单源最短路建图,分层图
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/905/
acwing 903.昂贵的聘礼

把每一个物品看作是一个点,此题是一定有解的,因为最坏的情况也是花费10000金币直接给酋长。所以这题将每个物品看作一个点,以替换的价值向替换的物品连边。就是一个最短路的问题。
不同的是,该题的物品是有等级划分的,也就是说要在一个等级区间内的物品才可以进行交易替换。所以我们要给最短路函数传入两个参数$up$和$down$,分别表示等级的上下界。然后以第一个物品的等级左右$m$为区间跑最短路算法取最小值。
还要注意的是,因为每个物品都可以直接购买,所以我们要建立一个虚拟源点0,指向每一个物品。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <queue> 4 #include <cstring> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 const int N = 110, M = N * N, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 9 int n, m; 10 int level[N];//存储等级的数组 11 int e[M], ne[M], w[M], h[N], idx; 12 int dis[N]; 13 bool st[N]; 14 15 void add(int a, int b, int c) 16 { 17 e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++; 18 } 19 20 int spfa(int down, int up) 21 { 22 memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis); 23 queue<int> q; 24 q.push(0); 25 st[0] = true; 26 dis[0] = 0; 27 28 while(q.size()) 29 { 30 int t = q.front(); 31 q.pop(); 32 33 st[t] = false; 34 35 for(int i = h[t] ; ~ i ; i = ne[i]) 36 { 37 int j = e[i]; 38 if(level[j] <= up && level[j] >= down) 39 { 40 if(dis[j] > dis[t] + w[i]) 41 { 42 dis[j] = dis[t] + w[i]; 43 if(!st[j]) 44 { 45 q.push(j); 46 st[j] = true; 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 return dis[1]; 53 } 54 55 56 57 int main(){ 58 cin >> m >> n; 59 60 memset(h, -1, sizeof h); 61 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) 62 { 63 int price, cnt; 64 cin >> price >> level[i] >> cnt; 65 add(0, i, price);//每个物品都要有一个虚拟源点指向 66 67 while(cnt --) 68 { 69 int id, cost; 70 cin >> id >> cost; 71 add(id, i, cost);//由该物品向可替换物品连边 72 } 73 } 74 75 int ans = INF; 76 for(int i = level[1] - m ; i <= level[1] ; i ++)ans = min(ans, spfa(i, i + m));//循环等级区间的左端点 77 78 cout << ans << endl; 79 return 0; 80 }
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1133/
acwing 1131.拯救大兵瑞恩

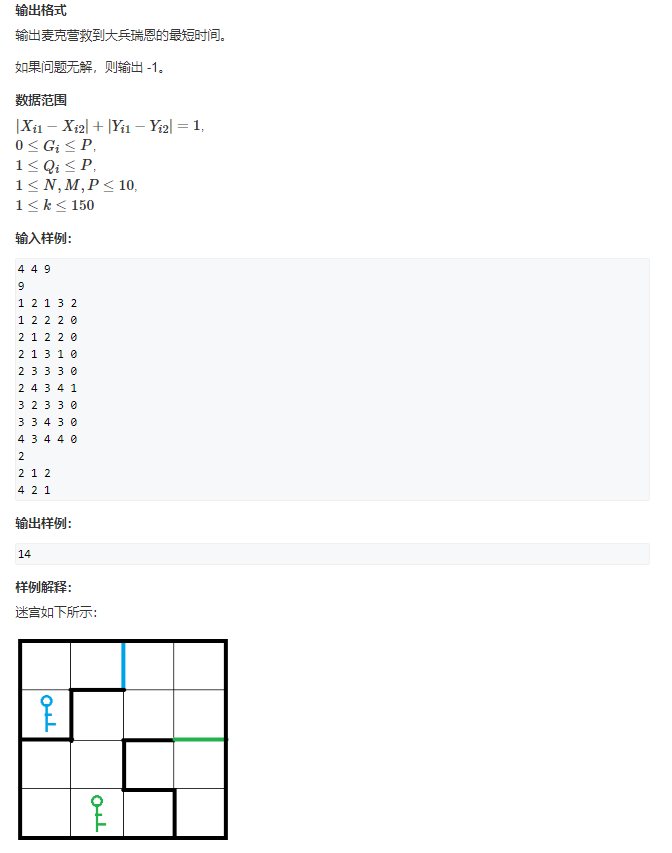
分层图。因为有门的存在需要有钥匙才可以过去,所以是需要有一维的参数是状态。考虑$dp$的思想,以$dis[x][y][state]$表示从起点走到$(x, y)$并且状态是state所花费的时间。由于本题捡起钥匙是不花费任何代价的,所以走到一个点有钥匙,就一定要将其拿起,,所以该点有钥匙的时候,很自然就能想到一个转移公式$dis[x][y][state | key] = dis[x][y][state]$。($ps:key$也是一个二进制数)。
而对于没有钥匙的情况,就是枚举上下左右四个方向,进行转移。
根据上面的分析,如果是有钥匙的转移,边权是0, 如果是四个方向的转移,边权为1,所以我们可以用双端队列,当边权为0加入队首,当边权为1,加入队尾。
另外,此为了方便起见,将图中的二维坐标映射为一维坐标,假设$n$为4, 即$(1, 1)$是1, $(1, 2)$是2,$(2, 1)$是5。这样就能将dis数组降为二维。
该题的图中有三种边,墙,无障碍,门。在读入时,将门建边,墙不建边(这样就等于无路可走),因为题目只读入墙和门,所以用一个$set$记录已经建过边的墙和门,剩下的都是属于无障碍,可以直接建边, 用一个$build$函数实现。
