实验二 进程/线程基本编程练习
实验二 进程/线程基本编程练习
0.多进程的创建
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid,pid2;
char *message;
int x;
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{ perror("fork failed");
exit(1);
}
if(pid == 0)
{
message="This is the child\n";
x = 0;
}
else
{
message = "This is the parent\n";
x = 10;
sleep(2);
}
printf("%s I'm %d,x =%d my father is:%d \n",message,getpid(),x,getppid());
return 0;
}
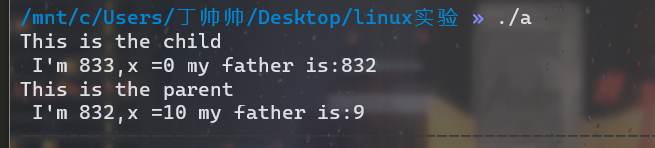
1. 分析理解多个进程的创建
若一个程序中有这样的代码,则有几个进程,父子关系如何?
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void){
pid_t pid,pid2;
char *message;
int x;
pid = fork();
pid2 = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{ perror("fork failed");
exit(1);
}
补充完整后面的代码,使多个进程输出各自身份,并符合正确的亲缘关系
if ( )
{ message = "This is the child\n";
x = 0; }
printf("%s I'm %d, x=%d,my father is:%d\n",message,x,getpid(),getppid());
return 0;
}//main
给出代码及执行效果抓图,并要有说明分析!!!!谁先谁后,为什么。
代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid,pid2;
pid = fork();
pid2 = fork();
if (pid < 0 || pid2 < 0)
{
perror("fork failed");
exit(1);
}
if(pid == 0 && pid2 > 0)//子进程1
{
printf("This is the first child pid:%d, myfather is :%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
sleep(10);
}
if(pid > 0 && pid2 == 0)//子进程2
{
printf("This is the second child pid:%d, myfather is :%d, i don't sleep\n",getpid(),getppid());
}
if(pid == 0 && pid2 == 0)//孙进程
{
printf("This is grandson pid:%d, myfather is :%d, no one waiting for me\n",getpid(),getppid());
exit(0);
}
if(pid > 0 && pid2 > 0)//父进程
{
printf("This is the father pid:%d, myfather is :%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
}
return 0;
}
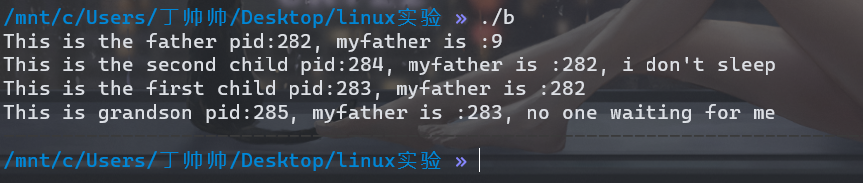
分析:
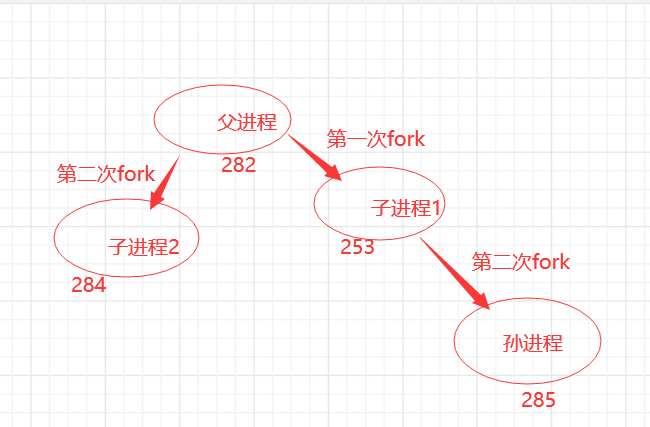
2.若有如下的代码
若有如下的代码
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
pid = fork();
……
请分析将产生多少个进程?要有说明分析!!!!
