Java Web系列:Spring依赖注入基础
一、Spring简介
1.Spring简化Java开发
Spring Framework是一个应用框架,框架一般是半成品,我们在框架的基础上可以不用每个项目自己实现架构、基础设施和常用功能性组件,而是可以专注业务逻辑。因此学习Spring Framework在架构和模式方面的结构和原理,对我们在架构和模块级别的理解帮助极大。Spring Framework(参考1)的宗旨是简化Java开发,主要的手段如下:
(1)在架构上解耦:通过DI(依赖注入)管理类型依赖,通过AOP分离关注点,减少重复代码。
(2)在设计上广泛采用DIP(依赖倒置)和ISP(接口隔离)等原则和Facade(外观)等模式:提供简化的调用接口并封装了众多出色的第三方组件。
(3)在语言层面上采用注解:通过配置文件和Annotation(参考.NET Attribute)简化应用配置。
2.Spring Framework的架构和模块:
Spring Framework本身的架构是典型的松散分层,外层可以按需引用全部内层,内层不能引用外层。Spring的基础组件如下图所示:
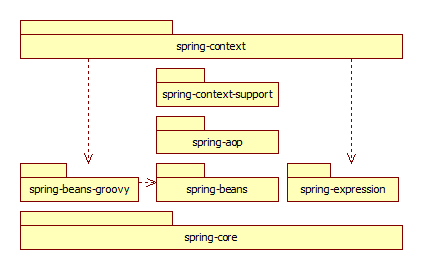
从图中可以看出,开始的模块只有从core\beans\aop\context四个组件,后来添加了context-support【1.2】扩展模块、expression【3.0】扩展模块和beans-groovy【4.0】扩展模块。
Spring上述模块的基础上,内建和封装了众多的实用的通用组件,主要的组件如图所示:
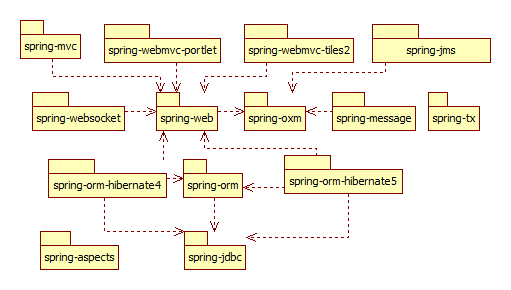
从图中可以看出,spring-oxm、spring-jdbc和spring-web是众多模块依赖的核心,spring-oxm提供了Object和XML的映射支持。
二、基础知识
1.DIP:DIP(依赖倒置原则)是DI(依赖注入)的核心(参考2)。
(1)高层模块不应该依赖于低层模块。两者都应该依赖于抽象。
(2)抽象不应该依赖于细节。细节应该依赖于抽象。
说人话就是:将对具体类的引用转换成对其接口的引用,具体类只引用接口(引用==依赖,接口==接口或抽象类)。事实上我们调用具体类的时候在头脑里也是只关心其提供的API而非实现,DIP则通过在设计和重构阶段在技术手段上保证了解耦。
2.DI:DI(依赖注入)让我们不必手写工厂代码来管理接口和实现类的映射、对象的创建和生命周期的管理。
(1)接口注入:必须实现特定的接口才可以,侵入性太强,现在已经无人关心和使用。
(2)构造函数注入:依赖体现在构造函数的参数上。
(3)属性注入:依赖体现在属性上。
由于在实现时,可以将类型注册为自己的兼容类型,这样依赖注入就可以直接替代new实例化对象,这样理解和使用依赖注入工具还不如不使用或手写工厂了。依赖注入工具在实现时肯定会实现成一个支持不同配置和不同生命周期的对象工厂,但即使没有提供一套添加依赖倒置原则限制的API,也不意味着我们把它当成new的替代品。如同映射工具虽然在实现时可以任意映射,但不是用来取代赋值的,而是用来处理领域实体和视图模型等有实际对应关系的对象之间的映射。
(1)依赖配置:依赖配置是依赖注入实现的基础。依赖注入工具都至少支持代码配置和文件配置。Java中可以通过Annotation(.NET中通过Attribute)简化配置。
(2)对象工厂:根据配置返回一个或多个对象。这是核心功能。
(3)生命周期管理:一般提供至少4种级别的支持:作用域、单例、线程、HTTP请求范围。
大多数依赖注入工具在支持依赖倒置原则的基础上,在技术手段上实现了更多的功能,如类型的兼容转换、对依赖命名、在配置时直接传入对象等。
三、Spring依赖注入的要点
Bean在Spring中就是POJO(.NET的POCO)。
Spring依赖注入需要掌握的核心是3个类型BeanDefinition、BeanFactory和ApplicationContext。
1.BeanFactory
BeanFactory是spring中依赖注入的核心接口,其设计主要采用了ISP(接口隔离原则),通过多层次的接口继承即保证了单个接口的内聚又保证了整个体系的简洁。这里我们要关注的核心是DefaultListableBeanFactory。
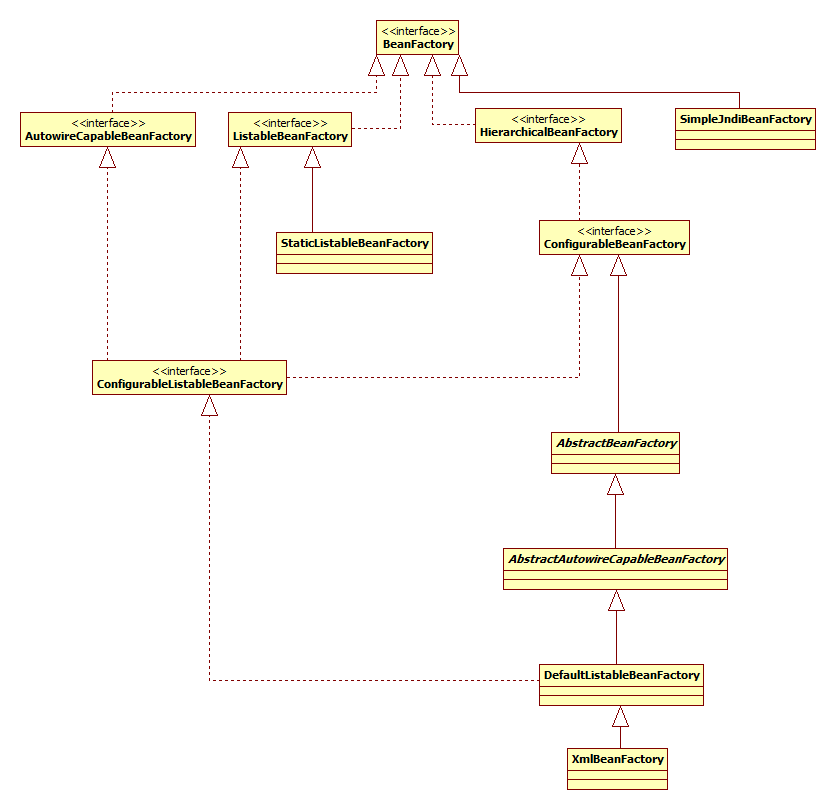
如图所示,查看XmlBeanFactory代码,可以看到XmlBeanFactory只是通过XmlBeanDefinitionReader载入了BeanDefinition配置,XmlBeanDefinitionReader负责将配置解析到BeanDefinition。DefaultListableBeanFactory是真正的实现类,其中定义了类型为Map<String, BeanDefinition>的beanDefinitionMap列表用于存储依赖配置。
2.BeanDefinition:
