会员
周边
新闻
博问
闪存
众包
赞助商
Chat2DB
所有博客
当前博客
我的博客
我的园子
账号设置
会员中心
简洁模式
...
退出登录
注册
登录
路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索
学以致用,不用则废
博客园
首页
新随笔
联系
订阅
管理
上一页
1
···
24
25
26
27
28
29
下一页
2021年11月18日
进制篇(-)复习
摘要: #进制 ##进制的定义 十进制的定义:由十个符号组成,分别是0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 逢十进一。 九进制的定义:由九个符号组成,分别是0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 逢九进一。 十六进制的定义:由十六个符号组成,分别是0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-11-18 11:10 不会笑的孩子
阅读(1259)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
2021年11月13日
反汇编分析递归和自己汇编实现
摘要: #汇编递归 这次通过简单的递归来分析递归对应的汇编 #递归求前n项和 ##描述 求序列的前n项和。输入一个整数n,输出1+2+3+4+...+n的前n项和。 ##输入输出示例 ###输入 5 ###输出 15(1+2+3+4+5) ###c语言实现代码 #include "stdafx.h" int
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-11-13 17:13 不会笑的孩子
阅读(269)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
2021年11月6日
python(django启动报错,之编码问题)UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xb2 in position 0: invalid start byte
摘要:
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-11-06 16:39 不会笑的孩子
阅读(411)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
2021年11月5日
保护模式(段描述符与段选择子3)
摘要: ###要点回顾: 上一篇段属性探测2中,我知道了当写一个段寄存器的时候,只给了16位的数,但段寄存器有96位,那剩下的80位从哪里来的?(从GDT中查出来的),这16位数是随便写的吗? ##GDT(Global Descriptor Table)全局描述符表和LDT(局部描述符表) GDT是一块内存
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-11-05 19:25 不会笑的孩子
阅读(249)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
保护模式(段寄存器属性探测2)
摘要: ###要点回顾: 上一节课我们知道了段寄存器共96位 Selector//16位 Attribute//16位 Base //32位 Limit //32位 我们可以通过MOV指令进行读写(LDTR和TR除外) 但是我们只能看见16位,那我们证明Attribute,Base,Limit的存在呢? #
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-11-05 17:15 不会笑的孩子
阅读(97)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
保护模式(段寄存器介绍1)
摘要: ##保护模式简介 CPU分为实模式、保护模式、虚拟8086模式,大多数操作系统运行在保护模式下。 * 保护模式具有两个特点:段、页、保护模式真正保护的是数据结构、寄存器、指令。 * 实模式:16位汇编,访问的都是物理地址,非常危险。 * 保护模式:保护的是对内存的访问,相对实模式安全。段层保护,页层
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-11-05 15:50 不会笑的孩子
阅读(214)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
C语言链表实现(郝斌数链表学习笔记)
摘要: #include "stdafx.h" #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> typedef struct Node { int data ;//数据域 struct Node * pNext; //指针域 这个指针域它指向的是跟它本身一样的数据类型的另一个节点
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-11-05 12:47 不会笑的孩子
阅读(92)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
2021年10月10日
硬编码结构示意图
摘要: 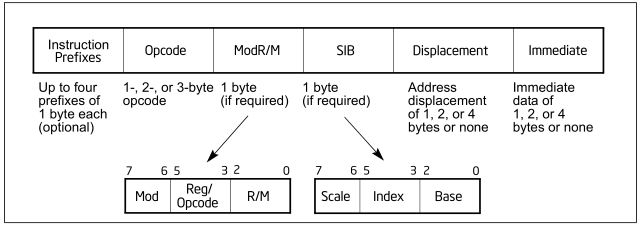
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-10-10 19:45 不会笑的孩子
阅读(76)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
2021年10月9日
跨函数使用内存
摘要: #include<stdio.h> #include<malloc.h> struct Student{ int sid; int age; } struct Student* CreateStudent(void); void ShowStudent(strucent Student*) int
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-10-09 11:15 不会笑的孩子
阅读(41)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
typedef函数的使用
摘要: typedef int INT; //相当于给int起了一个别名INT typedef struct Student { int sid; char name[100]; char sex; }ST; //ST st 就相当于struct Student st ,给struct Student 起了
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-10-09 11:13 不会笑的孩子
阅读(42)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
上一页
1
···
24
25
26
27
28
29
下一页
公告