Vue from 'vue' 106 import VueRouter from 'vue-router' 107 108 109 import Home from '../components/Home' 110 import Course from '../components/Course' 111 import Login from '../components/Login' 112 113 114 Vue.use(VueRouter) 115 116 const router = new VueRouter({ 117 routes: [ 118 { 119 path: '/home', 120 name: "Home", 121 component: Home 122 }, 123 { 124 path: '/course', 125 name: "Course", 126 component: Course 127 }, 128 { 129 path: '/login', 130 name: "Login", 131 component: Login 132 }, 133 ] 134 }) 135 136 export default router 137 ``` 138 139 - components/Login.vue 140 141 ```html 142 <template> 143 <div> 144 <input type="text" v-model="info.username" placeholder="用户名"> 145 <input type="password" v-model="info.password" placeholder="密码"> 146 <input type="button" value="登录" @click="doLogin"/> 147 </div> 148 </template> 149 150 <script> 151 export default { 152 name: "Login", 153 data() { 154 return { 155 info: { 156 username: "", 157 password: "" 158 } 159 } 160 }, 161 methods: { 162 doLogin: function () { 163 // 1.用户登录 164 this.$store.commit('login', this.info); 165 // 2.登录成功修改状态 跳转到home页面 166 this.$router.push({name: 'Home'}); 167 } 168 } 169 } 170 </script> 171 172 <style scoped> 173 174 </style> 175 ```
在vue的组件中有一个computed属性(计算属性),监听关联的数据,如果发生变化则重新计算并显示。
<template>
<div>
<h1>主页 {{v1}} {{ v2}}</h1> // 两个变量
<div>总数:{{totalData}}</div> // 自动执行get方法 得到返回值
<input type="button" value="点我" @click="addData"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data() {
return {
v1: 123,// 声明两个变量
v2: 456
}
},
computed: {
totalData: {
get() { // 读取
let data = this.v1 + this.v2;
return data + 1000;
},
set(value) { // 设置
this.v1 = value;
}
}
},
methods: {
addData() {
this.totalData = 999;// totalData是计算属性 先执行set方法 把值放在value里 赋值的时候想怎么写怎么写 get也会相应变化
// this.v2 = 1000; // 直接修改v2,get返回值肯定发生变化
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
所以,上述案例也可以用computed属性来实现,例如:App.vue改成:

1 <template> 2 <div id="app"> 3 <div class="menu"> 4 <div class="container"> 5 <router-link to="/home">首页</router-link> 6 <router-link to="/course">课程</router-link> 7 8 <div style="float: right"> 9 <a v-if="userState"> // 通过计算属性实现 10 {{userName}} // 通过计算属性实现 11 </a> 12 <router-link v-else to="/login">登录</router-link> 13 14 </div> 15 </div> 16 </div> 17 <div class="container"> 18 <router-view></router-view> 19 </div> 20 </div> 21 </template> 22 23 <script> 24 25 export default { 26 name: 'App', 27 data() { 28 return {} 29 }, 30 computed: {// 计算属性 31 userState: { // 只读 没有赋值 32 get() { 33 return this.$store.state.isLogin; 34 } 35 }, 36 userName() {// 只有只读可以简写 37 return this.$store.state.userInfo.username; 38 }, 39 40 }, 41 components: {}, 42 } 43 </script> 44 45 <style> 46 body { 47 margin: 0; 48 } 49 50 .container { 51 width: 1100px; 52 margin: 0 auto; 53 } 54 55 .menu { 56 height: 48px; 57 background-color: #499ef3; 58 line-height: 48px; 59 60 } 61 62 .menu a { 63 color: white; 64 text-decoration: none; 65 padding: 0 10px; 66 } 67 68 69 </style>