BeanDefinition定义了配置元数据,无论使用java code、xml、Annotation还是Groovy脚本方式,不同的配置方式通过不同的BeanDefinitionReader解析为BeanDefinition。
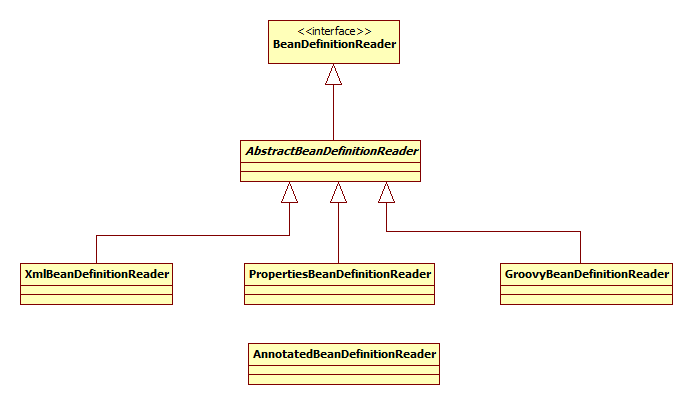
3.ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext的核心都是将对象工厂功能委托给BeanFactory的实现类DefaultListableBeanFactory。目前最常用的是基于注解的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext和AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext。

四、Spring依赖注入快速上手
1.使用Java配置代替xml配置
Java配置的核心是@Configuration和@Bean。定义生命周期使用@Scope,需要引入其他配置文件时使用@Import。
(1)@Configuration:应用了@Configuration注解的POCO成为了配置类。相当于xml配置文件。
(2)@Bean:配置类中应用了@Bean注解的方法成为了配置项。相当于xml中的Bean节点。
package me.test.spring_ioc; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext container = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); String message = container.getBean(IAppService.class).Test(); System.out.println(message); container.close(); } } @Configuration class AppConfig { @Bean public IAppService IAppService() { return new AppService(new Repository<SimpleEntity>()); } } class SimpleEntity { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } interface IAppService { String Test(); } interface IRepository<T> { String Test(); } class AppService implements IAppService { private IRepository<SimpleEntity> _repo; public AppService(IRepository<SimpleEntity> repo) { _repo = repo; } @Override public String Test() { return this._repo.Test(); } } class Repository<T> implements IRepository<T> { @Override public String Test() { return this.getClass().getName(); } }
如果是Web应用程序,应该使用AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext,在JSP中可通过WebApplicationContextUtils获取ApplicationContext对象。
<%@page import="swp.IAppService"%> <%@page import="org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext"%> <%@page import=" org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils"%> <html> <body> <% WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils .getRequiredWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext()); String message = context.getBean(IAppService.class).print(); out.print(message); %> </body> </html>
2.基于Annotation的自动装配
自动装配主要使用@ComponentScan、@Component和@Autowired。
