手写 Promise 源码之禁止循环调用
手写 Promise 源码之禁止循环调用
场景
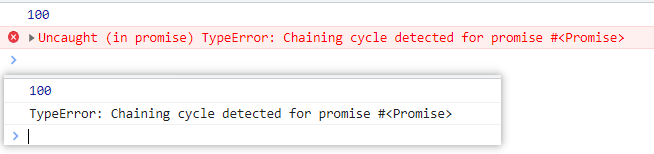
演示错误的 promise 循环调用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise 测试</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
resolve(100)
})
var p1 = promise.then(function(value) {
console.log(value)
return p1
})
p1.then(function() {}, function(reason) {
console.log(reason)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
代码实现
// resolvePromise()
// then 链式调用,promise 对象返回其自己(循环调用)
if (promise2 === x) {
return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>'))
}
const PENDING = 'pengding' // 等待
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled' // 成功
const REJECTED = 'rejected' /// 失败
class MyPromise {
constructor(exectuor) {
exectuor(this.resolve, this.reject)
}
// promise 状态
status = PENDING
// 成功之后的值
value = undefined
// 失败之后的原因
reason = undefined
// 成功回调
successCallback = []
// 失败回调
failCallback = []
// 此处的箭头函数是为了使 this 指向该函数的实例对象
resolve = value => {
// 如果状态不是等待,阻止程序向下执行
if (this.status !== PENDING) return
// 将状态更改为成功
this.status = FULFILLED
// 保存成功之后的值
this.value = value
// 判断成功回调是否存在,如果存在就调用
// this.successCallback && this.successCallback(this.value)
while (this.successCallback.length) {
this.successCallback.shift()(this.value)
}
}
reject = reason => {
// 如果状态不是等待,阻止程序向下执行
if (this.status !== PENDING) return
// 将状态更改为失败
this.status = REJECTED
// 保存失败后的原因
this.reason = reason
// 判断失败回调是否存在,如果存在就调用
// this.failCallback && this.failCallback(this.reason)
while (this.failCallback.length) {
this.failCallback.shift()(this.reason)
}
}
then(successCallback, failCallback) {
// 实现链式调用
let promise2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
// 判断状态
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
// 解决 resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) 获取不到 promise2 的问题
setTimeout(() => {
let x = successCallback(this.value)
// 判断 X 的值是普通值还是 promise 对象
// 如果是普通值,直接调用 resolve
// 如果是 promise 对象,查看 promise 对象返回的结果
// 再根据 promise 对象返回的结果,决定调用 resolve 还是调用 reject
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)
}, 0)
} else if (this.status === REJECTED) {
failCallback(this.reason)
} else {
// 等待
// 将成功回调和失败回调存储起来
this.successCallback.push(successCallback)
this.failCallback.push(failCallback)
}
})
return promise2
}
}
function resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) {
// then 链式调用,promise 对象返回其自己(循环调用)
if (promise2 === x) {
return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>'))
}
if (x instanceof MyPromise) {
// promise 对象
// x.then(value => resolve(value), reason => reject(reason))
// 简化成如下代码
x.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
// 普通值
resolve(x)
}
}
// node 环境下导出
module.exports = MyPromise
测试
const MyPromise = require('./myPromise')
let promise = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
// setTimeout(() => {
// resolve('成功 ......')
// }, 2000)
resolve('成功')
// reject('失败')
})
function other() {
return new MyPromise((resolve, rejct) => {
resolve('other')
})
}
let p1 = promise.then(value => {
console.log(value)
return p1
})
p1.then(value => {
console.log(value)
}, reason => {
console.log(reason.message)
})



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号