MySQL2
MySQL1-常用配置和常用指令
MySQL2-DQL和DML
MySQL3-DDL和TCL
MySQL4-查询练习
SQL数据类型
数值型:
整型:
tinyint 1字节 -128~127/0~255
smallint 2字符
mediumint 3字符
int、integer 4字符-2,147,483,648~2,147,483,647/0~4,294,967,295
bigint 8字符
小数:
D,M可以省略
定点数
dec、decimal(M,D) 有效范围用M,D定义
浮点数
float(M,D) 4字节
double(M,D) 8字节
字符型:
较短的文本:
char(M) M可省略,固定长度,耗费空间,效率高
varcher(M) M不可省略,可变长度,节省空间,效率低
binary、varbinary 二进制
enum('要插入的值1','要插入的值2','要插入的值3') 枚举
set('要插入的值1','要插入的值2','要插入的值3') 集合
较长的文本:
text
blob(较长的二进制数据)
日期型:
data 只有日期没有时间
datatime 有日期和时间不带时区 8字节 持续到9999年
timestamp 有日期和时间带有时区 4字节 持续到2038年
time 只有时间没有日期
year 只有年
数据设计规范
- 所有表都使用innodeDB的索引
- 字符集统一使用utf-8,如果储存emoj表情,则使用utfbmb4字符
- 所有表和字段都加有注释
- 单张表数据控制在500w以下
- 不使用分区表,不利于扩展和维护
- 冷热数据进行分离,减小表的宽度
- mysql每个表最多存储4096列,每行85535个字节
- 减少I/O磁盘操作,使用redis缓存
- 经常使用的列放同一个表中
- 不储存图片和文件
索引设计规范
- 每个表的索引不超过5个,索引在查询很有利,但是在删除和插入的时候会增加负担
- 不能给每一列都添加索引
- 每个innoDB都有主键,不使用更新频繁的列做索引
- 对于频发查询的使用覆盖索引,避免二次查询,把随机IO改为顺序IO
- 哈希索引,适用于全键的等值查询
- 位图索引,适合改变较少的,且取值范围较小的,可以大幅度增加效率,更新的可能锁表
- 函数索引,以f(x)作为索引,适合用于不区分大小写的查询,同时具有选择的唯一性
- 索引带来的问题,日期函数
DQL学习
DQL(Data QueryLanguage)数据查询语言
单行函数
select 函数名(实参列表) [from 表];
字符函数
length() 获取字符集的字节
select length('jojo');
ifnull()判断是否为空
select ifnull(commission_pct,0) as 奖金率 from commission_pct
concat() 拼接字符
select concat(last_name,first_name) as 姓名 from smployees;
upper()/lower() 变大写/变小写
select upper('jojo'); select lower('JOJO');
substr() 截取字符
索引从1开始
select substr('jojo的奇妙冒险之旅',8) out_put;
select substr('jojo的奇妙冒险之旅',1,4) out_put;
instr() 返回子串第一次出现的位置
没有为0.
select instr('jojo的奇妙冒险','奇妙') out_put;
trim() 去除指定值
不赋值为空格
select trim('aa' from 'aaaaajoaajoaaaaa') out_put;
lpad()/rpad() 用指定字符左/右填充指定长度.
select lpad('jojo',10,'*') out_put;
select rpad('jojo',10,'*') out_put;
replace() 替换
select replace('奇妙jojo的奇妙冒险奇妙','奇妙','怪怪') out_put
数学函数
round() 四舍五入
select round(-1.1415926,4);
ceil()/floor() 向上/下取整
select ceil(1.01); select floor(-9.9);
truncate() 阶段
select truncate(1.69999,1);
mod() 去余
select mod(10,3);
日期函数
now() 返回当前系统日期
select now();
curdata() 返回当前系统日期,不包含时间
select curdata();
curtime() 返回当前时间,不包含日期
select curtime();
获取指定部分
年year()
月month()/monthname()
日day()
时hour()
分minute()
秒second()
select year(now());
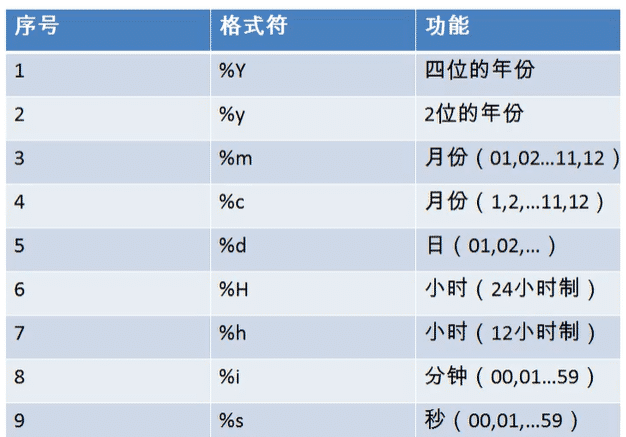
str_to_date() 将字符通过指定格式转换成日期
select str_to_date('1999-3-2','%Y-%c-%d') out_put;
date_format() 将日期转换成字符
select date_format(now(),'%y年%m月%d日') out_put;
其他函数
-- 查看数据库当前使用的版本
select version();
-- 查看当前所在的位置
select database();
-- 查看当前使用者
select user();
流程控制函数
if函数:if else 的效果
select if(10>5, '对','错');
case函数:多项选择
select salary 原始工资,department_id,
case department_id
when 30 then salary*1.1
when 40 then salary*1.2
when 50 then salary*1.3
else salary
end as 新工资
from employees;
case函数:多重if
select salary 原始工资,
case
when salary>20000 then'A'
when salary>15000 then'B'
when salary>10000 then'C'
else 'D'
end as 工资级别
分组函数
- sum(),avg()只支持数值类型的参数格式,
- sum(),avg(),max(),min(),count()全忽略null
- sum(),avg(),max(),min(),count()都可以和distinct[去重]搭配。
- count(*),count(1)统计所有行数,两者效率差不多。
- 和分组查询的字段有要求,分组函数一般是group by后的字段使用
sum求和
select sum(salary) from employees;
avg求平均值
select avg(salary) from employees;
max最大值
select max(salary) from employees;
min最小值
select min(salary) from employees;
