知识点总结
个人总结
1,git管理代码
git init git config --global user.email flf@example.com git config --global user.name "flf" git checkout -b master git add ./ git commi
这样就创建了一个分支名称为master的git 仓。
2,从ubuntu虚拟机拷贝镜像到windows
以下脚本自动拷贝image到windows,用法:
把脚本放到待拷贝目录,执行脚本,无需参数,就会在windows共享文件夹里创建相同工程名称的文件夹,并把镜像拷进去,有其他想拷贝的可以自行添加。
附脚本:
#!/bin/sh var=$PWD # current dir name # echo ${var##*/} # get destination dir, dir name is same with current dir destDir=/mnt/hgfs/`ls /mnt/hgfs/`/${var##*/} #echo $destDir if [ ! -d "$destDir" ]; then mkdir -p "$destDir" fi cp /opt1/template/x497/top_hw_platform/top.bit $destDir cp $PWD/images/linux/BOOT.BIN $destDir cp $PWD/images/linux/image.ub $destDir
3,驱动代码编译成模块
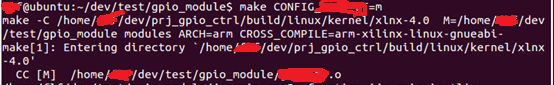
在linux开发系统上编译arm内核模块不同于本机(x86),需要指定内核源码config文件的位置、架构、交叉编译套件
3.1 Makefile 代码如下
# # Makefile for device drivers. # KDIR := /home/dev/prj_gpio_ctrl/build/linux/kernel/xlnx-4.0 ARCH = arm CROSS_COMPILE = arm-xilinx-linux-gnueabi- obj-$(CONFIG_GPIO_ST) += src_file.o all: make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=$(CROSS_COMPILE) # make CONFIG_MY_DEFINE=m -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=$(CROSS_COMPILE) clean: rm -f *.o *.ko *.order
1,KDIR是包含.config的文件夹,否则报错
make[2]: *** No rule to make target `include/config/auto.conf'. Stop.
2,ARCH是目标板(即开发板)的架构,一般都是arm
3,CROSS_COMPILE是交叉编译工具链,一直到gcc但不包含gcc,例如现在用的是arm-xilinx-linux-gnueabi-gcc
因为是在x86平台编译arm平台的内核模块,所以要用交叉编译工具链。
4,注意空白字符,tab、空格,格式错误会显示红色
3.2 模块编译
1,直接执行make 或者make all,可以在编译时添加config定义(Makefile里注释掉那一行),这样就不用单独改内核config文件。
2,make clean清除编译产生的文件

3.3 安装卸载模块
insmod、rmmod、lsmod
4. 编译app
arm-xilinx-linux-gnueabi-gcc app.c -o test
5. shell使用总结
5.1 特殊字符检测
判断变量前两个字符
${input_patch_file:0:2}
变量从第二个字符直至结尾
${input_patch_file:2}
e.g.
if [ ${input_patch_file:0:2} == "./" ]; then patch_file=$PWD${input_patch_file:1} elif [ ${input_patch_file:0:2} == "~/" ]; then patch_file=$HOME${input_patch_file:1} elif [ ${input_patch_file:0:1} != "/" ]; then patch_file=$PWD/$input_patch_file else patch_file=$input_patch_file fi
5.2 文件不存在
if [ ! -f "$patch_file" ]; then { 。。。 }
5.3 函数与变量
脚本的执行是从函数下面的脚本开始的。
shell里的变量都是全局变量,从定义开始起效。
判断上一条命令执行结果,是否正常返回
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
e.g.
#!/bin/sh function get_patch_file(){ echo "input patch file:" read patch_file echo -e "\nYour patch file is:\n"$patch_file"\n" cd / if [ ! -f "$patch_file" ]; then { echo -e "Your patch file is not exists, please check!\nAborting..." exit 0; } fi } function add_patch() { get_patch_file echo "<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< add patch begin >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>" cd $kernel_path patch -p1 -s < $patch_file if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then { echo "add patch failed!!!" } fi echo ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> add patch end <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<" } echo "Your choose:[1]" read choose if [ "$choose"x == "1"x ] || [ -z $choose ]; then add_patch fi
5.4 判断用户直接输入enter
可以通过独到的字符串长度为0 进行判断
echo "Your choose:[1]" read choose if [ "$choose"x == "1"x ] || [ -z $choose ]; then add_patch elif [ "$choose"x == "2"x ]; then revert_patch else echo "Invalid input! Bye!!!" fi
6. 字符串操作
1,sizeof() strlen()
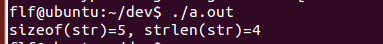
1.1 sizeof()在计算字符串长度时,会把截止符0算进去,所以结果是实际看到的长度加1。
e.g.
char str[] = "1234"; printf("sizeof(str)=%d, strlen(str)=%d\n", sizeof(str), strlen(str));
输出
1.2 strlen()是遇到截止字符前,字符串实际占用长度,不算截止字符。
e.g(到9出现了截止符,后面的被截止).
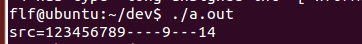
6 char *src = "123456789\0""123";
7
8 printf("src=%s----%d\n", src, strlen(src));
输出

