SpringBoot集成Thymeleaf(六)
SpringBoot集成Thymeleaf从入门到精通(全)
本篇文章的学习
在这之前可以补充springboot的基础
详情可看我之前的文章
SpringBoot集成Thymeleaf
- Thymeleaf 是一个流行的模板引擎,该模板引擎采用 Java 语言开发
- Thymeleaf 是另外的一种模板技术,它本身并不属于 Spring Boot,Spring Boot只是很好地集成这种模板技术,作为前端页面的数据展示
在创建模板的时候还需要多选择一个这个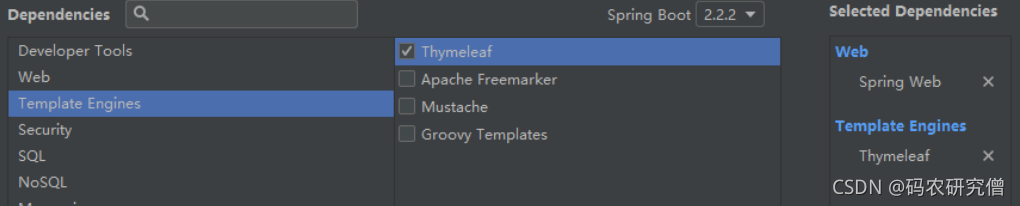
之后默认会自动添加这些依赖
Springboot 使 用 thymeleaf 作 为 视 图 展 示 , 约 定 将 模 板 文 件 放 置在src/main/resource/templates 目录下,静态资源放置在 src/main/resource/static 目录下
创建一个控制层面
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/message")
public String message(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("data","SpringBoot集成Thymeleaf模版引擎");
return "message";
}
}
页面这个要配置在特定的目录下
还要加上名称空间才能用她的函数xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
具体使用名称空间的text后的数据,如果有数据传入就会将其替代,如果没有数据才会显示后面的内容
具体底层是html,通过这个名称空间,以及他的函数才可以进行加载识别参数
xmlns:th=“http://www.thymeleaf.org”
xmlns -> 命名空间
命名空间后面的地址是一个约束文件,约束你使用thymeleaf表达式
的一个规则文件,就好比我们之前在xml文件中的一此dtd文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
thymeleaf模版引擎的页面必须得通过中央调度器
-->
<h2 th:text="${data}">展示要显示的内容0</h2>
</body>
</html>
配置后启动
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
也可以配置一个视图解析器
默认是有视图解析器的
所谓的视图解析器,下面才是真实跳转的路径
#设置thymeleaf模版引擎的前/后缀,(可选项)
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
为什么使用了th前缀就可以获取后台数据?
那是因为项目中添加了thymeleaf的核心依赖,它的核心依赖会去
解析thymeleaf自己定义的这些标签名称,通过thymeleaf自己的java核心代码来获取我们的后台数据
html 不会认识${}语法。
请求的流程是,发送请求给服务器,服务器接收请求后,处理请求,跳转到指定的静态 html 页面,在服务器端,Thymeleaf 模板引擎会按照它的语法,对动态数据进行处理,
所以如果要是 th 开头,模板引擎能够识别,会在服务器端进行处理,获取数据;如果没有以 th 开头,那么 Thymeleaf 模板引擎不会处理,直接返回给客户端了
1. 关闭缓存
不用再进行编译只有修改代码,刷新网页就会有显示
#设置thymeleaf模版引擎的缓存,设置为false关闭,默认为true开启
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
之所以thymeleaf可以代替jsp,是因为jsp要渲染,编译了才可执行
还需要额外配置启动的更新资源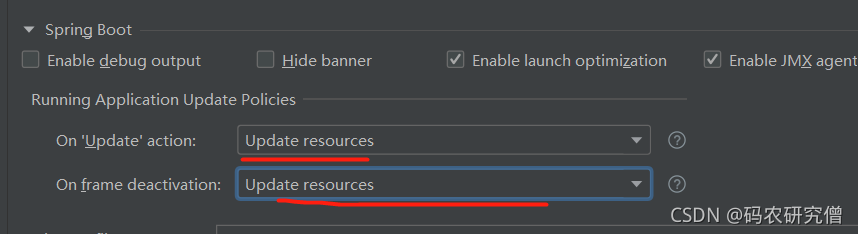
2. 表达式
要配置一个依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
Thymeleaf 中的变量表达式使用 ${变量名} 的方式获取 Controller 中 model 其中的数据
th:text="" 是 Thymeleaf 的一个属性,用于文本的显示
- 向 model 放入 User 对象
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private Integer age;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
- 创建 user.html 页面获取 User 对象数据
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/detail")
public ModelAndView userDetail() {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
User user = new User();
user.setId(1001);
user.setAge(23);
user.setUsername("lisi");
mv.setViewName("userDetail");
mv.addObject("user",user);
return mv;
}
标准变量表达式 ${} (推荐)
html页面的主要功能
<h1>标准变量表达式:${} -> (推荐)</h1>
用户编号:<span th:text="${user.id}"></span><br/>
用户姓名:<span th:text="${user.username}"></span><br/>
用户年龄:<span th:text="${user.age}"></span><br/>
选择变量表达式
{}必须使用th:object属性来绑定这个对象
在div子标签中使用来代替绑定的对象${user}
<h1>选择变量表达式(星号表达式):*{} -> (不推荐)</h1>
<!--
*{}必须使用th:object属性来绑定这个对象
在div子标签中使用*来代替绑定的对象${user}
-->
<div th:object="${user}">
用户编号:<span th:text="*{id}"></span><br/>
