JavaEE实验框架原理
实验一: Tomcat Embedded 启动(实现一个Servlet)
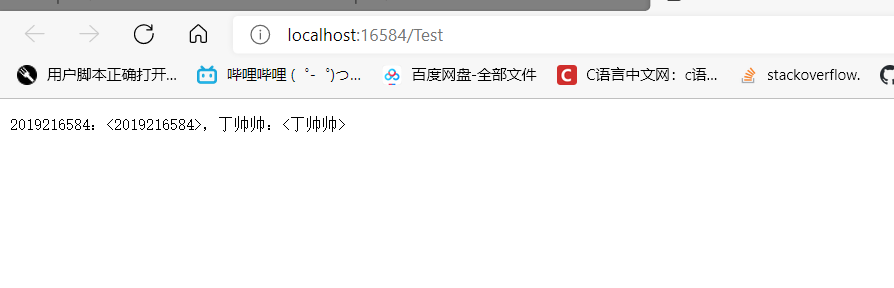
- 要求:使用Tomcat实现一个Servlet。 通过http://localhost:<学号后五位>/Test访问这个Servlet,返回文字“学号:<学号>,学生姓名:<学生姓名>”
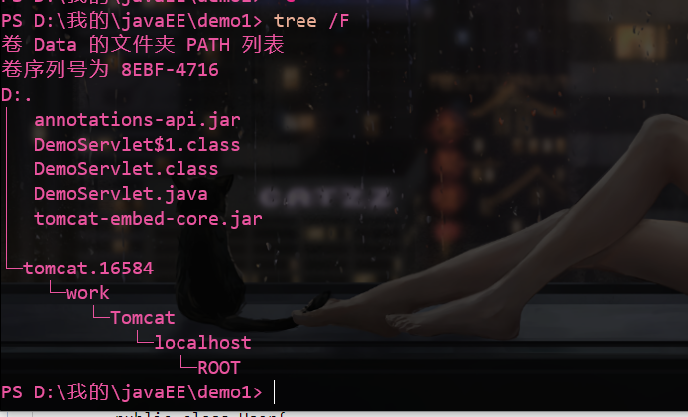
初始目录
源码
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.catalina.Context;
import org.apache.catalina.LifecycleException;
import org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat;
public class DemoServlet{
public static void main(String[] args)
throws LifecycleException, InterruptedException, ServletException {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
tomcat.setPort(16584); //设置端口号,学号后五位做端口号
Context ctx = tomcat.addContext("/", new File(".").getAbsolutePath());
Tomcat.addServlet(ctx, "Test", new HttpServlet() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setContentType("text/plain");
try (Writer writer = response.getWriter()) {
writer.write("2019216584:<2019216584>,丁帅帅:<丁帅帅>"); // 响应请求的内容
writer.flush();
}
}
});
ctx.addServletMappingDecoded("/*", "Test"); // 映射访问路径
tomcat.start();
tomcat.getServer().await();
}
}
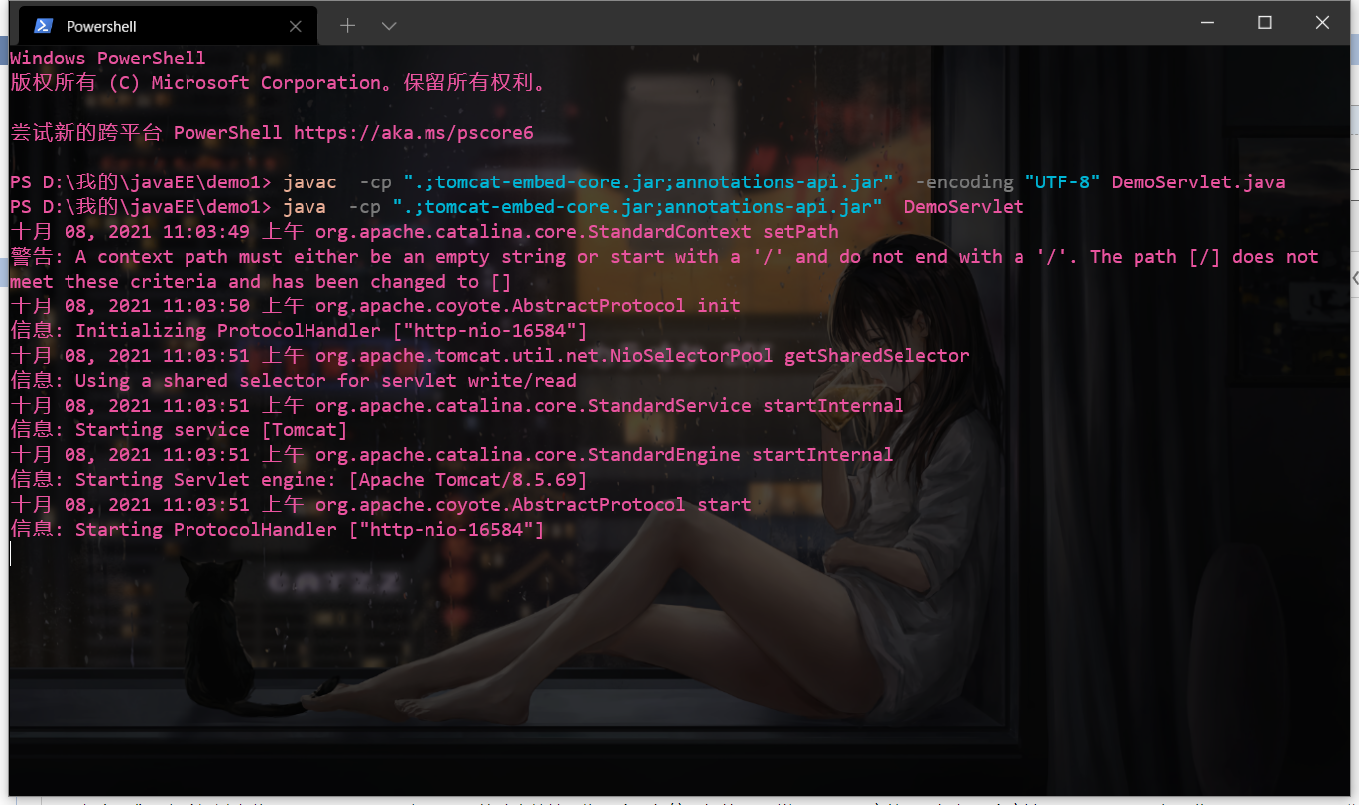
编译
javac -cp ".;tomcat-embed-core.jar;annotations-api.jar" -encoding "UTF-8" DemoServlet.java
运行
java -cp ".;tomcat-embed-core.jar;annotations-api.jar" DemoServlet
截图
测试
截图
结构图
实验二:Java的动态特性实现Java的动态特性实现
- 实验要求:实验通过字节码工具Javassist实现Java的动态特性。为一个已经编译好的Java类(.class文件),添加一个方法sayHi(),在屏幕上显示 "Hi! <学号>-<姓名>"。