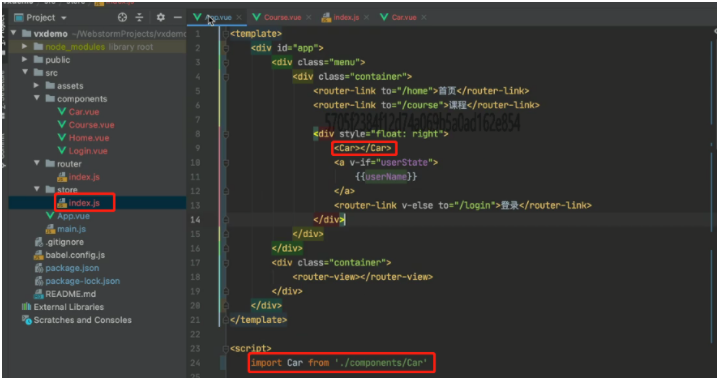
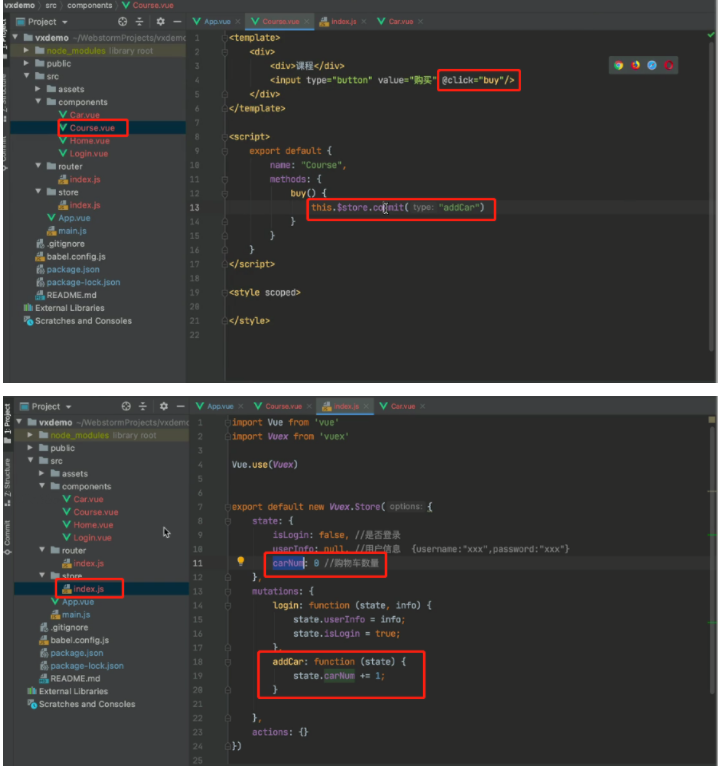
6.3 案例:购物车

1、创建一个组件car、
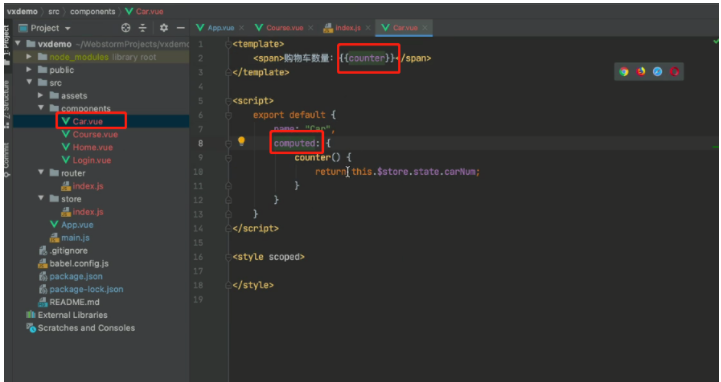
2、组件应用(固定的放在某个位置)
6.4 关于Action
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
-
Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
-
Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
-
![]() View Code
View Code1 代码示例: 2 3 ```javascript 4 const store = createStore({ 5 state: { 6 count: 0 7 }, 8 mutations: { 9 increment (state) { 10 state.count+=1; //更新state状态 11 } 12 }, 13 actions: { // 一般没用 有异步操作就有用了 14 15 increment (context) { 16 // 触发mutations 17 context.commit('increment') 18 } 19 } 20 }) 21 ``` 22 23 在组件中如果要触发action,则应该执行: 24 25 ```javascript 26 this.$store.dispatch('increment') 27 ``` 28 29 30 31 这就有点像脱裤子放屁,意义何在呢? 当有异步操作时,应该使用action、而不是mutation,例如: 32 33 ```javascript 34 import Vue from 'vue' 35 import Vuex from 'vuex' 36 37 Vue.use(Vuex) 38 39 40 export default new Vuex.Store({ 41 state: { 42 isLogin: false, //是否登录 43 userInfo: null, //用户信息 44 carNumber: 0, 45 xxxxx: 10 46 }, 47 mutations: { 48 login: function (state, info) { 49 state.userInfo = info; 50 state.isLogin = true; 51 }, 52 addCar: function (state) { 53 state.carNumber += 1; 54 }, 55 56 fetchAsync: function (state) { 57 // // 异步操作 发送ajax请求 58 setTimeout(function () { 59 state.xxxxx += 1; 60 }, 1000); // 1秒后 状态改变 61 } 62 63 }, 64 actions: {} 65 }) 66 67 ``` 68 69 ``` 70 // 按钮执行函数 71 this.$store.commit("fetchAsync"); 72 ``` 73 74 从效果上看是没有问题的,但是通过开发者工具就会发现,监测到的state的数据不准确。 75 76 官方图说 如果发送异步请求应该在actions里做 异步做完了回调函数再去做mutations 在去更改state状态 在mutations 安装一个浏览器插件devtools可以监听里面的状态的值(老师给的文件里有)
所以,这种情况可以选择用Action。 ```javascript import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { isLogin: false, //是否登录 userInfo: null, //用户信息 carNumber: 0, xxxxx: 10 }, mutations: { login: function (state, info) { state.userInfo = info; state.isLogin = true; }, addCar: function (state) { state.carNumber += 1; }, fetchAsync: function (state,data) { state.xxxxx += 1; console.log(data); } }, actions: { // 异步动作写在这 异步动作执行完再去改状态 能够保证mutations 里的状态值和整体是一样的 fetchAsync: function (context,data) { setTimeout(function () { context.commit("fetchAsync",data); }, 1000); } } }) ``` 再触发时,调用: ``` this.$store.dispatch('fetchAsync',{ amount: 10}) ```
