[Machine Learning for Trading] {ud501} Lesson 11: 02-01 So you want to be a hedge fund manager? | Lesson 12: 02-02 Market Mechanics
Computational Investing
MC2: Computational Investing
Lessons: In this mini-course, we focus on modeling the behavior of stock markets.
- So you want to be a hedge fund manager?
- Market mechanics
- What is a company worth?
- The Capital Assets Pricing Model (CAPM)
- How hedge funds use the CAPM
- Technical Analysis
- Dealing with data
- Efficient Markets Hypothesis
- The Fundamental Law of active portfolio management
- Portfolio optimization and the efficient frontier
Projects:
- Build a market simulator
- Invent your own technical indicator
- Write a strategy that generates orders
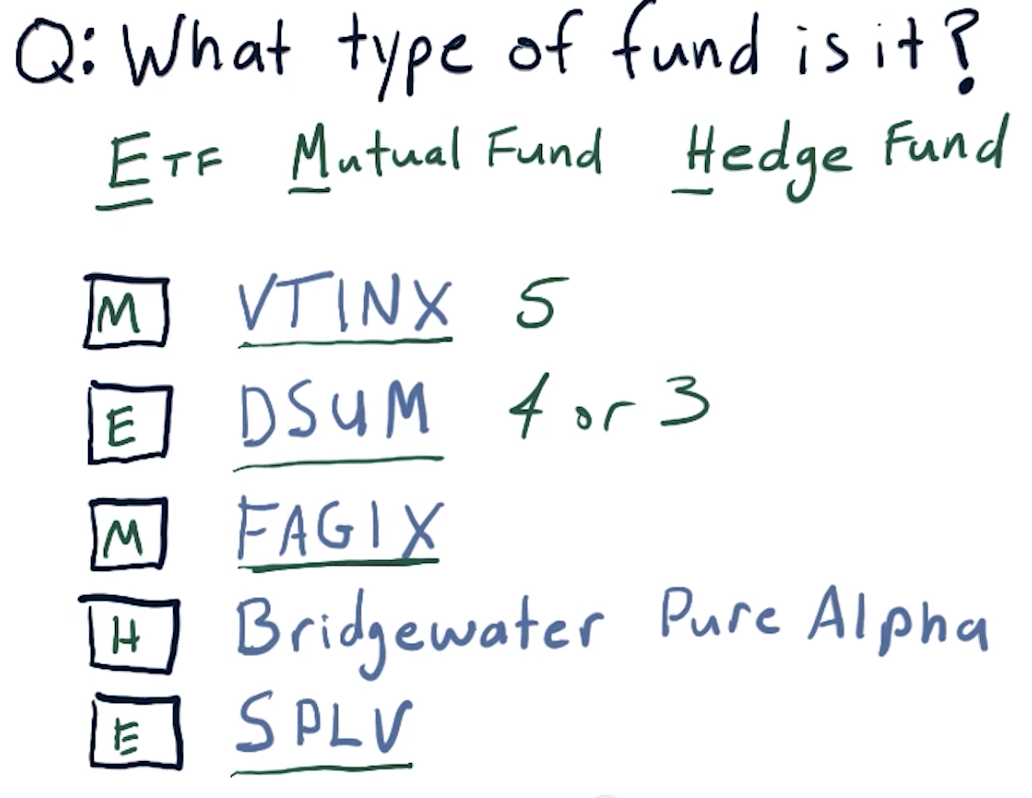
Types of funds

ETF = Exchange-Traded Fund
Liquidity and capitalization

liquidity => the ease with which one can buy or sell shares in a particular holding
large capitalization => how much is the company worth = shares that are outstanding × the price of the stock
Some popular sources for financial and investment data:
ETF => 4 or 3 letters
Mutual fund => 5 letters
Incentives for fund managers
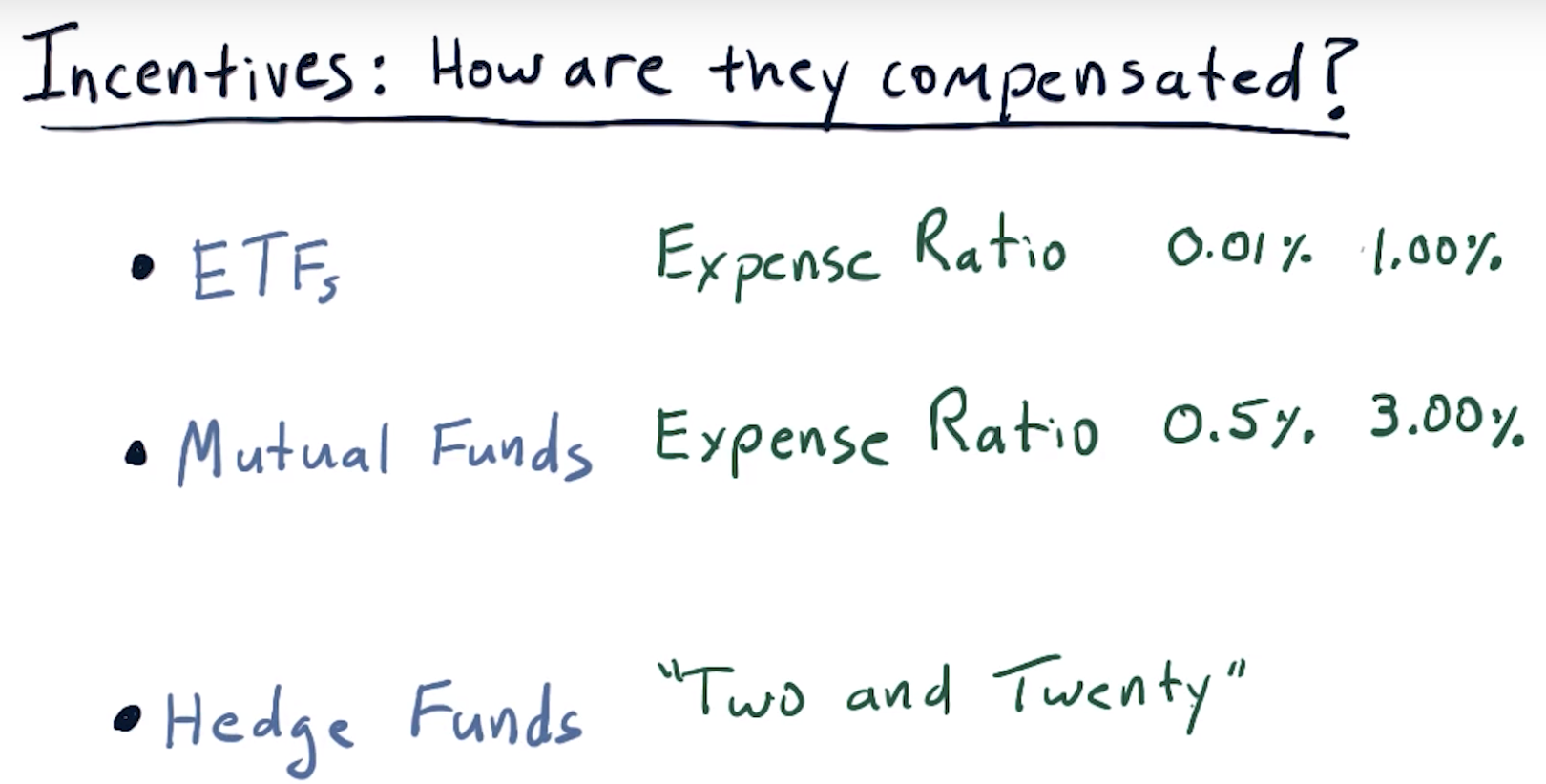
2 and 20 => 2% AUM and 20% profits
Assets Under Management (AUM) is the total amount of money being managed by the fund.
