迭代加深,剪枝
五大剪枝:
①优化搜索顺序:先搜答案数较小的分支,这样有很大概率能将后续的分支剪去
②排除等效冗余:例如1 2 3 4 要枚举这四个数的和,那么1 + 4和 2 + 3就只需要枚举一次就够了。
③可行性剪枝:在搜索过程中对当前状态进行检查,如果发现分支已经无法达到递归边界,就执行回溯。
④最优性剪枝:在搜索过程中对当前状态进行检查,如果发现分支已经比目前得知的最佳状态差,就执行回溯。
⑤记忆化:可以记录每个状态的搜索结果,在重复遍历一个状态时直接检索并返回。
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1486/1/
acwing 166 数独

这题是81的数独且行,列,九宫格都有互斥关系,所以需要的状态很多,考虑使用二进制来表示数字的使用与否,用$row,col,cell$三个数组分别存储行,列,九宫格在这个点位所能使用的数字。
例如000000001就表示只有1可以使用。其次因为使用的是二进制来表示这个数,所以还要建立一个$map$来映射这个二进制数是十进制的什么数字。
这题的搜索空间很大,考虑优化搜索顺序,从分支较少的点开始进行填数,也就是可填的数字最少的点,所以我们还需要预处理一下所有二进制数中1的个数,用$ones$数组存储下来。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstring> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int N = 9, M = 1 << N; 8 9 int ones[M], map[M]; 10 int row[N], col[N], cell[3][3]; 11 char str[100]; 12 13 void init() 14 { 15 for(int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++)row[i] = col[i] = (1 << N) - 1; 16 for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++) 17 for(int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; j ++) 18 cell[i][j] = (1 << N) - 1; 19 } 20 21 void draw(int x, int y, int t, bool is_set) 22 { 23 if(is_set)str[x * N + y] = '1' + t; 24 else str[x * N + y] = '.'; 25 26 int v = 1 << t; 27 if(!is_set)v = -v; 28 row[x] -= v; 29 col[y] -= v; 30 cell[x / 3][y / 3] -= v; 31 } 32 33 int lowbit(int x) 34 { 35 return x & -x; 36 } 37 38 int get(int x, int y) 39 { 40 return row[x] & col[y] & cell[x / 3][y / 3]; 41 } 42 43 bool dfs(int cnt) 44 { 45 if(!cnt)return true; 46 47 int minv = 10; 48 int x, y; 49 for(int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++) 50 for(int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++) 51 if(str[i * N + j] == '.') 52 { 53 int state = get(i, j); 54 if(ones[state] < minv) 55 { 56 minv = ones[state]; 57 x = i; 58 y = j; 59 } 60 } 61 int state = get(x, y); 62 for(int i = state ; i ; i -= lowbit(i)) 63 { 64 int t = map[lowbit(i)]; 65 draw(x, y, t, true); 66 if(dfs(cnt - 1))return true; 67 draw(x, y, t, false); 68 } 69 70 return false; 71 72 } 73 74 int main(){ 75 for(int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++)map[1 << i] = i; 76 for(int i = 0 ; i < 1 << N ; i ++) 77 for(int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++) 78 ones[i] += i >> j & 1; 79 80 while(cin >> str, str[0] != 'e') 81 { 82 init(); 83 84 int cnt = 0; 85 for(int i = 0, k = 0 ; i < N ; i ++) 86 for(int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++, k ++) 87 if(str[k] != '.') 88 { 89 int t = str[k] - '1'; 90 draw(i, j, t, true); 91 } 92 else cnt ++; 93 94 dfs(cnt); 95 96 puts(str); 97 } 98 return 0; 99 }