7.flex布局
在CSS3中flex可以非常便捷的可以帮助我们实现对页面的布局。
-
传统的页面布局,基于div+float来实现。
-
flex可以快速实现页面的布局(很方便)。
关于flex布局你必须要了解的有一下几点:
<div class="menu" 样式>// 容器里加样式 <div class="item" 样式>112</div> // 在元素里加样式 <div class="item">113</div> </div>
7.1 容器
7.1.1 flex布局
在容器元素上应用
<div class="menu"> <div class="item">112</div> <div class="item">113</div> </div> <style> .menu{ border: 1px solid red; width: 500px; display: flex; // 表示flex布局 } </style>
<div class="menu"> <div class="item">112</div> <div class="item">113</div> </div> <style> .menu{ border: 1px solid red; width: 500px; display: flex; // 表示flex布局 flex-direction: row; // row主轴是横向,副轴是纵向。column是主轴是纵轴 } </style>
justify-content,主轴上的元素的排列方式
align-items,副轴上的元素的排列方式。
<div class="menu"> <div class="item">11</div> <div class="item">112</div> <div class="item">112</div> </div> <style> .menu { width: 500px; border: 1px solid red; display: flex; flex-direction: row; // row主轴是横向,副轴是纵向 justify-content: flex-start; /* 主轴=横向,横向从左开始 */ justify-content: flex-end; /* 主轴=横向,横向从右开始 */ justify-content: space-between; /* 主轴=横向,左右定格,中间元素等分空白 */ justify-content: space-around; /* 主轴=横向,所有元素等分空白 */ justify-content: space-evenly; /* 主轴=横向,元素间距一样 */ } .item { border: 1px solid green; padding: 5px 50px; height: 50px; width: 40px; } </style>
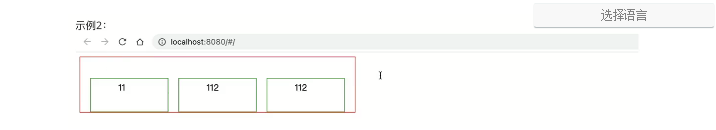
<div class="menu"> <div class="item">11</div> <div class="item">112</div> <div class="item">112</div> </div> <style> .menu { width: 500px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid red; display: flex; flex-direction: row; justify-content: flex-start; /* 主轴=横向,横向从左开始 */ justify-content: flex-end; /* 主轴=横向,横向从右开始 */ justify-content: space-between; /* 主轴=横向,左右定格,中间元素等分空白 */ justify-content: space-around; /* 主轴=横向,所有元素等分空白 */ justify-content: space-evenly; /* 主轴=横向,元素间距一样 */ align-items: center; /* 副轴=纵向,元素居中*/ align-items: flex-start; /* 副轴=纵向,元素顶部*/ align-items: flex-end; /* 副轴=纵向,元素底部*/ } .item { border: 1px solid green; padding: 5px 50px; height: 50px; width: 40px; } </style>
7.1.4 换行
-
flex-wrap: nowrap;元素超过容器,不换行 -
flex-wrap: wrap;元素超过容器,换行
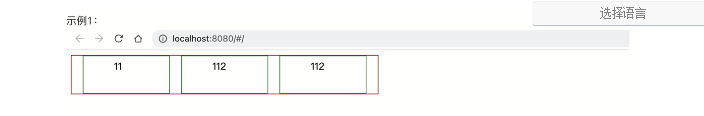
示例1:不换行
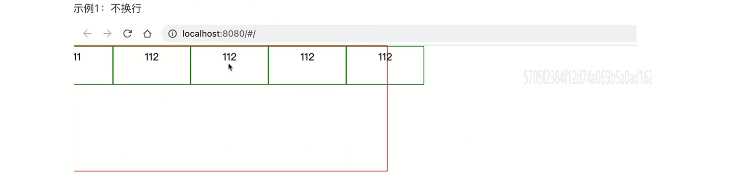
<div class="menu"> <div class="item">11</div> <div class="item">112</div> <div class="item">112</div> <div class="item">112</div> <div class="item">112</div> </div> <style> .menu { width: 500px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid red; display: flex; flex-direction: row; justify-content: space-evenly; /* 主轴=横向,元素间距一样 */ align-items: flex-start; /* 副轴=纵向,元素顶部*/ flex-wrap: nowrap; } .item { border: 1px solid green; padding: 5px 50px; height: 50px; width: 40px; } </style>
