Java中==比较运算符和equals详解
一、==比较运算符
==比较的是两个基本数据类型的值是否相等,或者两个对象的引用地址是否一样。
如下代码:
public static void main(String args[]) { int a = 1000, b = 1000; System.out.println(a == b); Integer c = 1000, d = 1000; System.out.println(c == d); Integer e = 100, f = 100; System.out.println(e == f); }
运行的结果为:true false true
原因:
(1)a和b都是基本数据类型,值也相等,所以 a==b 为true
(2)Integer c = 1000 是将一个基本数据类型的值赋给对象的引用。这里涉及到了装箱的概念,
就是把把基本类型用它们相应的引用类型包装起来,使其具有对象的性质。
编译器用的是public static Integer valueOf(int i)方法。
来看下它的源码:
public static Integer valueOf(int i) { final int offset = 128; if (i >= -128 && i <= 127) { // must cache return IntegerCache.cache[i + offset]; } return new Integer(i); }
当i的值在[-128,127]之间时,返回的是IntegerCache缓存的对象的已用,否则返回的是新的对象的引用。
因此,c 和 d 是两个不同的对象, e 和 f 是两个相同的对象。
通过调试也可以看到他们的id值也说明了这一点。
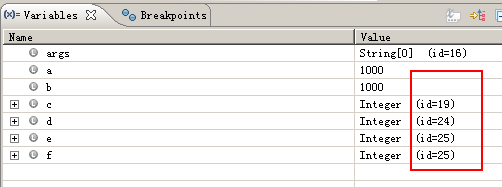
所以,c==d 为 false ,e==f 为 true。
二、equals
equals比较的是两个对象是否相等。由于每个类都是使用Object作为超类的,所以所有对象(包括数组)也实现这个类方法。
对于Object类的equals方法源代码如下:
public boolean equals(Object obj) { return (this == obj); }
可以看到它调用的就是 == 比较运算符。因此下面的代码结果就很容易看出为false了。
public static void main(String args[]) { Object obj1 = new Object(); Object obj2 = new Object(); System.out.println(obj1 == obj2); }
可是有时候会有特例出现,例如如下代码:
public static void main(String args[]) { String str1 = "abc"; String str2 = new String("abc"); String str3 = new String("abc"); System.out.println(str2.equals(str1)); System.out.println(str2.equals(str3)); }
运行的结构为: true true
原来String类重写了equals方法。我们来看一下源码:
public boolean equals(Object anObject) { if (this == anObject) { return true; } if (anObject instanceof String) { String anotherString = (String)anObject; int n = count; if (n == anotherString.count) { char v1[] = value; char v2[] = anotherString.value; int i = offset; int j = anotherString.offset; while (n-- != 0) { if (v1[i++] != v2[j++]) return false; } return true; } } return false; }
如果比较的是对象,就直接用==比较运算符。
如果比较的是String对象的实例,就比较这两个String的值是否相等。因此结果就都是true了。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号