count计算个数
select count(salary) from employees;
SQL92标准
等值连接
- 第一张表去匹配第二张表的内容,并对指定内容进行对比筛选。
- 多表等值连接的结果为多表的交集部分
- n表连接,至少需要n-1个连接条件句
- 多表的顺序没有要求
- 可以搭配前面的子句进行使用
-- 基本(两个表顺序可调换)
select e.last_name,e.job_id,j.job_title
from employees e,job j
where e.`job_id`=j.`job_id`;
-- 添加筛选
select last_name,department_name,commission_pct
from employees e,departments d
where e.`department_id`=d.`department_id`
and e.`commission_pct` is not null;
-- 添加分组
select count(*) 个数,city
from departments d,locations l
where d.`location_id`=l.`location_id`
group by city;
-- 添加排序
select job_title,count(*)
from employees e,jobs j
where e.`job_id`=j.`job_id`
group by job_title
order by count(*) desc;
-- 三表连接
select last_name,department_name,city
from employees e,departments d,locations l
where e.`department_id`=d.`department_id`
and d.`department_id`=l.`location_id`;
非等值连接
select salary,grade_level from employees e,job_grades g
where e.salary between g.lowest_sal and g.highest_sal;
自连接
select e.employee_id,e.last_name,m.employee_id,m.last_name from employees e,employees m
where e.`manager_id` = m.`smployee_id`;
SQL99标准
内连接
等值连接
select last_name,department_ment from departments d
inner join employees e on e.`department_id` = d.`department_id`
where e.'last_name' like "%e%";
非等值连接
select salary,grade_level from employees e
join job_grades g on e.`salary` between g.`lowest_sal` and g.`highest_sal`
group by grade_level having count(*)>20
order by grade_level desc;
自连接
select e.last_name,m.last_name from employees e
join employees m on e.`manager_id`=m.`employee_id`
where e.`last_name` like '%k%';
外连接
一般用于查询一个表中有,一个表中没有的记录
外连接的查询结果为主表中的所有记录
如果从表中有和它匹配的,则显示匹配的值
如果从表中没有和它匹配的,则显示null
外连接查询结果=内连接+主表中有从表中没有的记录
左外连接,left join左边的是主表
右外连接,right join右边的是主表
左外右外交换顺序可以实现同样的效果
全外连接,内连接的结果+表1中有但表2中没有的+表2中有但表1中没有的
左外连接
select b.name,bo.* from beauty b
left outer join boys bo on b.`boyfroend_id` = bo.`id`
where bo.`id` is null;
右外连接
select b.name,bo.* from boys bo
right outer join beauty b on b.`boyfroend_id` = bo.`id`
where bo.`id` is null;
全外连接
select b.* bo.* from beauty b
full outer join boys bo on b.`boyfriend_id` = bo.`id`;
交叉连接,笛卡尔乘积
select b.* bo.* from beauty bcross
join boys bo;
分组查询
-
分组筛选查询,分组前筛选和分组后筛选,
- 前后的筛选源不同,前筛选的是原表中的数据,后筛选的是分组表中的结果。
- 前后筛选语句位置不同,前筛选放在group by语句前,后筛选放在group by语句后
- 前后筛选关键字不同,前筛选使用where,后筛选使用having
-
order by 支持单个字段分组,多字段分组(用','隔开即可),表达式或函数分组(用的少)
-
分组后也可以添加排序,排序放在查询的最后
select 分组函数,列 from 表 [where 筛选条件] group by 分组列表 [order by 字句]
group by
-- 简单查询
select max(salary),job_id
from employees
group by job_id;
-- 分组前筛选查询
select avg(salary),department_id
from employees
where email like "%a%"
group by department_id;
-- 分组后筛选查询
select count(*),department_id
from employees
group by department_id
having count(*)>2;
-- 按照表达式或函数分组筛选查询
select count(*),length(last_name) len_name
from employees
group by length(last_name)
having count(*)>5;
-- 按多个字段分组
-- 字段顺序可更换,结果不变
select avg(salary),department_id,job_id
from employees
group by job_id,department_id;
-- 分组查询,添加排序
select avg(salary),department_id,job_id
from employees
where department_id is not null
group by job_id,department_id
having avg(salary)>10000
order by avg(salary) desc;
连接查询
笛卡尔乘积现象