因为钥匙是从1开始,我们用二进制表示,就将钥匙的数映射少一位,从0开始。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <deque> 5 #include <set> 6 7 #define x first 8 #define y second 9 using namespace std; 10 11 typedef pair<int,int> PII; 12 13 14 //对于一个n的图,每行的竖边有n - 1条,n条边就有n(n -1)条竖边,横边一样,并且还有双向边,所以总共有2 * 2 * n(n - 1) 15 //n为10带入有360,开400。一共最多有十把钥匙,用二进制的十位数表示。 16 const int N = 11, M = 400, P = 1 << 10; 17 18 int e[M], ne[M], w[M], h[N * N], idx; 19 int dis[N * N][P], g[N][N]; 20 bool st[N * N][P]; 21 int key[N * N]; 22 set<PII> edges; 23 int n, m, k, p; 24 25 void add(int a, int b, int c) 26 { 27 e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++; 28 } 29 30 void build() 31 { 32 int dx[4] = {0, 1, -1, 0}, dy[4] = {1, 0, 0, -1}; 33 34 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) 35 for(int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++) 36 for(int k = 0 ; k < 4 ; k ++) 37 { 38 int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k]; 39 if(!x || !y || x > n || y > m)continue; 40 int a = g[i][j], b = g[x][y]; 41 if(edges.count({a, b}) == 0)add(a, b, 0);//如果墙和门没建过,就是无障碍 42 } 43 } 44 45 int bfs() 46 { 47 memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis); 48 dis[1][0] = 0; 49 50 deque<PII> q; 51 q.push_back({1, 0}); 52 53 while(q.size()) 54 { 55 PII t = q.front(); 56 q.pop_front(); 57 58 if(st[t.x][t.y])continue; 59 st[t.x][t.y] = true; 60 61 if(t.x == n * m)return dis[t.x][t.y]; 62 63 if(key[t.x])//该点有钥匙的时候 64 { 65 int state = t.y | key[t.x]; 66 if(dis[t.x][state] > dis[t.x][t.y]) 67 { 68 dis[t.x][state] = dis[t.x][t.y]; 69 q.push_front({t.x, state}); 70 } 71 } 72 73 for(int i = h[t.x] ; ~ i ; i = ne[i])//枚举四个方向 74 { 75 int j = e[i]; 76 if(w[i] && !(t.y >> w[i] - 1 & 1))continue;//如果这条路是门,但没有钥匙 77 if(dis[j][t.y] > dis[t.x][t.y] + 1) 78 { 79 dis[j][t.y] = dis[t.x][t.y] + 1; 80 q.push_back({j, t.y}); 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 return -1; 85 } 86 87 int main(){ 88 cin >> n >> m >> p >> k; 89 90 for(int i = 1, t = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++)//映射一维坐标 91 for(int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++) 92 g[i][j] = t ++; 93 94 memset(h, -1, sizeof h); 95 while(k --) 96 { 97 int x1, x2, y1, y2, c; 98 cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> c; 99 int a = g[x1][y1], b = g[x2][y2]; 100 edges.insert({a, b}), edges.insert({b, a});//记录墙和门 101 if(c)add(a, b, c), add(b, a, c);//如果不是墙是门就建边 102 } 103 104 build(); 105 106 int s; 107 cin >> s; 108 while(s --) 109 { 110 int a, b, c; 111 cin >> a >> b >> c; 112 key[g[a][b]] |= 1 << c - 1;//该点有一个钥匙,坐标映射从0开始 113 } 114 115 116 cout << bfs() << endl; 117 118 return 0; 119 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号