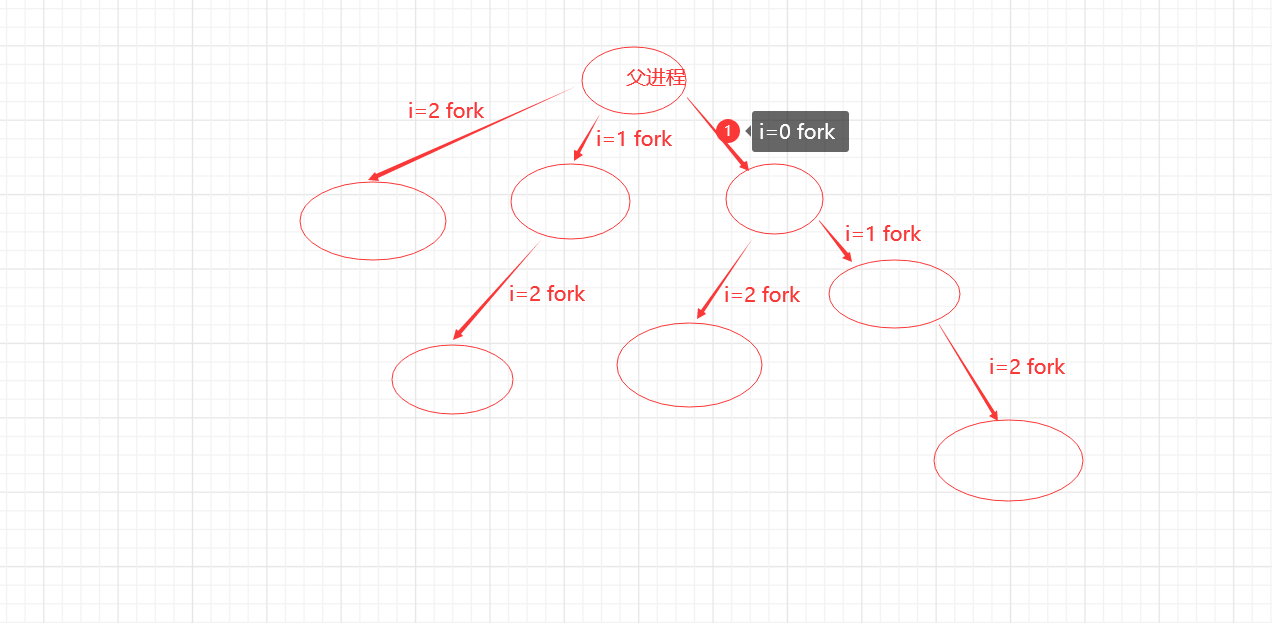
很明显I=2时就已经有23个进程了,所以i=4时会有25个进程
3.如果想产生4个子进程,应该如何编写代码,写出程序,分析抓图,考虑如何让进程的pid是顺序递增的
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int i;
pid_t pid;
printf("xxxxxxxxxxx\n");
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
break;
}
}
if (i < 4) {
sleep(i);
printf("I'am %d child , pid = %u,ppid = %u\n", i+1, getpid(),getppid());
} else {
sleep(i);
printf("I'm parent,pid = %u\n",getpid());
}
return 0;
}

4.解释执行效果
若有下面的功能代码,执行会有怎样的输出?不只有抓图,要有说明分析!!!!谁先谁后,哪里停顿过。
int main(void){
pid_t a;
a = fork();
if (a == 0) {
sleep(2);
execlp ("ps" ,"ps",NULL);
printf("%s I'm %d, x=%d,my father is:%d\n",message,getpid(),getppid());
}
else
printf("%s I'm %d, x=%d,my father is:%d\n",message,getpid(),getppid());return 0;
}
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t a;
a = fork();
if (a == 0)
{
sleep(2);
execlp ("ps" ,"ps",NULL);
printf("I'm %d, my father1 is:%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
}
else if(a > 0)
{
//execlp ("ls" ,"ls",NULL);
printf("I'm %d,my father2 is:%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
}else if (a < 0)
{ perror("fork failed");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}
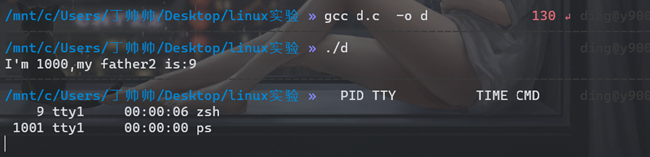
a fork()后 有两个返回值a>0打印父进程pid,还有子进程a==0 睡了2秒,执行了execlp,新载入的内容已经覆盖了其原来的内容所以其后面的内容就不打印了
5.体验进程/线程的顺序控制
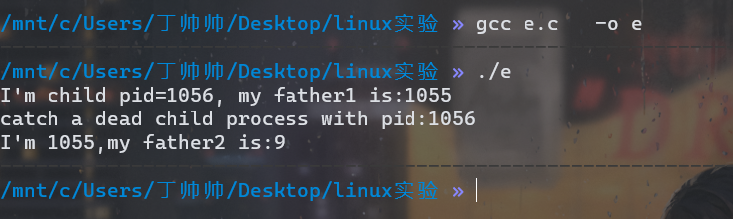
1)编写一个可产生父子进程的程序,使执行时子进程先printf输出内容,然后父进程再printf输出。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t a,w;
a = fork();
if (a == 0)
{