迭代加深搜索:当搜索的答案树很深,但是答案在比较浅的位置时适合使用。
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/172/
acwing 170 加成序列

按题目要求,序列可以为$1 \;2\; 4\; 8\; 16\; \cdot \cdot \cdot$每次倍增,所以最短的结果必然在比较浅层内,而搜索树又很大,所以考虑使用迭代加深,一层一层往下搜索。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstring> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int N = 110; 8 int path[N]; 9 int n; 10 11 bool dfs(int u, int depth) 12 { 13 if(u > depth)return false; 14 if(path[u - 1] == n)return true; 15 16 bool st[N] = {0}; 17 for(int i = u - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i --) 18 for(int j = i ; j >= 0 ; j --) 19 { 20 int s = path[i] + path[j]; 21 if(st[s] || s <= path[u - 1] || s > n)continue; 22 st[s] = true; 23 path[u] = s; 24 if(dfs(u + 1, depth))return true;; 25 } 26 return false; 27 } 28 29 int main(){ 30 while(cin >> n, n) 31 { 32 int depth = 1; 33 path[0] = 1; 34 while(!dfs(1, depth))depth ++; 35 36 for(int i = 0 ; i < depth ; i ++) 37 cout << path[i] << " "; 38 cout << endl; 39 } 40 return 0; 41 }
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/173/
acwing 171 送礼物
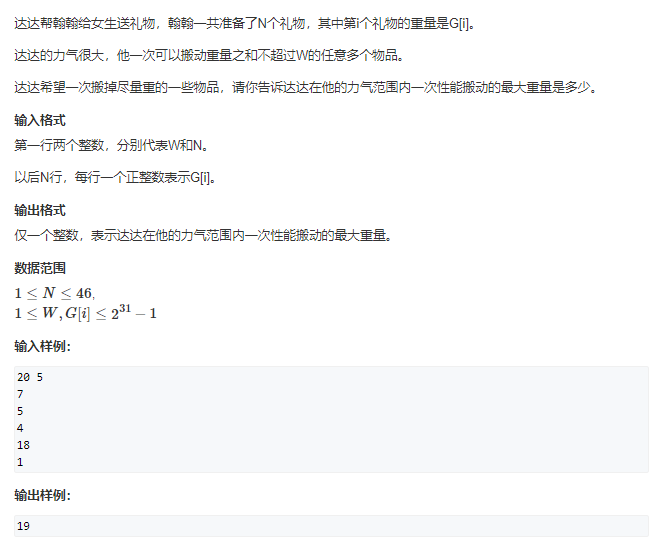
典型的双向深搜。对于这题来说,$M$的范围有$2^{31}$,$N$ 是 $46$,如果采用背包问题的求解,时间复杂度是$O(NM)$过大,考虑到$N$很小,所以可以用爆搜。
但是如果直接爆搜,复杂度有$2^{46}$。也是过大,所以考虑使用双向深搜,这样就可以吧复杂度降到$2^{\frac{N}{2}}+\frac{N}{2}2^{\frac{N}{2}}$。为了更均衡一下,可以使得$N = 25$,这样,复杂度就降的比较低。
所以最后先爆搜前$\frac{n}{2} + 2$个部分,预处理出结果,剩下的部分再进行爆搜。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstring> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 typedef long long LL; 8 9 const int N = 46; 10 11 int w[N], cnt = 1; 12 int weights[1 << 25]; 13 int n, m; 14 int ans, k; 15 16 void dfs1(int u, int s) 17 { 18 if(u == k) 19 { 20 weights[cnt ++] = s; 21 return; 22 } 23 dfs1(u + 1, s); 24 if((LL)s + w[u] <= m)dfs1(u + 1, s + w[u]); 25 } 26 27 void dfs2(int u, int s) 28 { 29 if(u == n) 30 { 31 int l = 0, r = cnt - 1; 32 while(l < r) 33 { 34 int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1; 35 if((LL)s + weights[mid] <= m)l = mid; 36 else r = mid - 1; 37 } 38 ans = max(ans, weights[l] + s); 39 return; 40 } 41 dfs2(u + 1, s); 42 if((LL)s + w[u] <= m)dfs2(u + 1, s + w[u]); 43 } 44 45 int main(){ 46 cin >> m >> n; 47 48 for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)cin >> w[i]; 49 50 sort(w, w + n); 51 reverse(w, w + n); 52 53 k = n / 2 + 2; 54 55 dfs1(0, 0); 56 57 sort(weights, weights + cnt); 58 cnt = unique(weights, weights + cnt) - weights; 59 60 dfs2(k, 0); 61 62 cout << ans << endl; 63 return 0; 64 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号