Two and twenty
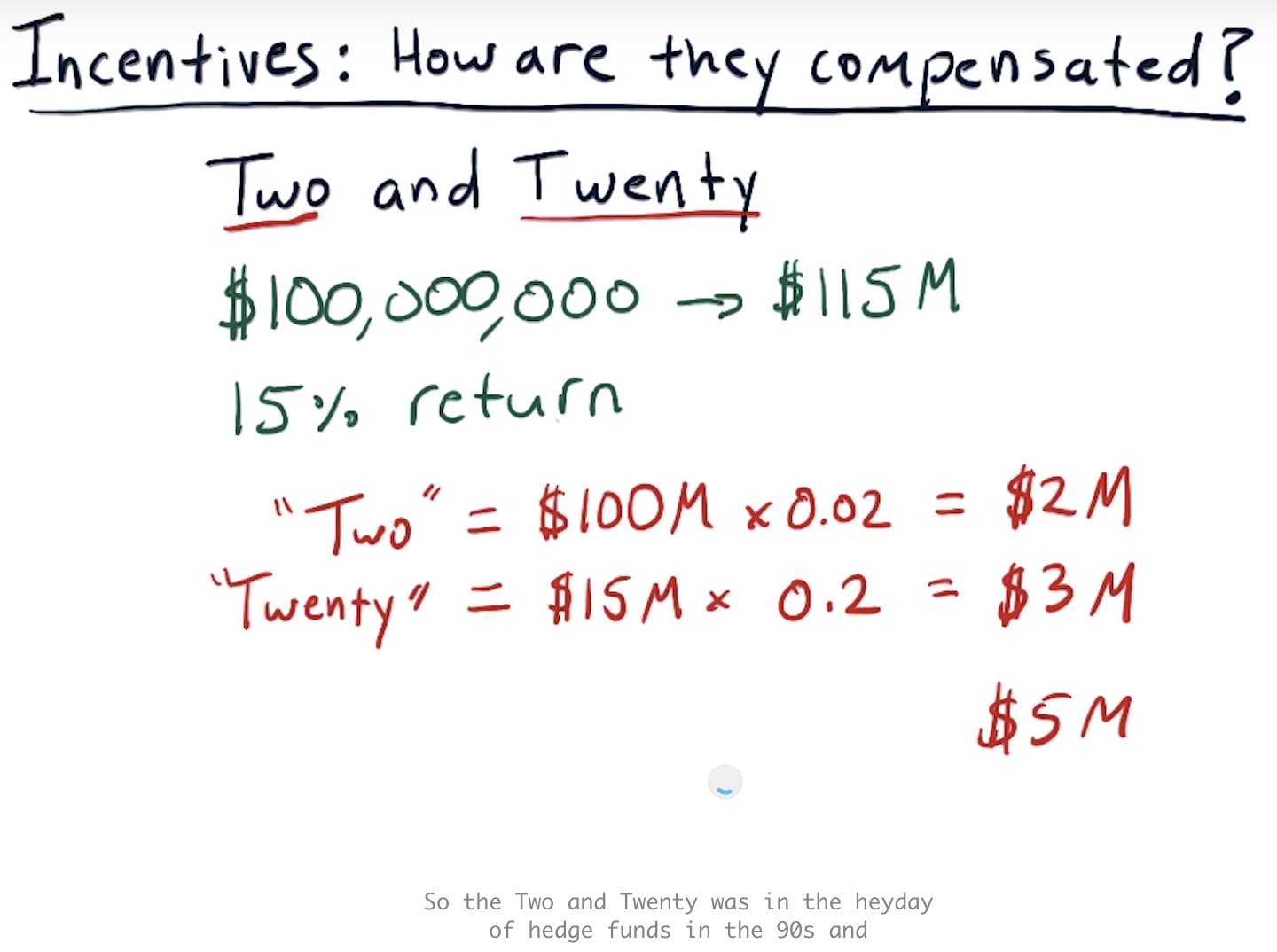
Incentives quiz

How funds attract investors

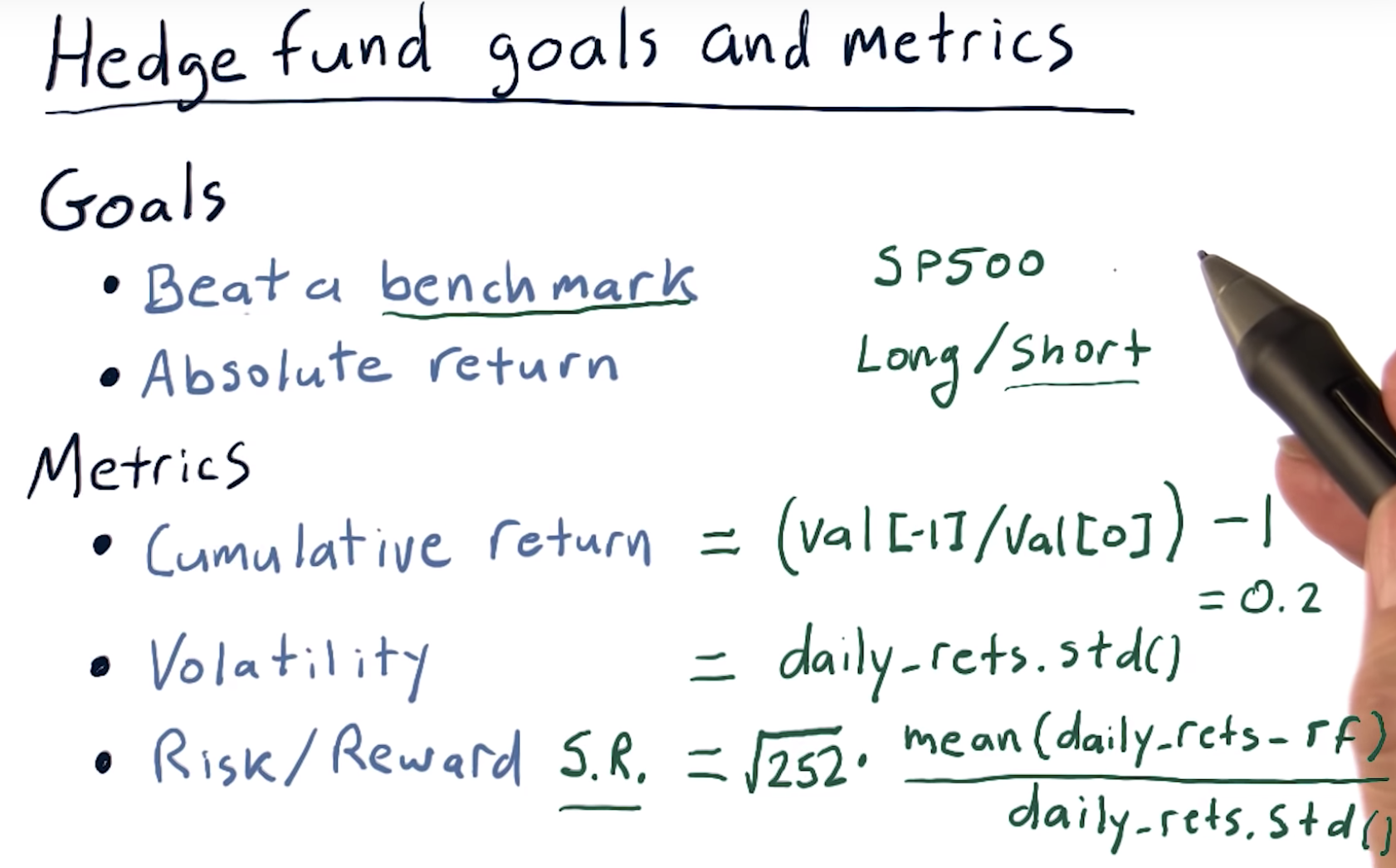
Hedge fund goals and metrics
The computing inside a hedge fund