printf("I'm child pid=%d, my father1 is:%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
}
else if(a > 0)
{
w = wait(NULL);
printf("catch a dead child process with pid:%d\n",w);
printf("I'm %d,my father2 is:%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
}else if (a < 0)
{ perror("fork failed");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}
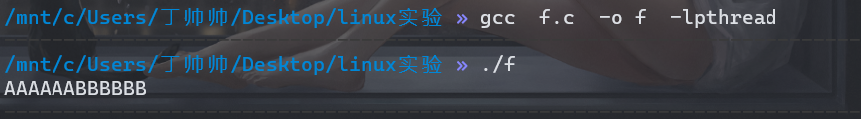
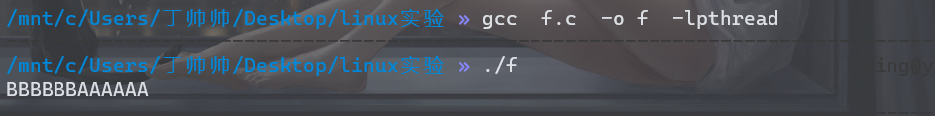
2)编写一个可产生两个线程(一个输出AAAAAA,一个输出BBBBBB)的程序,代码中要求控制线程的输出为AAAAAABBBBBB的顺序。然后修改控制代码,重新编译执行,得到另一种输出顺序,得到BBBBBBAAAAAA的输出。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
void *thread_function1(void *arg){
printf("AAAAAA");
}
int main(void)
{
int res;
pthread_t thread1 ;
void *thread_result;
res=pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,thread_function1,NULL);
if(res!=0){
perror("thread creation failed!");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//使主线程阻塞等待子线程返回后执行
res=pthread_join(thread1,&thread_result);
printf("BBBBBB\n");
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
void *thread_function1(void *arg){
printf("AAAAAA\n");
}
int main(void)
{
int res;
pthread_t thread1;
void *thread_result;
res=pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,thread_function1,NULL);
if(res!=0){
perror("thread creation failed!");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("BBBBBB");
//使主线程阻塞等待子线程返回后执行
res=pthread_join(thread1,&thread_result);
}
6.体验线程对共享变量的处理应互斥,否则会出现线程不安全问题。(选做)
两个线程对共享的进程变量做加1操作,结果加和是错的(例5-12),多次运行测试效果,体会程序执行原理,给出认识总结。
道阻且长,行则将至


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号