示例2:换行
<div class="menu"> <div class="item">111</div> <div class="item">112</div> <div class="item">112</div> <div class="item">112</div> <div class="item">112</div> </div> <style> body{ // 清除浏览器中默认的body的内外边距 margin: 0; } .menu { width: 500px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid red; display: flex; flex-direction: row; justify-content: space-evenly; /* 主轴=横向,元素间距一样 */ align-items: flex-start; /* 副轴=纵向,元素顶部*/ flex-wrap: wrap; } .item { border: 1px solid green; padding: 5px 50px; height: 50px; width: 40px; } </style>
7.1.5 多行对齐方式
align-content
align-content:flex-start;
flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | space-evenly | stretch(默认);
7.2 元素
7.2.1 顺序
order,默认0,用于决定项目排列顺序,数值越小,项目排列越靠前。
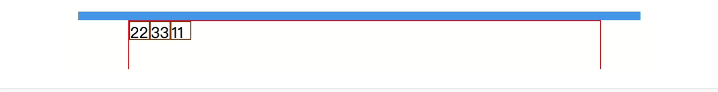
<div class="father"> <div class="son" style="order: 2">11</div> <div class="son" style="order: 0">22</div> <div class="son" style="order: 1">33</div> </div> <style scoped> .father { border: 1px solid red; width: 500px; height: 300px; display: flex; flex-direction: row; justify-content: flex-start; } .father .son { border: 1px solid saddlebrown; width: 20px; height: 18px; } </style>
7.2.2 剩余空间(是否占满)
flex-grow,默认0,用于决定项目在有剩余空间的情况下是否放大,默认不放大;

<div class="father"> <div class="son">11</div> <div class="son" style="flex-grow: 1">22</div> <div class="son" style="flex-grow: 1">33</div> </div>
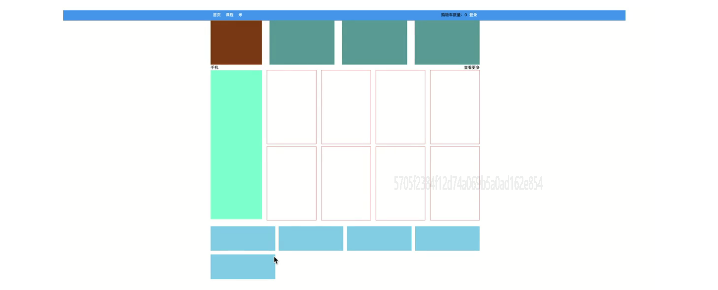

1 <template> 2 <div> 3 <div class="row1"> 4 <div class="company"></div> 5 <div class="pic"></div> 6 <div class="pic"></div> 7 <div class="pic"></div> 8 </div> 9 <div class="row2"> 10 <div class="title"> 11 <div>手机</div> 12 <div>查看更多</div> 13 </div> 14 <div class="pic-list"> 15 <div class="big"></div> 16 <div class="right-list"> 17 <div class="group"> 18 <div class="phone"></div> 19 <div class="phone"></div> 20 <div class="phone"></div> 21 <div class="phone"></div> 22 </div> 23 <div class="group"> 24 <div class="phone"></div> 25 <div class="phone"></div> 26 <div class="phone"></div> 27 <div class="phone"></div> 28 </div> 29 30 </div> 31 </div> 32 </div> 33 34 <div class="course-list"> 35 <div class="item"></div> 36 <div class="item"></div> 37 <div class="item"></div> 38 <div class="item"></div> 39 <div class="item"></div> 40 41 </div> 42 </div> 43 </template> 44 45 <script> 46 export default { 47 name: "Mi" 48 } 49 </script> 50 51 <style scoped> 52 // .row1 样式 53 .row1 { 54 display: flex; 55 flex-direction: row; 56 justify-content: space-between; 57 } 58 59 .row1 .company { 60 width: 210px; 61 height: 