live portfolio == order ==> target portfolio
dont want to do everything at once
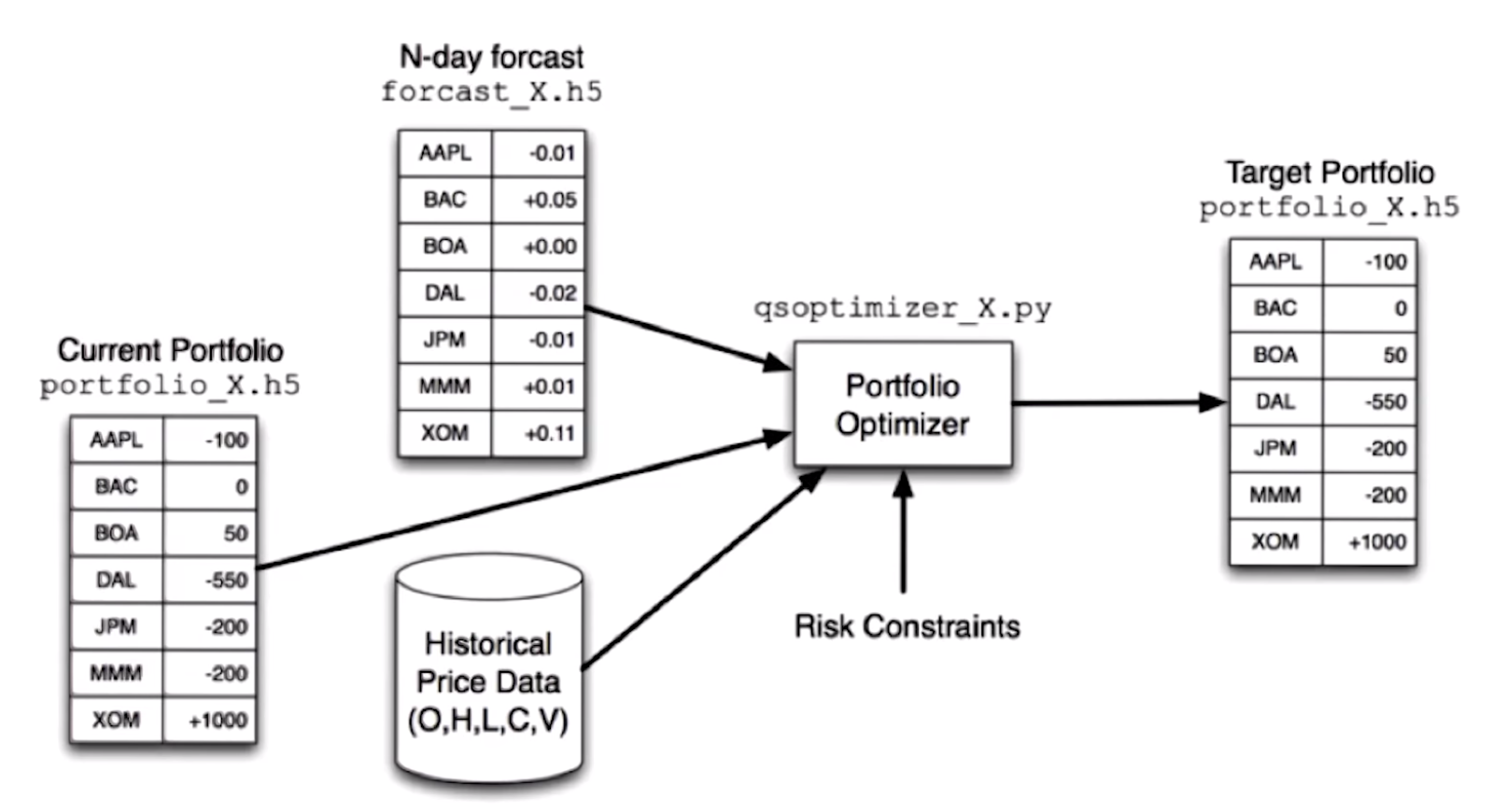
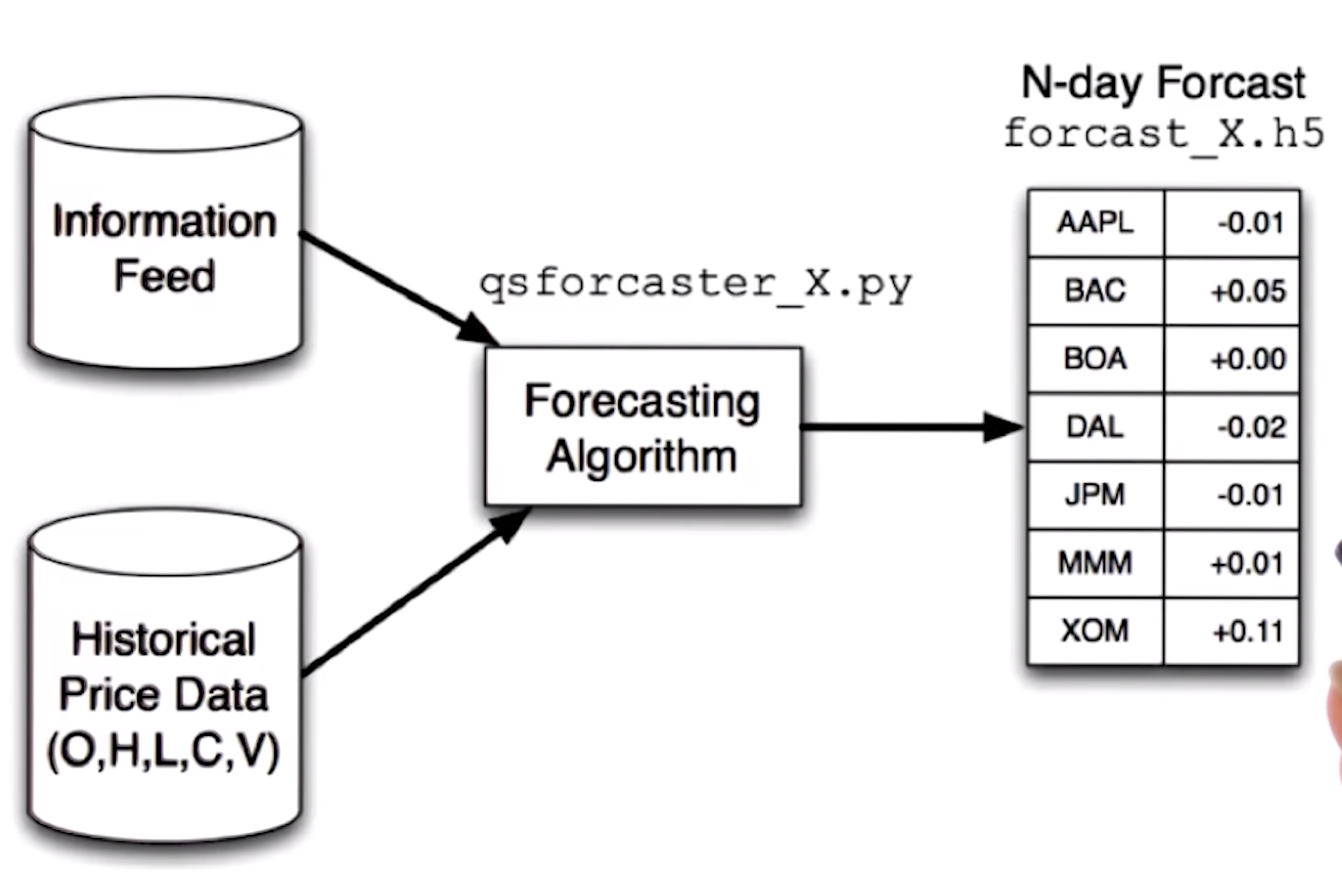
machine leanrnig => forcasting