用户姓名:<span th:text="*{username}"></span><br/>
用户年龄:<span th:text="*{age}"></span><br/>
</div>
<h1>标准变量表达式与选择变量表达式的混合使用(不推荐)</h1>
用户编号<span th:text="{user.id}"></span><br/>
用户年龄<span th:text=""></span><br/>
用户姓名<span th:text="*{user.username}"></span><br/>
下面讲解的是路径表达式中常用的区别
路径表达式 @{...}
- 绝对路径跳转(不带参数)
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">传统写法:跳转至百度</a><br/>
<a th:href="@{http://www.baidu.com}">路径表达式:路径到百度</a><br/>
<a th:href="@{http://localhost:8080/user/detail1}">跳转至:/user/detail1</a><br/>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/user/detail1">传统写法跳转至:/user/detail1</a><br/>
- 相对路径跳转(不带参数)
<h2>URL路径表达式,相对路径[没有参数](实际开发中推荐使用的)</h2>
<a th:href="@{/user/detail1}">跳转至:/user/detail1</a><br/>
- 绝对路径跳转(带参数)
<h2>绝对路径(带参数)(不推荐使用)</h2>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/test?username='zhangsan'">绝对路径,带参数:/test,并带参数username</a><br/>
<a th:href="@{http://localhost:8080/test?username=zhangsan}">路径表达工写法,带参数:/test,并带参数username</a><br/>
- 相对路径跳转(带参数)
<h2>相对路径(带参数)</h2>
<a th:href="@{/test?username=lisi}">相对路径,带参数</a>
<h2>相对路径(带参数:后台获取的参数值)</h2>
<!--/test?username=1001-->
<a th:href="@{'/test?username='+${id}}">相对路径:获取后台参数值</a>
<h2>相对路径(带多个参数:后台获取的参数值)</h2>
<!--
/test1?id=1001&username=zhaoliu&age=28
-->
<a th:href="@{'/test1?id='+${id}+'&username='+${username}+'&age='+${age}}">相对路径(带多个参数:后台获取的参数值)</a>
<a th:href="@{/test1(id=${id},username=${username},age=${age})}">强烈推荐使用:@{}相对路径(带多个参数:后台获取的参数值)</a><br/>
<a th:href="@{'/test2/'+${id}}">请求路径为RESTful风格</a><br/>
<a th:href="@{'/test3/'+${id}+'/'+${username}}">请求路径为RESTful风格</a><br/>
在控制层面的代码为
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/detail1")
public String userDetail1(Model model) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1002);
user.setAge(24);
user.setUsername("wangwu");
model.addAttribute("user",user);
return "userDetail";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/url")
public String urlExpression(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("id",1001);
model.addAttribute("age",28);
model.addAttribute("username","zhaoliu");
return "url";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/test")
public @ResponseBody String test(String username) {
return "请求路径/test,参数是:" + username;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/test1")
public @ResponseBody String test1(Integer id,String username,Integer age) {
return "请求路径/test1,参数id=" + id+",username="+username+",age="+age;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/test2/{id}")
public @ResponseBody String test2(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return "ID="+id;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/test3/{id}/{username}")
public @ResponseBody String test3(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("username") String username) {