源码
// 被加方法的类,可以是别的类
public class User{
private int id;
private String name;
}
import javassist.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class DemoModifyByteCode{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
try {
CtClass ct = pool.get("User"); //获得要修改的类对象
CtMethod sayHi = CtNewMethod.make("public void sayHi(){System.out.println(\"Hi! 2019216584-丁帅帅\");}",ct);
ct.addMethod(sayHi);
Class clazz = ct.toClass();
User u = new User();
Method getName = User.class.getDeclaredMethod("sayHi",new Class[]{});
getName.invoke(u);
//u.getName(); //不能直接调用
//ct.writeFile();
}
catch (NotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
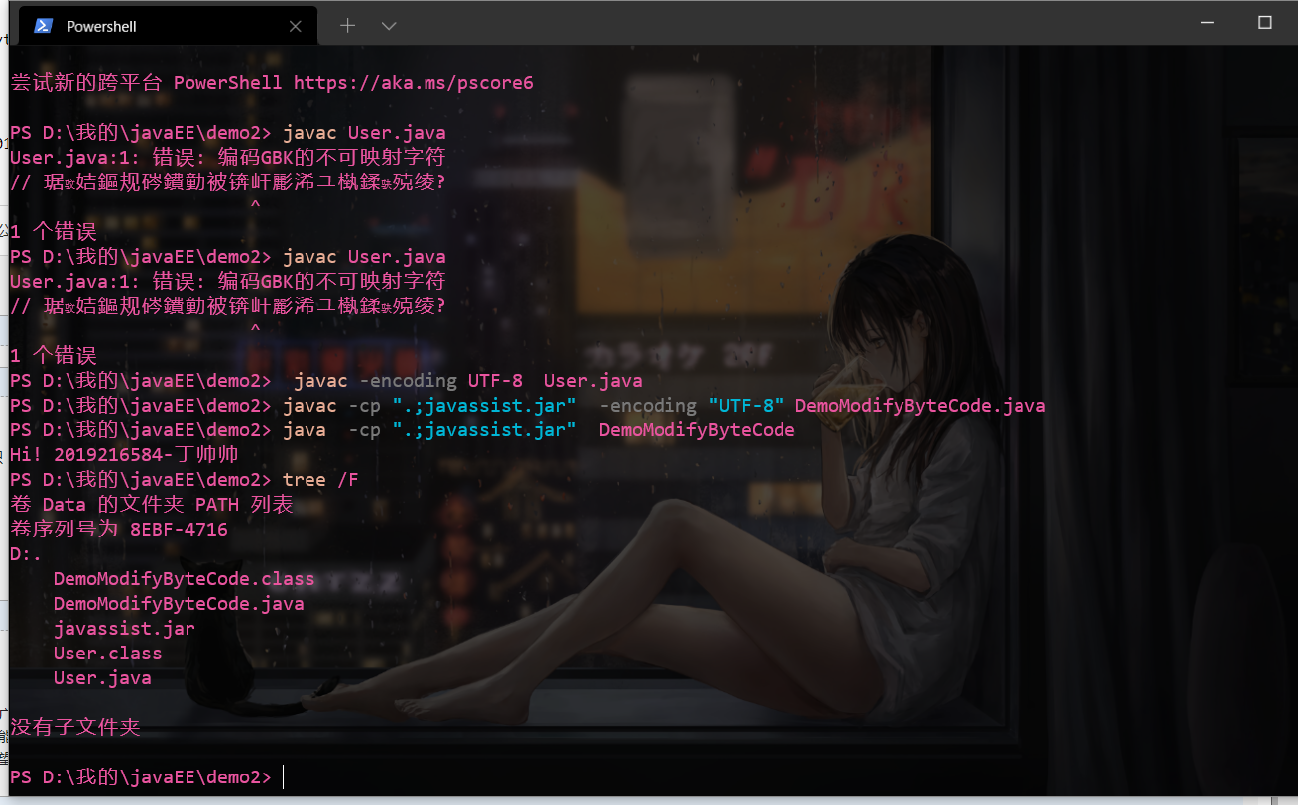
编译
javac -encoding UTF-8 User.java
javac -cp ".;javassist.jar" -encoding "UTF-8" DemoModifyByteCode.java
运行
java -cp ".;javassist.jar" DemoModifyByteCode
截图
实验三: 框架实现方法实验(反射与注解)
源码
// 注解(不用修改)
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RunTest{
//参数默认为空
String value() default "";
}
// 监听程序(不需要修改)
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.FileSystems;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardWatchEventKinds;
import java.nio.file.WatchEvent;
import java.nio.file.WatchKey;
import java.nio.file.WatchService;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.List;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
//import javassist.*;