What is in an order?

Market => not to specify the money
Limit => hand-craft some price limit for trading
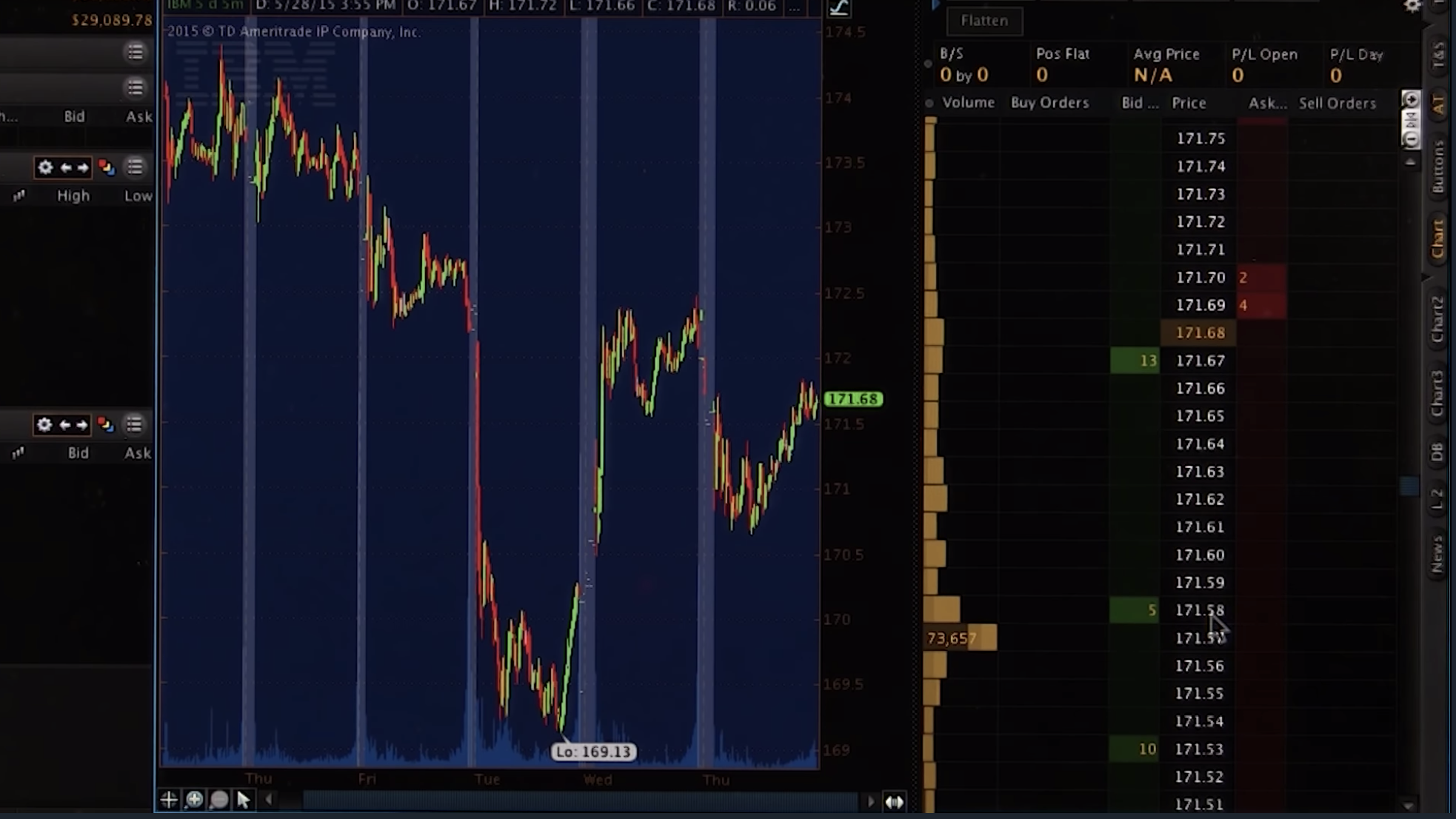
The order book

Up or down