return "ID="+id+"----username="+username;
}
3. 常用属性
属性 描述 th:action th:action 定义后台控制器的路径,类似标签的 action 属性,主要结合 URL 表达式,获取动态变量 th:method 设置请求方法 th:href 定义超链接,主要结合 URL 表达式,获取动态变量 th:src 用于外部资源引入,比如<script>标签的 src 属性,<img>标签的 src 属性,常与@{}表达式结合使用,在 SpringBoot 项目的静态资源都放到 resources 的 static 目录下。放到 static 路径下的内容,写路径时不需要写上 static th:id 类似 html 标签中的 id 属性 th:name 设置名称 th:value 类似 html 标签中的 value 属性,能对某元素的 value 属性进行赋值 th:attr 给 HTML 中某元素的某属性赋值,好处是可以给 html 中没有定义的属性动态的赋值 th:text 用于文本的显示,该属性显示的文本在标签体中,如果是文本框,数据会在文本框外显示,要想显示在文本框内,使用 th:value th:object 用于数据对象绑定,通常用于选择变量表达式(星号表达式) th:onclick 点击按钮 th:style 设置样式 th:each 后台传来一个对象集合那么就可以使用此属性遍历输出,它与JSTL 中的<c: forEach>类似,此属性既可以循环遍历集合,也可以循环遍历数组及 Map th:inline 有三个取值类型 (text, javascript 和 none),值为 none 什么都不做,没有效果
比如
<form method="get" action="http://localhost:8080/test1">
用户编号:<input type="text" name="id" /><br/>
用户姓名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br/>
用户年龄<input type="text" name="age" /><br/>
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>
</form>
内敛文本(th:inline=”text”)
<div th:inline="text">
数据:[[${data}]]
</div>
//或者直接使用
数据outside:[[${data}]]
内敛脚本(th:inline=”javascript”)
<h1>内敛脚本 th:inline="javascript"</h1>
<script type="text/javascript" th:inline="javascript">
function showData() {
alert([[${data}]]);
alert("----");
}
</script>
<button th:onclick="showData()">展示数据</button>
4. 遍历元素
此处只po出关键代码
遍历List 集合
@RequestMapping("/each/list")
public String eachList(Model model) {
List userList = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(100 + i);
user.setNick("张" + i);
user.setPhone("1361234567" + i);
user.setAddress("北京市大兴区" + i);
userList.add(user);
}
model.addAttribute("userList", userList);
model.addAttribute("data", "SpringBoot");
return "eachList";
}
user 当前循环的对象变量名称(随意)
userStat 当前循环对象状态的变量(可选默认就是对象变量名称+Stat)
${userList} 当前循环的集合
count: 当前迭代对象的个数(从 1 开始计算)这两个用的较多
size: 被迭代对象的大小
current: 当前迭代变量
even/odd: 布尔值,当前循环是否是偶数/奇数(从 0 开始计算)
first: 布尔值,当前循环是否是第一个
last: 布尔值,当前循环是否是最后一个
注意:循环体信息 interStat 也可以不定义,则默认采用迭代变量加上 Stat 后缀,即 userStat
<div th:each="user,userStat:${userList}">
<span th:text="${userStat.index}"></span>
<span th:text="${userStat.count}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.id}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.nick}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.phone}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.address}"></span>
</div>
<div></div>
<div th:each="user:${userList}">
<span th:text="${userStat.index}"></span>
<span th:text="${userStat.count}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.id}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.nick}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.phone}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.address}"></span>
</div>
遍历Map 集合
@RequestMapping(value = "/each/map")
public String eachMap(Model model) {