public class ClassMonitor {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 需要监听的文件目录(只能监听目录)
String path = "./classes";
WatchService watchService = FileSystems.getDefault().newWatchService();
Path p = Paths.get(path);
p.register(watchService, StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_MODIFY,
StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_DELETE,
StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_CREATE);
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
while(true){
WatchKey watchKey = watchService.take();
List<WatchEvent<?>> watchEvents = watchKey.pollEvents();
for(WatchEvent<?> event : watchEvents){
//根据事件类型采取不同的操作
System.out.println("["+path+"/"+event.context()+"]文件发生了["+event.kind()+"]事件");
if(event.kind().equals(StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_CREATE)||
event.kind().equals(StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_MODIFY))
{
System.out.println(event.context());
String s = event.context().toString();
if(s.contains(".class"))
{
try{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);
Class clazz = Class.forName(s.replace(".class",""));
File newfile = new File(s);
byte[] bytes = new byte[(int)newfile.length()];
new FileInputStream(newfile).read(bytes);
System.out.println("类的名字是:"+clazz.getName());
System.out.println("类的属性是:");
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field fd : fields)
{
System.out.println(fd);
}
System.out.println("类的方法是:");
//获取该类的所有方法,不包括父类(仅自定义)
Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method md : declaredMethods)
{
System.out.println(md);
RunTest declaredAnnotation = md.getDeclaredAnnotation(RunTest.class);
//获取到他的值
if(declaredAnnotation != null){
String value = declaredAnnotation.value();
System.out.println(value);
md.invoke(clazz.getConstructor().newInstance());
}
}
clazz = null;
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
}
watchKey.reset();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread.setDaemon(false);
thread.start();
// 增加jvm关闭的钩子来关闭监听
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> {
try {
watchService.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}));
}
}
// 测试类
public class Test{
public int id;
public String name;
@RunTest("Test Run")
public void print()
{
System.out.println("==============");
System.out.println("测试注解");
}
@RunTest("测试注解的变量")
public void show()
{
System.out.println("Show test world");
}
@RunTest
public void show2()
{
System.out.println("show TTTTT");
}
}
编译
javac -encoding "UTF-8" RunTest.java
javac -encoding "UTF-8" ClassMonitor.java
javac -encoding "UTF-8" Test.java
运行
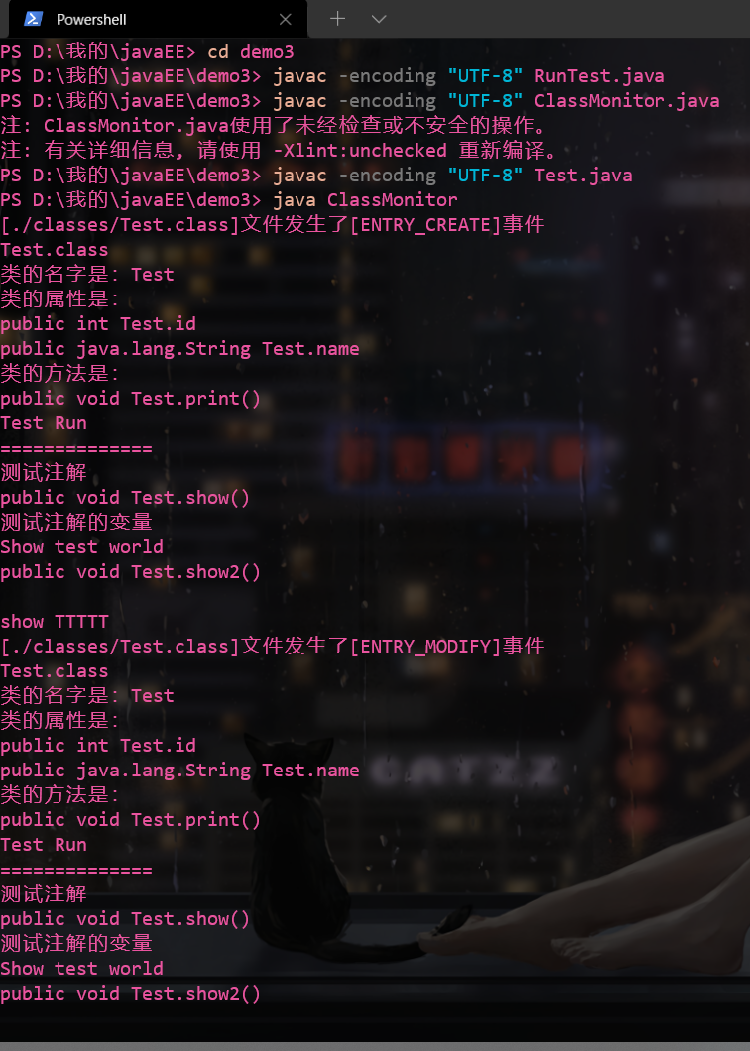
java ClassMonitor
测试
mkdir classes
copy Test.class classes
观察运行java ClassMonitor的窗口变化
截图

道阻且长,行则将至


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号