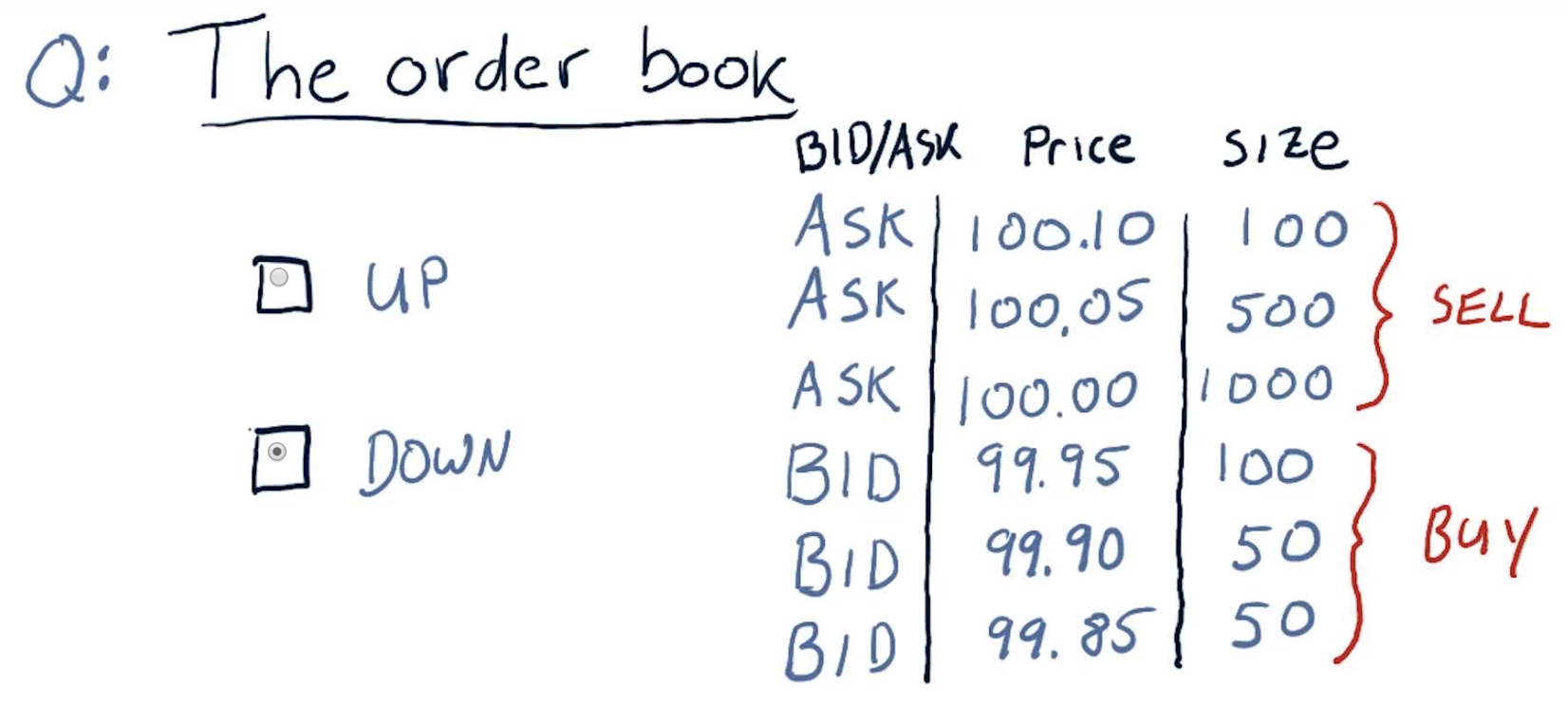
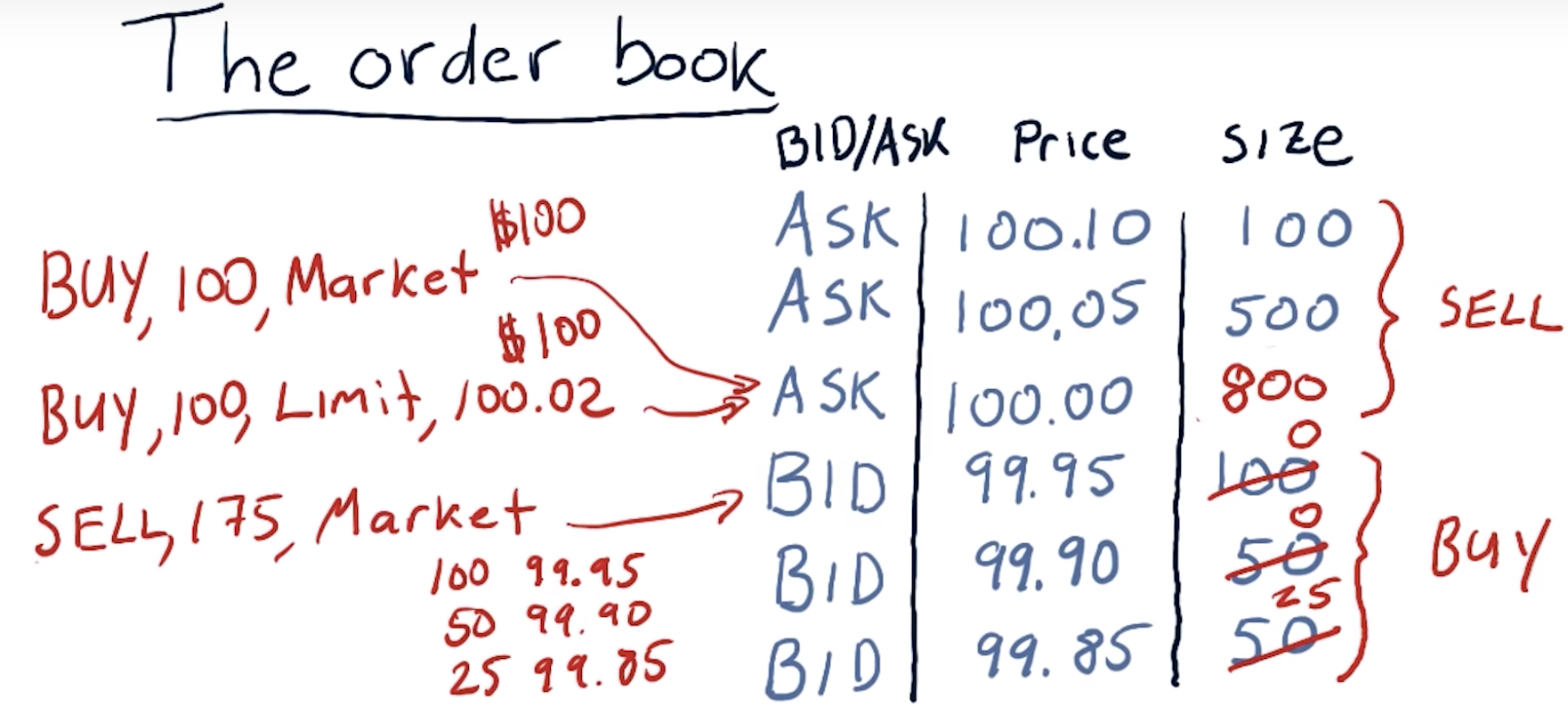
If you put in a SELL order (at market value), you will sell the first 100 shares at $99.95, the next 50 at $99.90, and so on.