(1)@ComponentScan:作用在配置类上,启用组件扫描。扫描并注册标注了@Component(@Controller\@Service\@Repository)的类型。@Configuration已经应用了@Component注解。
(2)@Autowired:按类型自动装配。@Autowired和使用@Inject(JSR-330)或@Resource(JSR-250)的效果是类似的。@Autowired和@Inject默认按类型注入,@Resource默认按名称注入。
package me.test.spring_ioc; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext container = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); String message = container.getBean(IAppService.class).Test(); System.out.println(message); container.close(); } } @Configuration @ComponentScan class AppConfig { /*@Bean public IAppService IAppService() { return new AppService(new Repository<SimpleEntity>()); }*/ } class SimpleEntity { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } interface IAppService { String Test(); } interface IRepository<T> { String Test(); } @Component class AppService implements IAppService { private IRepository<SimpleEntity> _repo; @Autowired public AppService(IRepository<SimpleEntity> repo) { _repo = repo; } @Override public String Test() { return this._repo.Test(); } } @Component class Repository<T> implements IRepository<T> { @Override public String Test() { return this.getClass().getName(); } }
小结:
你至少应该知道的:
(1)BeanFactory和BeanDefinition
(2)DefaultListableBeanFactory和ApplicationContext
(3)AnnotationConfigApplicationContext和AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
(4)@Configuraton和@Bean
Spring的依赖注入在配置上是基于对象而不是类型,最先支持的是xml而不是注解,到现在也没有比较方便的代码配置机制。虽然现在已经从xml过渡到了注解方式,但基于对象的基础仍然是影响很多方面的缺点。
参考
1.http://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/html/overview.html
2.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dependency_inversion_principle
3.http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-guice.html
4.https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/webservices/ws-springjava/
5.http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-spring-iocannt/
6.https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-spring25-ioc/
7.http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-beanannotation/
8.http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-guice.html
9.http://www.yiibai.com/spring/spring-dependency-checking-with-required-annotation.html


