Traps and system calls
4 Traps and system calls
以系统调用write为例,深入trap的整体流程
Trap流程
ecall
执行ecall指令,它主要完成3件事:
- user mode -> supervisor mode
- pc -> sepc
- stvec -> pc
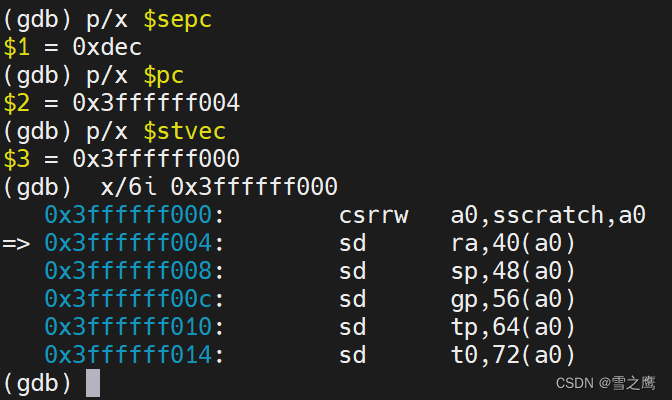
按Robert的说法,由于gdb的问题自己执行了csrrw指令,所以pc+4
跳转到的0x3ffffff000位于虚拟地址尾部,存放trampline的代码
uservec:
.globl uservec
uservec:
#
# trap.c sets stvec to point here, so
# traps from user space start here,
# in supervisor mode, but with a
# user page table.
#
# sscratch points to where the process's p->tf is
# mapped into user space, at TRAPFRAME.
#
// 用户态寄存器保存
# swap a0 and sscratch
# so that a0 is TRAPFRAME
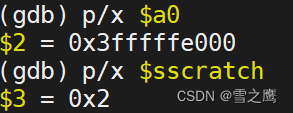
csrrw a0, sscratch, a0 // 交换sscratch和a0的内容 sscratch=2(write系统调用号),a0=0x3fffffe000
# save the user registers in TRAPFRAME
sd ra, 40(a0)
sd sp, 48(a0)
sd gp, 56(a0)
sd tp, 64(a0)
sd t0, 72(a0)
sd t1, 80(a0)
sd t2, 88(a0)
sd s0, 96(a0)
sd s1, 104(a0)
sd a1, 120(a0)
sd a2, 128(a0)
sd a3, 136(a0)
sd a4, 144(a0)
sd a5, 152(a0)
sd a6, 160(a0)
sd a7, 168(a0)
sd s2, 176(a0)
sd s3, 184(a0)
sd s4, 192(a0)
sd s5, 200(a0)
sd s6, 208(a0)
sd s7, 216(a0)
sd s8, 224(a0)
sd s9, 232(a0)
sd s10, 240(a0)
sd s11, 248(a0)
sd t3, 256(a0)
sd t4, 264(a0)
sd t5, 272(a0)
sd t6, 280(a0)
# save the user a0 in p->tf->a0
csrr t0, sscratch
sd t0, 112(a0) //sscratch存的是之前a0的数据,相当于a0入栈。至此寄存器的保存工作完毕。
// 内核态寄存器恢复
# restore kernel stack pointer from p->tf->kernel_sp
ld sp, 8(a0)
# make tp hold the current hartid, from p->tf->kernel_hartid 当前运行在哪个核上
ld tp, 32(a0)
# load the address of usertrap(), p->tf->kernel_trap
ld t0, 16(a0)
# restore kernel page table from p->tf->kernel_satp
ld t1, 0(a0)
csrw satp, t1
sfence.vma zero, zero // 页表在此转换成内核页表
# a0 is no longer valid, since the kernel page
# table does not specially map p->tf.
# jump to usertrap(), which does not return
jr t0 //跳转到usertrap()
csrrw a0, sscratch, a0
sscratch寄存器主要就是起一个暂存的作用,在这里存放0x3fffffe000(trapframe的地址)。因为我们即将保存31个寄存器,以其中任何一个寄存器作传递都将破坏里面的数据,所以我们将sscratch和a0做交换,a0的数据保存在sscratch中,sscratch中保存的0x3fffffe000传递给a0,a0指向trapframe,用于保存31个寄存器
usertrap():
//
// handle an interrupt, exception, or system call from user space.
// called from trampoline.S
//
void
usertrap(void)
{
int which_dev = 0;
if((r_sstatus() & SSTATUS_SPP) != 0)
panic("usertrap: not from user mode");
// send interrupts and exceptions to kerneltrap(),
// since we're now in the kernel.
w_stvec((uint64)kernelvec); // 现在处于内核态,再发生trap就是由内核发起的,所以设置stvec为kernelvec,kernelvec是另一套处理流程
struct proc *p = myproc();
// save user program counter.
p->tf->epc = r_sepc(); // 同时可能会有另一个进程执行系统调用,sepc的值会被覆盖,所以保存。至此trapframe全部保存
// 判断trap来源
if(r_scause() == 8){
// system call
if(p->killed)
exit(-1);
// sepc points to the ecall instruction,
// but we want to return to the next instruction.
p->tf->epc += 4;
// an interrupt will change sstatus &c registers,
// so don't enable until done with those registers.