In case of a BUY order, the market value won't change for the first 1000 shares.
So, depending on your volume of trade, the value of the stock will likely go down.
How orders affect the order book
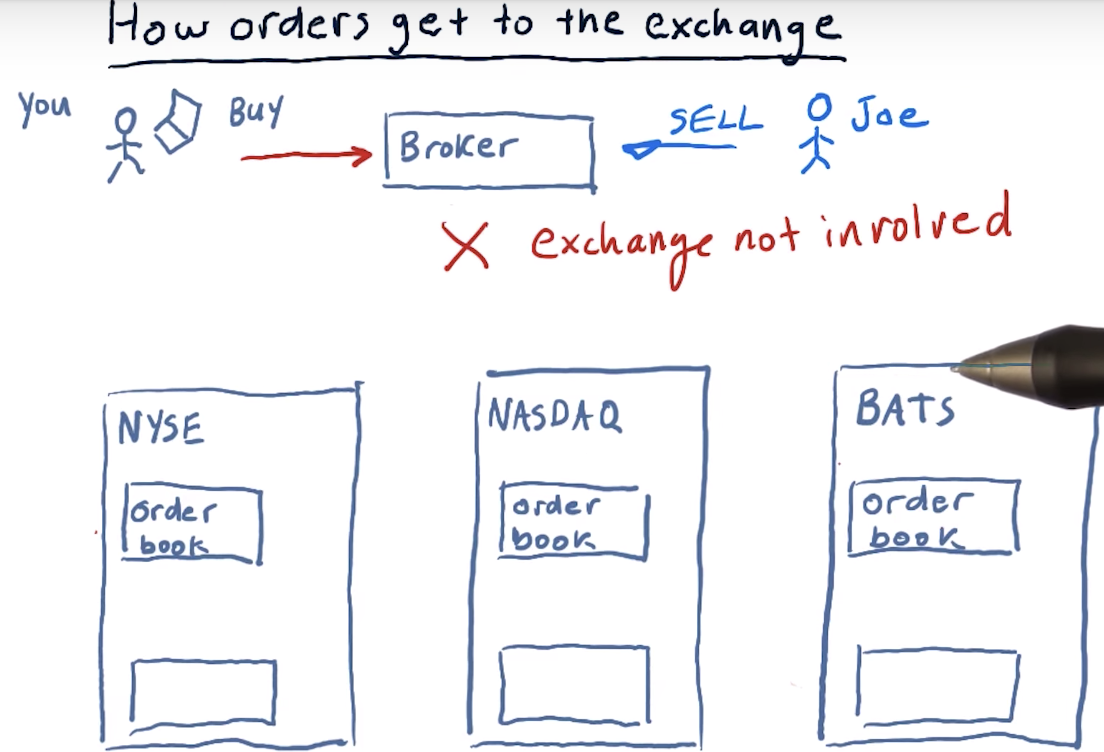
How orders get to the exchange
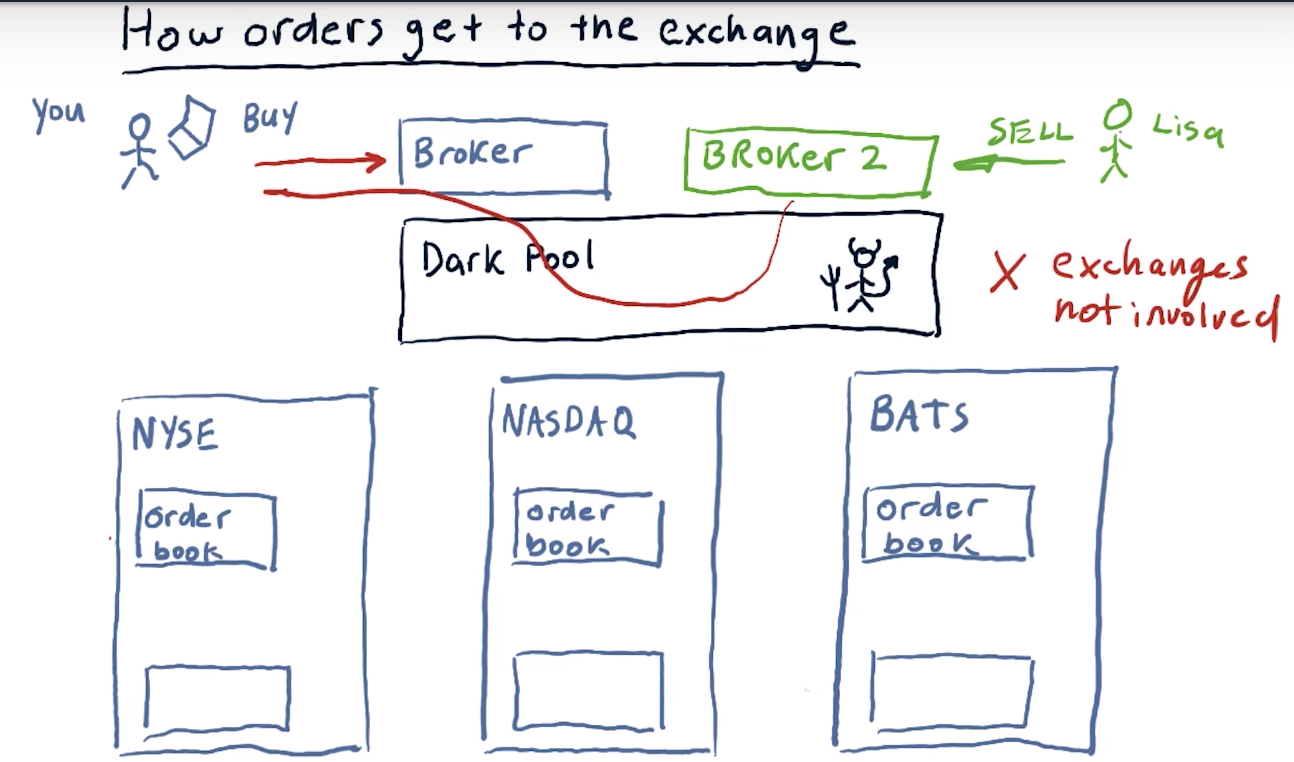