beauty表有12条数据,boys表有4条数据,最终输出出来48行数据
select `name`,boyName from beauty,boys;
-- 解决
select `name`,boyName from boys,beauty
where beauty.boyfriend_id=boys.id;
子查询
出现在其他语句当中的select语句称为子查询,外部的查询语句称为主查询
子查询放在小括号内,一般子查询的条件语句放在右侧,标量子查询一般搭配单行操作符使用,列子查询一般搭配多行操作符使用
子查询出现的位置:select后(标量子查询),from后(表子查询),where或having后(都支持),exists后(表子查询)
子查询结果行列数不同:标量子查询(一行一列),列子查询(多行一列),行子查询(一行多列),表子查询(多行多列)
标量子查询
-- where后
select last_name,job_id,salary
from employees
where job_id = (
select job_id
from employees
where employee_id = 141
) and salary>(
select salary
from employees
where employee_id = 142
);
-- having后
select min(salary),department_id
from employees
group by department_id
having min(salary)>(
select min(salary)
from employees
where department_id = 50
);
列子查询
select last_name from employees
where department_id in(
select distinct department_id
from departments
where location_id in (1400,1700)
);
行子查询
-- where后
select *
from employees
where (employee_id,salary) = (
select min(employee_id),max(salary)
from employees
);
-- select
select d.*,(
select count(*)
from employees e
where e.`department_id` = d.`department_id`
) 个数 from departments d;
表子查询
select ag_dep *,g.`grade_level` from ( select avg(salary) ag,department_id from employees
group by department_id ) ag_dep
inner join job_grades g on ag_dep.ag between lowset _sal and highest_sal;
相关子查询
exists(完整的查询语句)结果为1或0,有值为1没值为0
select exists(select employee_id from employees);
select department_name from departments d
where exists( select * from employees e
where d.`department_id` = e.`department_id`);
分页查询
一页显示不全,需要分页进行sql请求
limit offset(起始索引,从0开始),size(显示条目数);
select * from employees
where commission_pct is not null order by salary desc
limit (page-1)*size,size;
联合查询
union 将多条查询语句的结果合并成一个结果,应用于查询的结果来源于多个表,且表之间没有关联
使用多个union可以连接多个句子
select * from employees
where email like '%a%' union all select * from employees
where department_id > 90;
DML学习
DML(Data Manipulation Language)即数据操纵语句,用来查询、添加、更新、删除等
插入语句
插入语句内容需要对应列,省略列名默认安表列进行对应
第一种方法可以一次插入多行,支持子查询
insert into beauty(id,name,sex,borndate,phone,photo,boyfriend_id)
value(13,'jojo1','男','1881-4-23','18988888',null,2),
(14,'jojo2','男','1881-4-23','18988888',null,2),
(15,'jojo3','男','1881-4-23','18988888',null,2);
-- 简写
insert into beauty
set id=19,name='乔纳森·乔斯达',phone='999';
-- 子查询插入
insert into beauty (id,name,phone)
select id,boyname,'123456789'
from boys where id<3;
修改语句
修改单表语句
-- 将name以唐开头的phone字段修改为18888888
update beauty set `phone`='18888888'
where name like '唐%';
修改多表语句
92语法
updata 表1 别名,表2 别名
set 列=值,...
where 连接条件
and 筛选条件;
99语法
updata 表1 别名
inner|left|right join 表2 别名
on 连接条件
set 列=值,...
where 筛选条件;
update boys bo
inner join beauty
on bo.`id`=b.`boyfriend_id`
set b.`phone`='114'
where bo.`boyname`=`张无忌`
删除语句
单表删除
-- 删除表内id为1的一行数据
-- 可以回滚
delete from stuinfo where id=1;
-- 清空表,不能筛选,效率高,自增长从新开始,不可以回滚
truncate table stuinfo;
多表删除
92语法
delete 表1的别名,表2的别名
from 表1 别名,表2 别名
where 连接条件
and 筛选条件;
99语法
delete 表1的别名,表2的别名
from 表1 别名
inner|left|right join 表2 别名
on 连接条件
where 筛选条件;
delete b,bo from beauty b
inner join boys bo on b.`boyfriend_id`=bo.`id`
where bo.`boyname`=`黄晓明`;



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号