intr_on(); // trap硬件会关闭中断,在保存完必要的寄存器后,要快速打开中断
syscall(); // 系统调用执行
} else if((which_dev = devintr()) != 0){
// ok
} else {
printf("usertrap(): unexpected scause %p (%s) pid=%d\n", r_scause(), scause_desc(r_scause()), p->pid);
printf(" sepc=%p stval=%p\n", r_sepc(), r_stval());
p->killed = 1;
}
if(p->killed)
exit(-1);
// give up the CPU if this is a timer interrupt.
if(which_dev == 2)
yield();
usertrapret();
}
从头部注释可以看到,无论是中断、异常还是系统调用,只要是来自用户空间,都会进入usertrap()。但进入之后不会根据这三种情况进行处理,而是分为:
- user trap
- kernel trap
- system call
总结
trap类型分为三类:interrupts、exception、system call
trap处理方式分为三类:user trap、kernel trap、system call
systemcall():
void syscall(void)
{
int num;
struct proc *p = myproc();
num = p->tf->a7;
if (num > 0 && num < NELEM(syscalls) && syscalls[num])
{
p->tf->a0 = syscalls[num](); // 系统调用执行(涉及函数指针数组的知识)
if (p->trace_mask > 0 && (p->trace_mask & (1 << num)))
{
printf("%d : syscall %s -> %d\n", p->pid, syscall_names[num], p->tf->a0);
}
}
else
{
printf("%d %s: unknown sys call %d\n",
p->pid, p->name, num);
p->tf->a0 = -1;
}
}
此时的寄存器组已经由内核使用,用户态的各种信息(参数,系统调用号…)保存在它的trapframe里,所以要从p->trapframe获取
usertrapret():
//
// return to user space
//
void usertrapret(void)
{
struct proc *p = myproc();
// turn off interrupts, since we're switching
// now from kerneltrap() to usertrap().
intr_off(); // 因为马上要设置stvec为用户态trap地址,此时处于内核态,发生中断会导致异常(页表不对应)
// send syscalls, interrupts, and exceptions to trampoline.S
w_stvec(TRAMPOLINE + (uservec - trampoline));
// set up trapframe values that uservec will need when
// the process next re-enters the kernel.
p->tf->kernel_satp = r_satp(); // kernel page table
p->tf->kernel_sp = p->kstack + PGSIZE; // process's kernel stack
p->tf->kernel_trap = (uint64)usertrap;
p->tf->kernel_hartid = r_tp(); // hartid for cpuid()
// set up the registers that trampoline.S's sret will use
// to get to user space.
// set S Previous Privilege mode to User.
unsigned long x = r_sstatus();
x &= ~SSTATUS_SPP; // clear SPP to 0 for user mode
x |= SSTATUS_SPIE; // enable interrupts in user mode
w_sstatus(x); // 控制sret的行为
// set S Exception Program Counter to the saved user pc.
w_sepc(p->tf->epc);
// tell trampoline.S the user page table to switch to.
uint64 satp = MAKE_SATP(p->pagetable); // 设置user pgtable,但是不切换,因为还不在trampoline中
// jump to trampoline.S at the top of memory, which
// switches to the user page table, restores user registers,
// and switches to user mode with sret.
uint64 fn = TRAMPOLINE + (userret - trampoline);
((void (*)(uint64, uint64))fn)(TRAPFRAME, satp);
}
userret:
.globl userret
userret:
# userret(TRAPFRAME, pagetable)
# switch from kernel to user.
# usertrapret() calls here.
# a0: TRAPFRAME, in user page table.
# a1: user page table, for satp.
# switch to the user page table.
csrw satp, a1
sfence.vma zero, zero // 切换到user pgtable
# put the saved user a0 in sscratch, so we
# can swap it with our a0 (TRAPFRAME) in the last step.
ld t0, 112(a0)
csrw sscratch, t0 // 将系统调用返回值a0保存,以便使用a0
# restore all but a0 from TRAPFRAME
ld ra, 40(a0)
ld sp, 48(a0)
ld gp, 56(a0)
ld tp, 64(a0)
ld t0, 72(a0)
ld t1, 80(a0)
ld t2, 88(a0)
ld s0, 96(a0)
ld s1, 104(a0)
ld a1, 120(a0)
ld a2, 128(a0)
ld a3, 136(a0)
ld a4, 144(a0)
ld a5, 152(a0)
ld a6, 160(a0)
ld a7, 168(a0)
ld s2, 176(a0)
ld s3, 184(a0)
ld s4, 192(a0)
ld s5, 200(a0)
ld s6, 208(a0)
ld s7, 216(a0)
ld s8, 224(a0)
ld s9, 232(a0)
ld s10, 240(a0)
ld s11, 248(a0)
ld t3, 256(a0)
ld t4, 264(a0)
ld t5, 272(a0)
ld t6, 280(a0)
# restore user a0, and save TRAPFRAME in sscratch
csrrw a0, sscratch, a0
# return to user mode and user pc.
# usertrapret() set up sstatus and sepc.
sret //sret会重新打开中断
执行sret指令,功能如下:
- sepc -> pc
- 读取sstatus
- SPP:0 - User mode 1 - Supervisor mode
- SIE:User mode interrupts: 1 - enable 0 - disable



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号