但sizeof就是算全部的,即使中间有截止符也不会停止,但输出src时由于中间有截止符会停止。
6 char src[] = "123456789\0""123"; 7 8 printf("src=%s----%d---%d\n", src, strlen(src), sizeof(src));
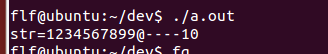
1.3 对于定义好的数组str,这时sizeof(str)也是10,并不会加1.因为str包含截止符最多可以有10个字符。
e.g.
char str[10] = "123456789987654321"; printf("str=%s----%d\n", str, sizeof(str));
输出sizeof(str) 是10.
总结:
sizeof会计算字符串数组的全部,然后加上一个截止符。
strlen和字符串属于一样,遇到截止符停止,不包含截止符。
2,字符串数组与字符串指针
字符串指针的sizeof是这个指针占用空间,不是字符串占用空间!
str是指针,sizeof(str)是指针占用的空间并不是字符串!
而str_arry是字符串占用空间(看到的长度+截止符)
这两个用strlen()得到的结果都是3,表示字符串看到的长度。
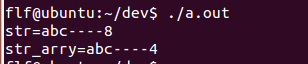
char *str = "abc"; char str_arry[] = "abc"; printf("str=%s----%d\n", str, sizeof(str)); printf("str_arry=%s----%d\n", str_arry, sizeof(str_arry));
3. strncmp
int strncmp(const char *str1, const char *str2, size_t n)
参数
- str1 -- 要进行比较的第一个字符串。
- str2 -- 要进行比较的第二个字符串。
- n -- 要比较的最大字符数。
返回值
该函数返回值如下:
- 如果返回值 < 0,则表示 str1 < str2。
- 如果返回值 > 0,则表示 str1 > str2。
- 如果返回值 = 0,则表示 str1 = str2。
4. snprintf
int snprintf(char*str, size_t size,constchar*format, ...);
函数说明:
最多从源串中拷贝size-1个字符到目标串中,然后再在后面加一个0。所以如果目标串的大小为size的话,将不会溢出。
函数返回值:
若成功则返回欲写入的字符串长度,若出错则返回负值。
e.g.
char str[10]={0}; snprintf(str, sizeof(str), "123456789012345678"); printf("str=%s\n", str);
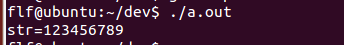
字符串长度10(包含截止符),snprintf拷贝size-1即9个字符到str,然后给最后一个字符加截止符。
可以利用snprintf 截取字符串最后一段数据
char dest[3] = {0}; char src[] = "123456789"; snprintf(dest, sizeof(dest), src+strlen(src)-sizeof(dest)+1); printf("dest=%s\n", dest);
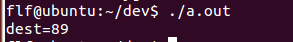
字符串总共可以存储两个数据加截止符,这段代码把最后两个数据存入dest,然后添加截止符。
5. kernel 字符串转换为数字
int kstrtoul(const char *s, unsigned int base, unsigned long *res)
s: 字符串
base:进制格式,如十进制,是10
res: 转换结果
返回值:成功返回0,否则返回非0.
利用strlen, strncmp, snprintf, strtoul 系列可以进行字符串的任意比较、截取、转换,多构思,多设计。
7. ubuntu更换软件下载的镜像源
https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/ubuntu/
-------
end




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号