How hedge funds exploit market mechanics


Additional order types

Mechanics of short selling: Entry
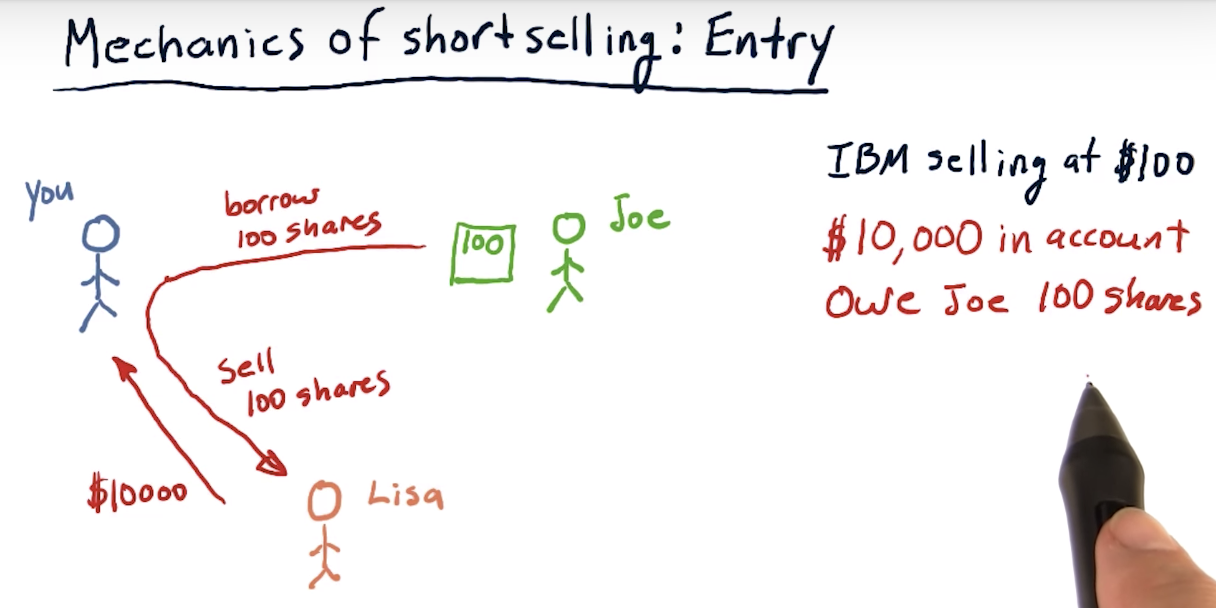
Short selling
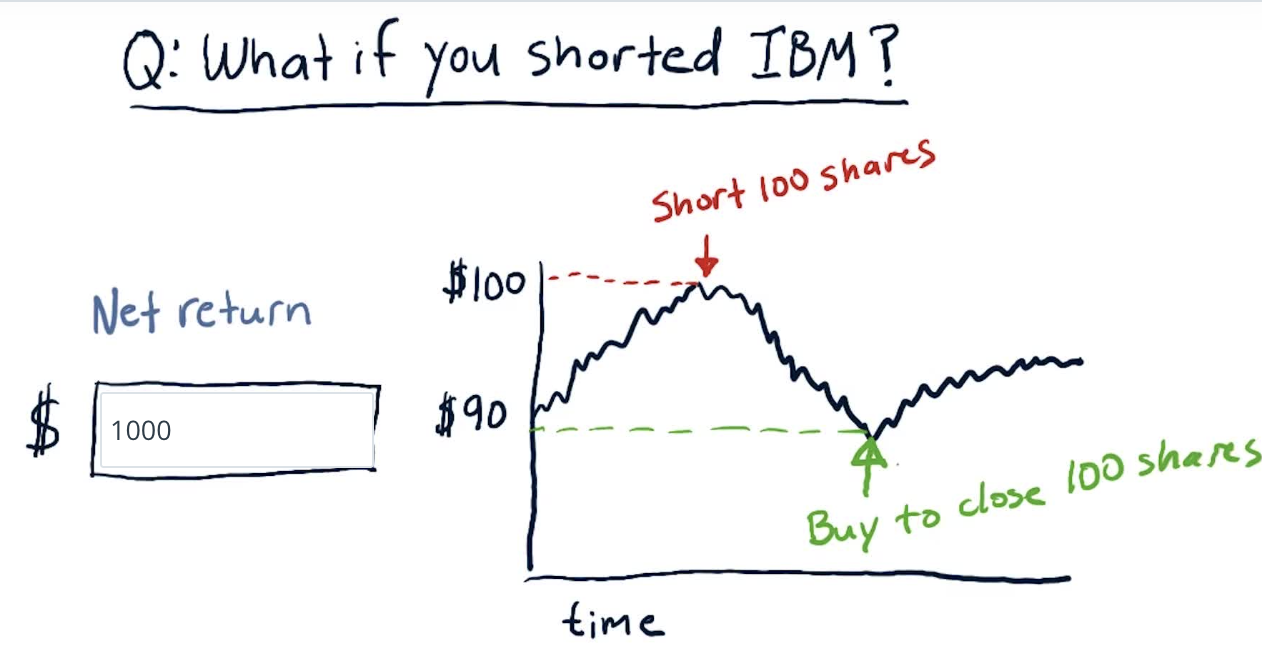
The buying occurred after selling, but nonetheless, you sold the stocks for more than you paid - so profit!