Map userMaps = new HashMap();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(i);
user.setNick("李四" + i);
user.setPhone("1390000000" + i);
user.setAddress("天津市" + i);
userMaps.put(i, user);
}
model.addAttribute("userMaps", userMaps);
return "eachMap";
}
<div th:each="userMap,userMapStat:${userMaps}">
<span th:text="${userMapStat.count}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMapStat.index}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.key}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value.id}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value.nick}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value.phone}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value.address}"></span>
</div>
<div th:each="userMap:${userMaps}">
<span th:text="${userMapStat.count}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMapStat.index}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.key}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value.id}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value.nick}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value.phone}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value.address}"></span>
</div>
遍历数组
@RequestMapping(value = "/each/array")
public String eachArray(Model model) {
User[] userArray = new User[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(i);
user.setNick("赵六" + i);
user.setPhone("1380000000" + i);
user.setAddress("深圳市" + i);
userArray[i] = user;
}
model.addAttribute("userArray", userArray);
return "eachArray";
}
<h1>循环遍历Array数组(使用方法同list一样)</h1>
<div th:each="user,userStat:${userArray}">
<span th:text="${userStat.index}"></span>
<span th:text="${userStat.count}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.id}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.nick}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.phone}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.address}"></span>
</div>
遍历混合组合
List 里面放 Map,Map 里面又放的是 List
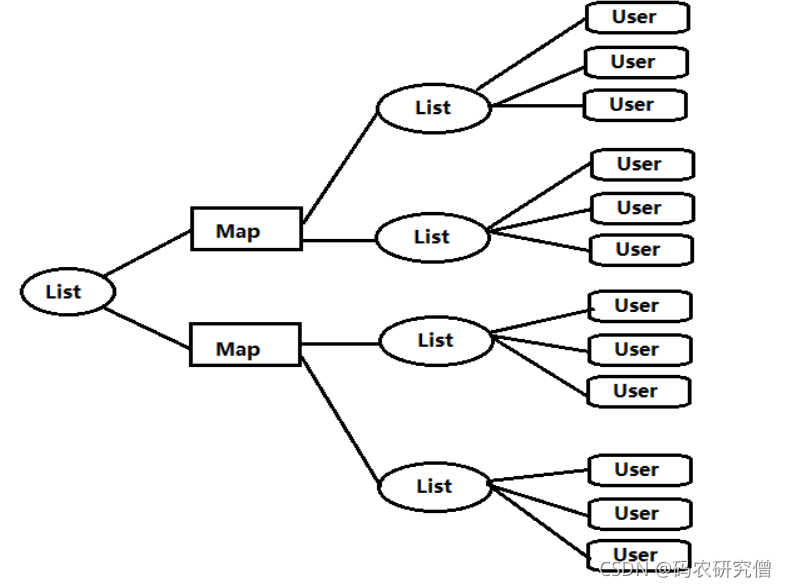
@RequestMapping(value = "/each/all")
public String eachAll(Model model) {
//list -> Map -> List -> User
List>> myList = new ArrayList>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
Map<Integer, List<User>> myMap = new HashMap<Integer, List<User>>();
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
List<User> myUserList = new ArrayList<User>();
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(k);
user.setNick("张三" + k);
user.setPhone("1350000000" + k);
user.setAddress("广州市" + i);
myUserList.add(user);
}
myMap.put(j, myUserList);
}
myList.add(myMap);
}
model.addAttribute("myList", myList);
return "eachAll";
}
<h2>循环遍历复杂集合:list -> Map -> list -> User</h2>
<div th:each="myListMap:${myList}">
<div th:each="myListMapObj:${myListMap}">