180px; 62 background-color: saddlebrown; 63 } 64 65 .row1 .pic { 66 width: 266px; 67 height: 180px; 68 background-color: cadetblue; 69 } 70 // .row2 样式 71 .row2 .title { 72 display: flex; 73 flex-direction: row; 74 justify-content: space-between; 75 } 76 77 .row2 .pic-list { 78 display: flex; 79 flex-direction: row; 80 justify-content: space-between; 81 } 82 83 .row2 .pic-list .big { 84 background-color: aquamarine; 85 height: 610px; 86 width: 210px; 87 margin-right: 20px; 88 } 89 90 .row2 .pic-list .right-list { 91 /*background-color: antiquewhite;*/ 92 flex-grow: 1; 93 } 94 95 .row2 .pic-list .right-list .group { 96 97 98 display: flex; 99 flex-direction: row; 100 justify-content: space-between; 101 flex-wrap: wrap; 102 } 103 104 .row2 .pic-list .right-list .phone { 105 margin-bottom: 10px; 106 border: 1px solid red; 107 width: 200px; 108 height: 300px; 109 } 110 111 .course-list { 112 display: flex; 113 justify-content: space-between; 114 flex-wrap: wrap; 115 } 116 117 .course-list .item { 118 width: 24%; 119 height: 100px; 120 background-color: skyblue; 121 margin-top: 15px; 122 } 123 124 // 如果最后一个元素,是第3个,右边距=一个位置 + 所有空白位置/3(有三个空白位置) 125 .course-list .item:last-child:nth-child(4n - 1) { 126 margin-right: calc(24% + 4% / 3); 127 } 128 129 // 如果最后一个元素,是第2个,右边距=两个位置 + 所有空白位置/3*2(有三个空白位置) 130 .course-list .item:last-child:nth-child(4n - 2) { 131 margin-right: calc(48% + 8% / 3); 132 } 133 </style>
至此,结合以上的知识点,我们就可以来开发一个项目,但很多的页面按钮、标签、提示框等都需要自己手动,太费劲。
所以,接下来就要给大家的来聊一个UI框架 - ElementUI,他的内部提供了很多方便的样式和组件,可以加速我们开发。
8.ElementUI
Element,是有 饿了吗 团队开发一套为开发者、设计师和产品经理准备的基于 Vue 2.0 的组件库(也支持vue3.x)。
在他的基础上来开发,可以大大提升开发进度。
想要在项目中进行使用element-ui需要提前安装并引入。
8.1 引入
方式1:完整引入
- 安装 ``` cd 项目目录 npm install element-ui ``` - 引入 ```javascript import Vue from 'vue'; import ElementUI from 'element-ui'; import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'; // 主题 颜色背景 import App from './App.vue'; Vue.use(ElementUI); // 引入 use一下就可以了 new Vue({ render: h => h(App), }).$mount('#app') ``` - 在组件中使用 ```html <el-button type="success">哈哈哈</el-button> ``` **方式2**:局部引入 - 安装 ``` cd 项目目录 npm install element-ui ``` - 引入 ```javascript import Vue from 'vue'; import { Button, Select } from 'element-ui'; // 引入指定组件 import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'; import App from './App.vue'; Vue.use(Button) Vue.use(Select) new Vue({ render: h => h(App), }).$mount('#app') ``` - 在组件中使用 ```html <el-button type="success">哈哈哈</el-button> ``` 完整组件名称:https://element.eleme.cn/#/zh-CN/component/quickstart
8.2 组件的使用
参见官方文档,在后续的项目开发中来应用并使用。








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号