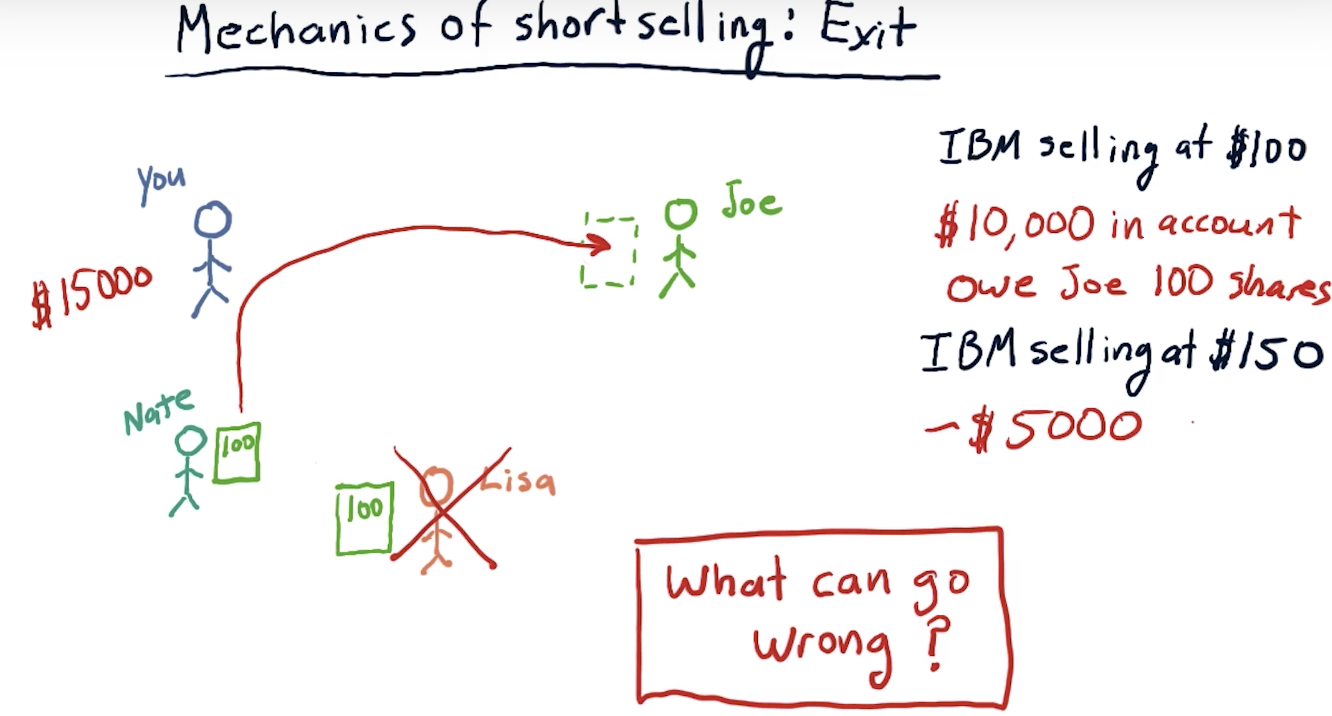
Mechanics of short selling: Exit
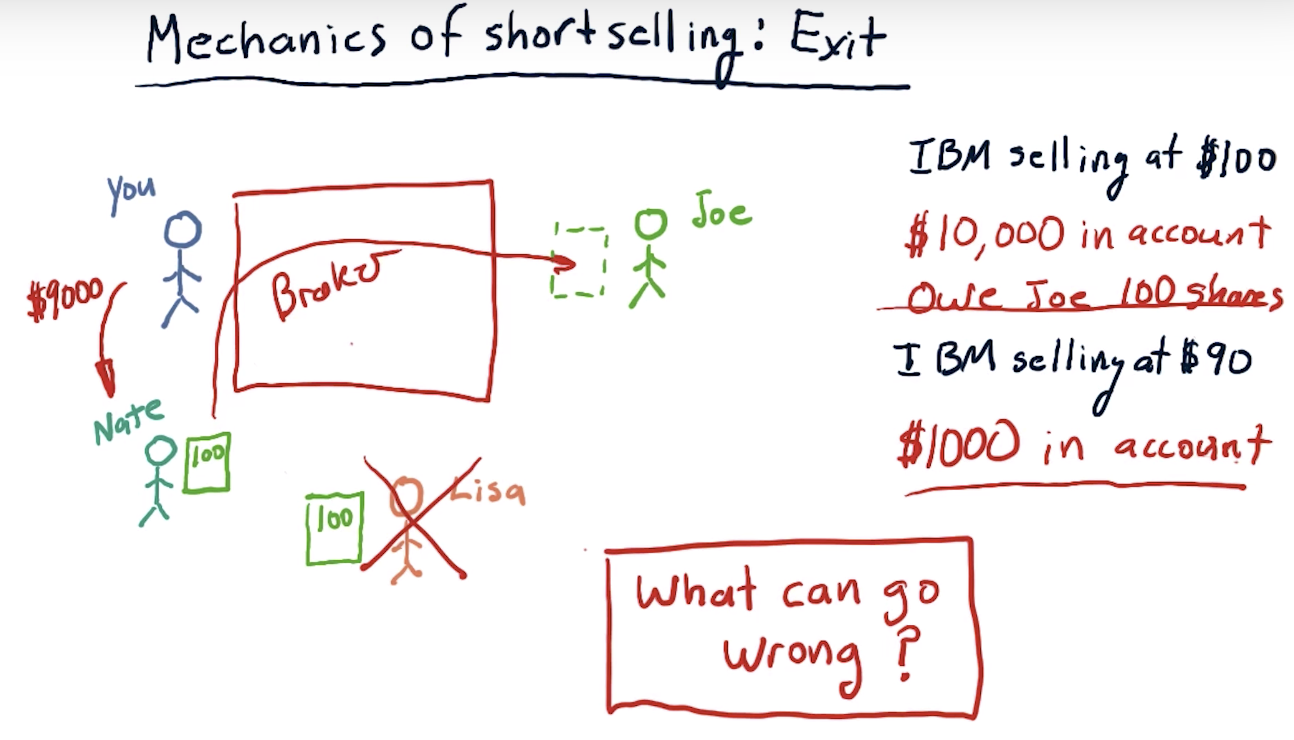
What can go wrong?



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号