Map集合的key:<span th:text="${myListMapObj.key}"></span>
<div th:each="myListMapObjList:${myListMapObj.value}">
<span th:text="${myListMapObjList.id}"></span>
<span th:text="${myListMapObjList.nick}"></span>
<span th:text="${myListMapObjList.phone}"></span>
<span th:text="${myListMapObjList.address}"></span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
5. 条件判断
控制层类的代码没变
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/condition")
public String condition(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("sex",1);
model.addAttribute("flag",true);
model.addAttribute("productType",0);
return "condition";
}
}
主要的区别是在于
下面的判断语句
if判断
<h1>th:if 用法:如果满足条件显示(执行),否则相反</h1>
<div th:if="${sex eq 1}">
男
</div>
<div th:if="${sex eq 0}">
女
</div>
unless判断
<h1>th:unless 用法:与th:if用法相反,即条件判断取反</h1>
<div th:unless="${sex ne 1}">
女
</div>
switch判断
<h1>th:switch/th:case用法</h1>
<div th:switch="${productType}">
<span th:case="0">产品0</span>
<span th:case="1">产品1</span>
<span th:case="*">无此产品</span>
</div>
6. 字面量
字面量主要有
- 文本字面量,用单引号’…'的字符串就是字面量
- 数字字面量,用双引号数字就是字面量
- boolean字面量
- null字面量
主要的部分代码展示如下
<h1>文本字面量,用单引号'....'的字符串就是字面量</h1>
<a th:href="@{'/user/detail?sex=' + ${sex}}">查看性别</a>
<span th:text="Hello"></span>
<h1>数字字面量</h1>
今年是<span th:text="2020">1949</span>年<br/>
20年后是<span th:text="2020+20">1969</span>年<br/>
<h1>boolean字面量</h1>
<div th:if="${flag}">
执行成功
</div>
<div th:if="${!flag}">
不成功
</div>
<h1>null字面量</h1>
<span th:text="${user.id}"></span>
<div th:unless="${userDetail eq null}">
对象已创建,地址不为空
</div>
<div th:if="${userDetail.id eq null}">
空
</div>
7. 字符串拼接
这个拼接类似java代码
在html代码中的展示
<span th:text="'共'+${totalRows}+'条'+${totalPage}+'页,当前第'+${currentPage}+'页,首页 上一页 下一页 尾页'"></span>
8. 数学运算
三元运算 :表达式?” 正确结果”:” 错误结果”
算术运算:+ , - , * , / , %
关系比较:> , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
相等判断:== , != ( eq , ne )
表达式 描述 ne not equal eq equal ge great equal le little equal gt great lt little
部分代码展示
<h1>三元运算符 表达式?正确:错误</h1>
<div th:text="${sex eq 1 ? '男':'女'}"></div>
<div th:text="${sex == 1 ? '男':'女'}"></div>
<h1>算术运算</h1>
20+5=<span th:text="20+5"></span><br/>
20-5=<span th:text="20-5"></span><br/>
205=<span th:text="205"></span><br/>
20/5=<span th:text="20/5"></span><br/>
20%3=<span th:text="20%3"></span><br/>
<h1>关系比较</h1>
5>2为<span th:if="5 gt 2">真</span><br/>
5>2为<span th:if="5 > 2">真</span><br/>
5<2<span th:unless="5 lt 2">真</span><br/>
5<2<span th:unless="5 < 2">真</span><br/>
1>=1<span th:if="1 ge 1">真</span><br/>
1>=1<span th:if="1 >= 1">真</span><br/>
1<=1<span th:if="1 le 1">真</span><br/>
1<=1<span th:if="1 <= 1">真</span><br/>
<h1>相等判断</h1>
<span th:if="${sex == 1}">男</span>
<span th:if="${sex eq 1}">男</span>
<span th:unless="${sex ne 1}">女</span>
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47872288/article/details/121031656


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号