异步编程Future、CompletableFuture实战
1、简介
直接继承Thread或者实现Runnable接口都可以创建线程,但是这两种方法都有一个问题就是:没有返回值,也就是不能获取执行完的结果。因此java1.5就提供了Callable接口来实现这一场景,而 Future和FutureTask就可以和Callable接口配合起来使用。
@FunctionalInterface public interface Runnable { public abstract void run(); } @FunctionalInterface public interface Callable<V> { V call() throws Exception; }
Runnable没有返回值,不能抛异常。 Callable的call方法可以有返回值,可以声明抛出异常。
2、关于FutureTask
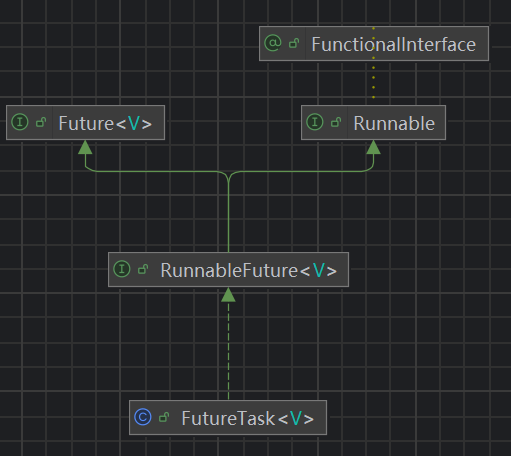
FutureTask对象可以看成异步执行后设置结果,当前线程通过get()方法阻塞获取结果的中间对象。把 Callable 实例当作 FutureTask 构造函数的参数,生成 FutureTask 的对象,然后把这个对象当 作一个 Runnable 对象,放到线程池中或另起线程去执行,最后还可以通过 FutureTask 获取任务执行 的结果。
public class FutureTaskDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { Task task = new Task(); //构建futureTask FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(task); //作为Runnable入参 new Thread(futureTask).start(); System.out.println("task运行结果:"+futureTask.get()); } static class Task implements Callable<Integer> { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { System.out.println("子线程正在计算"); int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { sum += i; } return sum; } } }
Future的局限性
- 无法对多个任务进行链式调用:如果你希望在计算任务完成后执行特定动作,比如发邮件,但Future却没有提供 这样的能力;
- 无法组合多个任务:如果你运行了10个任务,并期望在它们全部执行结束后执行特定动作,那么在Future中这是 无能为力的;
- 没有异常处理:Future接口中没有关于异常处理的方法;
3、CompletableFuture使用详解
CompletableFuture 是 Java 8 引入的强大异步编程工具,支持函数式编程风格,可以优雅地处理异步任务编排。CompletableFuture是Future接口的扩展和增强。
1、创建异步任务:
// 创建没有返回值的任务 public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) // 创建没有返回值的任务,并指定使用的线程池 public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor) // 创建有返回值的任务 public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
没有指定Executor的方法会使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。如果指定线程池, 则使用指定的线程池运行。
示例:
// 无返回值任务 CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { System.out.println("异步执行无返回值任务"); // 模拟耗时操作 sleep(1000); }); // 有返回值任务 CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println("异步执行有返回值任务"); sleep(1000); return "Result"; }); // 指定线程池 ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); CompletableFuture<String> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return "使用自定义线程池"; }, executor);
2、获取结果
- join(): 方法抛出的是uncheck异常 (即未经检查的异常), 不会强制开发者抛出。
- get(): 方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException 需要用户手动处理(抛出或者 try catch)。
3、结果处理
完成或者异常时回调,返回的结果是原始的值。
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action) public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action) public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor) public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn)
- Action的类型是BiConsumer,它可以处理正常的计算结果,或者异常情况。
- 方法不以Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同 的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。
- 这几个方法都会返回CompletableFuture,当Action执行完毕后它的结果返回原始的CompletableFuture的计算结果或者返回异常。
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println("异步执行有返回值任务"); try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } return "Result"; }).whenComplete(new BiConsumer<String, Throwable>() { @Override public void accept(String t, Throwable action) { System.out.println(t + " 执行完成!"); } }) .exceptionally(ex -> { System.err.println("发生异常: " + ex.getMessage()); return "Default Value"; // 提供默认值 });
4、结果转换
所谓结果转换,就是将上一段任务的执行结果作为下一阶段任务的入参参与重新计算,产生新的结 果。
1、thenApply
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)
示例:
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> { return 2; }).thenApply(a->a+1).get();
2、thenCompose - 链式依赖(串行)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn); public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) ; public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor) ;
示例:
// 一个任务的结果作为下一个任务的输入 CompletableFuture<User> future = getUserAsync(1) .thenCompose(user -> getOrdersAsync(user.getId())) .thenCompose(orders -> calculatePriceAsync(orders)); // 模拟实现 CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello") .thenCompose(s -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> s + " World"));
thenApply 和 thenCompose的区别
- thenApply 转换的是泛型中的类型,返回的是同一个CompletableFuture;
- thenCompose 将内部的 CompletableFuture 调用展开来并使用上一个CompletableFutre 调用的结果在下一步的 CompletableFuture 调用中进行运算,是生成一个新CompletableFuture。
5、结果消费
与结果处理和结果转换系列函数返回一个新的 CompletableFuture 不同,结果消费系列函数只对结果执行Action,而不返回新的计算值。
根据对结果的处理方式,结果消费函数又分为:
- thenAccept系列:对单个结果进行消费。
- thenAcceptBoth系列:对两个结果进行消费。
- thenRun系列:不关心结果,只对结果执行Action。
1、thenAccept:
通过观察该系列函数的参数类型可知,它们是函数式接口Consumer,这个接口只有输入,没有返回 值。
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action); public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action); public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
2、thenAcceptBoth
thenAcceptBoth 函数的作用是,当两个 CompletionStage 都正常完成计算的时候,就会执行提供的action消费两个异步的结果。
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action); public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action); public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor);
示例:
CompletableFuture<Integer> fu1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return 1; }); CompletableFuture<Integer> fu2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return 2; }); CompletableFuture<Void> fu3 = fu1.thenAcceptBoth(fu2, (a, b) -> { System.out.println(a + b); }); // 返回null System.out.println(fu3.join());
3、thenRun
thenRun 也是对线程任务结果的一种消费函数,与thenAccept不同的是,thenRun 会在上一阶段 CompletableFuture 计算完成的时候执行一个Runnable,Runnable并不使用该 CompletableFuture 计 算的结果。
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action); public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action); public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor);
6、结果组合
thenCombine 方法,合并两个线程任务的结果,并进一步处理。
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn); public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn); public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,Executor executor);
示例:
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { sleep(1000); return "Hello"; }); CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { sleep(800); return "World"; }); // 等两个都完成后合并结果 CompletableFuture<String> combined = future1.thenCombine(future2, (s1, s2) -> s1 + " " + s2); System.out.println(combined.get()); // "Hello World"
7、任务交互
看谁先完成、其中一个完成或者全部完成执行下一个动作。
1、applyToEither
两个线程任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的转化操作。
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn); public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn); public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn,Executor executor);
2、acceptEither
两个线程任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的消费操作。
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action); public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action); public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
3、runAfterEither
两个线程任务相比较,有任何一个执行完成,就进行下一步操作,不关心运行结果。
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor executor);
4、anyOf
anyOf 方法的参数是多个给定的 CompletableFuture,当其中的任何一个完成时,方法返回这个 CompletableFuture。
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
5、allOf
allOf方法用来实现多 CompletableFuture 的同时返回。
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
示例:
// 模拟三个异步任务 CompletableFuture<String> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { sleep(1000); return "Task 1 Result"; }); CompletableFuture<String> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { sleep(800); return "Task 2 Result"; }); CompletableFuture<String> task3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { sleep(1200); return "Task 3 Result"; }); // 等待所有任务完成 CompletableFuture<Void> allTasks = CompletableFuture.allOf(task1, task2, task3); // 阻塞等待所有任务完成 allTasks.join(); System.out.println("所有任务已完成"); // 获取各个任务的结果 System.out.println("Task1: " + task1.join()); System.out.println("Task2: " + task2.join()); System.out.println("Task3: " + task3.join());
业务示例:
public CompletableFuture<OrderDetailDTO> getOrderDetail(Long orderId) { // 并行查询订单的不同信息 CompletableFuture<OrderInfo> orderFuture = getOrderInfo(orderId); CompletableFuture<UserInfo> userFuture = getUserInfo(orderId); CompletableFuture<List<OrderItem>> itemsFuture = getOrderItems(orderId); CompletableFuture<PaymentInfo> paymentFuture = getPaymentInfo(orderId); CompletableFuture<DeliveryInfo> deliveryFuture = getDeliveryInfo(orderId); // 等待所有查询完成 return CompletableFuture.allOf(orderFuture, userFuture, itemsFuture, paymentFuture, deliveryFuture) .thenApply(v -> { try { // 组装完整订单信息 return OrderDetailDTO.builder() .order(orderFuture.get()) .user(userFuture.get()) .items(itemsFuture.get()) .payment(paymentFuture.get()) .delivery(deliveryFuture.get()) .build(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new CompletionException("组装订单详情失败", e); } }) .exceptionally(ex -> { log.error("获取订单详情失败: orderId={}", orderId, ex); return OrderDetailDTO.error(ex.getMessage()); }); }
8、常见问题与解决方案
1、任务间有依赖关系
// ❌ 错误的做法:使用 allOf 处理有依赖的任务 CompletableFuture<String> task1 = fetchUserData(); CompletableFuture<String> task2 = task1.thenCompose(userId -> fetchOrders(userId)); CompletableFuture<String> task3 = task2.thenCompose(orders -> calculateTotal(orders)); // allOf 在这里不合适,因为任务有串行依赖 CompletableFuture.allOf(task1, task2, task3); // 可能 task1 还没完成 task2 就开始了 // ✅ 正确的做法:使用 thenCompose 链式调用 CompletableFuture<String> result = fetchUserData() .thenCompose(userId -> fetchOrders(userId)) .thenCompose(orders -> calculateTotal(orders));
2、丢失异常
// ❌ 问题:异常堆栈被吞掉 CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { throw new RuntimeException("错误"); }); // ✅ 解决方案1:使用 exceptionally CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { throw new RuntimeException("错误"); }).exceptionally(ex -> { log.error("任务失败", ex); return null; }); // ✅ 解决方案2:使用 handle CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { throw new RuntimeException("错误"); }).handle((result, ex) -> { if (ex != null) { // 处理异常 } return null; });
总结:
-
链式调用:使用
thenApply、thenAccept、thenRun进行结果处理。 -
任务组合:使用
thenCompose(串行)、thenCombine(并行)、allOf/anyOf(多任务)。 -
异常处理:使用
exceptionally、handle、whenComplete -
超时控制:Java 9+ 用
orTimeout/completeOnTimeout -
线程池管理:根据任务类型选择合适的线程池。
-
避免阻塞:尽量使用回调而非阻塞获取结果。
-
资源清理:及时关闭自定义线程池。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号